ByteBuffer正确使用步骤
- 向 buffer 写入数据,如调用
int n = channel.read(buffer);如果返回值n = -1,则代表读取完毕。 - 调用
flip()切换至读模式 - 从 buffer 读取数据,例如调用
buffer.get(); - 调用
clear()或compact()切换至写模式 - 循环重复 1 ~ 4 步骤
ByteBuffer 源码
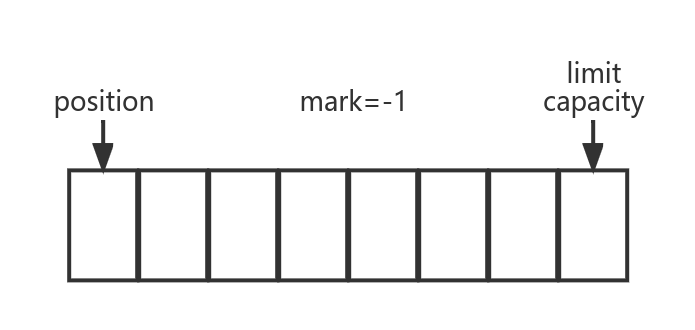
ByteBuffer 主要参数:
// Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
private int mark = -1; // 当调用 mark() 方法后,会把 position 赋值给 mark
private int position = 0; // 表示下一个被读取或者写入的位置
private int limit; // 表示第一个不可以被读取或者写入的元素的位置
private int capacity; // ByteBuffer,表示可以容纳的元素数量ByteBuffer 一共有两个构造器,且都是 protected 的,因此我们不可以使用 new 的方法构造对象
// Creates a new buffer with the given mark, position, limit, capacity,
// backing array, and array offset
//
ByteBuffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap, // package-private
byte[] hb, int offset)
{
super(mark, pos, lim, cap);
this.hb = hb;
this.offset = offset;
}
// Creates a new buffer with the given mark, position, limit, and capacity
//
ByteBuffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap) { // package-private
this(mark, pos, lim, cap, null, 0);
}我们可以使用 allocate() 和 allocateDirect() 构造 ByteBuffer。
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) {
return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity);
}
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw createCapacityException(capacity);
return new HeapByteBuffer(capacity, capacity);
}内部原理
当通过 allocate() 或 allocateDirect() 构造一个新的 ByteBuffer后
positon = 0; mark = -1; limit = capacity;当前模式是写模式时:position 即下一个要写入的位置
切换读写模式
当使用 flip() 切换至读模式时候:limit 设置为下一个写入字节的位置position 为下一个要读取字节的位置,每次读取完后 position++;
读取的时候如果 position 超过 limit 则抛出 BufferUnderflowException
public Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}当使用 clear() 切换至读模式时:
即恢复到初始状态,下一个写入字节的位置为 0
该方法相当于清除 ByteBuffer 所有状态
public Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}还可以使用 compact() 方法切换至读模式,相对于 clear() 方法,该方法会保留上次未读取完的字节,拷贝到内部字节数组前部,然后使得 position 为未读完字节长度。
重要方法
get()
get() 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
- 调用
rewind()方法将position重新置为 0 - 调用
get(int i)方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
rewind()
把 position 设为 0 ,相当于从头开始读
public Buffer rewind() {
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}mark() & reset()
注意:rewind() 和 flip() 都会清除 mark 位置
把当前读写位置 position 赋值给 mark 做一个标记,后续可以通过 reset() 方法恢复至标记的位置
public Buffer mark() {
mark = position;
return this;
}转变当前 position 为上次保留的读写位置,设置 position 为 mark
public Buffer reset() {
int m = mark;
if (m < 0)
throw new InvalidMarkException();
position = m;
return this;
}字符字节互转
字符串转为字节:
// 字符串直接转为字节数组
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
buffer1.put("hello".getBytes());// Charset
ByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");// warp
ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());字节转化为字符:
// ByteBuffer 转 String
String s = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString();
System.out.println(s);分散读集中写
当文本文件中为 onetwothree 时,我们可以一次性读取到大的 ByteBuffer 然后进行分割,这样会造成效率不高
我们可以采取分散读,分别读到对应长度的 ByteBuffer 中去,然后再进行后续处理
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("ScatteringReads.txt", "r").getChannel();) {
ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
// 分开读取到对应长度 ByteBuffer 中
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});
b1.flip();
b2.flip();
b3.flip();
System.out.println(b1); // one
System.out.println(b2); // two
System.out.println(b3); // three
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}当我们需要把一批数据写入到文件中去,可以分别写,这样会造成 IO 效率低下,可以采用集中写,聚集到一起,一次性写入到文件中
ByteBuffer b1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello"); // 5个字节
ByteBuffer b2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("world"); // 5个字节
ByteBuffer b3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好"); // 6个字节
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("GatheringWrites.txt", "rw").getChannel();) {
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}