为什么Netty受欢迎?
如第一部分所述,netty是一款收到大公司青睐的框架,在我看来,netty能够受到青睐的原因有三:
- 并发高
- 传输快
- 封装好
Netty为什么并发高
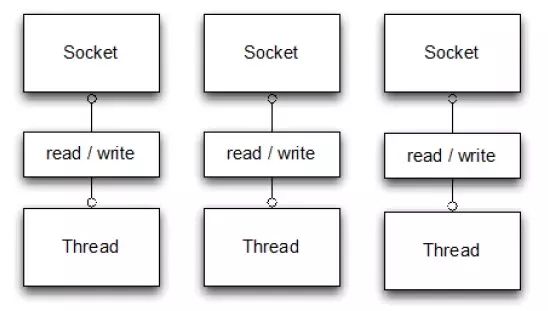
Netty是一款基于NIO(Nonblocking I/O,非阻塞IO)开发的网络通信框架,对比于BIO(Blocking I/O,阻塞IO),他的并发性能得到了很大提高,两张图让你了解BIO和NIO的区别:
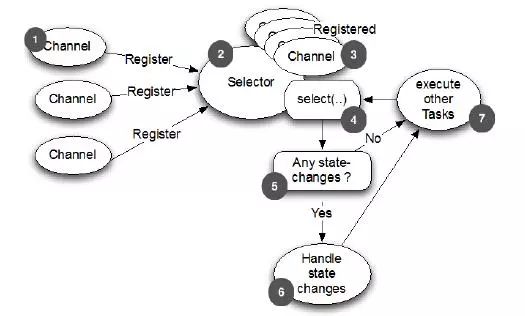
这两图可以看出,NIO的单线程能处理连接的数量比BIO要高出很多,而为什么单线程能处理更多的连接呢?原因就是图二中出现的
Selector。
当一个连接建立之后,他有两个步骤要做,第一步是接收完客户端发过来的全部数据,第二步是服务端处理完请求业务之后返回response给客户端。NIO和BIO的区别主要是在第一步。
在BIO中,等待客户端发数据这个过程是阻塞的,这样就造成了一个线程只能处理一个请求的情况,而机器能支持的最大线程数是有限的,这就是为什么BIO不能支持高并发的原因。
而NIO中,当一个Socket建立好之后,Thread并不会阻塞去接受这个Socket,而是将这个请求交给Selector,Selector会不断的去遍历所有的Socket,一旦有一个Socket建立完成,他会通知Thread,然后Thread处理完数据再返回给客户端——这个过程是阻塞的,这样就能让一个Thread处理更多的请求了。
下面两张图是基于BIO的处理流程和netty的处理流程,辅助你理解两种方式的差别:
Netty为什么传输快
Netty的传输快其实也是依赖了NIO的一个特性——零拷贝。我们知道,Java的内存有堆内存、栈内存和字符串常量池等等,其中堆内存是占用内存空间最大的一块,也是Java对象存放的地方,一般我们的数据如果需要从IO读取到堆内存,中间需要经过Socket缓冲区,也就是说一个数据会被拷贝两次才能到达他的的终点,如果数据量大,就会造成不必要的资源浪费。
Netty针对这种情况,使用了NIO中的另一大特性——零拷贝,当他需要接收数据的时候,他会在堆内存之外开辟一块内存,数据就直接从IO读到了那块内存中去,在netty里面通过ByteBuf可以直接对这些数据进行直接操作,从而加快了传输速度。
为什么说Netty封装好?
要说Netty为什么封装好,这种用文字是说不清的,直接上代码:
- 阻塞I/O
public class PlainOioServer {
public void serve(int port) throws IOException {
final ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket(port); //1
try {
for (;;) {
final Socket clientSocket = socket.accept(); //2
System.out.println("Accepted connection from " + clientSocket);
new Thread(new Runnable() { //3
@Override
public void run() {
OutputStream out;
try {
out = clientSocket.getOutputStream();
out.write("Hi!\r\n".getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); //4
out.flush();
clientSocket.close(); //5
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
clientSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
// ignore on close
}
}
}
}).start(); //6
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 非阻塞IO
public class PlainNioServer {
public void serve(int port) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ServerSocket ss = serverChannel.socket();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(port);
ss.bind(address); //1
Selector selector = Selector.open(); //2
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //3
final ByteBuffer msg = ByteBuffer.wrap("Hi!\r\n".getBytes());
for (;;) {
try {
selector.select(); //4
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
// handle exception
break;
}
Set readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //5
Iterator iterator = readyKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
try {
if (key.isAcceptable()) { //6
ServerSocketChannel server =
(ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel client = server.accept();
client.configureBlocking(false);
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE |
SelectionKey.OP_READ, msg.duplicate()); //7
System.out.println(
"Accepted connection from " + client);
}
if (key.isWritable()) { //8
SocketChannel client =
(SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer =
(ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
if (client.write(buffer) == 0) { //9
break;
}
}
client.close(); //10
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
key.cancel();
try {
key.channel().close();
} catch (IOException cex) {
// 在关闭时忽略
}
}
}
}
}
}
- Netty
public class NettyOioServer {
public void server(int port) throws Exception {
final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer(
Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hi!\r\n", Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
EventLoopGroup group = new OioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); //1
b.group(group) //2
.channel(OioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {//3
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { //4
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);//5
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync(); //6
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); //7
}
}
}
相比之下,netty的代码量少了太多,而且netty还提供自定义协议。
名词解释
- Channel,表示一个连接,可以理解为每一个请求,就是一个Channel。
- ChannelHandler,核心处理业务就在这里,用于处理业务请求。
- ChannelHandlerContext,用于传输业务数据。
- ChannelPipeline,用于保存处理过程需要用到的ChannelHandler和ChannelHandlerContext。
- ByteBuf是一个存储字节的容器,最大特点就是使用方便,它既有自己的读索引和写索引,方便你对整段字节缓存进行读写,也支持get/set,方便你对其中每一个字节进行读写,他的数据结构如下图所示:
以上摘抄https://www.jianshu.com/p/b9f3f6a16911
理解了netty的理论知识,下面就是我们实战的时候了。
服务端的搭建
NettyServer
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class NettyServer {
private static final int port = 6789; //设置服务端端口
private static EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 通过nio方式来接收连接和处理连接
private static ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
/**
* Netty创建全部都是实现自AbstractBootstrap。
* 客户端的是Bootstrap,服务端的则是 ServerBootstrap。
**/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
try {
b.group(group);
b.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
b.childHandler(new NettyServerFilter()); //设置过滤器
// 服务器绑定端口监听
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("服务端启动成功...");
// 监听服务器关闭监听
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully(); ////关闭EventLoopGroup,释放掉所有资源包括创建的线程
}
}
}
new ChannelInitializer()
public class NettyServerFilter extends ChannelInitializer {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline ph = ch.pipeline();
// 以("\n")为结尾分割的 解码器
ph.addLast("framer", new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(8192, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
// 解码和编码,应和客户端一致
ph.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
ph.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
ph.addLast("handler", new NettyServerHandler());// 服务端业务逻辑
}
}
NettyServerHandler
public class NettyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
/*
* 收到消息时,返回信息
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg)
throws Exception {
// 收到消息直接打印输出
System.out.println("服务端接受的消息 : " + msg);
if("quit".equals(msg)){//服务端断开的条件
ctx.close();
}
Date date=new Date();
// 返回客户端消息
ctx.writeAndFlush(date+"\n");
}
/*
* 建立连接时,返回消息
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("连接的客户端地址:" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
ctx.writeAndFlush("客户端"+ InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostName() + "成功与服务端建立连接! \n");
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
}
客户端搭建
NettyClient
public class NettyClient {
public static String host = "127.0.0.1"; //ip地址
public static int port = 6789; //端口
/// 通过nio方式来接收连接和处理连接
private static EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
private static Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
private static Channel ch;
/**
* Netty创建全部都是实现自AbstractBootstrap。
* 客户端的是Bootstrap,服务端的则是 ServerBootstrap。
**/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
System.out.println("客户端成功启动...");
b.group(group);
b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
b.handler(new NettyClientFilter());
// 连接服务端
ch = b.connect(host, port).sync().channel();
star();
}
public static void star() throws IOException{
String str="Hello Netty";
ch.writeAndFlush(str+ "\r\n");
System.out.println("客户端发送数据:"+str);
}
}
new ChannelInitializer()
public class NettyClientFilter extends ChannelInitializer {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline ph = ch.pipeline();
/*
* 解码和编码,应和服务端一致
* */
ph.addLast("framer", new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(8192, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
ph.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
ph.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
ph.addLast("handler", new NettyClientHandler()); //客户端的逻辑
}
}
NettyClientHandler
public class NettyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("客户端接受的消息: " + msg);
}
//
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("正在连接... ");
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("连接关闭! ");
super.channelInactive(ctx);
}
}
最终效果
服务端
客户端
项目地址https://github.com/DespairYoke/netty/tree/master/netty-hello