AL游戏中的自动寻路——A*算法详解(C++实现)
目录
一、A*算法的一个应用实例:迷宫寻路
二、A*算法简介
三、A*算法的原理和步骤
四、算法实现
①将用户调用的算法接口与A*算法实现接口分开
②A*算法实现
③寻找列表F值最小节点
④判断指定结点是否对另一结点可达
⑦ 寻找可达节点
⑧A*算法完善
⑨对可达节点的处理
⑩A*算法最终实现
程序资源清理
一、A*算法的一个应用实例:迷宫寻路
【下面是A*算法的一个应用实例:迷宫寻路,将迷宫地图信息录入后即可自动实现路径的搜索。
以下是迷宫寻路中的全部代码,大家可以直接拷贝运行。
AStar.h
#pragma once
#include
const int kCost1 = 1; //直移一格的消耗
const int kCost2 = 2; //斜移一格的消耗
typedef struct _Point {
int x, y; //点坐标,x - 横排 y - 竖排
int F, G, H; //F=G+H
struct _Point* parent;
}Point;
/******************************
* 功能:分配一格结点
* 输入:
* x - 二维数组行
* y - 二维数组列
* 返回:
* 已初始化的结点的指针
******************************/
Point* AllocPoint(int x, int y);
/******************************
* 功能:初始化地图
* 输入:
* _maze - 二维数组地址
* _lines - 二维数组行数
* _columns - 二维数组列数
* 返回:
* 无
******************************/
void InitAstarMaze(int* _maze, int _lines, int _colums);
/******************************
* 功能:寻找路径
* 输入:
* startPoint - 起始位置
* endPoint - 终点位置
* 返回:
* 返回路径链表的头节点
******************************/
std::list GetPath(Point* startPoint, Point* endPoint);
/******************************
* 功能:资源清理
* 输入:
* 无
* 返回:
* 无
******************************/
void ClearAstarMaze();
AStar.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include"AStar.h"
static int* maze; // 迷宫对应的二维数组,用一级指针表示
static int cols; // 二维数组列数
static int lines; // 二维数组对应的行数
static std::listopenList; // 开放列表
static std::listcloseList; // 关闭列表
Point* AllocPoint(int x, int y);
static std::vectorgetSurroundPoints(const Point* point);
static Point* isInList(std::list& list, const Point* point);
/******************************
* 功能:查找openList中F值最小节点
* 输入:
* 无
* 返回:
* F值最小节点
******************************/
static Point* getLeastFpoint() {
if (!openList.empty()) {
Point* resPoint = openList.front();
std::list::const_iterator itor;
for (itor = openList.begin(); itor != openList.end(); ++itor) {
Point* p = *itor; // itor是list类型迭代器,所以*itor是Poit *类型
if (p->F < resPoint->F) {
resPoint = *itor;
}
}
return resPoint;
}
//是空值情况
return NULL;
}
/******************************
* 功能:计算指定结点到父节点的G值
* 输入:
* parent - 父节点
* point - 指定结点
* 返回:
* 指定结点到父节点的G值
******************************/
static int calcG(Point* parrent, Point* point) {
//如果可以直走额外消耗量为kCost1,如果需要斜走额外消耗量为kCost2
//int extraG=abs(parrent->x - point->x) + abs(parrent->y - point->y) == 1 ? kCost1 : kCost2;
int extraG = kCost2; // 规定只能直着走
int parentG = (point->parent == NULL ? NULL : point->parent->G);
return parentG + extraG;
}
/******************************
* 功能:计算指定结点到终点结点的H值
* 输入:
* point - 指定结点
* endPoint - 终点结点
* 返回:
* 指定结点到终点结点的H值
******************************/
static int calcH(Point* point, Point* end) {
//考虑斜移
//return (int)sqrt((double)(end->x - point->x) * (double)(end->x - point->x) + (double)(end->y - point->y) + (double)(end->y - point->y));
//规定只能直走
return (end->x - point->x) + (end->y - point->y);
}
/******************************
* 功能:计算指定结点的F值
* 输入:
* point - 指定结点
* 返回:
* 指定结点的F值
******************************/
static int calcF(Point* point) {
return point->G + point->H;
}
/******************************
* 功能:A*算法实现
* 输入:
* startPoint - 起始位置
* endPoint - 终点位置
* 返回:
* 终点位置的结点
******************************/
static Point* findPath(Point* startPoint, Point* endPoint) {
//置入起点,拷贝开辟一格节点,内外隔离
openList.push_back(AllocPoint(startPoint->x, startPoint->y));
//openList不为空时,不停的取openList中L的最小值
while (!openList.empty()) {
//查找openList中F最小值节点
Point* curPoint = getLeastFpoint();
//把最小值节点放到关闭列表中
openList.remove(curPoint); // 从openList中移除
closeList.push_back(curPoint); // 放入closeList中
//找到当前节点周围可达节点处理
std::vectorsurroundPoints = getSurroundPoints(curPoint);
std::vector::const_iterator iter;
for (iter = surroundPoints.begin(); iter != surroundPoints.end(); ++iter) {
Point* target = *iter;
//对某一结点,如果不在openList中,则加入到openList中,并设置其父节点;如果在openList中,则重新计算F值,选取min(F)的结点
Point* exist = isInList(openList, target);
//不在openList中
if (!exist) {
target->parent = curPoint;
target->G = calcG(curPoint, target);
target->H = calcH(target, endPoint);
target->F = calcF(target);
openList.push_back(target);
}// 在开放列表中,重新计算G值,保留min(F)
else {
int tempG = calcG(curPoint, target);
if (tempG < target->G) {
exist->parent = curPoint;
exist->G = tempG;
exist->F = calcF(target);
}
delete target;
}
} // end for
surroundPoints.clear();
//判断终点是否在openList中
Point* resPoint = isInList(openList, endPoint);
if (resPoint) {
return resPoint;
}
}
//如果while执行完毕则表明没有找到
return NULL;
}
/******************************
* 功能:判断指定节点是否在指定链表中
* 输入:
* list - 指定链表
* point - 指定节点
* 返回:
* Point* - 判断节点在链表中,返回该在链表中地址
* NULL - 不在节点中
******************************/
static Point* isInList(std::list& list, const Point* point) {
std::list::const_iterator itor;
for (itor = list.begin(); itor != list.end(); ++itor) {
if ((*itor)->x == point->x && (*itor)->y == point->y) {
return *itor;
}
}
return NULL;
}
/******************************
* 功能:判断某点是否可达指定点
* 输入:
* point - 指定节点
* target - 待判断节点
* 返回:
* true - 可达
* false - 不可达
******************************/
static bool isCanreach(const Point* point, const Point* target) {
int x = target->x;
int y = target->y;
//待测节点超过二维数组,或待测节点是障碍物,或者待测节点与指定节点重合,或待测节点在closeList链表中。则不可达
if (x < 0 || x >= lines || y < 0 || y >= cols
|| maze[x * cols + y] == 0
|| (x == point->x && y == point->y)
|| isInList(closeList, target)) {
return false;
}
if (abs(point->x - target->x) + abs(point->y - target->y) == 1) {
//待测点与指定点相邻
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
/******************************
* 功能:获得当前节点的周围可达节点(这里只考虑直着走)
* 输入:
* point - 指定节点
* 返回:
* 周围可达节点vector数组
******************************/
static std::vectorgetSurroundPoints(const Point* point) {
//定义存储可达节点的数组
std::vectorsurroundPoints;
for (int x = point->x - 1; x <= point->x + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = point->y - 1; y <= point->y + 1; ++y) {
Point* temp = AllocPoint(x, y);
if (isCanreach(point, temp)) {
surroundPoints.push_back(temp);
}
else {
//不可达则释放资源
delete temp;
}
}
}
return surroundPoints;
}
/******************************
* 功能:初始化地图
* 输入:
* _maze - 二维数组地址
* _lines - 二维数组行数
* _columns - 二维数组列数
* 返回:
* 无
******************************/
void InitAstarMaze(int* _maze, int _lines, int _colums) {
maze = _maze;
cols = _colums;
lines = _lines;
}
/******************************
* 功能:分配一格结点
* 输入:
* x - 二维数组行
* y - 二维数组列
* 返回:
* 已初始化的结点的指针
******************************/
Point* AllocPoint(int x, int y) {
Point* temp = new Point;
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(Point)); //初始值清零
temp->x = x;
temp->y = y;
return temp;
}
/******************************
* 功能:调用A*算法,寻找路径
* 输入:
* startPoint - 起始位置
* endPoint - 终点位置
* 返回:
* 返回路径链表的头节点
******************************/
std::list GetPath(Point* startPoint, Point* endPoint) {
Point* result = findPath(startPoint, endPoint);
std::listpath;
//返回路径,如果没有找到路径,返回空链表
while (result) {
path.push_front(result);
result = result->parent;
}
//path.reverse();
return path;
}
/******************************
* 功能:资源清理
* 输入:
* 无
* 返回:
* 无
******************************/
void ClearAstarMaze() {
maze = NULL;
lines = 0;
cols = 0;
std::list::iterator itor;
for (itor = openList.begin(); itor != openList.end();) {
delete* itor;
itor = openList.erase(itor); //从链表中删除某个结点,并返回下一个结点
}
for (itor = closeList.begin(); itor != closeList.end();) {
delete* itor;
itor = closeList.erase(itor); //从链表中删除某个结点,并返回下一个结点
}
} 迷宫地图代码
迷宫寻路中的图片下载地址 人物图片;墙壁图片;地板图片;终点图片;迷宫背景图片
#include"AStar.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef enum _PROPS {
WALL, //墙
FLOOR, //地板
BOX_DES,//箱子目的地
MAN, //小人
}PRPOS;
#define RATIO 23
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 880
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 775
#define START_X 116
#define START_Y 54
#define RECT 9
IMAGE images[4];
//记录小人位置
typedef struct _POS {
int x;
int y;
}POS;
POS man;
int map[29][28] = {//二维数组在内存顺序存储的
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,2,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0},
{0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0},
{0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0},
{0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0},
{0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,3,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}
};
/*******************************
* 功能:小人行走时更改图片显示
* 输入:
* 无
* 输出:
* 无
*******************************/
void changeMap(int x, int y, PRPOS prpos) {
if (prpos == MAN) {
putimage(START_X + y * RATIO, START_Y + x * RATIO, &images[prpos]);
}
else if (prpos == FLOOR) {
putimage(START_X + y * RATIO, START_Y + x * RATIO, &images[prpos]);
setcolor(LIGHTCYAN);
setfont(RECT, 0, _T("楷体"));
outtextxy(START_X + y * RATIO + (RATIO - RECT) / 2, START_Y + x * RATIO + (RATIO - RECT) / 2, _T("■"));
}
}
/*******************************
* 功能:初始化画布,加载迷宫
* 输入:
* 无
* 输出:
* 无
*******************************/
void init_graph() {
IMAGE bg_img;
initgraph(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT);
//图片的宽,高最后一个参数“是否拉伸”
loadimage(&bg_img, _T("blackground.bmp"), SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, true);
putimage(0, 0, &bg_img);
loadimage(&images[WALL], _T("wall_right.bmp"), RATIO, RATIO, true);
loadimage(&images[FLOOR], _T("floor.bmp"), RATIO, RATIO, true);
loadimage(&images[BOX_DES], _T("des.bmp"), RATIO, RATIO, true);
loadimage(&images[MAN], _T("man.bmp"), RATIO, RATIO, true);
for (int i = 0; i < 29; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 28; ++j) {
if (map[i][j] == 3) {
man.x = i;
man.y = j;
}
putimage(START_X + j * RATIO, START_Y + i * RATIO, &images[map[i][j]]);
}
}
}
/*******************************
* 功能:调用A*算法获得路径链表
* 输入:
* 无
* 输出:
* 无
*******************************/
void AstartTest() {
InitAstarMaze(&map[0][0], 30, 28);
Point* start = AllocPoint(man.x, man.y);
Point* end = AllocPoint(0, 12);
listpath = GetPath(start, end);
list::const_iterator iter;
for (iter = path.begin(); iter != path.end();++iter) {
Point* cur = *iter;
changeMap(man.x, man.y, FLOOR);
man.x = cur->x;
man.y = cur->y;
changeMap(man.x, man.y, MAN);
Sleep(250);
}
ClearAstarMaze();
}
int main() {
init_graph();
AstartTest();
system("pause");
closegraph();
return 0;
}
 wall_right.bmp
wall_right.bmp  man.bmp
man.bmp  floor.bmp
floor.bmp
 des.bmp blackground.bmp
des.bmp blackground.bmp
二、A*算法简介
在日趋流行的3D游戏中,如何使非玩家控制角色准确实现自动寻路功能成为3D 开发技术中一大研究热点。其中A*算法得到大量运用。A*算法与传统路径规划算法相比,实时性更高、灵活性更强、寻路结果更贴近人工选择路径结果。A*寻路算法并不是找到最优路径,只是找到相对近的路径,因为赵最优路径要把所有可行路径都找出来进行对比,消耗性能太大,寻路效果只要相对近路径就行了。
三、A*算法的原理和步骤
教科书上的手段是:一大串文字摆在这里让大家自行理解。
- G 表示从起点移动到网格上指定方格的移动距离 (暂时不考虑沿斜向移动,只考虑上下左右移动)。
- H 表示从指定的方格移动到终点的预计移动距离,只计算直线距离 (H 有很多计算方法, 这里我们设定只可以上下左右移动,即该点与终点的直线距离)。
令 F = G + H ,F 即表示从起点经过此点预计到终点的总移动距离
1. 从起点开始, 把它作为待处理的方格存入一个预测可达的节点列表,简称 openList, 即把起点放入“预测可达节点列表”,可达节点列表 openList 就是一个等待检查方格的列表。
2. 寻找 openList 中 F 值最小的点 min(一开始只有起点)周围可以到达的点(可到达的意思是其不是障碍物,也不存在关闭列表中的方格,即不是已走过的方格)。计算 min 周围可到达的方格的 F 值。将还没在 openList 中点放入其中, 并设置它们的"父方格"为点 min,表示他们的上一步是经过 min 到达的。如果 min 下一步某个可到达的方格已经在 openList列表那么并且经 min 点它的 F 值更优,则修改 F 值并把其"父方格"设为点 min。
3. 把 2 中的点 min 从"开启列表"中删除并存入"关闭列表"closeList 中, closeList 中存放的都 是不需要再次检查的方格。如果 2 中点 min 不是终点并且开启列表的数量大于零,那么继续从第 2 步开始。如果是终点执行第 4 步,如果 openList 列表数量为零,那么就是找不到有效路径。
4.如果第 3 步中 min 是终点,则结束查找,直接追溯父节点到起点的路径即为所选路径。
好嘛~,这就是不打算让人理解呗,一会“可达列表”,一会“关闭列表”。
其实A*算法主要步骤是:每次从遍历openList列表,从中找到F值最小的节点,将此节点放到closeList列表中表示走经过这个结点,再寻找此节点周围的可达节点,将这些可达结点放入openList列中继续按遍历,直到将终点结点放入openList中。这样就会有一条以起点为头节点,终点为尾结点的链表生成,遍历这条链表即为要走的路径。
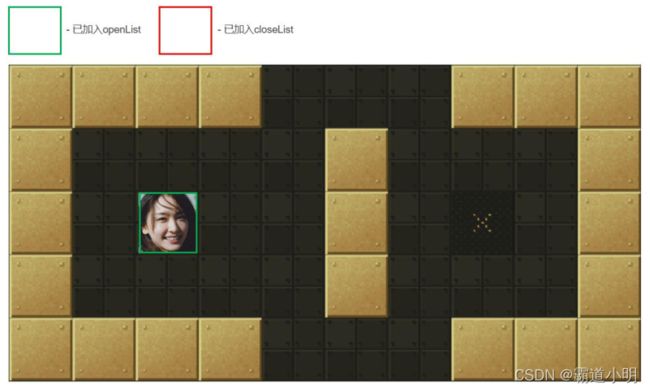
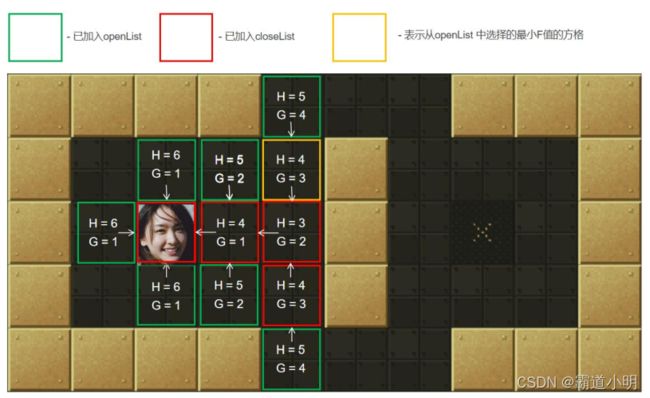
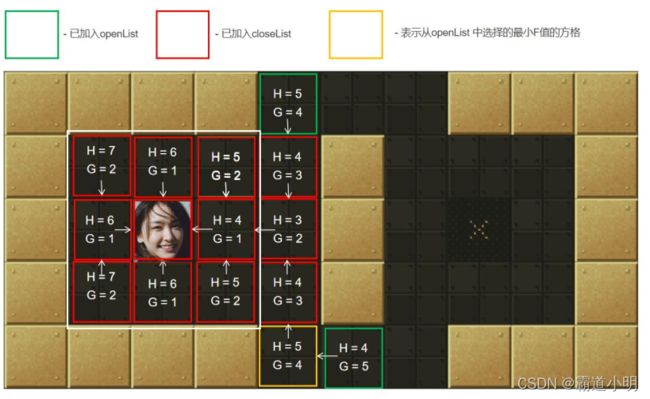
下面我用简单的迷宫寻路图示来给大家演示A*算法的步骤。
G 表示从起点移动到网格上指定方格的移动距离 (暂时不考虑沿斜向移动,只考虑上下左右移动)。
H 表示从指定的方格移动到终点的预计移动距离,只计算直线距离 (H 有很多计算方法, 这里我们设定只可以上下左右移动,即该点与终点的直线距离)。令F = G + H。
第一步:把起点加入openList中
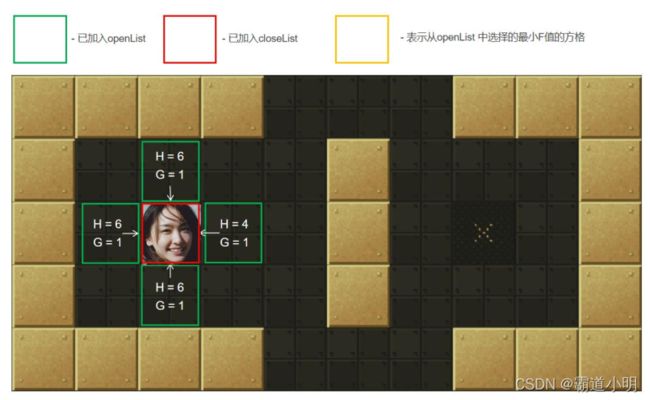
第二步:从openList中选择最小F值的点,此时只有起点一格节点。计算它周围的可达方块的G、H和F值,标记这些节点的父节点为当前选择节点(起点),并把它们加入到openList中
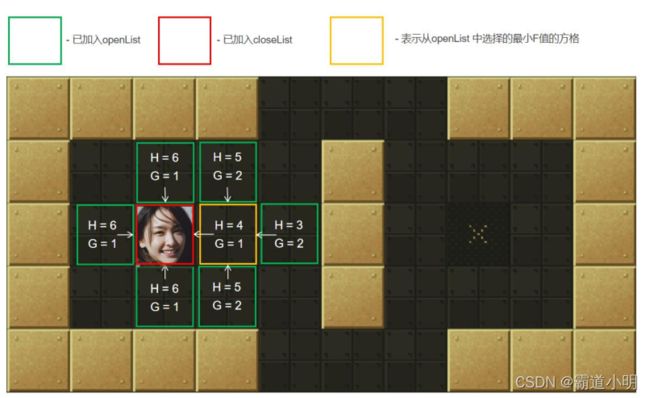
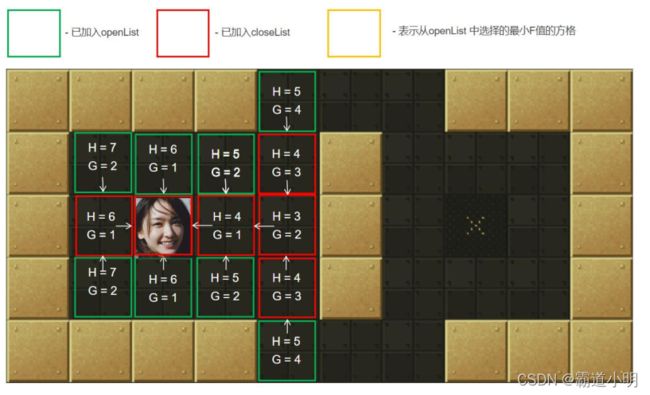
第四步:从openList中选择最小F值节点。如图黄色所示。计算它周围可达方块的G、H和F值,标记这些节点的父节点为当前许纳泽节点(起点),并把它们加入到openList中
第五步:把当前节点(上上图的黄色框)加入到closeLsit中
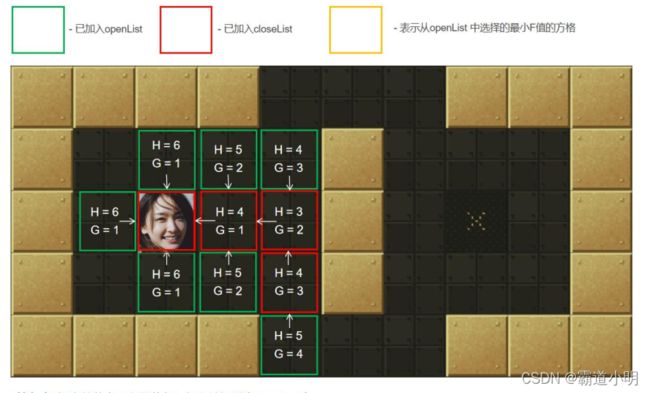
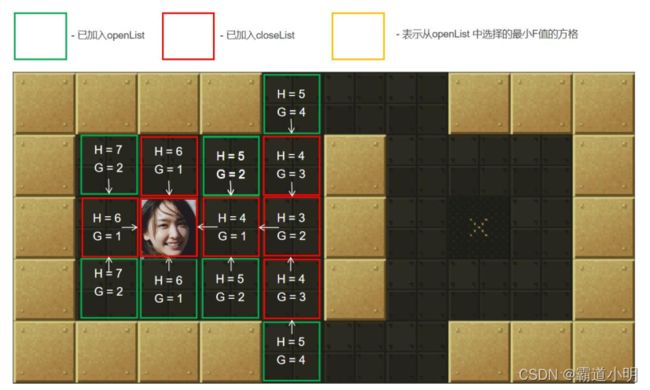
第六步:从openList中选择最小F值节点。如图黄色所示。计算它周围可达方块的G、H和F值,标记这些节点的父节点为当前许纳泽节点(起点),并把它们加入到openList中
第七步:把当前节点(上上图的黄色框)加入到closeLsit中
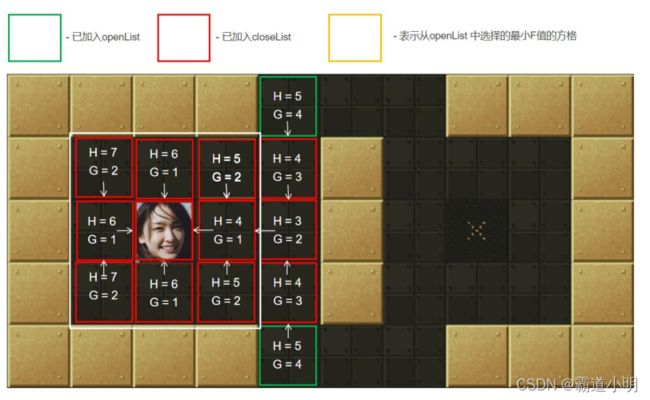
第八步:从openList中选择最小F值节点。如图黄色所示。计算它周围可达方块的G、H和F值,标记这些节点的父节点为当前许纳泽节点(起点),并把它们加入到openList中
第九步:把当前节点(上上图的黄色框)加入到closeLsit中
第十步:从openList中选择最小F值节点。如图黄色所示。计算它周围可达方块的G、H和F值,标记这些节点的父节点为当前许纳泽节点(起点),并把它们加入到openList中。当最小F值有重复时随便选取一个即可
第十一步:把当前节点(上上图的黄色框)加入到closeLsit中
第十二步:从openList中选择最小F值节点。如图黄色所示。计算它周围可达方块的G、H和F值,标记这些节点的父节点为当前许纳泽节点(起点),并把它们加入到openList中
第十三步:把当前节点(上上图的黄色框)加入到closeLsit中
第十四步:从openList中选择最小F值节点。如图黄色所示。计算它周围可达方块的G、H和F值,标记这些节点的父节点为当前许纳泽节点(起点),并把它们加入到openList中
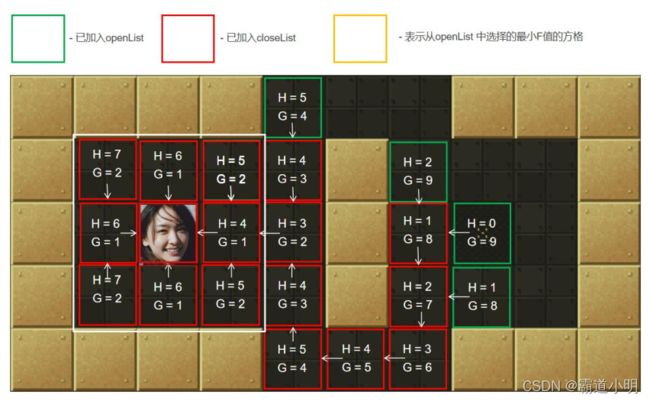
第十五步:把当前节点(上上图的黄色框)加入到closeLsit中
第十六步:按照第十四步和第十五步的步骤,白色区域中的绿色各自最终都会变成红色
第十七步:继续从openList中选择F值最小的节点 ,如黄色所示,继续按照前面的重复步骤寻路,最终当中带你也变成红色后,寻路结束
第十八步:最终结果
下面是代码实现过程
四、算法实现
程序通过链表存储最终路径,使用C++内置数据结构 sd::list<>
对可达结点使用动态数组std::vector<>存储
①将用户调用的算法接口与A*算法实现接口分开
/******************************
* 功能:调用A*算法,寻找路径
* 输入:
* startPoint - 起始位置
* endPoint - 终点位置
* 返回:
* 返回路径链表的头节点
******************************/
std::list GetPath(Point* startPoint, Point* endPoint) {
//返回终点,对终点进行回溯即为路径链表
Point* result = findPath(startPoint, endPoint);
std::listpath;
//返回路径,如果没有找到路径,返回空链表
while (result) {
path.push_front(result);
result = result->parent;
}
//path.reverse();
return path;
}
/******************************
* 功能:A*算法实现
* 输入:
* startPoint - 起始位置
* endPoint - 终点位置
* 返回:
* 终点位置的结点
******************************/
static Point* findPath(Point* startPoint, Point* endPoint) {
} ②A*算法实现
A*算法首先将起点放入openList中,每次将openList中F值最小的节点 移除,放入closeList列表中,再寻找此节点周围可达节点。因此在实现A*算法之前就有两个功能需要先完成,一个是寻找openList列表中F值最小节点getLeastPoint(),一个是寻找周围可达节点getSurroundPoints()。
③寻找列表F值最小节点
寻找F值最小节点,其实就是遍历整个链表,返回F值最小节点的拷贝,当然在遍历链表前应先保证链表不为空。
/******************************
* 功能:查找openList中F值最小节点
* 输入:
* 无
* 返回:
* F值最小节点
******************************/
static Point* getLeastFpoint() {
if (!openList.empty()) {
Point* resPoint = openList.front();
std::list::const_iterator itor;
for (itor = openList.begin(); itor != openList.end(); ++itor) {
Point* p = *itor; // itor是list类型迭代器,所以*itor是Poit *类型
if (p->F < resPoint->F) {
resPoint = *itor;
}
}
return resPoint;
}
//是空值情况
return NULL;
} ④判断指定结点是否对另一结点可达
在迷宫寻路中,人物每次只能上下左右走,因此我们要对上下左右的节点进行判断是否可达。对于待判断节点有四种可能情况:
1.节点超出游戏地图
2.节点是游戏中的障碍物体
3.节点已经在openList中
4.节点已经在closeList中
5.节点既不在openList列表也不在closeList列表
如果节点是1、2、4种情况,则节点不可达。因此我们可以先实现判断从指定节点是否到另一节点可达。
/******************************
* 功能:判断某点是否可达指定点
* 输入:
* point - 指定节点
* target - 待判断节点
* 返回:
* true - 可达
* false - 不可达
******************************/
static bool isCanreach(const Point* point, const Point* target) {
int x = target->x;
int y = target->y;
//待测节点超过二维数组,或待测节点是障碍物,或者待测节点与指定节点重合,或待测节点在closeList链表中。则不可达
if (x < 0 || x >= lines || y < 0 || y >= cols
|| maze[x * cols + y] == 0
|| (x == point->x && y == point->y)
|| isInList(closeList, target)) {
return false;
}
if (abs(point->x - target->x) + abs(point->y - target->y) == 1) {
//待测点与指定点相邻
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
/******************************
* 功能:判断指定节点是否在指定链表中
* 输入:
* list - 指定链表
* point - 指定节点
* 返回:
* Point* - 判断节点在链表中,返回该在链表中地址
* NULL - 不在节点中
******************************/
static Point* isInList(std::list& list, const Point* point) {
std::list::const_iterator itor;
for (itor = list.begin(); itor != list.end(); ++itor) {
if ((*itor)->x == point->x && (*itor)->y == point->y) {
return *itor;
}
}
return NULL;
} ⑦ 寻找可达节点
我们已经实现了判断指定节点是否到另一节点可达,接下来只要对指定节点的上下左右节点依次判断,即可找出指定节点的所有可达节点。因为可达节点的数量未知,我们可以使用动态数组vector
/******************************
* 功能:获得当前节点的周围可达节点(这里只考虑直着走)
* 输入:
* point - 指定节点
* 返回:
* 周围可达节点vector数组
******************************/
static std::vectorgetSurroundPoints(const Point* point) {
//定义存储可达节点的数组
std::vectorsurroundPoints;
for (int x = point->x - 1; x <= point->x + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = point->y - 1; y <= point->y + 1; ++y) {
Point* temp = AllocPoint(x, y);
if (isCanreach(point, temp)) {
surroundPoints.push_back(temp);
}
else {
//不可达则释放资源
delete temp;
}
}
}
return surroundPoints;
} ⑧A*算法完善
将已经完成的“寻找最小F值节点”以及“寻找周围可达节点”功能完善到A*算法中。
static Point* findPath(Point* startPoint, Point* endPoint) {
//置入起点,拷贝开辟一格节点,内外隔离
openList.push_back(AllocPoint(startPoint->x, startPoint->y));
//openList不为空时,不停的取openList中L的最小值
while (!openList.empty()) {
//查找openList中F最小值节点
Point* curPoint = getLeastFpoint();
//把最小值节点放到关闭列表中
openList.remove(curPoint); // 从openList中移除
closeList.push_back(curPoint); // 放入closeList中
//找到当前节点周围可达节点处理
std::vectorsurroundPoints = getSurroundPoints(curPoint);
//to do
......
}
} ⑨对可达节点的处理
通过 getSurroundPoints()我们已经拿到指定节点的周围可达节点,接下来便是对这些可达节点 的处理。对于这些节点无外乎两种情况:
1.节点在openList列表中
2.节点在既不在openList列表,也不在closeList列表
对如果是可达节点Point的处理,如果是第二种情况,那么我们可以放心的将Point添加到openList列表中;而对于第一种情况,那么我们就要计算如果让当前的F值最小节点curPoint作为Point节点的父节点的话,Point节点的F值会是多少,保留F值最小的那个作为其父节点。换句话说就是重新计算到达Point节点的“代价”是多少,如果比原来“代价”小了,则更换Point的父节点,否则不更换父节点。
std::vector::const_iterator iter;
for (iter = surroundPoints.begin(); iter != surroundPoints.end(); ++iter) {
Point* target = *iter;
Point* exist = isInList(openList, target);
//不在openList中
if (!exist) {
//calcG()计算G值,calcH计算H值,calcF计算F值
target->parent = curPoint;
target->G = calcG(curPoint, target);
target->H = calcH(target, endPoint);
target->F = calcF(target);
openList.push_back(target);
}// 在开放列表中,重新计算G值,保留min(F)
else {
int tempG = calcG(curPoint, target);
if (tempG < target->G) {
exist->parent = curPoint;
exist->G = tempG;
exist->F = calcF(target);
}
//动态数组存储的是new开辟的节点,如果添加到openList则不做处理,如果不需要添加到openList则需要释放
delete target;
}
} // end for /******************************
* 功能:计算指定结点到父节点的G值
* 输入:
* parent - 父节点
* point - 指定结点
* 返回:
* 指定结点到父节点的G值
******************************/
static int calcG(Point* parrent, Point* point) {
//如果可以直走额外消耗量为kCost1,如果需要斜走额外消耗量为kCost2
//int extraG=abs(parrent->x - point->x) + abs(parrent->y - point->y) == 1 ? kCost1 : kCost2;
int extraG = kCost2; // 规定只能直着走
int parentG = (point->parent == NULL ? NULL : point->parent->G);
return parentG + extraG;
}
/******************************
* 功能:计算指定结点到终点结点的H值
* 输入:
* point - 指定结点
* endPoint - 终点结点
* 返回:
* 指定结点到终点结点的H值
******************************/
static int calcH(Point* point, Point* end) {
//考虑斜移
//return (int)sqrt((double)(end->x - point->x) * (double)(end->x - point->x) + (double)(end->y - point->y) + (double)(end->y - point->y));
//规定只能直走
return (end->x - point->x) + (end->y - point->y);
}
/******************************
* 功能:计算指定结点的F值
* 输入:
* point - 指定结点
* 返回:
* 指定结点的F值
******************************/
static int calcF(Point* point) {
return point->G + point->H;
}⑩A*算法最终实现
每次添加结束后在openList寻找终点endPoint有没有在列表里,如果有则表明路径已经找到,返回endPoint,在于用户定义的接口中回溯得到的链表即为最终路径,如果endPoint没有在openList列表中则继续重复上面步骤,直到openList内的所有结点都移除到closeList列表,循环结束。
static Point* findPath(Point* startPoint, Point* endPoint) {
//置入起点,拷贝开辟一格节点,内外隔离
openList.push_back(AllocPoint(startPoint->x, startPoint->y));
//openList不为空时,不停的取openList中L的最小值
while (!openList.empty()) {
//查找openList中F最小值节点
Point* curPoint = getLeastFpoint();
//把最小值节点放到关闭列表中
openList.remove(curPoint); // 从openList中移除
closeList.push_back(curPoint); // 放入closeList中
//找到当前节点周围可达节点处理
std::vectorsurroundPoints = getSurroundPoints(curPoint);
std::vector::const_iterator iter;
for (iter = surroundPoints.begin(); iter != surroundPoints.end(); ++iter) {
Point* target = *iter;
//对某一结点,如果不在openList中,则加入到openList中,并设置其父节点;如果在openList中,则重新计算F值,选取min(F)的结点
Point* exist = isInList(openList, target);
//不在openList中
if (!exist) {
target->parent = curPoint;
target->G = calcG(curPoint, target);
target->H = calcH(target, endPoint);
target->F = calcF(target);
openList.push_back(target);
}// 在开放列表中,重新计算G值,保留min(F)
else {
int tempG = calcG(curPoint, target);
if (tempG < target->G) {
exist->parent = curPoint;
exist->G = tempG;
exist->F = calcF(target);
}
//动态数组存储的是new开辟的节点,如果添加到openList则不做处理,如果不需要添加到openList则需要释放
delete target;
}
} // end for
surroundPoints.clear();
//判断终点是否在openList中
Point* resPoint = isInList(openList, endPoint);
if (resPoint) {
return resPoint;
}
}
//如果while执行完毕则表明没有找到
return NULL;
} 程序资源清理
在整个程序中,所有开辟的结点分别存储在openList列表和closeLsit列表,因此在A*算法结束后要定义一个资源清理的接口让用户使用。
/******************************
* 功能:资源清理
* 输入:
* 无
* 返回:
* 无
******************************/
void ClearAstarMaze() {
maze = NULL;
lines = 0;
cols = 0;
std::list::iterator itor;
for (itor = openList.begin(); itor != openList.end();) {
delete* itor;
itor = openList.erase(itor); //从链表中删除某个结点,并返回下一个结点
}
for (itor = closeList.begin(); itor != closeList.end();) {
delete* itor;
itor = closeList.erase(itor); //从链表中删除某个结点,并返回下一个结点
}
} 程序整合运行