LeetCode刷题日记精选例题(代码+链接)
文章目录
- 一、对称二叉树
- 二、相同的树
- 三、另一棵树的子树
- 四、二叉树的最大深度
- 五、二叉树的最小深度
- 六、完全二叉树的节点个数
- 七、平衡二叉树
- 八、二叉树的所有路径
相见即是有缘,如果对你有帮助,给博主一个免费的点赞以示鼓励把QAQ
一、对称二叉树
题目链接
二叉树的对称是指二叉树的左子树与右子树互相翻转后是否相等,我们的第一种思路是使用队列,从最外侧向内侧进行扫描,判断每次扫描的两个节点的值是否相等
节点为空的话会出现以下几种情况
- 左节点为空,右节点不为空 返回false
- 左节点不为空,右节点为空 返回false
节点不为空会出现下列情况返回false
- 左右节点不为空,但是值不相等
1.使用队列解决本题
//使用队列解决本题
public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return true;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.offer(root.left);
queue.offer(root.right);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node1 = queue.poll();
TreeNode node2 = queue.poll();
if (node1==null&&node2==null){
continue;
}
if (node2==null||node1==null||node1.val!=node2.val){
return false;
}
queue.offer(node1.left);
queue.offer(node2.right);
queue.offer(node1.right);
queue.offer(node2.left);
}
return true;
}
使用递归解决本题
public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root){
return compareTree(root.left,root.right);
}
private static boolean compareTree(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
if ((left==null&&right!=null)||(left!=null&&right==null)){
return false;
}
if (left==null&&right==null){
return true;
}
if (left.val!=right.val){
return false;
}
return compareTree(left.left,right.right)&& compareTree(left.right,right.left);
}
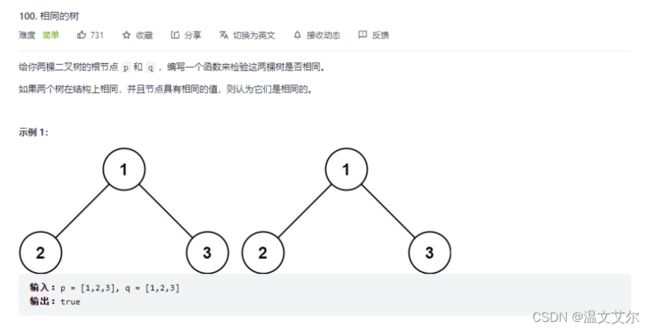
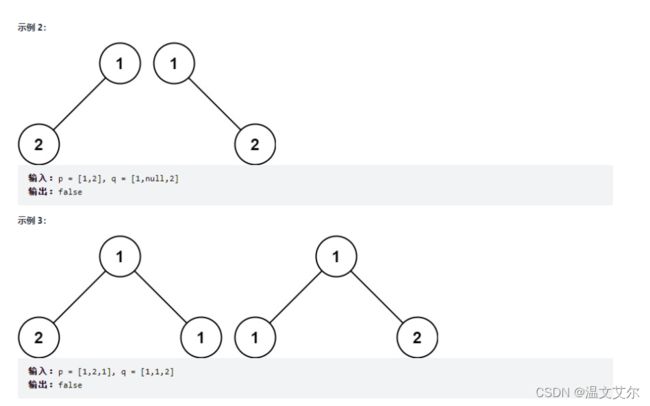
二、相同的树
题目链接
//使用队列
public static boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Deque<TreeNode> deque =new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(p);
deque.offer(q);
while (!deque.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node1 = deque.poll();
TreeNode node2 = deque.poll();
if (node1==null&&node2==null){
continue;
}
if (node1==null||node2==null||node1.val!=node2.val){
return false;
}
deque.push(node1.left);
deque.push(node2.left);
deque.push(node1.right);
deque.push(node2.right);
}
return true;
}
//使用递归
public static boolean isSameTree2(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
return compareTree(p,q);
}
private static boolean compareTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p==null&&q==null){
return true;
}
if (p==null&&q!=null){
return false;
}
if (p!=null&&q==null){
return false;
}
if (q.val!=p.val){
return false;
}
return compareTree(p.left,q.left)&&compareTree(p.right,q.right);
}
三、另一棵树的子树
题目链接
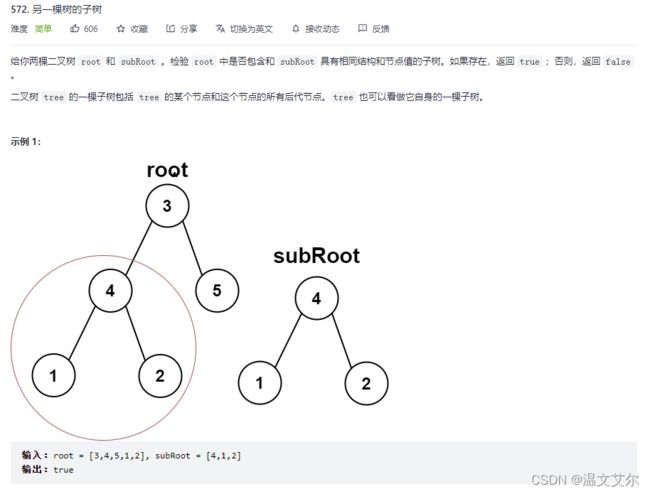

本题可以通过递归将其转换为是否是相同树的问题,subRoot是否是子树的问题可以转换为或的问题
- 是当前树
- 是当前树的左子树
- 是当前树的右子树
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if (subRoot==null)return true;
if (root==null) return false;
return check(root,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.right,subRoot);
}
private boolean check(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
//转换成是否是相同树的问题了
if (root==null&&subRoot!=null){
return false;
}
if (root!=null&&subRoot==null){
return false;
}
if (root==null&&subRoot==null){
return true;
}
if (root.val!=subRoot.val){
return false;
}
return check(root.left,subRoot.left)&&check(root.right,subRoot.right);
}
//队列解决
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if (subRoot==null)return true;
if (root==null) return false;
return check(root,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.right,subRoot);
}
private boolean check(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
//转换成是否是相同树的问题了
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList();
deque.offer(root);
deque.offer(subRoot);
while (!deque.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node1 = deque.poll();
TreeNode node2 = deque.poll();
if (node1==null&&node2==null){
continue;
}
if (node1==null||node2==null||node1.val!=node2.val){
return false;
}
deque.offer(node1.left);
deque.offer(node2.left);
deque.offer(node1.right);
deque.offer(node1.right);
}
return true;
}
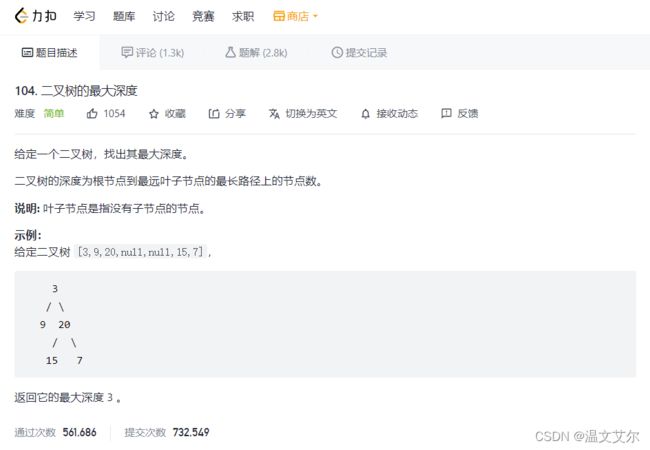
四、二叉树的最大深度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
五、二叉树的最小深度
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
if (root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return 1;
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (root.left!=null){
min = Math.min(minDepth(root.left),min);
}
if (root.right!=null){
min = Math.min(minDepth(root.right),min);
}
return min+1;
}
六、完全二叉树的节点个数
题目链接
//深度优先遍历
public int countNodes2(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
int left = countNodes2(root.left);
int right = countNodes2(root.right);
return left+right+1;
}
//广度优先遍历
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
int sum = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
sum+=len;
for (int i=0;i<len;i++){
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
if (top.left!=null) queue.offer(top.left);
if (top.right!=null) queue.offer(top.right);
}
}
return sum;
}
以上是针对普通二叉树的解法,我们还可以根据完全二叉树的性质来进行解析
完全二叉树除了最后一层,其它层全满,且最后一层叶节点从左向右连续,计算满二叉树的公式是2^深度-1
我们对左子树和右子树进行递归,并统计其深度,当左右子树深度一致,证明左子树为满二叉树,此时递归右子树,反之右子树为满二叉树,递归左子树
public int countNodes3(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
int leftDep = getDep(root.left);
int rightDep = getDep(root.right);
if (leftDep==rightDep){
//左子树为满二叉树
return (1<<leftDep)+countNodes3(root.right);
}else {
//右子树为满二叉树
return (1<<rightDep)+countNodes3(root.left);
}
}
private int getDep(TreeNode root) {
int dep = 0;
while (root!=null){
root=root.left;
dep++;
}
return dep;
}
七、平衡二叉树
必须满足的条件是,当前节点的左子树与右子树的高度差不超过1,当前节点满足,则继续判断它的左子树和右子树是否也满足
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return true;
}
return Math.abs(getDep(root.left)-getDep(root.right))<=1&&isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right);
}
private int getDep(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(getDep(root.left),getDep(root.right))+1;
}
上述的递归的缺点是,同一节点会被重复的调用height方法,时间复杂度较高,我们可以采用后序遍历,这样时间复杂度为O(n)
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return true;
}
return Height(root)>0;
}
private int Height(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
int leftDep = Height(root.left);
if (leftDep==-1){
return -1;
}
int rightDep = Height(root.right);
if (rightDep==-1){
return -1;
}
if (Math.abs(leftDep-rightDep)>1){
return -1;
}
return Math.max(leftDep,rightDep)+1;
}
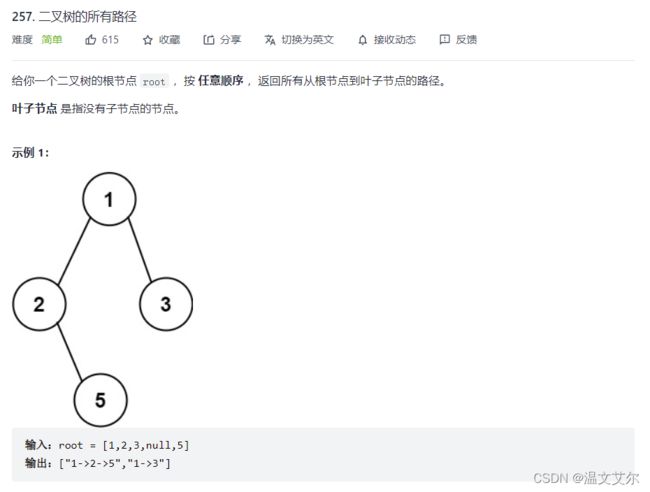
八、二叉树的所有路径
题目链接
本题应该使用前序遍历,这样才有利于记录路径,我们需要合理利用递归地回溯来记录每一组路径,我们将经过的节点记录到list集合中,每次遇到叶子结点都对集合中的数字进行拼接,将拼接好的数据装入res中,最后将res返回即可
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> paths = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root==null){
return res;
}
traversal(root,paths,res);
return res;
}
private void traversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> paths, List<String> res) {
paths.add(root.val);
if (root.left==null&&root.right==null){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<paths.size()-1;i++){
sb.append(paths.get(i)+"->");
}
sb.append(paths.get(paths.size()-1));
res.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
if (root.left!=null) {
traversal(root.left,paths,res);
paths.remove(paths.size()-1);
};
if (root.right!=null) {
traversal(root.right,paths,res);
paths.remove(paths.size()-1);
};
}
相见即是有缘,如果对你有帮助,给博主一个免费的点赞以示鼓励把QAQ