- Windows 11 24H2 中文版、英文版 (x64、ARM64) 下载 (2025 年 3 月更新)
windows
Windows1124H2中文版、英文版(x64、ARM64)下载(2025年3月更新)Windows11,version24H2EnterpriseArm64x64(updatedMar2025)请访问原文链接:https://sysin.org/blog/windows-11/查看最新版。原创作品,转载请保留出处。作者主页:sysin.org全新Windows体验,让您与热爱的人和事物离得更近
- python arm64_PyTorch-aarch64
人类0663号
pythonarm64
PyTorch源码编译步骤:1、源码编译环境:操作系统:debian9.12交换空间:1GPython版本:3.5硬件:CPU:RK3399(aarch64)内存:4G2、下载依赖包:下载pytorch及其依赖包时,默认从github上下载,如果网络不好、容易断开时,可在gitee上找到对应包克隆链接,然后修改对应配置文件,进行下载。需要细致耐心。3、编译主要参数:设置最大作业数:exportMA
- Pycharm2018 激活
Deng.Pan
SoftwareactivationPycharmPycharmPatch
测试条件:WIN10+JetBrainsPyCharm2018.2.2x64使用破解补丁激活方式可以使用很久。下载附件JetbrainsCrack-3.1-release-enc.jar,并放置到pycharm安装目录的\bin目录下,其实位置可随意,只要配置时文件填写对应的路径即可。找到Pycharm安装目录的\bin目录下找到pycharm.exe.vmoptions和pycharm64.ex
- 《Linux运维总结:基于银河麒麟V10+ARM64架构部署多机elasticsearch7.17.21分布式集群+单机kibana7.17.21二进制版ssl集群》
东城绝神
《Linux运维实战总结》运维linuxelasticsearchssl
总结:整理不易,如果对你有帮助,可否点赞关注一下?更多详细内容请参考:Linux运维实战总结一、背景elasticsearch是一个分布式、实时、高性能的搜索和分析引擎,它广泛应用于企业级搜索、日志分析、实时数据处理等领域。随着elasticsearch的广泛应用,安全性变得越来越重要。这里将从安全策略和访问控制两方面来部署elasticsearch集群安全策略涉及到数据安全、访问安全和操作安全等
- 银河麒麟(kylin)下载
张太行_
kylinlinux
银河麒麟版本:(1)银河麒麟V4桌面版ARM64:Kylin-4.0.2-desktop-sp4-20200728.J1-arm64.iso(2)银河麒麟V4桌面版X86_64:Kylin-4.0.2-desktop-sp4-20200728.J1-x86_64.iso(3)银河麒麟V10桌面版ARM64:Kylin-Desktop-V10-SP1-General-Release-2303-arm
- stressapptest交叉编译(ARM64)
单车少年ing
arm64linux
一、代码下载:https://github.com/stressapptest/stressapptest二、编译:cdstressapptest#注意:XXX是你的目标主机。也就是你交叉编译工具链gnu前缀。比如你的交叉编译工具链是:aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc,那XXX就是aarch64-linux-gnuCC="xxx/aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu-gcc
- arm64 ubuntu20.4 安装 mysql5.7 脚本
因你而在的梦
linuxubuntuarm64mysql5.7
1.安装依赖sudoaptupdatesudoaptinstall-ylibaio*2.下载压缩包wgethttps://obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/obs-mirror-ftp4/database/mysql-5.7.27-aarch64.tar.gz3.添加mysql组和mysql用户sudogroupaddmysqlsudouseradd-r-gmysq
- 深入解析Linux进程调度器-CPU负载
Linux内核站
linux运维服务器Linux内核CPU负载
说明:Kernel版本:4.14ARM64处理器,Contex-A53,双核使用工具:SourceInsight3.5,Visio1.概述CPU负载(cpuload)指的是某个时间点进程对系统产生的压力。来张图来类比下(参考UnderstandingLinuxCPULoad)CPU的运行能力,就如大桥的通行能力,分别有满负荷,非满负荷,超负荷等状态,这几种状态对应不同的cpuload值;单CPU满
- Linux arm64架构修改软件apt\yum源 (统信UOS,麒麟kylin系统修改阿里源、华为源) 国产系统UOS修改apt源
longerxin2020
linux
本文参考链接Linuxarm64架构修改软件源(统信UOS,麒麟系统修改阿里源、华为源)国产系统UOS修改apt源_uos如何快速换源-CSDN博客本文介绍华为arm架构主机使用国内源配置1.备份系统之前的源cp/etc/apt/sources.list/etc/apt/sources.list.bak2.修改源文件/etc/apt/sources.listvim/etc/apt/sources.
- docker拉取不同架构的镜像
舞灬辉
docker架构容器
使用如下命令拉取:dockerpull--platformarm64镜像名:版本号如我拉取dotnet的6.0版本dockerpull--platformarm64mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0拉取完成后检查镜像架构:dockerinspect镜像id|grepArchitecture,输出为:“Architecture”:“arm64”,说明镜像拉取完成
- ollama官方安装包
哈拉少12
人工智能
一、官方安装包基本信息最新版本Windows版:v0.6.0.0(国内镜像版,大小999.8M)Linux版:v0.6.0(官方版,大小1.59G)macOS版:支持通过官网直接下载(版本号与Windows/Linux同步)支持平台桌面端:Windows(Win7及以上)、Linux(x86_64/ARM64)、macOS容器化部署:支持Docker(需配合DockerDesktop)
- arm架构安装chrome
GIS-CL
chrome
在ARM架构设备上安装谷歌软件或应用通常涉及到几个步骤,这取决于你要安装的具体谷歌产品,比如谷歌浏览器、GooglePlay服务或者是其他谷歌开发的软件。下面我会给出一些常见的指导步骤,以安装谷歌浏览器为例:在LinuxARM64上安装GoogleChrome如果你是在基于ARM64架构的Linux系统上(如RaspberryPiOS或UbuntuonARM),可以尝试以下步骤来安装GoogleC
- android 32位crc,android arm64硬件实现加速crc32算法
Luo Patrick
android32位crc
在androidarm64平台下,crc32,aes等常用算法有指令集实现。故在android下,可借助这些指令实现代码加速。如何判断自己的手机是否支持crc32呢?有三个方法:方法1,直接查看/proc/cpuinfo方法2,使用ELF辅助向量APIunsignedlonghwcap=getauxval(AT_HWCAP);if(hwcap&HWCAP_CRC32)return1;}return
- ARM64环境部署EFK8.15.3收集K8S集群容器日志
llody_55
kubernetes容器云原生运维esjavaelasticsearch
环境规划主机IP系统部署方式ES版本CPU架构用户名密码192.168.1.225Ubuntu22.04.4LTSdockerelasticsearch:8.15.3ARM64elasticllodyi4TMmZDES集群部署创建持久化目录(所有节点)mkdir-p/data/es/{data,certs,logs,plugins}mkdir-p/data/es/certs/{ca,es01}服务
- 人脸识别,dlib优化,Dlib/OpenCV交叉编译
yiyayiya557
linux嵌入式
参考文章:GitRepo镜像使用帮助https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/git-repo/交叉编译Dlib+OpenCV交叉编译移植到ARM64-v8平台(编译不通过,不可用)https://blog.csdn.net/kaychangeek/article/details/80365320Qt移植到ARM64-v8平台(NXPi.MX8M)笔记(未
- Orbbec 深度相机SDK(Python)
-烂笔头-
嵌入式开发pythonsdk
1、支持系统1)开发板ARM32和ARM642)window系统2、支持的Orbbec深度摄像头型号1)AstraPlus2)AstraPro3)Astramini4)Deeyea5)Gemini3、代码功能1)数据采集和可视化2)定时唤醒任务3)磁盘空间检测4)数据采集服务监测和中断重续4、Githubhttps://github.com/zhangge2016/Orbbec_Python
- C语言SM2算法实现(基于GMSSL)
深度视觉机器
C语言
最近项目中需要通过C语言实现SM2、SM4国密算法,这里我基于GMSSL来进行实现,已在5种环境下实现,并已使用在生产环境中。1、GMSSL编译GMSSL编译在不同环境下都不一样,这里我提供Window64、Arm64、Linux64、Android、himix200海思芯片环境编译方法,传送门如下:Gmssl官网地址Gmssl各平台编译方法【绝对可用】如果各位都是比较懒得人,我这里也给各位提供上
- iOS安全和逆向系列教程 第17篇:探讨ARM64架构与Swift逆向分析技术
自学不成才
iOS安全和逆向系列教程ios安全架构
iOS安全和逆向系列教程第17篇:探讨ARM64架构与Swift逆向分析技术前言欢迎来到iOS安全和逆向系列教程的第17篇。在前面的文章中,我们已经学习了iOS逆向工程的基础知识,以及各种分析工具的使用方法。今天,我们将深入探讨ARM64架构以及Swift语言的逆向分析技术,这两者对于现代iOS应用的逆向工程至关重要。随着Apple全面迁移到ARM64架构和Swift语言的广泛应用,掌握这些技术已
- arm centos7 安装mysql5.7
qq_42331499
mysqllinux数据库
ARM架构下安装MySQL-学习日记ARM64架构下安装mysql5.7.22的全过程_Mysql_脚本之家错误信息:InstallingMySQLsystemtables..../bin/mysqld:errorwhileloadingsharedlibraries:libaio.so.1:cannotopensharedobjectfile:Nosuchfileordirectory解决办法:
- YashanDB安装前服务器准备
数据库
本文内容来自YashanDB官网,原文内容请见https://doc.yashandb.com/yashandb/23.3/zh/%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85%...服务器配置项目推荐配置最低配置操作系统CentOS7.6以上,KylinOSV10,openEuler22.03如需使用大页内存,则要求Linux内核版本为2.6及以上CPUX86\_64,ARM64超线程,非超线程推荐4C及
- addPointers - overlap with incoming pointers 异常分析
惠(xi)斌
framework稳定性android
一.描述项目做老化测试,遇到systemserver重启,导致执行中间.报错信息:Buildfingerprint:'Dish/Spence/T715DS:15/AP3A.240905.015.A2/1732765343:user/release-keys'Revision:'0'ABI:'arm64'Timestamp:2024-12-0510:45:07.201198654+0800Proce
- android hal层编译,Android Hal层接入Opencv(踩坑篇)
古巴比伦
androidhal层编译
文章目录[x]1:尝试接入OpencvAndroidSDK2:寻找问题3:解决方法为了在AOSP的Hal层相机添加图片处理的一些功能。我尝试接入OpenCV4.5.1来实现该功能,本文将介绍接入过程中所遇到的坑和对应的解决方法。尝试接入OpencvAndroidSDK首先,我尝试接入4.5.1版本的AndroidSDK版本,需要将SDK包下的arm32位动态库和arm64位动态库添加到AOSP的模
- Ubuntu Docker 安装
Mr_One_Zhang
学习Dockerubuntudockerlinux
DockerEngine-Community支持以下的Ubuntu版本:Xenial16.04(LTS)Bionic18.04(LTS)Cosmic18.10Disco19.04其他更新的版本……DockerEngine-Community支持上x86_64(或amd64)armhf,arm64,s390x(IBMZ),和ppc64le(IBM的Power)架构。使用官方安装脚本自动安装安装命令如
- 5g核心网开源协议栈:open5GS安装教程(详解)_核心网 ip 协议栈
2501_90225911
5G开源协议tcp/ip
sudoaptinstallgnupgcurl-fsSLhttps://pgp.mongodb.com/server-6.0.asc|sudogpg-o/usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-6.0.gpg--dearmorecho“deb[arch=amd64,arm64signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-6.0
- arm64 kvm 常用 macro
GoGoGavin
kvm
Linuxkernel:5.12cpu:arm64generalpurpose寄存器赋值:以后更新sys寄存器:__vcpu_sys_reg(vcpu,reg)__vcpu_sys_reg(vcpu,reg)=val;#define__vcpu_sys_reg(v,r)(ctxt_sys_reg(&(v)->arch.ctxt,(r)))#definectxt_sys_reg(c,r)(*__ct
- 技术教程 | 如何实现1v1音视频通话(含源码)
网易数智
WebRTC音视频ai人工智能实时音视频语音识别实时互动信息与通信
今天,给大家讲一下怎么实现1v1音视频通话,以下是教程内容:开发环境开发环境要求如下:环境要求说明JDK版本1.8.0及以上版本AndroidAPI版本API21、AndroidStudio5.0及以上版本CPU架构ARM64、ARMV7IDEAndroidStudio其他依赖Androidx,不支持support库。注意事项1对1娱乐社交场景方案的呼叫能力基于云信呼叫组件,技术原理一对一通话功能
- Arm64架构的Linux服务器安装jdk8
web_15534274656
面试学习路线阿里巴巴服务器架构linux
一、下载JDK8打开浏览器,访问oracle官网找到适用于自己服务器的arm64架构的JDK8安装包。二、安装JDK8将下载好的JDK压缩包上传到服务器上解压JDK压缩包:tar-zxvfjdk-8uXXX-linux-arm64.tar.gz选择安装目录,我将JDK安装到/usr/local/目录下:mvjdk1.8.0_XXX/usr/local/jdk8三、配置环境变量打开环境变量配置文件:
- 几种常见的处理器架构应用场景
红栈说BSP
架构硬件工程linuxstm32单片机
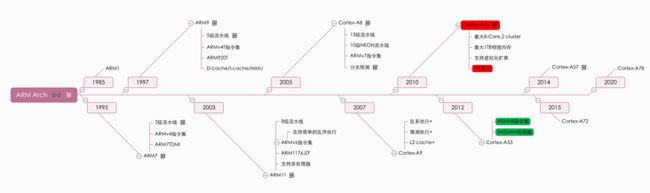
序本文主要为IT小白在处理器架构方面提供一个大概的认知,不周之处,还请见谅。文章目录序通用型1、x861-1、x86_64(即AMD64)非通用型示例:嵌入式1、80512、ARM2-1、ARMLinux性能成本社区支持兼容性定制化安全性2-2、ARM64研究意义通用型1、x86常见于日常PC的使用,是计算机软件的处理器架构基础。例:IntelCORE、IntelN100等。1-1、x86_64(
- 《Linux运维总结:基于ARM64+X86_64架构CPU使用docker-compose一键离线部署redis 6.2.14容器版哨兵集群》
东城绝神
《Linux运维实战总结》运维linux架构redis哨兵集群
总结:整理不易,如果对你有帮助,可否点赞关注一下?更多详细内容请参考:《Linux运维篇:Linux系统运维指南》一、部署背景由于业务系统的特殊性,我们需要面向不通的客户安装我们的业务系统,而作为基础组件中的redis针对不同的客户环境需要多次部署集群,作为一个运维工程师,提升工作效率也是工作中的重要一环。所以我觉得有必要针对X86_64+ARM64CPU架构redis6.2.14容器版哨兵集群编
- 「qt交叉编译arm64」支持xcb、X11
Alexios.W
qt嵌入式linux
完整的交叉编译好支持xcb的qt库(qt5.15.2、arm64、xcb、no-opengl)已安装xcb、X11库的交叉编译器(x86_64-aarch64-linux-gnu)文章目录1.修改qmake.conf,指定交叉编译器2.配置编译选项,执行configureLicenseHeader获取脚本所在目录并定位`configure`创建`qtbase`目录并进入执行配置命令使用方法3.不直
- windows下源码安装golang
616050468
golang安装golang环境windows
系统: 64位win7, 开发环境:sublime text 2, go版本: 1.4.1
1. 安装前准备(gcc, gdb, git)
golang在64位系
- redis批量删除带空格的key
bylijinnan
redis
redis批量删除的通常做法:
redis-cli keys "blacklist*" | xargs redis-cli del
上面的命令在key的前后没有空格时是可以的,但有空格就不行了:
$redis-cli keys "blacklist*"
1) "blacklist:12:
[email protected]
- oracle正则表达式的用法
0624chenhong
oracle正则表达式
方括号表达示
方括号表达式
描述
[[:alnum:]]
字母和数字混合的字符
[[:alpha:]]
字母字符
[[:cntrl:]]
控制字符
[[:digit:]]
数字字符
[[:graph:]]
图像字符
[[:lower:]]
小写字母字符
[[:print:]]
打印字符
[[:punct:]]
标点符号字符
[[:space:]]
- 2048源码(核心算法有,缺少几个anctionbar,以后补上)
不懂事的小屁孩
2048
2048游戏基本上有四部分组成,
1:主activity,包含游戏块的16个方格,上面统计分数的模块
2:底下的gridview,监听上下左右的滑动,进行事件处理,
3:每一个卡片,里面的内容很简单,只有一个text,记录显示的数字
4:Actionbar,是游戏用重新开始,设置等功能(这个在底下可以下载的代码里面还没有实现)
写代码的流程
1:设计游戏的布局,基本是两块,上面是分
- jquery内部链式调用机理
换个号韩国红果果
JavaScriptjquery
只需要在调用该对象合适(比如下列的setStyles)的方法后让该方法返回该对象(通过this 因为一旦一个函数称为一个对象方法的话那么在这个方法内部this(结合下面的setStyles)指向这个对象)
function create(type){
var element=document.createElement(type);
//this=element;
- 你订酒店时的每一次点击 背后都是NoSQL和云计算
蓝儿唯美
NoSQL
全球最大的在线旅游公司Expedia旗下的酒店预订公司,它运营着89个网站,跨越68个国家,三年前开始实验公有云,以求让客户在预订网站上查询假期酒店时得到更快的信息获取体验。
云端本身是用于驱动网站的部分小功能的,如搜索框的自动推荐功能,还能保证处理Hotels.com服务的季节性需求高峰整体储能。
Hotels.com的首席技术官Thierry Bedos上个月在伦敦参加“2015 Clou
- java笔记1
a-john
java
1,面向对象程序设计(Object-oriented Propramming,OOP):java就是一种面向对象程序设计。
2,对象:我们将问题空间中的元素及其在解空间中的表示称为“对象”。简单来说,对象是某个类型的实例。比如狗是一个类型,哈士奇可以是狗的一个实例,也就是对象。
3,面向对象程序设计方式的特性:
3.1 万物皆为对象。
- C语言 sizeof和strlen之间的那些事 C/C++软件开发求职面试题 必备考点(一)
aijuans
C/C++求职面试必备考点
找工作在即,以后决定每天至少写一个知识点,主要是记录,逼迫自己动手、总结加深印象。当然如果能有一言半语让他人收益,后学幸运之至也。如有错误,还希望大家帮忙指出来。感激不尽。
后学保证每个写出来的结果都是自己在电脑上亲自跑过的,咱人笨,以前学的也半吊子。很多时候只能靠运行出来的结果再反过来
- 程序员写代码时就不要管需求了吗?
asia007
程序员不能一味跟需求走
编程也有2年了,刚开始不懂的什么都跟需求走,需求是怎样就用代码实现就行,也不管这个需求是否合理,是否为较好的用户体验。当然刚开始编程都会这样,但是如果有了2年以上的工作经验的程序员只知道一味写代码,而不在写的过程中思考一下这个需求是否合理,那么,我想这个程序员就只能一辈写敲敲代码了。
我的技术不是很好,但是就不代
- Activity的四种启动模式
百合不是茶
android栈模式启动Activity的标准模式启动栈顶模式启动单例模式启动
android界面的操作就是很多个activity之间的切换,启动模式决定启动的activity的生命周期 ;
启动模式xml中配置
<activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:launchMode="standard&quo
- Spring中@Autowired标签与@Resource标签的区别
bijian1013
javaspring@Resource@Autowired@Qualifier
Spring不但支持自己定义的@Autowired注解,还支持由JSR-250规范定义的几个注解,如:@Resource、 @PostConstruct及@PreDestroy。
1. @Autowired @Autowired是Spring 提供的,需导入 Package:org.springframewo
- Changes Between SOAP 1.1 and SOAP 1.2
sunjing
ChangesEnableSOAP 1.1SOAP 1.2
JAX-WS
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 0: Primer (Second Edition)
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 1: Messaging Framework (Second Edition)
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 2: Adjuncts (Second Edition)
Which style of WSDL
- 【Hadoop二】Hadoop常用命令
bit1129
hadoop
以Hadoop运行Hadoop自带的wordcount为例,
hadoop脚本位于/home/hadoop/hadoop-2.5.2/bin/hadoop,需要说明的是,这些命令的使用必须在Hadoop已经运行的情况下才能执行
Hadoop HDFS相关命令
hadoop fs -ls
列出HDFS文件系统的第一级文件和第一级
- java异常处理(初级)
白糖_
javaDAOspring虚拟机Ajax
从学习到现在从事java开发一年多了,个人觉得对java只了解皮毛,很多东西都是用到再去慢慢学习,编程真的是一项艺术,要完成一段好的代码,需要懂得很多。
最近项目经理让我负责一个组件开发,框架都由自己搭建,最让我头疼的是异常处理,我看了一些网上的源码,发现他们对异常的处理不是很重视,研究了很久都没有找到很好的解决方案。后来有幸看到一个200W美元的项目部分源码,通过他们对异常处理的解决方案,我终
- 记录整理-工作问题
braveCS
工作
1)那位同学还是CSV文件默认Excel打开看不到全部结果。以为是没写进去。同学甲说文件应该不分大小。后来log一下原来是有写进去。只是Excel有行数限制。那位同学进步好快啊。
2)今天同学说写文件的时候提示jvm的内存溢出。我马上反应说那就改一下jvm的内存大小。同学说改用分批处理了。果然想问题还是有局限性。改jvm内存大小只能暂时地解决问题,以后要是写更大的文件还是得改内存。想问题要长远啊
- org.apache.tools.zip实现文件的压缩和解压,支持中文
bylijinnan
apache
刚开始用java.util.Zip,发现不支持中文(网上有修改的方法,但比较麻烦)
后改用org.apache.tools.zip
org.apache.tools.zip的使用网上有更简单的例子
下面的程序根据实际需求,实现了压缩指定目录下指定文件的方法
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWrit
- 读书笔记-4
chengxuyuancsdn
读书笔记
1、JSTL 核心标签库标签
2、避免SQL注入
3、字符串逆转方法
4、字符串比较compareTo
5、字符串替换replace
6、分拆字符串
1、JSTL 核心标签库标签共有13个,
学习资料:http://www.cnblogs.com/lihuiyy/archive/2012/02/24/2366806.html
功能上分为4类:
(1)表达式控制标签:out
- [物理与电子]半导体教材的一个小问题
comsci
问题
各种模拟电子和数字电子教材中都有这个词汇-空穴
书中对这个词汇的解释是; 当电子脱离共价键的束缚成为自由电子之后,共价键中就留下一个空位,这个空位叫做空穴
我现在回过头翻大学时候的教材,觉得这个
- Flashback Database --闪回数据库
daizj
oracle闪回数据库
Flashback 技术是以Undo segment中的内容为基础的, 因此受限于UNDO_RETENTON参数。要使用flashback 的特性,必须启用自动撤销管理表空间。
在Oracle 10g中, Flash back家族分为以下成员: Flashback Database, Flashback Drop,Flashback Query(分Flashback Query,Flashbac
- 简单排序:插入排序
dieslrae
插入排序
public void insertSort(int[] array){
int temp;
for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){
temp = array[i];
for(int k=i-1;k>=0;k--)
- C语言学习六指针小示例、一维数组名含义,定义一个函数输出数组的内容
dcj3sjt126com
c
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int * p; //等价于 int *p 也等价于 int* p;
int i = 5;
char ch = 'A';
//p = 5; //error
//p = &ch; //error
//p = ch; //error
p = &i; //
- centos下php redis扩展的安装配置3种方法
dcj3sjt126com
redis
方法一
1.下载php redis扩展包 代码如下 复制代码
#wget http://redis.googlecode.com/files/redis-2.4.4.tar.gz
2 tar -zxvf 解压压缩包,cd /扩展包 (进入扩展包然后 运行phpize 一下是我环境中phpize的目录,/usr/local/php/bin/phpize (一定要
- 线程池(Executors)
shuizhaosi888
线程池
在java类库中,任务执行的主要抽象不是Thread,而是Executor,将任务的提交过程和执行过程解耦
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
public class RunMain implements Executor{
@Override
pub
- openstack 快速安装笔记
haoningabc
openstack
前提是要配置好yum源
版本icehouse,操作系统redhat6.5
最简化安装,不要cinder和swift
三个节点
172 control节点keystone glance horizon
173 compute节点nova
173 network节点neutron
control
/etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward =
- 从c面向对象的实现理解c++的对象(二)
jimmee
C++面向对象虚函数
1. 类就可以看作一个struct,类的方法,可以理解为通过函数指针的方式实现的,类对象分配内存时,只分配成员变量的,函数指针并不需要分配额外的内存保存地址。
2. c++中类的构造函数,就是进行内存分配(malloc),调用构造函数
3. c++中类的析构函数,就时回收内存(free)
4. c++是基于栈和全局数据分配内存的,如果是一个方法内创建的对象,就直接在栈上分配内存了。
专门在
- 如何让那个一个div可以拖动
lingfeng520240
html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml
- 第10章 高级事件(中)
onestopweb
事件
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- 计算两个经纬度之间的距离
roadrunners
计算纬度LBS经度距离
要解决这个问题的时候,到网上查了很多方案,最后计算出来的都与百度计算出来的有出入。下面这个公式计算出来的距离和百度计算出来的距离是一致的。
/**
*
* @param longitudeA
* 经度A点
* @param latitudeA
* 纬度A点
* @param longitudeB
*
- 最具争议的10个Java话题
tomcat_oracle
java
1、Java8已经到来。什么!? Java8 支持lambda。哇哦,RIP Scala! 随着Java8 的发布,出现很多关于新发布的Java8是否有潜力干掉Scala的争论,最终的结论是远远没有那么简单。Java8可能已经在Scala的lambda的包围中突围,但Java并非是函数式编程王位的真正觊觎者。
2、Java 9 即将到来
Oracle早在8月份就发布
- zoj 3826 Hierarchical Notation(模拟)
阿尔萨斯
rar
题目链接:zoj 3826 Hierarchical Notation
题目大意:给定一些结构体,结构体有value值和key值,Q次询问,输出每个key值对应的value值。
解题思路:思路很简单,写个类词法的递归函数,每次将key值映射成一个hash值,用map映射每个key的value起始终止位置,预处理完了查询就很简单了。 这题是最后10分钟出的,因为没有考虑value为{}的情