promise是es6推出适用于异步请求的构造函数,帮助解决回调地狱的问题,以下内容将自定义实现promise,只包括基本使用,所以一些边界情况考虑没有在内。
如果对promise用法还不熟悉的朋友可移步
Promise的理解与使用(一)
Promise的理解和使用(二)
executor
首先建立promise的基本结构
定义构造函数
promise的executor部分是放到主线程中直接执行的
class icePromise {
constructor(executor){
const resolve = () => {
console.log('resolve被调用')
}
const reject = () => {
console.log('reject被调用')
}
}
executor(resolve, reject)
}
const promise = new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
resolve()
})定义状态
1、定义常量
const STATUS_PENDING = 'pending'
const STATUS_FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const STATUS_REJECTED = 'rejected'2、通过构造函数创建实例时,就应该需要状态,所以在类中定义
this.status = STATUS_PENDING 3、resolve和reject方法里通过状态判断
当为pending时,才能执行resolve或者reject方法,执行前先修改状态
then方法
onFulfilled/onRejected中要执行then里面的回调函数,将两个函数绑定到实例的属性上
1、在类中定义一个then方法
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
this.onFulfilled = onFulfilled
this.onRejected = onRejected
}2、在resolve和reject中分别执行this.onFulfilled和this.onRejected中
此时会报错,因为executor会立刻执行,而then里面的函数是微任务,
会在主线程执行完成之后执行
3、resolve和reject中加入 queueMicrotask (微任务)
整体架构的初版就完成了
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onFulfilled(value);
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onRejected(reason);
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
this.onFulfilled = onFulfilled;
this.onRejected = onRejected;
}
}
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve");
reject("reject");
});
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("success1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("fail1", reason);
}
);
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("success2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("fail2", reason);
}
);返回两次promise的状态,只执行第一个resolve,then方法中对应执行的成功或者失败的函数也正确
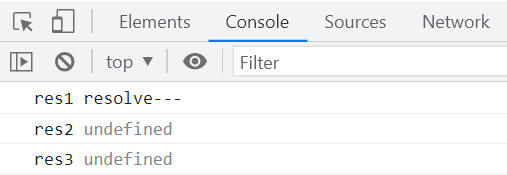
但存在的问题是,执行两次then方法,只执行了第二个,以下对then方法进行优化。
then
解决多次调用then方法的问题
1、constructor中定义变量用于收集所有的成功/失败的回调函数
this.onFulfilledCallbacks = []
this.onRejectedCallbacks = []2、 在then方法中通过push添加到数组中
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.push()
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push()3、在resolve和reject中遍历
this.onFulfilledCallbacks和this.onRejectedCallbacks中的方法
此时代码如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve---");
reject("----reject");
});
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
);
// 确定状态后再调用
setTimeout(() => {
promise.then(
(res) => {
console.log("res3", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("err3", err);
}
);
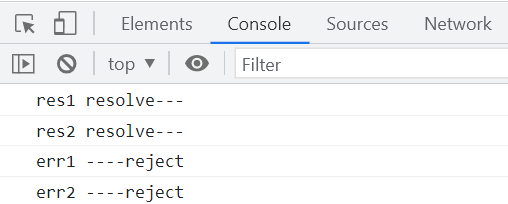
}, 1000);解决then的多次调用的问题,但仍有其它的问题,一个是resolve和reject方法同时执行,二是通过定时器延迟执行的promise的then方法没有输出响应结果
解决延迟调用的问题
1、保存value和reason
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefinedresolve和reject方法分别给this.value和this.reason赋值
2、then方法中进行状态的判断
当状态为pending时,继续向onFulfilledCallbacks、onRejectedCallbacks数组中添加函数;当状态不为pending时,直接执行onFulfilled或onRejected方法
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
onRejected(this.reason);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}3、pending状态的变化
① queueMicrotask中判断不为pending则return
② 修改pending状态
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
onRejected(this.reason);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve---");
reject("----reject");
});
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
);
// 确定状态后再调用
setTimeout(() => {
promise.then(
(res) => {
console.log("res3", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("err3", err);
}
);
}, 1000);
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res4", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err4", reason);
}
).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res5", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err5", reason);
}
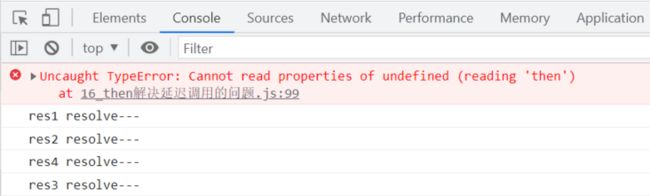
)解决了resolve和reject多次调用及计时器延迟调用的问题,但此时发现then无法进行链式调用
解决链式调用的问题
1、then方法里返回一个 new icePromise,将判断逻辑放进去
2、this.onFulfilledCallbacks 和 this.onRejectedCallbacks 传入回调函数,
回调函数返回resolve或者reject函数的执行结果
3、封装工具函数,用于处理try catch
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve---");
reject("----reject");
});
promise
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
)
.then(
(res) => {
console.log("res3", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("err3", err);
}
);此时then函数就已经可以链式调用啦,基本功能已经实现~
catch
catch函数接收一个失败的回调
1、调用then方法,将onRejected方法加到第二个promise的回调中
catch(onRejected){
this.then(null, onRejected)
}2、then方法中对传入的 onRejected进行判断,当没有传递时,就抛出异常
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;整体实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
}
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("----reject");
resolve("resolve---");
});
// 测试代码
promise
.then((value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
})
.then((value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
})
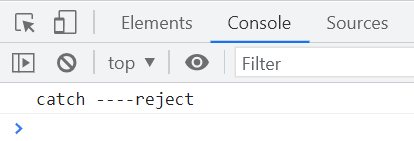
.catch((error) => {
console.log("catch", error);
});执行结果如下
finally
finally方法无论执行resolve或者reject的方法后都会执行
finally(onFinally){
this.then(()=>{
onFinally()
}, ()=>{
onFinally()
})
}整体实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("----reject");
});
promise
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
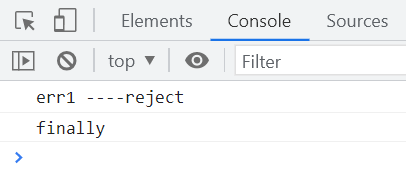
.finally(() => {
console.log("finally");
});
resolve/reject
resolve和reject是Promise的类方法,也可以通过调用then方法来实现
static resolve(value){
return new icePromise((resolve)=>resolve(value))
}
static reject(reason){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>reject(reason))
}完整实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise((onResolve) => {
onResolve(value);
});
}
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((onResolve, onRejected) => {
onRejected(reason);
});
}
}
// 测试代码
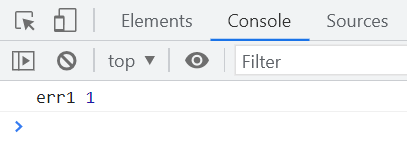
const promise = Promise.reject(1);
promise
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
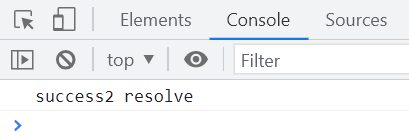
)执行结果如下
all/allSettled
all和allSettled方法都是promise的类方法
1、all方法
只要有一个promise执行reject的方法就会执行reject,当所有promise都返回resolve时,才执行resolve方法。
2、allSettled方法
当所有promise都执行完成时,才执行resolve方法,返回所有promise的状态和结果。
static all(promise){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
const values = []
promises.forEach(promise => {
promise.then(res => {
values.push(res)
if (values.length === promises.length) {
resolve(values)
}
}, err => {
reject(err)
})
})
})
})
}
static allSettled(promise){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
const values = []
promise.then(res=>{
values.push({ status: '', value: '' })
if(values.length === promise.length){
resolve(values)
}
}, err=>{
values.push({ status: '', value: '' })
if(values.length === promise.length){
resolve(values)
}
})
})
}完整实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise((onResolve) => {
onResolve(value);
});
}
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((onResolve, onRejected) => {
onRejected(reason);
});
}
static all(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push(value);
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
reject(reason);
}
);
});
});
}
static allSettled(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_FULFILLED,
value,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_REJECTED,
reason,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
}
);
});
});
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise1 = IcePromise.resolve(1);
const promise2 = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(2);
});
});
const promise3 = IcePromise.resolve(3);
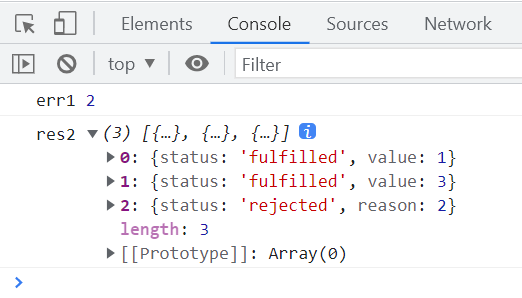
IcePromise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
);
IcePromise.allSettled([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
);执行结果如下
race/any
race和any都是promise的类方法。
1、race方法
只要有一个promise执行完成,就会返回它所执行的结果
2、any方法
① 有fulfilled状态,会等到这个fullfilled执行完成,执行resolve,结果为value
② 如果所有的Promise都是reject的,那么也会等到所有的Promise都变成rejected状态后报一个AggregateError的错误。
static race(promises){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
promises.forEach(promise=>{
promise.then(resolve, reject)
})
})
}
static any(promises){
const reasons = []
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
promises.forEach(promise=>{
promise.then(resolve, err=>{
reasons.push(err)
if(reasons.length === promises.length){
reject(new AggregateError(reasons))
}
})
})
})
}整体实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise((onResolve) => {
onResolve(value);
});
}
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((onResolve, onRejected) => {
onRejected(reason);
});
}
static all(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push(value);
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
reject(reason);
}
);
});
});
}
static allSettled(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_FULFILLED,
value,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_REJECTED,
reason,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
}
);
});
});
}
static race(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(resolve, reject);
});
});
}
static any(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reasons = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(resolve, (reason) => {
reasons.push(reason);
if (reasons.length === promises.length) {
reject(new AggregateError(reasons));
}
});
});
});
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise1 = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(1);
});
});
const promise2 = IcePromise.reject(2);
const promise3 = IcePromise.reject(3);
IcePromise.race([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
);
IcePromise.any([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
);以上就是自定义promise的所有代码啦,关于js高级,还有很多需要开发者掌握的地方,可以看看我写的其他博文,持续更新中~