RESTful API风格
在开发之前先回顾一下,RESTful API 是什么? RESTful 是一种 API 设计风格,并不是一种强制规范和标准,它的特点在于请求和响应都简洁清晰,可读性强。不管 API 属于哪种风格,只要能够满足需要,就足够了。API 格式并不存在绝对的标准,只存在不同的设计风格。
API 风格
一般来说 API 设计包含两部分: 请求和响应。
- 请求:请求URL、请求方法、请求头部信息等。
- 响应:响应体和响应头部信息。
先来看一个请求 url 的组成:
https://www.baidu.com:443/api/articles?id=1
// 请求方法:GET
// 请求协议:protocal: https
// 请求端口:port: 443
// 请求域名:host: www.baidu.com
// 请求路径:pathname: /api/articles
// 查询字符串:search: id=1
根据 URL 组成部分:请求方法、请求路径和查询字符串,我们有几种常见的 API 风格。比如当删除 id=1 的作者编写的类别为 2 的所有文章时:
// 纯请求路径
GET https://www.baidu.com/api/articles/delete/authors/1/categories/2
// 一级使用路径,二级以后使用查询字符串
GET https://www.baidu.com/api/articles/delete/author/1?category=2
// 纯查询字符串
GET https://www.baidu.com/api/deleteArticles?author=1&category=2
// RESTful风格
DELETE https://www.baidu.com/api/articles?author=1&category=2
前面三种都是 GET 请求,主要的区别在于多个查询条件时怎么传递查询字符串,有的通过使用解析路径,有的通过解析传参,有的两者混用。同时在描述 API 功能时,可以使用 articles/delete ,也可以使用 deleteArticles 。而第四种 RESTful API 最大的区别在于行为动词 DELETE 的位置,不在 url 里,而在请求方法中.
RESTful设计风格
REST(Representational State Transfer 表现层状态转移) 是一种设计风格,而不是标准。主要用于客户端和服务端的API交互,我认为它的约定大于它的定义,使得 api 在设计上有了一定的规范和原则,语义更加明确,清晰。
我们一起来看看 RESTFul API 有哪些特点:
- 基于“资源”,数据也好、服务也好,在
RESTFul设计里一切都是资源,
资源用URI(Universal Resource Identifier 通用资源标识)来表示。 - 无状态性。
-
URL中通常不出现动词,只有名词。 -
URL语义清晰、明确。 - 使用
HTTP的GET、POST、DELETE、PUT来表示对于资源的增删改查。 - 使用
JSON不使用XML。
举个栗子,也就是后面要实现的 api 接口:
GET /api/blogs:查询文章
POST /api/blogs:新建文章
GET /api/blogs/ID:获取某篇指定文章
PUT /api/blogs/ID:更新某篇指定文章
DELETE /api/blogs/ID:删除某篇指定文章
关于更多RESTful API 的知识,小伙伴们可以戳:这里。
项目初始化
什么是Koa2
Koa官方网址。官方介绍:Koa 是一个新的 web 框架,由 Express 幕后的原班人马打造, 致力于成为 web 应用和 API 开发领域中的一个更小、更富有表现力、更健壮的基石。
Koa2的安装与使用对Node.js的版本也是有要求的,因为node.js 7.6版本 开始完全支持async/await,所以才能完全支持Koa2。
Koa2 是 Koa 框架的最新版本,Koa3 还没有正式推出,Koa1.X 正走在被替换的路上。Koa2 与 Koa1 的最大不同,在于 Koa1 基于 co 管理 Promise/Generator 中间件,而 Koa2 紧跟最新的 ES 规范,支持到了 Async Function(Koa1 不支持),两者中间件模型表现一致,只是语法底层不同。
在 Express 里面,不同时期的代码组织方式虽然大为不同,但纵观 Express 多年的历程,他依然是相对大而全,API 较为丰富的框架,它的整个中间件模型是基于 callback 回调,而 callback 常年被人诟病。
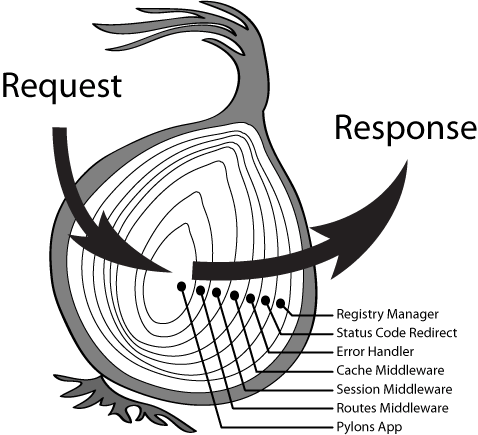
简单来说 Koa 和 Express 的最大的区别在于 执行顺序 和 异步的写法 ,同时这也映射了 js 语法在处理异步任务上的发展历程。关于异步和两种框架区别,不在这里做过多探讨。来看看 Koa 中间件洋葱圈模型:
创建Koa2项目
创建文件 blog-api ,进入到该目录:
npm init
安装 Koa:
yarn add koa
安装 eslint, 这个选择安装,可以根据自己的需求来规范自己的代码,下面是我配置的 eslint:
yarn add eslint -D
yarn add eslint-config-airbnb-base -D
yarn add eslint-plugin-import -D
根目录下新建文件 .eslintrc.js 和 .editorconfig:
// .eslintrc.js
module.exports = {
root: true,
globals: {
document: true,
},
extends: 'airbnb-base',
rules: {
'no-underscore-dangle': 0,
'func-names': 0,
'no-plusplus': 0,
},
};
// .editorconfig
root = true
[*]
indent_style = space
indent_size = 2
end_of_line = lf
charset = utf-8
trim_trailing_whitespace = true
insert_final_newline = true
在根目录下新建文件 app.js:
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
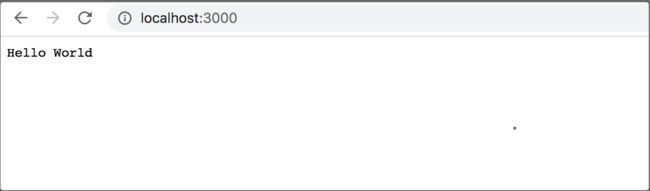
app.use(async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000);
通过命令启动项目:
node app.js
在浏览器打开 http://localhost:3000/:
项目开发
目录结构
规划项目结构,创建对应的文件夹:
blog-api
├── bin // 项目启动文件
├── config // 项目配置文件
├── controllers // 控制器
├── dbhelper // 数据库操作
├── error // 错误处理
├── middleware // 中间件
├── models // 数据库模型
├── node_modules
├── routers // 路由
├── util // 工具类
├── README.md // 说明文档
├── package.json
├── app.js // 入口文件
└── yarn.lock
自动重启
在编写调试项目,修改代码后,需要频繁的手动close掉,然后再重新启动,非常繁琐。安装自动重启工具 nodemon :
yarn add nodemon -D
再安装 cross-env,主要为设置环境变量兼容用的 :
yarn add cross-env
在 package.json 的 scripts 中增加脚本:
{
"name": "blog-api",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "个人博客后台api",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development nodemon ./app.js",
"rc": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production nodemon ./app.js",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "Mingme <[email protected]>",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"cross-env": "^7.0.2",
"koa": "^2.13.0",
"koa-router": "^10.0.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"eslint": "^7.13.0",
"eslint-config-airbnb-base": "^14.2.1",
"eslint-plugin-import": "^2.22.1",
"nodemon": "^2.0.6"
}
}
这时候就能通过我们设置的脚本运行项目,修改文件保存后就会自动重启了。
以生产模式运行
yarn rc
// 或者
npm run rc
以开发模式运行
yarn dev
// 或者
npm run dev
koa 路由
路由(Routing)是由一个 URI(或者叫路径) 和一个特定的 HTTP 方法 (GET、POST 等) 组成的,涉及到应用如何响应客户端对某个网站节点的访问。
yarn add koa-router
接口统一以 /api 为前缀,比如:
http://localhost:3000/api/categories
http://localhost:3000/api/blogs
在 config 目录下创建 index.js:
// config/index.js
module.exports = {
apiPrefix: '/api',
};
在 routers 目录下创建 index.js , category.js , blog.js :
// routers/category.js
const router = require('koa-router')();
router.get('/', async (ctx) => {
// ctx 上下文 context ,包含了request 和response等信息
ctx.body = '我是分类接口';
});
module.exports = router;
// routers/blog.js
const router = require('koa-router')();
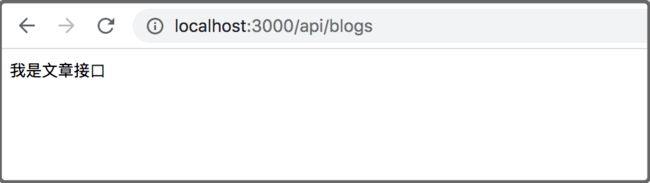
router.get('/', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = '我是文章接口';
});
module.exports = router;
// routers/index.js
const router = require('koa-router')();
const { apiPrefix } = require('../config/index');
const blog = require('./blog');
const category = require('./category');
router.prefix(apiPrefix);
router.use('/blogs', blog.routes(), blog.allowedMethods());
router.use('/categories', category.routes(), category.allowedMethods());
module.exports = router;
在 app.js 中修改代码,引入路由:
// app.js
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const routers = require('./routers/index');
// routers
app.use(routers.routes()).use(routers.allowedMethods());
app.listen(3000);
本地启动项目,看看效果:
根据不同的路由显示不同的内容,说明路由没问题了。
GET 请求
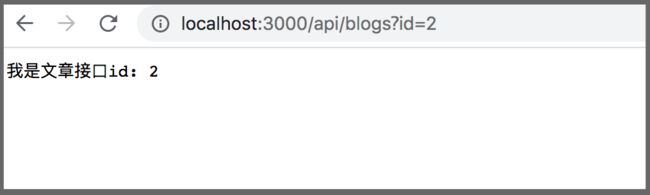
接下来看一下参数传递,假如是请求 id 为 1 的文章,我们 GET 请求一般这么写:
http://localhost:3000/api/blogs/1
http://localhost:3000/api/blogs?id=1
// routers/blog.js
const router = require('koa-router')();
router.get('/', async (ctx) => {
/**
在 koa2 中 GET 传值通过 request 接收,但是接收的方法有两种:query 和 querystring。
query:返回的是格式化好的参数对象。
querystring:返回的是请求字符串。
*/
ctx.body = `我是文章接口id: ${ctx.query.id}`;
});
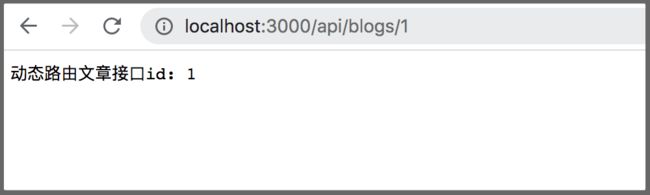
// 动态路由
router.get('/:id', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = `动态路由文章接口id: ${ctx.params.id}`;
});
module.exports = router;
如图:
POST/PUT/DEL
GET 把参数包含在 URL 中,POST 通过 request body 传递参数。
为了方便使用 koa-body 来处理 POST 请求和文件上传,或者使用 koa-bodyparser 和 koa-multer 也可以。
yarn add koa-body
为了统一数据格式,使数据JSON化,安装 koa-json:
yarn add koa-json
使用 koa-logger 方便调试:
yarn add koa-logger
在 app.js 里引入中间件:
const Koa = require('koa');
const path = require('path');
const app = new Koa();
const koaBody = require('koa-body');
const json = require('koa-json');
const logger = require('koa-logger');
const routers = require('./routers/index');
// middlewares
app.use(koaBody({
multipart: true, // 支持文件上传
formidable: {
formidable: {
uploadDir: path.join(__dirname, 'public/upload/'), // 设置文件上传目录
keepExtensions: true, // 保持文件的后缀
maxFieldsSize: 2 * 1024 * 1024, // 文件上传大小
onFileBegin: (name, file) => { // 文件上传前的设置
console.log(`name: ${name}`);
console.log(file);
},
},
},
}));
app.use(json());
app.use(logger());
// routers
app.use(routers.routes()).use(routers.allowedMethods());
app.listen(3000);
在 routers/blog.js 下添加路由:
// routers/blog.js
const router = require('koa-router')();
router.get('/', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = `我是文章接口id: ${ctx.query.id}`;
});
// 动态路由
router.get('/:id', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = `动态路由文章接口id: ${ctx.params.id}`;
});
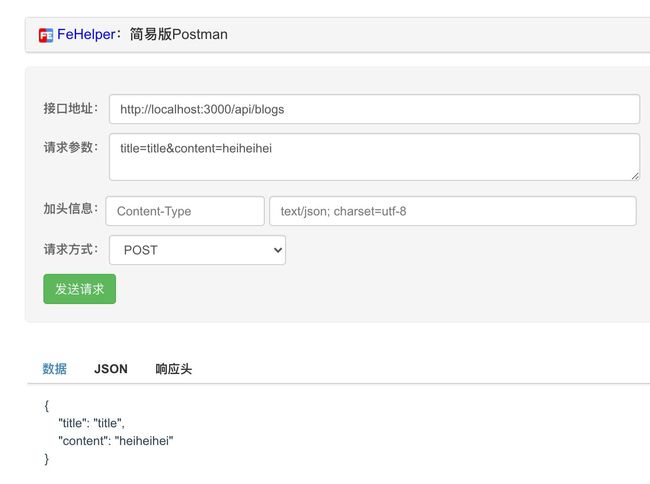
router.post('/', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = ctx.request.body;
});
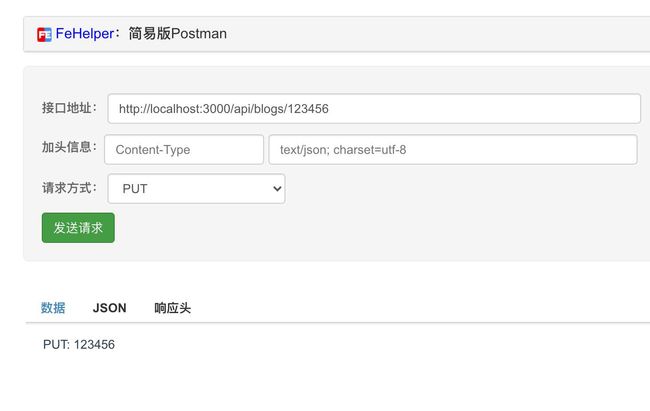
router.put('/:id', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = `PUT: ${ctx.params.id}`;
});
router.del('/:id', async (ctx) => {
ctx.body = `DEL: ${ctx.params.id}`;
});
module.exports = router;
测试一下:
错误处理
在请求过程中,还需要将返回结果进行一下包装,发生异常时,如果接口没有提示语,状态码的返回肯定是不友好的,下面定义几个常用的错误类型。
在 error 目录下创建 api_error_map.js 、 api_error_name.js 、 api_error.js:
// error/api_error_map.js
const ApiErrorNames = require('./api_error_name');
const ApiErrorMap = new Map();
ApiErrorMap.set(ApiErrorNames.NOT_FOUND, { code: ApiErrorNames.NOT_FOUND, message: '未找到该接口' });
ApiErrorMap.set(ApiErrorNames.UNKNOW_ERROR, { code: ApiErrorNames.UNKNOW_ERROR, message: '未知错误' });
ApiErrorMap.set(ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_ID, { code: ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_ID, message: 'id 不合法' });
ApiErrorMap.set(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID, { code: ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID, message: 'id 不存在' });
ApiErrorMap.set(ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_FILE_TYPE, { code: ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_FILE_TYPE, message: '文件类型不允许' });
ApiErrorMap.set(ApiErrorNames.NO_AUTH, { code: ApiErrorNames.NO_AUTH, message: '没有操作权限' });
module.exports = ApiErrorMap;
// error/api_error_name.js
const ApiErrorNames = {
NOT_FOUND: 'not_found',
UNKNOW_ERROR: 'unknow_error',
LEGAL_ID: 'legal_id',
UNEXIST_ID: 'unexist_id',
LEGAL_FILE_TYPE: 'legal_file_type',
NO_AUTH: 'no_auth',
};
module.exports = ApiErrorNames;
// error/api_error.js
const ApiErrorMap = require('./api_error_map');
/**
* 自定义Api异常
*/
class ApiError extends Error {
constructor(errorName, errorMsg) {
super();
let errorInfo = {};
if (errorMsg) {
errorInfo = {
code: errorName,
message: errorMsg,
};
} else {
errorInfo = ApiErrorMap.get(errorName);
}
this.name = errorName;
this.code = errorInfo.code;
this.message = errorInfo.message;
}
}
module.exports = ApiError;
在 middleware 目录下创建 response_formatter.js 用来处理 api 返回数据的格式化:
// middleware/response_formatter.js
const ApiError = require('../error/api_error');
const ApiErrorNames = require('../error/api_error_name');
const responseFormatter = (apiPrefix) => async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.request.path.startsWith(apiPrefix)) {
try {
// 先去执行路由
await next();
if (ctx.response.status === 404) {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.NOT_FOUND);
} else {
ctx.body = {
code: 'success',
message: '成功!',
result: ctx.body,
};
}
} catch (error) {
// 如果异常类型是API异常,将错误信息添加到响应体中返回。
if (error instanceof ApiError) {
ctx.body = {
code: error.code,
message: error.message,
};
} else {
ctx.status = 400;
ctx.response.body = {
code: error.name,
message: error.message,
};
}
}
} else {
await next();
}
};
module.exports = responseFormatter;
顺便安装 koa 的错误处理程序 hack :
yarn add koa-onerror
在 app.js 中添加代码:
const Koa = require('koa');
const path = require('path');
const app = new Koa();
const onerror = require('koa-onerror');
const koaBody = require('koa-body');
const json = require('koa-json');
const logger = require('koa-logger');
const responseFormatter = require('./middleware/response_formatter');
const { apiPrefix } = require('./config/index');
const routers = require('./routers/index');
// koa的错误处理程序hack
onerror(app);
// middlewares
app.use(koaBody({
multipart: true, // 支持文件上传
formidable: {
formidable: {
uploadDir: path.join(__dirname, 'public/upload/'), // 设置文件上传目录
keepExtensions: true, // 保持文件的后缀
maxFieldsSize: 2 * 1024 * 1024, // 文件上传大小
onFileBegin: (name, file) => { // 文件上传前的设置
console.log(`name: ${name}`);
console.log(file);
},
},
},
}));
app.use(json());
app.use(logger());
// response formatter
app.use(responseFormatter(apiPrefix));
// routers
app.use(routers.routes()).use(routers.allowedMethods());
// 监听error
app.on('error', (err, ctx) => {
// 在这里可以对错误信息进行一些处理,生成日志等。
console.error('server error', err, ctx);
});
app.listen(3000);
在后续开发中,若遇到异常,将异常抛出即可。
连接数据库
mongoDB 数据库的安装教程 :Linux 服务器(CentOS)安装配置mongodb+node。
mongoose : nodeJS 提供连接 mongodb 的一个库。
mongoose-paginate :mongoose 的分页插件。
mongoose-unique-validator :可为 Mongoose schema 中的唯一字段添加预保存验证。
yarn add mongoose
yarn add mongoose-paginate
yarn add mongoose-unique-validator
在 config/index.js 中增加配置:
module.exports = {
port: process.env.PORT || 3000,
apiPrefix: '/api',
database: 'mongodb://localhost:27017/test',
databasePro: 'mongodb://root:[email protected]:27017/blog', // mongodb://用户名:密码@服务器公网IP:端口/库的名称
};
在 dbhelper 目录下创建 db.js:
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const config = require('../config');
mongoose.Promise = global.Promise;
const IS_PROD = ['production', 'prod', 'pro'].includes(process.env.NODE_ENV);
const databaseUrl = IS_PROD ? config.databasePro : config.database;
/**
* 连接数据库
*/
mongoose.connect(databaseUrl, {
useUnifiedTopology: true,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useFindAndModify: false,
useCreateIndex: true,
config: {
autoIndex: false,
},
});
/**
* 连接成功
*/
mongoose.connection.on('connected', () => {
console.log(`Mongoose 连接成功: ${databaseUrl}`);
});
/**
* 连接异常
*/
mongoose.connection.on('error', (err) => {
console.log(`Mongoose 连接出错: ${err}`);
});
/**
* 连接断开
*/
mongoose.connection.on('disconnected', () => {
console.log('Mongoose 连接关闭!');
});
module.exports = mongoose;
在 app.js 中引入:
...
const routers = require('./routers/index');
require('./dbhelper/db');
// koa的错误处理程序hack
onerror(app);
...
启动项目就可以看到log提示连接成功:
这里说一下在 db.js 中有这么一行代码:
mongoose.Promise = global.Promise;
加上这个是因为:mongoose 的所有查询操作返回的结果都是 query ,mongoose 封装的一个对象,并非一个完整的 promise,而且与 ES6 标准的 promise 有所出入,因此在使用 mongoose 的时候,一般加上这句 mongoose.Promise = global.Promise。
开发 API
Mongoose 的一切始于 Schema 。在开发接口之前,那就先来构建模型,这里主要构建文章分类,和文章列表两种类型的接口,在字段上会比较简陋,主要用于举例使用,小伙伴们可以举一反三。
在 models 目录下创建 category.js 和 blog.js:
// models/category.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const mongoosePaginate = require('mongoose-paginate');
const uniqueValidator = require('mongoose-unique-validator');
const schema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
unique: true,
required: [true, '分类 name 必填'],
},
value: {
type: String,
unique: true,
required: [true, '分类 value 必填'],
},
rank: {
type: Number,
default: 0,
},
}, {
timestamps: { createdAt: 'createdAt', updatedAt: 'updatedAt' },
});
// 自动增加版本号
/* Mongoose 仅在您使用时更新版本密钥save()。如果您使用update(),findOneAndUpdate()等等,Mongoose将不会 更新版本密钥。
作为解决方法,您可以使用以下中间件。参考 https://mongoosejs.com/docs/guide.html#versionKey */
schema.pre('findOneAndUpdate', function () {
const update = this.getUpdate();
if (update.__v != null) {
delete update.__v;
}
const keys = ['$set', '$setOnInsert'];
Object.keys(keys).forEach((key) => {
if (update[key] != null && update[key].__v != null) {
delete update[key].__v;
if (Object.keys(update[key]).length === 0) {
delete update[key];
}
}
});
update.$inc = update.$inc || {};
update.$inc.__v = 1;
});
schema.plugin(mongoosePaginate);
schema.plugin(uniqueValidator);
module.exports = mongoose.model('Category', schema);
// models/blog.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const uniqueValidator = require('mongoose-unique-validator');
const mongoosePaginate = require('mongoose-paginate');
const schema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String,
unique: true,
required: [true, '必填字段'],
}, // 标题
content: {
type: String,
required: [true, '必填字段'],
}, // 内容
category: {
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
required: [true, '必填字段'],
ref: 'Category',
}, // 分类_id,根据这个id我们就能从 category 表中查找到相关数据。
status: {
type: Boolean,
default: true,
}, // 状态
}, {
timestamps: { createdAt: 'createdAt', updatedAt: 'updatedAt' },
toJSON: { virtuals: true },
});
// 虚拟字段:根据_id查找对应表中的数据。
schema.virtual('categoryObj', {
ref: 'Category',
localField: 'category',
foreignField: '_id',
justOne: true,
});
// 自动增加版本号
/* Mongoose 仅在您使用时更新版本密钥save()。如果您使用update(),findOneAndUpdate()等等,Mongoose将不会 更新版本密钥。
作为解决方法,您可以使用以下中间件。参考 https://mongoosejs.com/docs/guide.html#versionKey */
schema.pre('findOneAndUpdate', function () {
const update = this.getUpdate();
if (update.__v != null) {
delete update.__v;
}
const keys = ['$set', '$setOnInsert'];
Object.keys(keys).forEach((key) => {
if (update[key] != null && update[key].__v != null) {
delete update[key].__v;
if (Object.keys(update[key]).length === 0) {
delete update[key];
}
}
});
update.$inc = update.$inc || {};
update.$inc.__v = 1;
});
schema.plugin(mongoosePaginate);
schema.plugin(uniqueValidator);
module.exports = mongoose.model('Blog', schema);
在 dbhelper 目录下,定义一些对数据库增删改查的方法,创建 category.js 和 blog.js:
// dbhelper/category.js
const Model = require('../models/category');
// TODO: 此文件中最好返回 Promise。通过 .exec() 可以返回 Promise。
// 需要注意的是 分页插件本身返回的就是 Promise 因此 Model.paginate 不需要 exec()。
// Model.create 返回的也是 Promise
/**
* 查找全部
*/
exports.findAll = () => Model.find().sort({ rank: 1 }).exec();
/**
* 查找多个 筛选
*/
exports.findSome = (data) => {
const {
page = 1, limit = 10, sort = 'rank',
} = data;
const query = {};
const options = {
page: parseInt(page, 10),
limit: parseInt(limit, 10),
sort,
};
const result = Model.paginate(query, options);
return result;
};
/**
* 查找单个 详情
*/
exports.findById = (id) => Model.findById(id).exec();
/**
* 增加
*/
exports.add = (data) => Model.create(data);
/**
* 更新
*/
exports.update = (data) => {
const { id, ...restData } = data;
return Model.findOneAndUpdate({ _id: id }, {
...restData,
},
{
new: true, // 返回修改后的数据
}).exec();
};
/**
* 删除
*/
exports.delete = (id) => Model.findByIdAndDelete(id).exec();
// dbhelper/blog.js
const Model = require('../models/blog');
// TODO: 此文件中最好返回 Promise。通过 .exec() 可以返回 Promise。
// 需要注意的是 分页插件本身返回的就是 Promise 因此 Model.paginate 不需要 exec()。
// Model.create 返回的也是 Promise
const populateObj = [
{
path: 'categoryObj',
select: 'name value',
},
];
/**
* 查找全部
*/
exports.findAll = () => Model.find().populate(populateObj).exec();
/**
* 查找多个 筛选
*/
exports.findSome = (data) => {
const {
keyword, title, category, status = true, page = 1, limit = 10, sort = '-createdAt',
} = data;
const query = {};
const options = {
page: parseInt(page, 10),
limit: parseInt(limit, 10),
sort,
populate: populateObj,
};
if (status !== 'all') {
query.status = status === true || status === 'true';
}
if (title) {
query.title = { $regex: new RegExp(title, 'i') };
}
if (category) {
query.category = category;
}
// 关键字模糊查询 标题 和 content
if (keyword) {
const reg = new RegExp(keyword, 'i');
const fuzzyQueryArray = [{ content: { $regex: reg } }];
if (!title) {
fuzzyQueryArray.push({ title: { $regex: reg } });
}
query.$or = fuzzyQueryArray;
}
return Model.paginate(query, options);
};
/**
* 查找单个 详情
*/
exports.findById = (id) => Model.findById(id).populate(populateObj).exec();
/**
* 新增
*/
exports.add = (data) => Model.create(data);
/**
* 更新
*/
exports.update = (data) => {
const { id, ...restData } = data;
return Model.findOneAndUpdate({ _id: id }, {
...restData,
}, {
new: true, // 返回修改后的数据
}).exec();
};
/**
* 删除
*/
exports.delete = (id) => Model.findByIdAndDelete(id).exec();
编写路由:
// routers/category.js
const router = require('koa-router')();
const controller = require('../controllers/category');
// 查
router.get('/', controller.find);
// 查 动态路由
router.get('/:id', controller.detail);
// 增
router.post('/', controller.add);
// 改
router.put('/:id', controller.update);
// 删
router.del('/:id', controller.delete);
module.exports = router;
// routers/blog.js
const router = require('koa-router')();
const controller = require('../controllers/blog');
// 查
router.get('/', controller.find);
// 查 动态路由
router.get('/:id', controller.detail);
// 增
router.post('/', controller.add);
// 改
router.put('/:id', controller.update);
// 删
router.del('/:id', controller.delete);
module.exports = router;
在路由文件里面我们只定义路由,把路由所对应的方法全部都放在 controllers 下:
// controllers/category.js
const dbHelper = require('../dbhelper/category');
const tool = require('../util/tool');
const ApiError = require('../error/api_error');
const ApiErrorNames = require('../error/api_error_name');
/**
* 查
*/
exports.find = async (ctx) => {
let result;
const reqQuery = ctx.query;
if (reqQuery && !tool.isEmptyObject(reqQuery)) {
if (reqQuery.id) {
result = dbHelper.findById(reqQuery.id);
} else {
result = dbHelper.findSome(reqQuery);
}
} else {
result = dbHelper.findAll();
}
await result.then((res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 查 动态路由 id
*/
exports.detail = async (ctx) => {
const { id } = ctx.params;
if (!tool.validatorsFun.numberAndCharacter(id)) {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_ID);
}
await dbHelper.findById(id).then((res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 添加
*/
exports.add = async (ctx) => {
const dataObj = ctx.request.body;
await dbHelper.add(dataObj).then((res) => {
ctx.body = res;
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 更新
*/
exports.update = async (ctx) => {
const ctxParams = ctx.params;
// 合并 路由中的参数 以及 发送过来的参数
// 路由参数 以及发送的参数可能都有 id 以 发送的 id 为准,如果没有,取路由中的 id
const dataObj = { ...ctxParams, ...ctx.request.body };
await dbHelper.update(dataObj).then((res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 删除
*/
exports.delete = async (ctx) => {
const ctxParams = ctx.params;
// 合并 路由中的参数 以及 发送过来的参数
// 路由参数 以及发送的参数可能都有 id 以 发送的 id 为准,如果没有,取路由中的 id
const dataObj = { ...ctxParams, ...ctx.request.body };
if (!tool.validatorsFun.numberAndCharacter(dataObj.id)) {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_ID);
}
await dbHelper.delete(dataObj.id).then((res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
// controllers/blog.js
const dbHelper = require('../dbhelper/blog');
const tool = require('../util/tool');
const ApiError = require('../error/api_error');
const ApiErrorNames = require('../error/api_error_name');
/**
* 查
*/
exports.find = async (ctx) => {
let result;
const reqQuery = ctx.query;
if (reqQuery && !tool.isEmptyObject(reqQuery)) {
if (reqQuery.id) {
result = dbHelper.findById(reqQuery.id);
} else {
result = dbHelper.findSome(reqQuery);
}
} else {
result = dbHelper.findAll();
}
await result.then((res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 查 详情
*/
exports.detail = async (ctx) => {
const { id } = ctx.params;
if (!tool.validatorsFun.numberAndCharacter(id)) {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_ID);
}
await dbHelper.findById(id).then(async (res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 增
*/
exports.add = async (ctx) => {
const dataObj = ctx.request.body;
await dbHelper.add(dataObj).then((res) => {
ctx.body = res;
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 改
*/
exports.update = async (ctx) => {
const ctxParams = ctx.params;
// 合并 路由中的参数 以及 发送过来的参数
// 路由参数 以及发送的参数可能都有 id 以 发送的 id 为准,如果没有,取路由中的 id
const dataObj = { ...ctxParams, ...ctx.request.body };
await dbHelper.update(dataObj).then((res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* 删
*/
exports.delete = async (ctx) => {
const ctxParams = ctx.params;
// 合并 路由中的参数 以及 发送过来的参数
// 路由参数 以及发送的参数可能都有 id 以 发送的 id 为准,如果没有,取路由中的 id
const dataObj = { ...ctxParams, ...ctx.request.body };
if (!tool.validatorsFun.numberAndCharacter(dataObj.id)) {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.LEGAL_ID);
}
await dbHelper.delete(dataObj.id).then((res) => {
if (res) {
ctx.body = res;
} else {
throw new ApiError(ApiErrorNames.UNEXIST_ID);
}
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
上面使用了两个方法,isEmptyObject 判断是否是空对象,numberAndCharacter 对 id 格式做一个简单的检查。
// util/tool.js
/**
* @desc 检查是否为空对象
*/
exports.isEmptyObject = (obj) => Object.keys(obj).length === 0;
/**
* @desc 常规正则校验表达式
*/
exports.validatorsExp = {
number: /^[0-9]*$/,
numberAndCharacter: /^[0-9a-zA-Z]+$/,
nameLength: (n) => new RegExp(`^[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]{${n},}$`),
idCard: /^(\d{6})(\d{4})(\d{2})(\d{2})(\d{3})([0-9]|X)$/,
backCard: /^([1-9]{1})(\d{15}|\d{18})$/,
phone: /^1[3456789]\d{9}$/,
email: /^\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*$/,
};
/**
* @desc 常规正则校验方法
*/
exports.validatorsFun = {
number: (val) => exports.validatorsExp.number.test(val),
numberAndCharacter: (val) => exports.validatorsExp.numberAndCharacter.test(val),
idCard: (val) => exports.validatorsExp.idCard.test(val),
backCard: (val) => exports.validatorsExp.backCard.test(val),
};
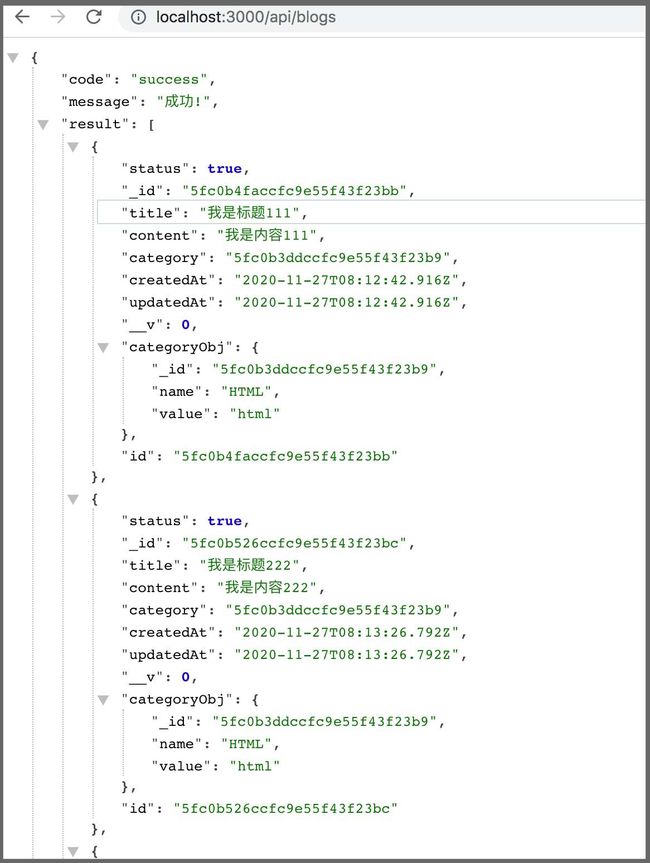
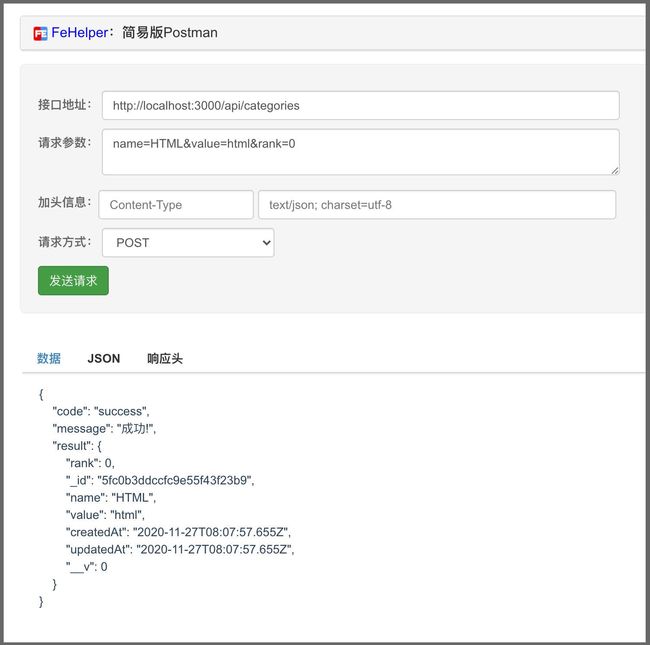
到此,分类和文章相关的接口基本完成了,测试一下:
鉴权
这里我使用的是 token 来进行身份验证的: jsonwebtoken
根据路由对一些非 GET 请求的接口做 token 验证。
// app.js
...
// 检查请求时 token 是否过期
app.use(tokenHelper.checkToken([
'/api/blogs',
'/api/categories',
...
], [
'/api/users/signup',
'/api/users/signin',
'/api/users/forgetPwd',
]));
...
// util/token-helper.js
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const config = require('../config/index');
const tool = require('./tool');
// 生成token
exports.createToken = (user) => {
const token = jwt.sign({ userId: user._id, userName: user.userName }, config.tokenSecret, { expiresIn: '2h' });
return token;
};
// 解密token返回userId,userName用来判断用户身份。
exports.decodeToken = (ctx) => {
const token = tool.getTokenFromCtx(ctx);
const userObj = jwt.decode(token, config.tokenSecret);
return userObj;
};
// 检查token
exports.checkToken = (shouldCheckPathArray, unlessCheckPathArray) => async (ctx, next) => {
const currentUrl = ctx.request.url;
const { method } = ctx.request;
const unlessCheck = unlessCheckPathArray.some((url) => currentUrl.indexOf(url) > -1);
const shouldCheck = shouldCheckPathArray.some((url) => currentUrl.indexOf(url) > -1) && method !== 'GET';
if (shouldCheck && !unlessCheck) {
const token = tool.getTokenFromCtx(ctx);
if (token) {
try {
jwt.verify(token, config.tokenSecret);
await next();
} catch (error) {
ctx.status = 401;
ctx.body = 'token 过期';
}
} else {
ctx.status = 401;
ctx.body = '无 token,请登录';
}
} else {
await next();
}
};
在注册个登录的时候生成设置 token :
// controllers/users.js
/**
* @desc 注册
*/
...
exports.signUp = async (ctx) => {
const dataObj = ctx.request.body;
await dbHelper.signUp(dataObj).then((res) => {
const token = tokenHelper.createToken(res);
const { password, ...restData } = res._doc;
ctx.res.setHeader('Authorization', token);
ctx.body = {
token,
...restData,
};
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
/**
* @desc 登录
*/
exports.signIn = async (ctx) => {
const dataObj = ctx.request.body;
await dbHelper.signIn(dataObj).then((res) => {
const token = tokenHelper.createToken(res);
const { password, ...restData } = res;
ctx.res.setHeader('Authorization', token);
ctx.body = {
token,
...restData,
};
}).catch((err) => {
throw new ApiError(err.name, err.message);
});
};
...
项目部署
部署就比较简单了,将项目文件全部上传到服务器上,然后全局安装 pm2,用 pm2 启动即可。
在 bin 目录下创建 pm2.config.json :
{
"apps": [
{
"name": "blog-api",
"script": "./app.js",
"instances": 0,
"watch": false,
"exec_mode": "cluster_mode"
}
]
}
在 package.json 中添加启动脚本:
{
...
"scripts": {
"dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development nodemon ./app.js",
"rc": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production nodemon ./app.js",
"pm2": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production NODE_LOG_DIR=/tmp ENABLE_NODE_LOG=YES pm2 start ./bin/pm2.config.json",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
...
}
然后,cd 到项目根目录:
npm run pm2
关于个人博客前台开发可以戳这里:Nuxt 开发搭建博客