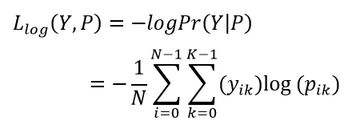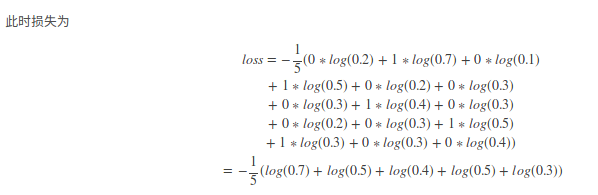1、criterion=nn.CrossEntropyLoss():交叉熵函数
criterion(prediction,lable)
分类问题中,交叉熵函数是比较常用也是比较基础的损失函数,能够表征真实样本标签和预测概率之间的差值.
1.1任务为二分类时
1)当某个样本的真实标签y=1时,Loss=−lop(p),分类器的预测概率p=Pr(y=1)的概率越小,则分类损失就越大;反之,分类器的预测概率p=Pr(y=1)的概率越大,则分类损失就越小。
2)对于真实标签y=0,Loss=−log(1−p),分类器的预测概率p=Pr(y=1)的概率越大,则损失越大。
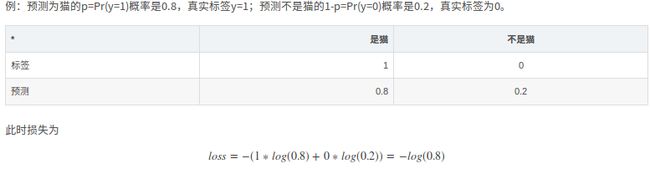
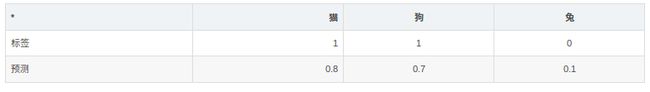
例:预测为猫的p=Pr(y=1)概率是0.8,真实标签y=1;预测不是猫的1-p=Pr(y=0)概率是0.2,真实标签为0。
1.2任务为多元分类时
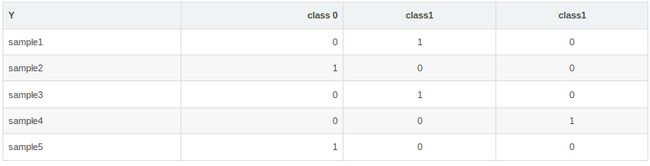
在多元分类的时候,假定有k个类,则类标签集合就是labels=(1,2,3,…,k).如果第i个样本的类标签是k的话,就记为yi,k=1。采用one-hot记法。每个样本的真实标签就是一个one-hot向量,其中只有一个位置记为1。
例:设共有5类,label =3时,one-hot形式如下
N个样本的真实类标签就是一个N行K列的矩阵:
分类器对N个样本的每一个样本都会预测出它属于每个类的概率,这样的概率矩阵P就是N行K列的。
整个样本集合上分类器的对数损失就可以如下定义:
1.3任务为多标签分类时
多标签是在一种图片有多个类别时,比如一张图片同时有猫狗。
与之前不一样的是,预测不再通过softmax计算,而是采用sigmoid把输出限制到(0,1)。正因此预测值得加和不再是1。这里交叉熵单独对每一个类别计算,每一个类别有两种可能的类别,即属于这个类的概率或不属于这个类的概率。
例:单张图片损失计算可以为
loss=loss猫+loss狗+loss兔
各类损失计算如下
loss猫=−(1∗log(0.8)+(1−0)∗log(1−0.8))=−log(0.8)
loss狗=−(1∗log(0.7)+0∗log(0.3))=−log(0.7)
loss兔=−(0∗log(0.1)+1∗log(0.9))=−log(0.9)
对于整体损失可以用下式:
注意:nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 包括了将output进行Softmax操作的,所以直接输入output即可。其中还包括将label转正one-hot编码,所以直接输入label。该函数限制了target的类型为torch.LongTensor。label_tgt = make_variable(torch.ones(feat_tgt.size(0)).long())可在后边直接.long()。其output,label的shape可以不一致
代码:
示例1
import torch
a=torch.tensor([[-0.3830,-0.0102,-1.4235,-0.5212,0.9011]])
#print(a) tensor([[-0.3830, -0.0102, -1.4235, -0.5212, 0.9011]])
b=torch.tensor([4])
#print(b) tensor([4])
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss=loss_fn(a,b)
#print(loss) tensor(0.7020)
示例2:
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
weight = torch.Tensor([1,2,1,1,10])
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduce=False, size_average=False, weight=weight)
input = Variable(torch.randn(3, 5)) # (batch_size, C)
target = Variable(torch.LongTensor(3).random_(5)) #这里应该为LongTensor
loss = loss_fn(input, target)
print(input); print(target); print(loss)
人工计算过程:
先把a(相当于output=model(input))进行softmax,
import torch.nn.functional as F
aa=F.softmax(a)
#print(aa) tensor([[0.1372, 0.1992, 0.0485, 0.1195, 0.4956]])
原来CrossEntropyLoss() 会把target变成ont-hot形式,我们现在例子的样本标签是 [4](从0开始计算)。那么转换成one-hot编码就是[0,0,0,0,1],
loss=-1*log(0.4956)
这里的log是10为底的(很奇怪)
示例3:
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
pred_concat = critic(feat_concat.detach())
#print(pred_concat.shape) torch.Size([100, 2])
label_src = make_variable(torch.ones(feat_src.shape[0]).long()) #1 is true
label_tgt = make_variable(torch.zeros(feat_tgt.shape[0]).long()) # 0 is false
label_concat = torch.cat((label_src, label_tgt))
loss_critic = criterion(pred_concat, label_concat)
2、criterion=nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
二分类用的交叉熵.
criterion(input,target):
注意input,target的shape必须相等,且input应该为FloatTensor的类型。
代码:
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
pred_concat = critic(feat_concat.detach()) #模型的输出:一个矩阵
#print(pred_concat.shape) torch.Size([100, 2])
prediction_concat=torch.squeeze(pred_concat.max(1)[0])
#print(prediction_concat.shape) torch.Size([100])
# prepare real and fake label
label_src = make_variable(torch.ones(feat_src.shape[0])) #1 is true
label_tgt = make_variable(torch.zeros(feat_tgt.shape[0])) # 0 is false
label_concat = torch.cat((label_src, label_tgt))
#print(label_concat.shape) torch.Size([100])
# compute loss for critic
loss_critic = criterion(prediction_concat, label_concat)