SpringBoot 缓存管理 @EnableCaching、@Cacheable
SpringBoot缓存管理
-
- 一、SpringBoot缓存管理
-
-
- 1、pom文件添加依赖
- 2、@EnableCaching开启缓存管理。
- 3、注册缓存管理Bean。
- 4、@Cacheable使用缓存。
-
- 二、集成redis
-
-
- 5、添加redis配置
- 6、修改cacheManager
- 7、查看redis进行验证:
-
- 三、注解使用事项
-
-
- 1、@Cacheable
- 2、@CachePut
- 3、@CacheEvict
- 4、@Caching
-
本文章介绍SpringBoot集成redis缓存管理。
一、SpringBoot缓存管理
1、pom文件添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId>
dependency>
2、@EnableCaching开启缓存管理。
3、注册缓存管理Bean。
@Configuration
@EnableCaching //1、@EnableCaching开启缓存管理
public class CacheUtils {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Bean //2、注册缓存管理Bean。
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager(){
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
return cacheManager;
}
}
4、@Cacheable使用缓存。
在通过注解@Cacheable时就比较灵活,可以在Controller层、Service层、Dao层使用,区别就是缓存的粒度大小不同。
@Service
public class EntityGroupServiceImpl implements EntityGroupService {
// 缓存前10页的分组数据
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "entityGroup::getList", key = "#entityGroupVo", condition = "#entityGroupVo.getPage() < 10")
@Override
public ResponseBean getList(EntityGroupVo entityGroupVo) throws Exception {
...
// my code
...
return ResponseBean.builder().code(100).msg("success").data(pageInfo).build();
}
}
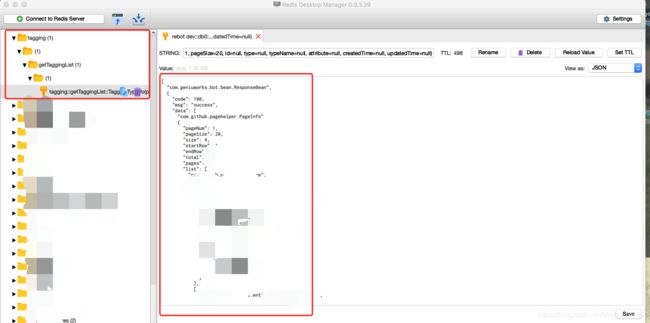
至此,springboot的缓存管理就能正常使用,通过mybatis日志打印,存在缓存直接走缓存,不进行mysql查库。
二、集成redis
5、添加redis配置
在application.properties配置文件添加redis配置,
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=6379
6、修改cacheManager
可以通过集成redis把缓存的数据落到redis中。
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheUtils {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// @Bean
// public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager(){
// ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
// return cacheManager;
// }
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(){
return new RedisCacheManager(
RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory()),
this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl( 60 * 10), // 默认策略,未配置的 key 会使用这个
this.getRedisCacheConfigurationMap() // 指定 key 策略
);
}
private Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> getRedisCacheConfigurationMap() {
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> redisCacheConfigurationMap = new HashMap<>();
// //自定义设置缓存时间
// redisCacheConfigurationMap.put("studentCache", this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(60 ));
return redisCacheConfigurationMap;
}
private RedisCacheConfiguration getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(Integer seconds) {
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
redisCacheConfiguration = redisCacheConfiguration.serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext
.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer)
).entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(seconds));
return redisCacheConfiguration;
}
}
7、查看redis进行验证:
三、注解使用事项
| 缓存注解 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| @EnableCaching | 开启缓存注解的支持 |
| @CacheConfig | 用于统一制定一些配置参数,这样在其他缓存注解里面就不用重复指定 |
| @Cacheable | 如果之前已经有缓存数据值直接返回缓存数据,否则执行方法,缓存方法的返回结果 |
| @CachePut | 能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用 |
| @CacheEvict | 能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空 |
| @Caching | 组合多个Cache注解的使用 |
下面说下几个重要的注解:
1、@Cacheable
@Cacheable可以标记在一个方法上,也可以标记在一个类上。当标记在一个方法上时表示该方法是支持缓存的,当标记在一个类上时则表示该类所有的方法都是支持缓存的。对于一个支持缓存的方法,Spring会在其被调用后将其返回值缓存起来,以保证下次利用同样的参数来执行该方法时可以直接从缓存中获取结果,而不需要再次执行该方法。
@Cacheable可以指定三个属性,value、key和condition。
- value属性
value属性是必须指定的,其表示当前方法的返回值是会被缓存在哪个Cache上的,对应Cache的名称。其可以是一个Cache也可以是多个Cache,当需要指定多个Cache时其是一个数组。
新版本value和cacheNames是一样的,配置一个就可以。
// 下面三种写法作用一样
@Cacheable("cache1")//Cache是发生在cache1上的
@Cacheable(value = "cache1")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache1")
public User find(Integer id) {
returnnull;
}
@Cacheable({"cache1", "cache2"})//Cache是发生在cache1和cache2上的
public User find(Integer id) {
returnnull;
}
-
key属性
key属性是用来指定Spring缓存方法的返回结果时对应的key的。该属性支持SpringEL表达式。当我们没有指定该属性时,Spring将使用默认策略生成key。自定义策略是指我们可以通过Spring的EL表达式来指定我们的key。这里的EL表达式可以使用方法参数及它们对应的属性。使用方法参数时我们可以直接使用“#参数名”或者“#p参数index”。下面是几个使用参数作为key的示例。
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#id")
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0")
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#user.id")
public User find(User user) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0.id")
public User find(User user) {
return null;
}
除了上述使用方法参数作为key之外,Spring还为我们提供了一个root对象可以用来生成key。通过该root对象我们可以获取到以下信息。
| 属性名称 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| methodName | 当前方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | 当前方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | 当前被调用的对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | 当前被调用的对象的class | #root.targetClass |
| args | 当前方法参数组成的数组 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | 当前被调用的方法使用的Cache | #root.caches[0].name |
当我们要使用root对象的属性作为key时我们也可以将“#root”省略,因为Spring默认使用的就是root对象的属性。如:
@Cacheable(value={"users", "xxx"}, key="caches[1].name")
public User find(User user) {
return null;
}
-
condition属性
有的时候我们可能并不希望缓存一个方法所有的返回结果。通过condition属性可以实现这一功能。condition属性默认为空,表示将缓存所有的调用情形。其值是通过SpringEL表达式来指定的,当为true时表示进行缓存处理;当为false时表示不进行缓存处理,即每次调用该方法时该方法都会执行一次。如下示例表示只有当user的id为偶数时才会进行缓存。
// 只缓存前10页数据
@Cacheable(value = "entityGroup::getList", key = "#entityGroupVo", condition = "#entityGroupVo.getPage() < 10")
2、@CachePut
在支持Spring Cache的环境下,对于使用@Cacheable标注的方法,Spring在每次执行前都会检查Cache中是否存在相同key的缓存元素,如果存在就不再执行该方法,而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回,否则才会执行并将返回结果存入指定的缓存中。
@CachePut也可以声明一个方法支持缓存功能。与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
//每次都会执行方法,并将结果存入指定的缓存中
@CachePut("users")
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
3、@CacheEvict
@CacheEvict是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的。当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有的方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作。@CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation。其中value、key和condition的语义与@Cacheable对应的属性类似。即value表示清除操作是发生在哪些Cache上的(对应Cache的名称);key表示需要清除的是哪个key,如未指定则会使用默认策略生成的key;condition表示清除操作发生的条件。下面我们来介绍一下新出现的两个属性allEntries和beforeInvocation。
- allEntries属性
allEntries是boolean类型,表示是否需要清除缓存中的所有元素。默认为false,表示不需要。当指定了allEntries为true时,Spring Cache将忽略指定的key。有的时候我们需要Cache一下清除所有的元素,这比一个一个清除元素更有效率。
@CacheEvict(value="users", allEntries=true)
public void delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("delete user by id: " + id);
}
- beforeInvocation属性
清除操作默认是在对应方法成功执行之后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回时也不会触发清除操作。使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定该属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素。
@CacheEvict(value="users", beforeInvocation=true)
public void delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("delete user by id: " + id);
}
4、@Caching
@Caching注解可以让我们在一个方法或者类上同时指定多个Spring Cache相关的注解。其拥有三个属性:cacheable、put和evict,分别用于指定@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict。
@Caching(cacheable = @Cacheable("users"), evict = { @CacheEvict("cache2"),
@CacheEvict(value = "cache3", allEntries = true) })
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44971379/article/details/106605772
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21383435/article/details/104047558
https://www.cnblogs.com/fashflying/p/6908028.html