一、样例和原理
常规使用
int i = 3;
// == 1.初始化
CountDownLatch cd = new CountDownLatch(i);
while (i>0){
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1L);
System.out.println("Biz-Thread is over");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// == 3.计数递减
cd.countDown();
}).start();
i--;
}
// == 2.阻塞
cd.await();共享模式
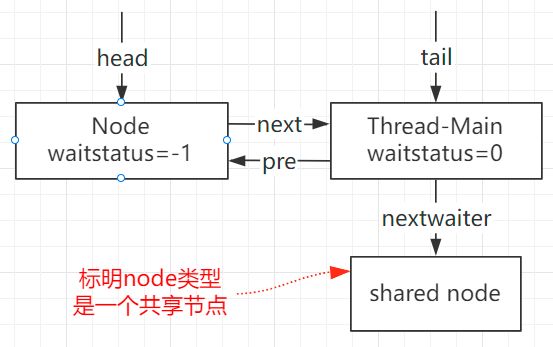
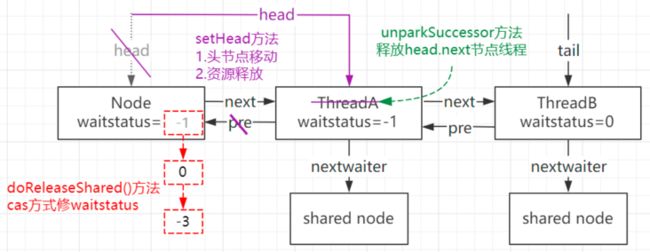
结构如图,与AQS家族的ReentrantLock对比,最大的差别在于——CountDownLatch是共享模式,ReentrantLock是独占模式
差异体现在两个层面
一、代码层面
Node节点:
static final class Node {
/** 共享 */
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
/** 独占 */
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
二、功能层面
共享模式会释放全部的共享节点的绑定线程(head节点会向下移动,head=head.next);而独占模式只会释放head.next节点绑定的线程
共享模式的特性,在下一章逆向使用部分更为清晰
逆向使用
int i = 2;
CountDownLatch cd = new CountDownLatch(1);
while (i>0){
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 准备工作完成,等待主业务");
cd.await(); // == 业务线程阻塞在此处
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 业务开始");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1L);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 业务结束");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
i--;
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3L);
// == 释放全部的业务线程
cd.countDown();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 主业务结束");
循环中,图中的三个方法配合,shared类型的节点会挨个得到释放
(当然next的指向也会释放,只是图中未体现)
二、源码分析
1.初始化
public CountDownLatch(int count) {
if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
this.sync = new Sync(count);
}
java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch.Sync#Sync
protected final void setState(int newState) {
// ## 将state赋值
state = newState;
}2.await
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// -- a.尝试获取(判断state状态)
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
// -- b.获取共享锁
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}a.尝试获取(判断state状态)
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
// 例子中state是个正数,返回-1
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}b-1.获取共享锁
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
// == 队列构建
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// == head.next尝试获取
if (p == head) {
// $$ 1.countdown()方法将state计数清0时,返回1;未清0,返回-1
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
// $$ 3.state清0情况(最后一个countDown执行后)
// ##### b-2.头节点重新设置,并释放shared
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
// $$ 2.ReentrantLock时分析过这部分,直接附上结论不再展开
// 第1次将waitstatus设置成signal返回false
// 第2次判断waitstatus==signal返回true
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node)
// === 线程阻塞(唤醒时,从此处继续执行)
&& parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}上述代码的这部分(##### b-2.头节点重新设置,并释放shared)需要仔细分析下,
具体见下一章节
b-2.头节点重新设置,并释放shared
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head;
// == 头节点移动(入参node此时是head.next),head=head.next
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null
// 共享节点都会执行下面的释放逻辑
|| s.isShared()){
// ## countDown也会调用这个方法,此处不做分析
doReleaseShared();
}
}
}
// == 头节点移动,资源释放
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}3.countDown
public void countDown() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
// == a.state递减
// 递减后state>0,返回false
// 递减后state=0,返回true(进入b逻辑)
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// == b.释放
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}a.state递减
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0)
return false;
// cas方式-1
int nextc = c-1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// -1后state=0则返回true
return nextc == 0;
}
}
b.释放
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
// 当前节点设置为头节点
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared())
// == 释放共享锁
doReleaseShared();
}
}
// == 释放共享锁
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
// ### cas将waitstatus由-1改成0失败,再次循环
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0)){
continue;
}
// ### cas将waitstatus由-1改成0成功,h.next绑定的线程解除阻塞
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0
// 头节点的waitstatus由0改成-3
&& !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)){
continue;
}
}
// -- 如果执行过程中头节点未改变,跳出循环;
// -- 如果执行过程中头节点发生变化,再次在循环中执行以上操作
if (h == head)
break;
}
}重点观察这部分逻辑
### cas将waitstatus由-1改成0成功,h.next绑定的线程解除阻塞
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 确保waitstatus由-1改成0(cas方式)
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
// 尾节点或cancle节点特殊处理
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
// == 解锁node.next绑定的线程
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}