问题描述:字串匹配搜索
假设现在我们面临这样一个问题:有一个文本串S,和一个模式串P,现在要查找P在S中的位置,怎么查找呢?
暴力匹配算法
如果用暴力匹配的思路,并假设现在文本串S匹配到 i 位置,模式串P匹配到 j 位置,则有:
1、如果当前字符匹配成功(即S[i] == P[j]),则i++,j++,继续匹配下一个字符;
2、如果失配(即S[i]! = P[j]),令i = i - (j - 1),j = 0。相当于每次匹配失败时,i 回溯,j 被置为0。
理清楚了暴力匹配算法的流程及内在的逻辑,咱们可以写出暴力匹配的代码,如下:
int ViolentMatch(char* s, char* p)
{
int sLen = strlen(s);
int pLen = strlen(p);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < sLen && j < pLen)
{
if (s[i] == p[j])
{
//①如果当前字符匹配成功(即S[i] == P[j]),则i++,j++
i++;
j++;
}
else
{
//②如果失配(即S[i]! = P[j]),令i = i - (j - 1),j = 0
i = i - j + 1;
j = 0;
}
}
//匹配成功,返回模式串p在文本串s中的位置,否则返回-1
if (j == pLen)
return i - j;
else
return -1;
}KMP 算法
Knuth-Morris-Pratt 字符串查找算法,简称为 “KMP算法”,常用于在一个文本串S内查找一个模式串P 的出现位置,这个算法由Donald Knuth、Vaughan Pratt、James H. Morris三人于1977年联合发表,故取这3人的姓氏命名此算法。
The algorithm of Knuth, Morris and Pratt [KMP 77] makes use of the information gained by previous symbol comparisons. It never re-compares a text symbol that has matched a pattern symbol. As a result, the complexity of the searching phase of the Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm is in O(n).
However, a preprocessing of the pattern is necessary in order to analyze its structure. The preprocessing phase has a complexity of O(m). Since mless or equaln, the overall complexity of the Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm is in O(n).
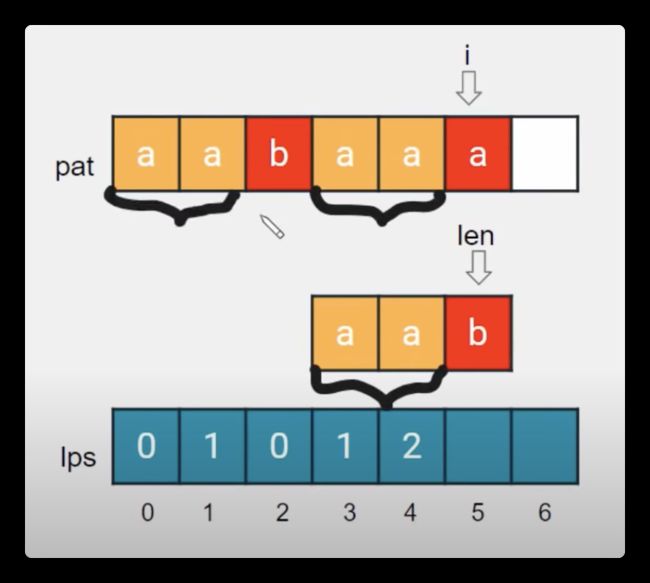
KMP 算法核心原理示意图
求解前缀表的核心思想
把前缀 P[0:j] 当成是 P 的模式串(P[0:i] ),P 本身当成是查找的文本。
next 前缀表数组,上图中是 lps 数组。
KMP源代码
极简版本的 KMP 算法源代码:
next数组首位用-1来填充,这样在处理长度的时候,思维上不会很绕。
/**
* getNext (pattern) 函数: 计算字符串 pattern 的最大公共前后缀的长度 (max common prefix suffix length)
*/
fun getNext(P: String): IntArray {
val M = P.length
val next = IntArray(M + 1, { -1 })
// i: current index of P
var i = 0
// j: current index of the longest prefix of P
var j = -1
next[0] = -1 // next[i] = j
// compute next[i]
while (i < M) {
// 如果当前字符匹配失败(即P[i] != P[j]) && j != 0 ,则令 i 不变,j = next[j]。
// 此举意味着失配时,"模式串"即前缀P[0:j], 不再从 0 位置开始比对,直接从 j = next [j] 位置开始比对。
while (j >= 0 && P[i] != P[j]) {
j = next[j]
}
i++
j++
next[i] = j
}
return next
}
/**
* kmp substring search algorithm
* @param S : the source text string
* @param P : the search pattern string
*/
fun kmp(S: String, P: String): Int {
val N = S.length
val M = P.length
if (P.isEmpty()) {
return 0
}
// j: the current index of P
var j = 0
// i: the current index of T
var i = 0
// next array
val next = getNext(P)
while (i < N) {
while (j >= 0 && S[i] != P[j]) {
j = next[j]
}
i++
j++
// when j == M, then pattern is founded in text, return the index (i - j)
if (j == M) {
return i - j
}
}
return -1
}
fun main() {
var text = "addaabbcaabffffggghhddabcdaaabbbaab"
var pattern = "aabbcaab"
print("${getNext(pattern).joinToString { it.toString() }} \n")
var index = kmp(text, pattern)
println("$pattern is the substring of $text, the index is: $index")
text = "hello"
pattern = "ll"
print("${getNext(pattern).joinToString { it.toString() }} \n")
index = kmp(text, pattern)
println("$pattern is the substring of $text, the index is: $index")
text = "abbbbbbcccddddaabaacabdcddaabbbbaad"
pattern = "aabaacab"
print("${getNext(pattern).joinToString { it.toString() }} \n")
index = kmp(text, pattern)
println("$pattern is the substring of $text, the index is: $index")
}
// 输出:
//-1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3
//aabbcaab is the substring of addaabbcaabffffggghhddabcdaaabbbaab, the index is: 3
//-1, 0, 1
//ll is the substring of hello, the index is: 2
//-1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0
//aabaacab is the substring of abbbbbbcccddddaabaacabdcddaabbbbaad, the index is: 14另外一个版本代码:
/**
* getNext (pattern) 函数: 计算字符串 pattern 的最大公共前后缀的长度 (max common prefix suffix length)
*/
fun getNext(P: String): IntArray {
val M = P.length
val next = IntArray(M, { -1 })
// i: current index of P
var i = 1
// j: current index of the longest prefix of P
var j = 0
next[0] = 0
// compute next[i]
while (i < M) {
if (P[i] == P[j]) { // ①
val len = j + 1
next[i] = len
i++
j++
} else {
// 如果当前字符匹配失败(即P[i] != P[j]) && j != 0 ,则令 i 不变,j = next[j-1]。
// 此举意味着失配时,"模式串"即前缀P[0:j], 不再从 0 位置开始比对,直接从 next [j-1] 位置开始比对。
if (j != 0) {
j = next[j - 1] // j shift left, jmp ①
} else {
next[i] = 0 // now j is 0, next i
i++
}
}
}
return next
}
/**
* kmp substring search algorithm
* @param S : the source text string
* @param P : the search pattern string
*/
fun kmp(S: String, P: String): Int {
val N = S.length
val M = P.length
if (P.isEmpty()) {
return 0
}
// j: the current index of P
var j = 0
// i: the current index of T
var i = 0
// next array
val next = getNext(P)
while (i < N - M + 1) {
if (S[i] == P[j]) {
i++
j++
} else {
if (j > 0) {
// 当前字符匹配失败(即S[i] != P[j]),则令 i 不变,j = next[j-1]。
// 此举意味着失配时,模式串P 不再从 0 位置开始比对,直接从 next [j-1] 位置开始比对。
j = next[j - 1]
} else {
i++
}
}
// when j == M, then pattern is founded in text
if (j == M) {
return i - M
}
}
return -1
}
fun main() {
var text = "addaabbcaabffffggghhddabcdaaabbbaab"
var pattern = "aabbcaab"
print("${getNext(pattern).joinToString { it.toString() }} \n")
var index = kmp(text, pattern)
println("$pattern is the substring of $text, the index is: $index")
text = "hello"
pattern = "ll"
print("${getNext(pattern).joinToString { it.toString() }} \n")
index = kmp(text, pattern)
println("$pattern is the substring of $text, the index is: $index")
text = "abbbbbbcccddddaabaacabdcddaabbbbaad"
pattern = "aabaacab"
print("${getNext(pattern).joinToString { it.toString() }} \n")
index = kmp(text, pattern)
println("$pattern is the substring of $text, the index is: $index")
}
// 输出:
//0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3
//aabbcaab is the substring of addaabbcaabffffggghhddabcdaaabbbaab, the index is: 3
//0, 1
//ll is the substring of hello, the index is: 2
//0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0
//aabaacab is the substring of abbbbbbcccddddaabaacabdcddaabbbbaad, the index is: 14参考资料
https://www.inf.hs-flensburg.de/lang/algorithmen/pattern/kmpen.htmhttps://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7041827