Java之----如何进行单元测试来测试代码
我们可以看一个例子:
1)创建一个工程,叫SuiteUnitTesting,在这个工程中创建4个类,如下图所示:
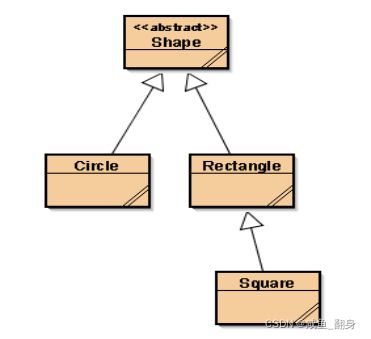
代码清单如下:
public abstract class Shape
{
public abstract double perimeter();//计算周长,抽象方法
public abstract double area();//计算面积,抽象方法
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape
{
int a;//边长
int b;//边长
public Rectangle(int x,int y)
{
a=x;
b=y;
}
public double perimeter()
{
return 2*(a+b);
}
public double area()
{
return a*b;
}
}
public class Circle extends Shape
{
private int r;//半径
public Circle(int x)
{
r=x;
}
public double perimeter()
{
return 2*3.14*r;
}
public double area()
{
return 3.14*r*r;
}
}
public class Square extends Rectangle
{
public Square(int x,int y)
{
super(x,y);
}
public double perimeter()
{
return 4*a;
}
public double area()
{
return a*a;
}
}
2)针对我们要测试的Rectangle、Circle、Square3个类设计测试用例。
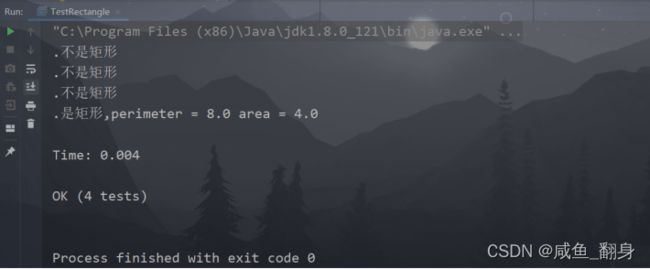
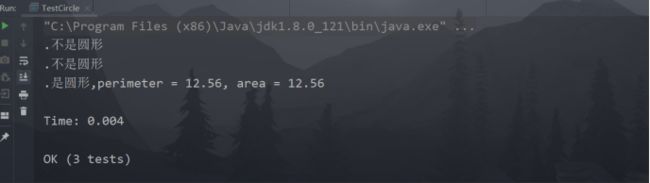
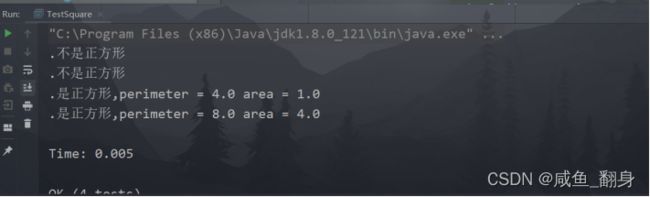
3)在SuiteUnitTesting工程下创建三个新类TestRectangle、TestCircle和TestSquare,分别实现我们在第二步设计的测试用例。
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestRectangle extends TestCase {
public TestRectangle(String arg){
super(arg);
}
@Test
public String isRectangle(int x,int y){
if(x>0&&y>0){
Rectangle rec = new Rectangle(x,y);
return "是矩形,"+"perimeter = "+rec.perimeter()+" area = "+rec.area();
}else{
return "不是矩形";
}
}
@Test
public void testOne(){
System.out.println(isRectangle(0,0));
}
@Test
public void testTwo(){
System.out.println(isRectangle(-1,2));
}
@Test
public void testThree(){
System.out.println(isRectangle(1,-2));
}
@Test
public void testFour(){
System.out.println(isRectangle(2,2));
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
junit.textui.TestRunner.run(TestRectangle.class);
}
}
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestCircle extends TestCase {
public TestCircle(String arg){
super(arg);
}
public String isCircle(int r){
if(r>0){
Circle circle = new Circle(r);
return "是圆形,"+"perimeter = "+circle.perimeter()+", area = "+circle.area();
}else{
return "不是圆形";
}
}
@Test
public void testOne(){
System.out.println(isCircle(-1));
}
@Test
public void testTwo(){
System.out.println(isCircle(0));
}
@Test
public void testThree(){
System.out.println(isCircle(2));
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
junit.textui.TestRunner.run(TestCircle.class);
}
}
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestSquare extends TestCase {
public TestSquare(String arg){
super(arg);
}
public String isSquare(int x,int y){
if(x>0){
Square square = new Square(x,y);
return "是正方形,"+"perimeter = "+square.perimeter()+" area = "+square.area();
}else{
return "不是正方形";
}
}
@Test
public void testOne(){
System.out.println(isSquare(0,0));
}
@Test
public void testTwo(){
System.out.println(isSquare(-1,2));
}
@Test
public void testThree(){
System.out.println(isSquare(1,-2));
}
@Test
public void testFour(){
System.out.println(isSquare(2,2));
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
junit.textui.TestRunner.run(TestSquare.class);
}
}
4)建立一个Suite,组装自己的测试,我们在这里,组装TestRectangle和TestCircle,代码如下:
import junit.framework.*;
public class TestShape {
public static Test suite() throws Exception
{
TestSuite suite =new TestSuite("Some tests from part 1 ");
suite.addTestSuite(TestRectangle.class);
suite.addTestSuite(TestCircle.class);
return suite;
}
}
5)在开始—〉运行—〉cmd,在命令行提示符下,输入:
java junit.swingui.TestRunner TestShape