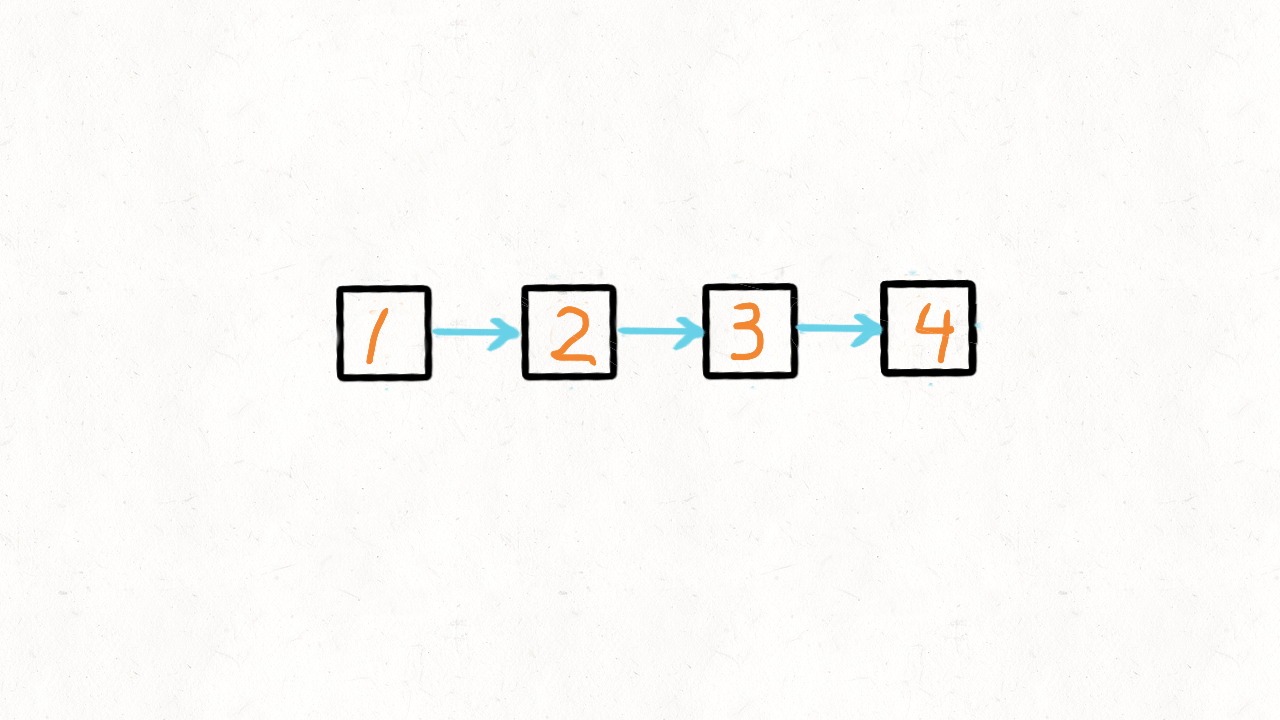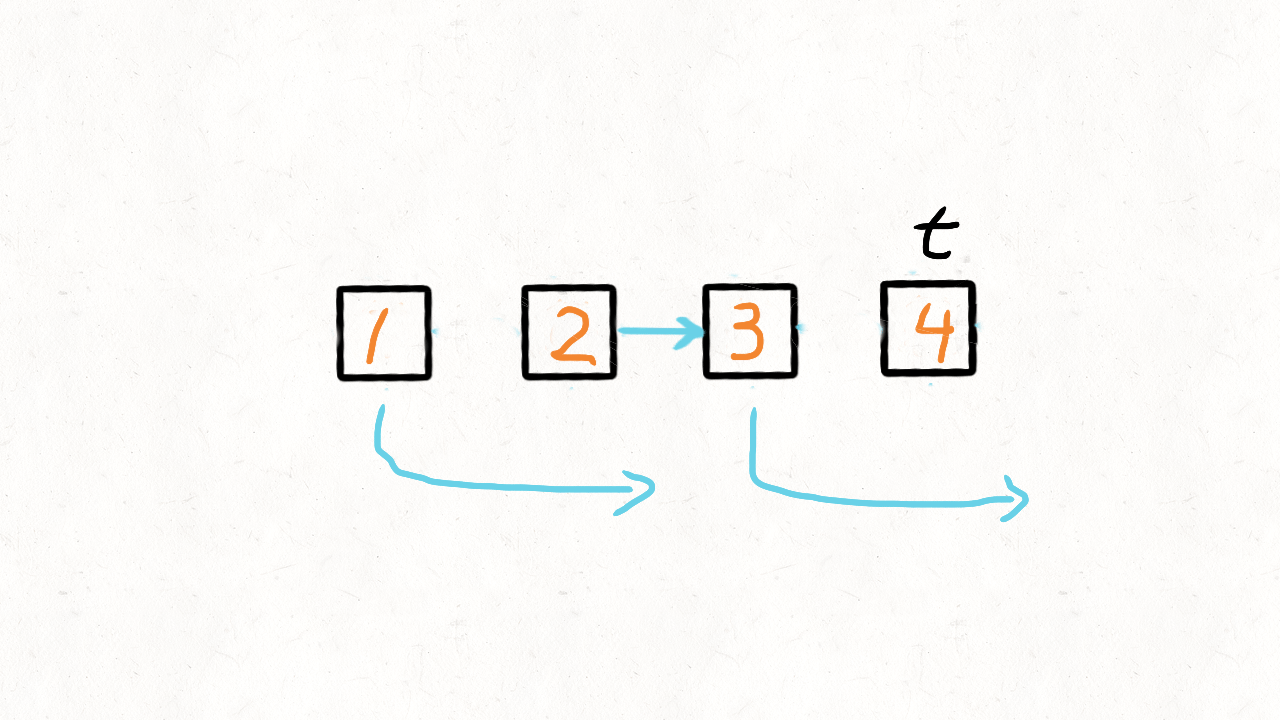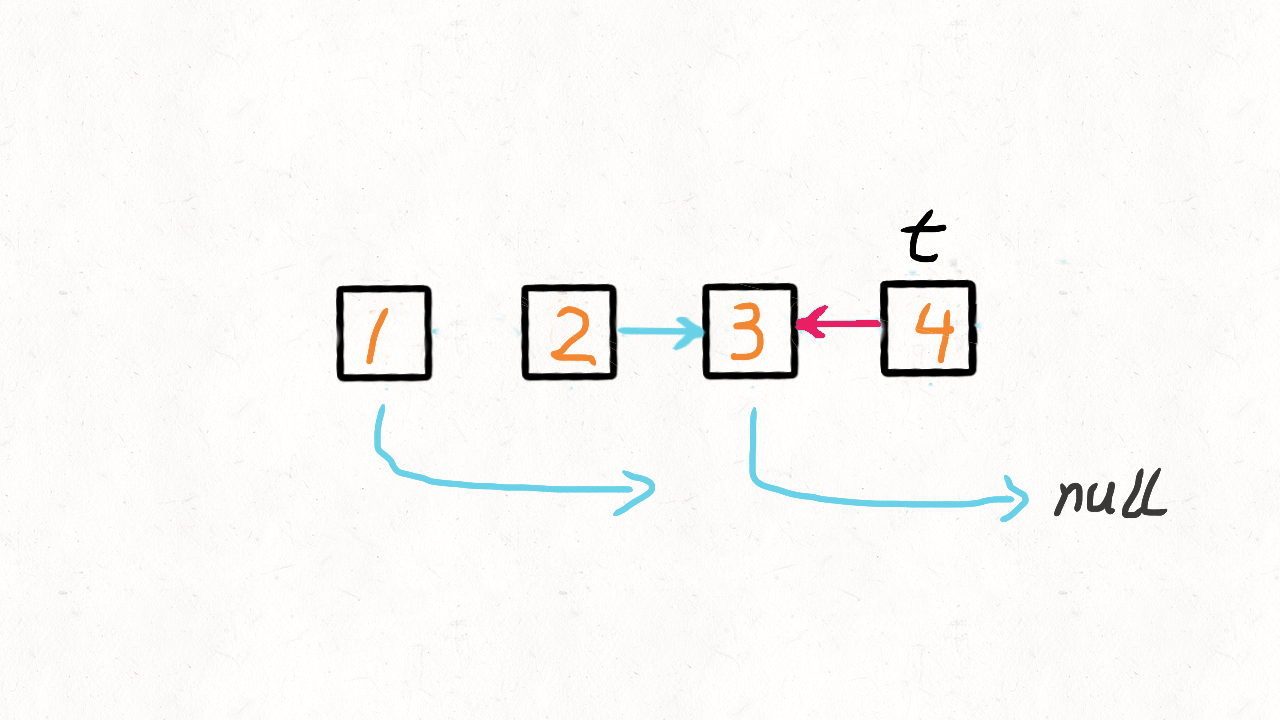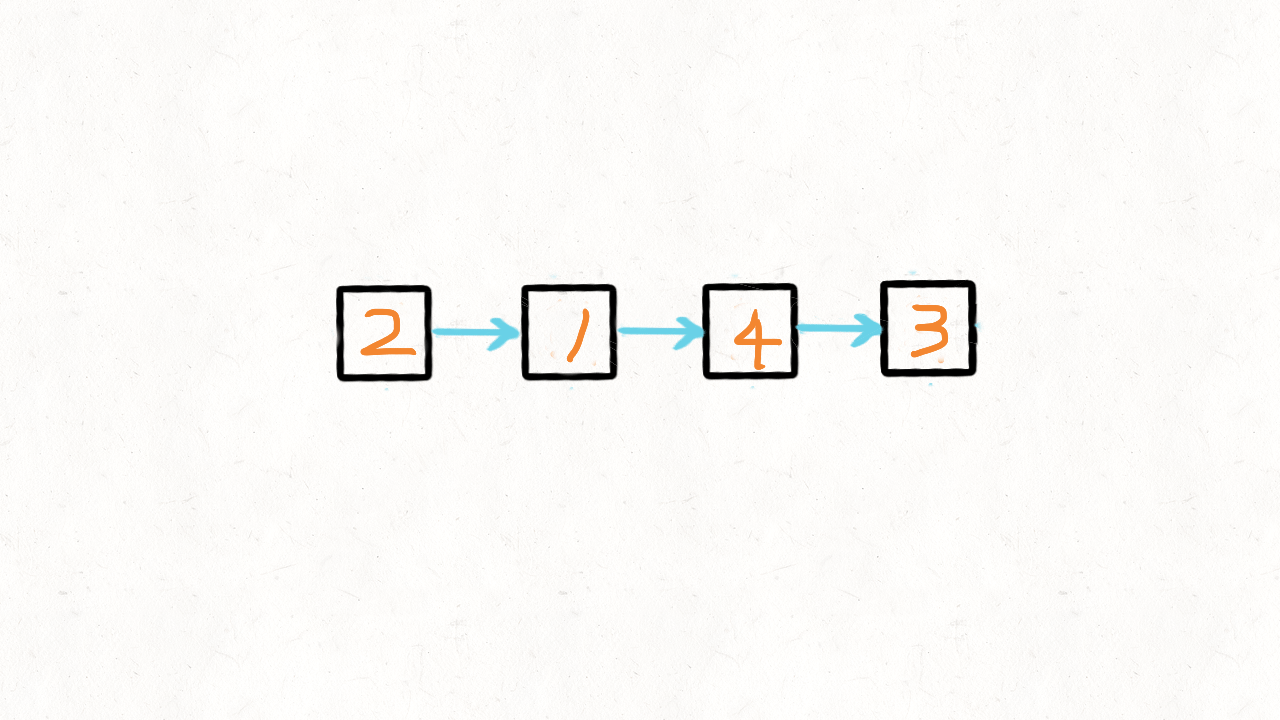Java复习常用的数据结构和常用面试题之数组和链表
文章目录
- 前言
- 1. 数组、链表(Array、Linked List)
-
- Array特点(数组)
-
- 1.读取快
- 2.插入和删除慢
- Linked List特点(链表)
-
- 单链表内存模型
- 插入和删除
- 特点总结
-
- 各自的优缺点
- 实战题目
-
- 个人解题思路
-
- 206.反转链表
- 24.两两交换链表中的节点
- 141.环形链表
- 142.环形链表II
- [25. K 个一组翻转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/?utm_source=LCUS&utm_medium=ip_redirect&utm_campaign=transfer2china)
- 进阶:栈和队列
前言
提示:算法学习不努力,秋招春招是弟弟
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容来自极客时间系列教程,下面案例可供参考
1. 数组、链表(Array、Linked List)
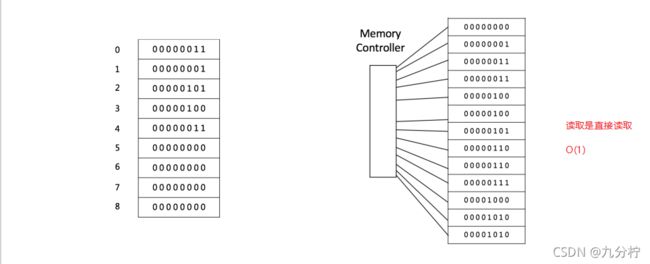
Array:在内存中,数组是一块连续的区域
Linked List:链表在内存中可以存在任何地方,不要求连续。
Array特点(数组)
1.读取快
2.插入和删除慢

Array由于内存连续的特点,插入和删除往往需要一个个往后挪位置,除非你插入的是最后一个位置。
时间复杂度
Array
• Access: O(1)
• Insert: 平均 O(n)
• Delete: 平均 O(n)
Linked List特点(链表)
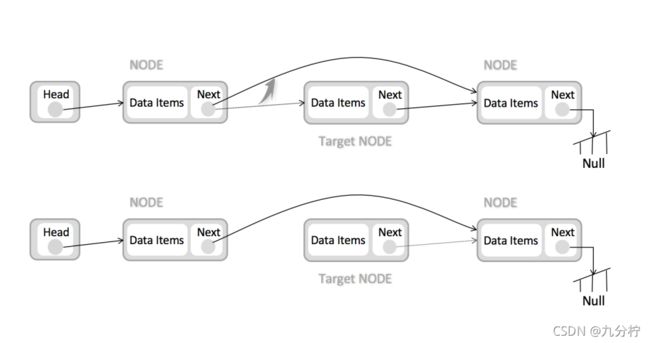
单链表内存模型

每一个节点都保存了下一个数据的内存地址,通过这个地址找到下一个数据。
可以知道,这种数据结构的查找需要一个一个节点的寻址下去,效率是比较低的
插入和删除
插入操作
先让新增节点的下一节点指针域指向原有的尾部,再挂到要插入的节点
时间复杂度
时间复杂度
space O(n)
prepend O(1)
append O(1)
lookup O(n)
insert O(1)
delete O(1)
特点总结
| – | 数组(Array) | 链表(Linked List) |
|---|---|---|
| 读取 | O(1) | O(n) |
| 插入 | O(n) | O(1) |
| 删除 | O(n) | O(1) |
各自的优缺点
数组的优点:
- 随机访问性强
- 查找速度快
数组的缺点
- 插入和删除效率低
- 可能浪费内存
- 内存空间要求高,必须有足够的连续内存空间。
- 数组大小固定,不能动态拓展
链表的优点
- 插入删除速度快
- 内存利用率高,不会浪费内存
- 大小没有固定,拓展很灵活。
链表的缺点
- 不能随机查找,必须从第一个开始遍历,查找效率低
实战题目
- 206.反转链表:https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
- 24.两两交换链表中的节点:https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs
- 141.环形链表:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle
- 142.环形链表II:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
- 25.K 个一组翻转链表https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/
个人解题思路
自定义ListNode
package LinkedList;
public class ListNode {
//数据域
public int val;
//下一节点域
public ListNode next;
ListNode() {
}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
206.反转链表
package com.gdpu.day1;
import LinkedList.ListNode;
/**
* 反转链表
* https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
*
*/
public class NO_206_ReverseLinkedList {
//迭代解法
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
//前面的指针
ListNode prev =null;
//当前指针
ListNode curr = head;
//当还没到最后一个指针
while (curr!=null){
//反转一个的操作
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
//向后移动
prev =curr;
curr =next;
}
return prev;
}
//递归解法
public ListNode recursive(ListNode head){
//递归终止条件
//head是null,或者已经到最后一个节点,出口
if (head ==null ||head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode p = recursive(head.next);
//一个环形指回前面
head.next.next = head;
//把目前的下一个设为null
head.next =null;
return p;
}
}
24.两两交换链表中的节点
package com.gdpu.day1;
import LinkedList.ListNode;
import java.util.Stack;
public class NO_24_swapPairs {
/**
* 递归出口:当前节点或者下一个节点为空,返回
* 方法内容:当前节点next,指向当前节点,指针互换
* 返回值:返回交换完成的节点
*/
public ListNode swapPairsRecursive(ListNode head) {
//递归的终止条件
if(head==null || head.next==null) {
return head;
}
//假设链表是 1->2->3->4
//这句就先保存节点2
ListNode tmp = head.next;
//继续递归,处理节点3->4
//当递归结束返回后,就变成了4->3
//于是head节点就指向了4,变成1->4->3
head.next = swapPairsRecursive(tmp.next);
//将2节点指向1
tmp.next = head;
return tmp;
}
//用栈
public ListNode swapPairsByStack(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null) {
return head;
}
//用stack保存每次迭代的两个节点
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<ListNode>();
ListNode p = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
//head指向新的p节点,函数结束时返回head.next即可
head = p;
while(cur!=null && cur.next!=null) {
//将两个节点放入stack中
stack.add(cur);
stack.add(cur.next);
//当前节点往前走两步
cur = cur.next.next;
//从stack中弹出两个节点,然后用p节点指向新弹出的两个节点
p.next = stack.pop();
p = p.next;
p.next = stack.pop();
p = p.next;
}
//注意边界条件,当链表长度是奇数时,cur就不为空
if(cur!=null) {
p.next = cur;
} else {
p.next = null;
}
return head.next;
}
}
141.环形链表
利用set集合的不可重复的特性
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!seen.add(head)) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
快慢双指针迭代
/**
* 快慢指针迭代
*/
public boolean hasCycle1(ListNode head) {
//如果是空或者只有一个节点
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return false;
//起点差一步
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
//起点快,步数快,还能相遇肯定有环
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
//慢的走一步
slow = slow.next;
//快的走两步
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
142.环形链表II
- 利用set集合不可重复的特性
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return null;
}
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<>();
while(head!=null){
if(!seen.add(head)){
return head;
}
head = head.next;
}
return null;
}
- 利用双指针
/**
* 用双指针
*/
public ListNode detectCycle1(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (true) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) break;
}
fast = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
25. K 个一组翻转链表
package com.gdpu.day1;
import LinkedList.ListNode;
import java.util.List;
public class NO_25_reverseKGroup {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode tail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//剩余数量小于k的话,则不需要反转。
if (tail == null) {
return head;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
// 反转前 k 个元素
ListNode newHead = reverse(head, tail);
//下一轮的开始的地方就是tail
head.next = reverseKGroup(tail, k);
return newHead;
}
/**
* 反转某段链表
*/
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head,ListNode tail){
ListNode prev=null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr!=tail){
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
进阶:栈和队列
Java复习常用的数据结构和常用面试题之栈和队列