前言
其实,我也不懂,关于源码,我看了两次,只看懂了40%,丢脸了,但是还是硬着头皮,写篇文章,mark一下吧,源码来自 《深入React技术栈》这本书....我只是大自然的搬运工
React 生命周期
学习一个框架,最重要的莫过于对生命周期的理解了。嗯,很懵,但是人傻就是要多看书,多看掘金上的优秀文章,看了两篇React生命周期的文章之后,大概也能懂得个大概。就记录一下吧 ~
[注意] 这是 react16.3之前的生命周期
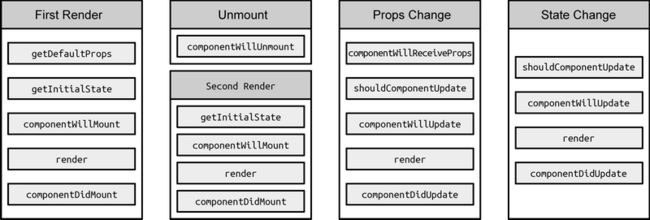
先看图,再看字
《深入React技术栈》中对生命周期的说明:
渲染的过程:
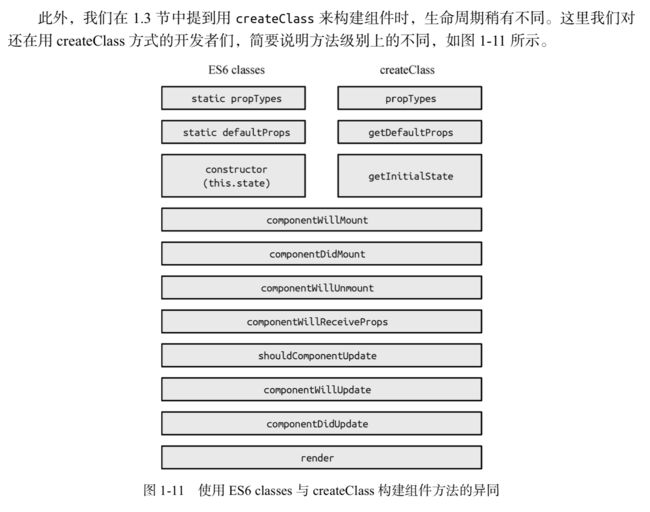
上图中的getDefaultProps和getInitialState分别对应ES6中的static defaultProps = {}与构造函数construct中的this.state ={}赋值
生命周期 - 初次渲染
一个初始化组件 (以ES6 classes为例子)
// 当使用 ES6 classes 编写 React 组件时,其实就是调用内部方法 createClass 创建组件
import React, { Component } from 'react'
class Index extends Component {
static propTypes = {
// code...
}
static defaultProps = {
// code...
}
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
// code...
}
}
componentWillMount () {
// code...
}
componentDidMount () {
}
render () {
return (
// code...
)
}
}
我们来看看《深入React技术》中如何解读源码
var React = {
// ...
createClass: ReactClass.createClass,
// ...
}
var ReactClass = {
createClass: function(spec) {
var Constructor = function(props, context, updater) {
// 自动绑定
if (this.__reactAutoBindPairs.length) {
bindAutoBindMethods(this);
}
this.props = props;
this.context = context;
this.refs = emptyObject;
this.updater = updater || ReactNoopUpdateQueue;
this.state = null;
// ReactClass 没有构造函数,通过 getInitialState 和 componentWillMount 来代替
var initialState = this.getInitialState ? this.getInitialState() : null;
this.state = initialState;
}
// 原型继承父类
Constructor.prototype = new ReactClassComponent();
Constructor.prototype.constructor = Constructor;
Constructor.prototype.__reactAutoBindPairs = [];
// 合并 mixin
injectedMixins.forEach(
mixSpecIntoComponent.bind(null, Constructor)
);
mixSpecIntoComponent(Constructor, spec);
// 所有 mixin 合并后初始化 defaultProps(在整个生命周期中,getDefaultProps 只执行一次)
if (Constructor.getDefaultProps) {
Constructor.defaultProps = Constructor.getDefaultProps();
}
// 减少查找并设置原型的时间
for (var methodName in ReactClassInterface) {
if (!Constructor.prototype[methodName]) {
Constructor.prototype[methodName] = null;
}
}
return Constructor;
}
}
// React Constructor 说明
React规定constructor有三个参数,分别是props、context和updater。
· props是属性,它是不可变的。
· context是全局上下文。
· updater是包含一些更新方法的对象
// this.setState最终调用的是this.updater.enqueueSetState方法
// this.forceUpdate最终调用的是this.updater.enqueueForceUpdate方法
mountComponent 组件挂载代码
// 当组件挂载时,会分配一个递增编号,表示执行 ReactUpdates 时更新组件的顺序
var nextMountID = 1
// 初始化组件,渲染标记,注册事件监听器
mountComponent: function(transaction, nativeParent, nativeContainerInfo, context) {
// 当前元素对应的上下文
this._context = context
this._mountOrder = nextMountID
this._nativeParent = nativeParent
this._nativeContainerInfo = nativeContainerInfo
var publicProps = this._processProps(this._currentElement.props)
var publicContext = this._processContext(context)
var Component = this._currentElement.type
// 初始化公共类
var inst = this._constructComponent(publicProps, publicContext)
var renderedElement;
// 判断组件是否为无状态组件,无状态组件没有状态更新队列,它只专注于渲染
if (!shouldConstruct(Component) && (inst == null || inst.render == null)) {
renderedElement = inst
warnIfInvalidElement(Component, renderedElement)
inst = new StatelessComponent(Component)
}
// 这些初始化参数本应该在构造函数中设置,在此设置是为了便于进行简单的类抽象
inst.props = publicProps
inst.context = publicContext
inst.refs = emptyObject
inst.updater = ReactUpdateQueue
this._instance = inst
// 将实例存储为一个引用
ReactInstanceMap.set(inst, this)
// 初始化 state
var initialState = inst.state
if (initialState === undefined) {
inst.state = initialState = null
}
// 初始化更新队列
this._pendingStateQueue = null
this._pendingReplaceState = false
this._pendingForceUpdate = false
var markup;
// 如果挂载出现错误
if (inst.upstable_handleError) {
markup = this.performInitialMountWithErrorHandling(renderedElement, nativeParent, nativeContainerInfo, transaction, context)
} else {
// 初始化挂载
markup = this.performInitialMount(renderedElement, nativeParent, nativeContainerInfo, transaction,
context)
}
// 如果存在 componentDidMount , 则调用
if (inst.componentDidMount) {
transaction.getReactMountReady().enqueue(inst.componentDidMount, inst)
}
return markup
}
// 挂载错误处理
performInitialMountWithErrorHandling: function(renderedElement, nativeParent, nativeContainerInfo, transaction, context) {
var markup;
var checkpoint = transaction.checkpoint()
try {
// 捕捉错误,没有错误则初始化挂载
markup = this.performInitialMount(renderedElement, nativeParent, nativeContainerInfo, transaction,
context)
} catch (e) {
transaction.rollback(checkpoint)
this._instance.unstable_handleError(e)
if (this._pendingStateQueue) {
this._instance.state = this._processPendingState(this._instance.props, this._instance.context)
}
checkpoint = transaction.checkpoint()
// 如果捕捉到错误,则执行 unmountComponent 后,再初始化挂载
this._renderedComponent.unmountComponent(true)
transaction.rollback(checkpoint)
markup = this.performInitialMount(renderedElement, nativeParent, nativeContainerInfo, transaction, context)
}
return markup
}
// 挂载组件
performInitialMount: function(renderedElement, nativeParent, nativeContainerInfo, transaction, context) {
var inst = this._instance
// 如果存在 componentWillMount, 则调用
if (inst.componentWillMount) {
inst.componentWillMount()
// componentWillMount 调用 setState 时,不会触发 re-render 而是自动提前合并
if (this._pendingStateQueue) {
inst.state = this._processPendingState(inst.props, inst.context)
}
}
// 如果不是无状态组件,即可开始渲染
if (renderedElement === undefined) {
renderedElement = this._renderValidatedComponent()
}
this._renderedNodeType = ReactNodeTypes.getType(renderedElement)
// 得到 _currentElement 对应的 component 类实例
this._renderedComponent = this._instantiateReactComponent(renderedElement)
// render 递归渲染
var markup = ReactReconciler.mountComponent(this._renderedComponent, transaction, nativeParent,
nativeContainerInfo, this._processChildContext(context))
return markup
}
总结一下 - 初次渲染 ?
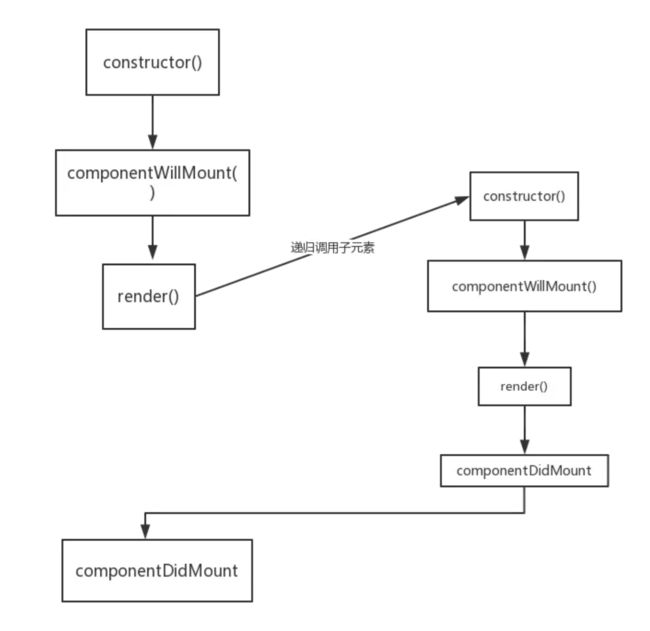
1 . 当使用 ES6 classes 编写 React 组件时,其实就是调用内部方法 createClass 创建组件, 该方法返回一个Constructor(props, context, updater) 用来生成组件实例,我们发现在调用React.createClass,已经执行了getDefaultProps(),并将其赋值于Constructor的原型中
2 . 由于通过ReactCompositeComponentBase 返回的是一个虚拟节点,所以需要利用 instantiateReactComponent去得到实例,再使用 mountComponent 拿到结果作为当前自定义元素的结果
当使用 React 创建组件时,首先会调用 instantiateReactComponent,这是初始化组件的入口 函数,它通过判断 node 类型来区分不同组件的入口 (具体看下边说明)
3 . 在React中,因为所有class组件都要继承自Component类或者PureComponent类,因此和原生class写法一样,要在constructor里首先调用super方法,才能获得this。通过 mountComponent 挂载组件,初始化序号、标记等参数,判断是否为无状态组件,并进行 对应的组件初始化工作,比如初始化 props、context 等参数。利用 getInitialState 获取初始化 state、初始化更新队列和更新状态。
4 . 若存在 componentWillMount,则执行。如果此时在 componentWillMount 中调用 setState 方法,是不会触发 re-render的,而是会进行 state 合并,且 inst.state = this._processPendingState (inst.props, inst.context) 是在 componentWillMount 之后执行的,因此 componentWillMount 中 的 this.state 并不是最新的,在 render 中才可以获取更新后的 this.state。
React 是利用更新队列 this._pendingStateQueue 以及更新状态 this._pendingReplaceState 和 this._pendingForceUpdate 来实现 setState 的异步更新机制。也就是说 this.setState 最终调用的是this.updater.enqueueSetState方法
5 . 当渲染完成后,若存在 componentDidMount,则调用。其实,mountComponent 本质上是通过递归渲染内容的,由于递归的特性,父组件的 componentWillMount 在其子组件的 componentWillMount 之前调用,而父组件的 componentDidMount 在其子组件的 componentDidMount 之后调用。
额外补充
instantiateReactComponent 入口组件
· 当 node 为空时,说明 node 不存在,则初始化空组件 ReactEmptyComponent.create(instantiateReactComponent)。
· 当 node 类型为对象时,即是 DOM 标签组件或自定义组件,那么如果 element 类型为字符串时 ,则初始化 DOM 标签组件ReactNativeComponent.createInternalComponent (element),否则初始化自定义组件 ReactCompositeComponentWrapper()
· 当 node 类型为字符串或数字时,则初始化文本组件 ReactNativeComponent.createInstanceForText(node)。
· 如果是其他情况,则不作处理
// instantiateReactComponent 方法源码, 初始化组件入口
function instantiateReactComponent(node, parentCompositeType) {
var instance;
// 空组件 (ReactEmptyComponent)
if (node === null || node === false) {
instance = ReactEmptyComponent.create(instantiateReactComponent)
}
// 对象类型
if (typeof node === 'object') {
var element = node
if (typeof element === 'string') {
instance = ReactNativeComponent.createInternalComponent (element)
} else if (isInternalComponentType(element.type)) {
// 不是字符串表示的自定义组件暂无法使用,此处将不做组件初始化操作
instance = new element.type(element)
} else {
// 自定义组件
instance = new ReactCompositeComponentWrapper()
}
} else if (typeof node === 'string' || typeof node === 'number') {
// 字符串或数字
instance = ReactNativeComponent.createInstanceForText(node)
} else {
// 不做处理
}
// 设置实例
instance.construct(node)
// 初始化参数
instance._mountIndex = 0
instance._mountImage = null
return instance
}
生命周期 - 更新阶段
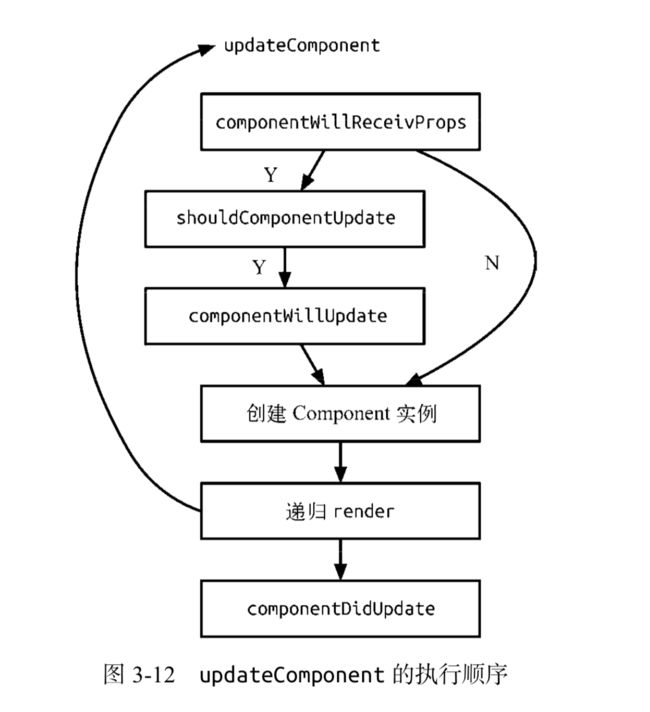
updateComponent 负责管理生命周期中的 componentWillReceiveProps、shouldComponentUpdate、componentWillUpdate、render 和 componentDidUpdate
首先通过 updateComponent 更新组件,如果前后元素不一致,说明需要进行组件更新
如果存在 componentWillReceiveProps, 则执行。如果此时在 componentWillReceiveProps 中调 用 setState,是不会触发 re-render 的,而是会进行 state 合并。且在 componentWillReceiveProps、 shouldComponentUpdate 和 componentWillUpdate 中也还是无法获取到更新后的 this.state,即此 时访问的 this.state 仍然是未更新的数据,需要设置 inst.state = nextState 后才可以,因此 只有在 render 和 componentDidUpdate 中才能获取到更新后的 this.state。
调用 shouldComponentUpdate 判断是否需要进行组件更新,如果存在 componentWillUpdate, 则执行。
updateComponent 本质上也是通过递归渲染内容的,由于递归的特性,父组件的 componentWillUpdate 是在其子组件的 componentWillUpdate 之前调用的,而父组件的 componentDidUpdate 也是在其子组件的 componentDidUpdate 之后调用的。
当渲染完成之后,若存在 componentDidUpdate,则触发
相关源码
// receiveComponent 是通过调用 updateComponent 进行组件更新的
receiveComponent: function(nextElement, transaction, nextContext) {
var prevElement = this._currentElement; var prevContext = this._context;
this._pendingElement = null;
this.updateComponent(transaction, prevElement, nextElement, prevContext, nextContext);
},
updateComponent: function(transaction, prevParentElement, nextParentElement, prevUnmaskedContext, nextUnmaskedContext) {
var inst = this._instance
var willReceive = false
var nextContext
var nextProps
// 上下文是否改变
if (this._context === nextUnmaskedContext) {
nextContext = inst.context
} else {
nextContext = this._processContext(nextUnmaskedContext)
willReceive = true
}
if (preParentElement === nextParentElement) {
// 元素相同,跳过元素类型检测
nextProps = nextParentElement.props
} else {
// 检查元素的类型
nextProps = this._processProps(nextParentElement.props)
willReceive = true
}
// 如果存在 compnentWillReceiveProps ,则调用
if (inst.componentWillReceiveProps && willReceive) {
inst.componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps, nextContext)
}
// 将新的state合并到更新的队列中, 此时的 nextState 是最新的 state
var nextState = this._processPendingState(nextProps, nextContext)
// 根据更新队列和 shouldComponentUpdate 的状态来判断是否需要更新组件
var shouldUpdate = this._pendingForceUpdate || !inst.shouldComponentUpdate || inst.shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext)
if (shouldUpdate) {
// 重置更新队列
this._pendingForceUpdate = false
// 即将更新 this.props 、 this.state 、 this.context
this._performComponentUpdate(nextParentElement, nextProps, nextState, nextContext, transaction, nextUnmaskedContext)
} else {
// 如果确定组件不更新,那么仍然要设置 props 和 state
this._currentElement = nextParentElement
this._context = nextUnmaskedContext
inst.props = nextProps
inst.state = nextState
inst.context = nextContext
}
},
// 当确定组件需要更新时,则调用
_performComponentUpdate: function(nextElement, nextProps, nextState, nextContext, transaction, unmaskedContext) {
var inst = this._instance
var hasComponentDidUpdate = Boolean(inst.componentDidUpdate)
var preProps
var preState
var preContext
// 如果存在 componentDidUpdate , 则将当前的 state, props, context 保存一份
if (hasComponentDidUpdate) {
preProps = inst.props
preState = inst.state
preContext = inst.context
}
// 如果存在 componentWillUpdate ,则调用
if (inst.componentWillUpdate) {
inst.componetWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext)
}
this._currentElement = nextParentElement
this._context = unmaskedContext
// 更新 this.props 、 this.state 、 this.context
inst.props = nextProps
inst.state = nextState
inst.context = nextContext
// 调用 render 渲染组件
this._updateRenderedComponent(transaction, unmaskedContext)
// 当组件完成更新后,如果存在 componentDidUpdate,则调用
if (hasComponentDidUpdate) {
transaction.getReactMountReady().enqueue(
inst.componentDidUpdate.bind(inst, prevProps, prevState, prevContext),inst
)
}
}
// 调用 render 渲染组件
_updateRenderedComponent: function (transaction, context) {
var preComponentInstance = this._renderedComponet
var preRenderedElement = prevComponentInstance._currentElement
var nextRenderedElement = this._renderValidatedComonet()
// 如果需要更新,则调用ReactReconciler.receiveComponent 继续更新组件
if (shouldUpdateReactComponent(preRenderedElement, nextRenderedElement)) {
ReactReconciler.receiveComponent(preComponentInstance, nextRenderedElement, transaction, this._processChildContext(context))
} else {
// 如果不需要更新, 则渲染组件
var oldNativeNode = ReactReconciler.getNativeNode(preComponentInstance)
ReactReconciler.unmountComponent(preComponentInstance)
this._renderedNodeType = ReactNodeTypes.getType(nextRenderedElement)
// 得到 nextRenderedElement 对应的component 类实例
this._renderedComponet = this._instantiateReactComponent(nextRenderedElement)
// 使用 render 递归渲染
var nextMarkup = ReactReconciler.mountComponent(this._renderedComponent,transaction, this._nativeParent, this._nativeContainerInfo, this._processChildContext(context))
tgus._replaceNodeWithMarkup(oldNativeNode, nextMarkup)
}
}
setState 循环调用的风险
禁止在 shouldComponentUpdate 和 componentWillUpdate 中调用this.setState,因为这样会造成循环调用,直到耗光浏览器内存后奔溃,那么为什么不能呢 ?
1 . 调用 setState 时,实际上会执行 enqueueSetState 方法,并对partialState和_pendingStateQueue更新队列进行合并操作,最终通过 enqueueUpdate 执行 state 的更新
2 . 而 performUpdateIfNecessary 方法会获取 _pendingElement、_pendingStateQueue、_pendingForceUpdate,并调用 receiveComponent 和 updateComponent 方法进行组件更新
3 . 如 果 在 shouldComponentUpdate 或 componentWillUpdate 方 法 中 调 用 setState , 此 时 this._pendingStateQueue != null,则 performUpdateIfNecessary 方法就会调用 updateComponent 方法进行组件更新,但 updateComponent 方法又会调用 shouldComponentUpdate 和 componentWill- Update 方法,因此造成循环调用,使得浏览器内存占满后崩溃
生命周期 - 卸载阶段
unmountComponent 负责管理生命周期中的 componentWillUnmount
如果存在 componentWillUnmount,则执行并重置所有相关参数、更新队列以及更新状态,如 果此时在 componentWillUnmount 中调用 setState,是不会触发 re-render 的,这是因为所有更新 队列和更新状态都被重置为 null,并清除了公共类,完成了组件卸载操作
相关源码
unmountComponent: function(safely) {
if (!this._renderedComponent) {
return
}
var inst = this._instance
// 如果存在 componentWillUnmount, 则调用
if (inst.componentWillUnmount) {
if (safely) {
var name = this.getName() + '.componentWillUnmount()'
ReactErrorUtils.invokeGuardedCallback(name, inst.componentWillUnmount.bind(inst))
} else {
inst.componentWillUnmount()
}
}
// 如果组件已经渲染,则对组件进行 unmountComponent 操作
if (this._renderedComponent) {
ReactReconciler.unmountComponent(this._renderedComponent, safely)
this._renderedNodeType = null
this._renderedComponent = null
this._instance = null
}
// 重置相关参数、更新队列以及更新状态
this._pendingStateQueue = null // 更新队列
this._pendingReplaceState = false // 更新状态
this._pendingForceUpdate = false
this._pendingCallbacks = null
this._pendingElement = null
this._context = null
this._rootNodeID = null
this._topLevelWrapper = null
// 清除公共类
ReactInstanceMap.remove(inst)
}
在 React 开发中,一个很重要的原则就是让组件尽可能是无状态的,无状态组件没有状态,没有生命周期,只是简单地接受 props 渲染生成 DOM 结构,是一个 纯粹为渲染而生的组件。
再看一个图总结生命周期
相关链接
我的博客: https://github.com/PDKSophia/blog.io
我的掘金: https://juejin.im/user/594ca8a35188250d892f4139