单目标跟踪通过CAM绘制heatmap图像(以SiamCAR为例)
论文链接:
SiamCAR: Siamese Fully Convolutional Classification and Regression for Visual Tracking
Group-CAM: Group Score-Weighted Visual Explanations for Deep Convolutional Networks
代码链接:
SiamCAR+Group-CAM:code
环境配置:
pip install -r requirements.txt
cd toolkit/utils/
python setup.py build_ext --inplace注:与SiamCAR环境配置相同,不同的是这里增加了一个python包:kornia
运行:
对于SiamCAR-CAM代码的运行,在终端上,参见下面的代码。
cd /path/to/SiamCAR-CAM
conda activate SiamCAR
export PYTHONPATH=./:$PYTHONPATH
python tools/CAM-demo.py \
--dataset_dir /path/to/dataset/root \ # dataset path
--dataset UAV123 \ # dataset name(OTB100, GOT-10k, LaSOT, UAV123)
--snapshot snapshot/general_model.pth \ # tracker_name
--format bmp \ # save fomat (pdf,png,jpg,bmp)
--save_dir /path/to/save \ # save dir
--config ./experiments/siamcar_r50/config.yaml \ # config file
--register_layer softmax \ # module register name值得注意的是,通过CAM进行可视化,只有最后一层分类分支或者SiamCAR中,经过归一化的Centerness分支的输出进行可视化才是有意义的。其余分支经过CAM进行可视化,会出现杂乱无章的状态,这对于我们做数据分析来说,是无用的。但是为了方便理解,在代码中,我们将SiamCAR其余的神经网络结构也进行了注册,方便进行可视化。
以上面代码为例,在配置好环境后,我们在终端下进行如下的指令运行:
cd /home/db306/桌面/SiamCAR-CAM
conda activate SiamCAR
export PYTHONPATH=./:$PYTHONPATH
python tools/CAM-demo.py \
--dataset_dir /media/db306/HUSHUO/Benchmark/ \
--dataset OTB100 \
--snapshot snapshot/general_model.pth \
--format bmp \
--save_dir ./test \
--config ./experiments/siamcar_r50/config.yaml \
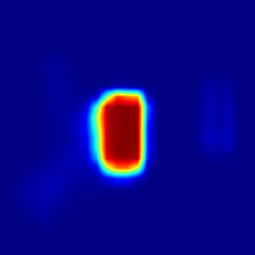
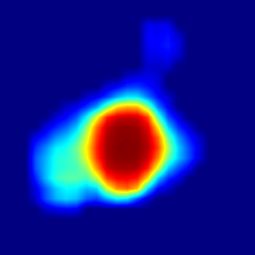
--register_layer softmax 最后绘制出SiamCAR的分类分支heatmap可视化的结果:
在OTB100基准下,不同视频不同帧的分类分支的heatmap可视化
CAM部分代码:
参见:
/path/to/SiamCAR-CAM/CAM/GroupCAM.py
/path/to/SiamCAR-CAM/pysot/tracker/siamcar_tracker_cam.py
/path/to/SiamCAR-CAM/tools/CAM-demo.py
注:由于未知原因,实际上经运行发现,不是所有的视频帧都会出现heatmap图像,这与Group-CAM有关,以及单目标跟踪中(pysot系列),通常不会将输入图像进行归一化有关,这篇代码中,对于CAM部分,我们进行了归一化操作,对于涉及到跟踪器的部分,我们进行了反归一化操作。故猜测可能是这一个问题造成的。
代码中的一些要点详解
GroupCAM.py
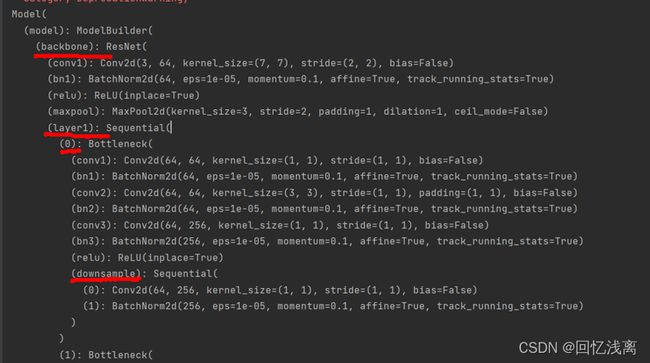
对于各个结构的查看,我们参见上图所示,假设查看上面标志的downsample这一模块从分类输出映射到downsample的heatmap图像,则target_layer应被赋值为backbone.layer1.0.downsample。
class GroupCAM(object):
def __init__(self, model, target_layer="layer4.2", groups=32):
super(GroupCAM, self).__init__()
self.model = model
self.groups = groups
self.gradients = dict()
self.activations = dict()
# 归一化
self.transform_norm = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# 反归一化
self.Nutransform = UnNormalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
self.target_layer = target_layer
# 模块注册,对于各模块名称,参见CAM-demo.py中,对模型的打印
# 对于各个模块,为了方便引用,因此,我们使用层级引用方式
if "backbone" in target_layer:
for module in self.model.model.model.backbone.named_modules():
if module[0] == '.'.join(target_layer.split('.')[1:]):
module[1].register_forward_hook(self.forward_hook)
module[1].register_backward_hook(self.backward_hook)
if 'down' in target_layer:
for module in self.model.model.model.down.named_modules():
module[1].register_forward_hook(self.forward_hook)
module[1].register_backward_hook(self.backward_hook)
if "neck" in target_layer:
for module in self.model.model.model.down.named_modules():
module[1].register_forward_hook(self.forward_hook)
module[1].register_backward_hook(self.backward_hook)
if 'car_head' in target_layer:
for module in self.model.model.model.car_head.named_modules():
if module[0] == '.'.join(target_layer.split('.')[1:]):
module[1].register_forward_hook(self.forward_hook)
module[1].register_backward_hook(self.backward_hook)
if "softmax" in target_layer:
for module in self.model.model.softmax.named_modules():
module[1].register_forward_hook(self.forward_hook)
module[1].register_backward_hook(self.backward_hook)CAM的计算
def forward(self, x, hp, retain_graph=False):
output = self.model.track_cam(x, hp)
cls = output["cls"]
# idx = output["idx"]
x_crop = output["x_crop"]
bbox = output["bbox"]
b, c, h, w = x_crop.size()
self.model.model.zero_grad()
idx = torch.argmax(cls)
score = cls.reshape(-1)[idx]
score.backward(retain_graph=retain_graph)
gradients = self.gradients['value'].data
activations = self.activations['value'].data
b, k, u, v = activations.size()
alpha = gradients.view(b, k, -1).mean(2)
weights = alpha.view(b, k, 1, 1)
activations = weights * activations
score_saliency_map = torch.zeros((1, 1, h, w))
if torch.cuda.is_available():
activations = activations.cuda()
score_saliency_map = score_saliency_map.cuda()
masks = activations.chunk(self.groups, 1)
with torch.no_grad():
x_crop = torch.cat([x_crop[:, 2, :, :][:, None, :, :],
x_crop[:, 1, :, :][:, None, :, :],
x_crop[:, 0, :, :][:, None, :, :]], dim=1)/ 255.0
norm_img = self.transform_norm(x_crop)
blur_img = blur(norm_img)
img = self.Nutransform(blur_img)
base_line = self.model.model.track(torch.cat([img[:, 2, :, :][:, None, :, :],
img[:, 1, :, :][:, None, :, :],
img[:, 0, :, :][:, None, :, :]], dim=1) * 255.0)["cls"][:, 1, :, :][:, None, :, :].reshape(-1)[idx]
for saliency_map in masks:
saliency_map = saliency_map.sum(1, keepdims=True)
saliency_map = F.relu(saliency_map)
threshold = np.percentile(saliency_map.cpu().numpy(), 70)
saliency_map = torch.where(
saliency_map > threshold, saliency_map, torch.full_like(saliency_map, 0))
saliency_map = F.interpolate(saliency_map, size=(h, w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
if saliency_map.max() == saliency_map.min():
continue
# normalize to 0-1
norm_saliency_map = (saliency_map - saliency_map.min()) / (saliency_map.max() - saliency_map.min())
# how much increase if keeping the highlighted region
# predication on masked input
blur_input = norm_img * norm_saliency_map + blur_img * (1 - norm_saliency_map)
norm_img = self.transform_norm(blur_input)
blur_img = blur(norm_img)
img = self.Nutransform(blur_img)
outcls = self.model.model.track(torch.cat([img[:, 2, :, :][:, None, :, :],
img[:, 1, :, :][:, None, :, :],
img[:, 0, :, :][:, None, :, :]], dim=1) * 255.0)["cls"][:, 1, :, :][:, None, :, :].reshape(-1)[idx]
score = outcls - base_line
# score_saliency_map += score * saliency_map
score_saliency_map += score * norm_saliency_map
score_saliency_map = F.relu(score_saliency_map)
score_saliency_map_min, score_saliency_map_max = score_saliency_map.min(), score_saliency_map.max()
if score_saliency_map_min == score_saliency_map_max:
return None, None, None
score_saliency_map = (score_saliency_map - score_saliency_map_min) / (
score_saliency_map_max - score_saliency_map_min).data
return score_saliency_map.cpu().data, x_crop.cpu().numpy(), bboxCAM-demo.py
引入Softmax模块:由于在SiamCAR中ModelBuilder类中,在__init__()初始化引入各个模块中,在car_head以ModelBuilder本身并未包含softmax模块,然而在测试阶段却引入了这一模块,为了绘制heatmap图像,将softmax模块引入进来是必须的,因此,在CAM-demo中,我们将ModelBuilder定义的模型进行了二次封装,这也是我们在代码中看到多个model.model结构的原因。我们也能发现,实际上这种封装,并未破坏模型的整体结构,只不过需要在测试阶段的代码中需要将siamcar_tracker.py中,track()里的softmax去除即可。至于为什么要加入softmax,这与模型的分类分支定义有直接关系,通常,对于二分类模型,即前景和背景进行分类的模型,若分类输出为两分支,都需要经过softmax来预测分数,而在SiamCAR中恰巧对于训练和推理阶段,都引入了Softmax函数,因此将softmax作为SiamCAR的一部分是必须的。同理,对于Centerness分支,由于推理阶段进行了归一化,为了方便查看heatmap输出情况,需要将Centerness的归一化方式也作为一个模块注册进来(这里,我们没有提供其归一化的模块注册,若想查看,可以自行修改代码),才能进行进一步分析。
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
super(Model,self).__init__()
self.model = model
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def template(self, z):
self.model.template(z)
def track(self, x):
outputs = self.model.track(x)
outputs['cls'] = self.softmax(outputs['cls'])
return outputs