wiki上对于soket的定义
1.起源:
起源于https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc147
2.套接字主要是在Internet模型的传输层中使用的概念。路由器和交换机等网络设备一般不需要传输层的实现,因为它们一般在链路层(交换机)或互联网层(路由器)上运行。
3.类型
- 数据报套接字,也称为无连接套接字,使用用户数据报协议(UDP)。
- 流套接字,也称为面向连接的套接字,使用传输控制协议(TCP),流控制传输协议(SCTP)或数据报拥塞控制协议(DCCP)。
- 原始套接字(或原始IP套接字),通常在路由器和其他网络设备中可用。这里绕过传输层,并且应用程序可以访问包头,并且地址中没有端口号,只有IP地址。
广义:socket有两种场景。
- [进程通讯方式]{https://www.jianshu.com/p/03f645af6ab8}
- 网络套接字
本篇重点:网络套接字以及Java关于socket api
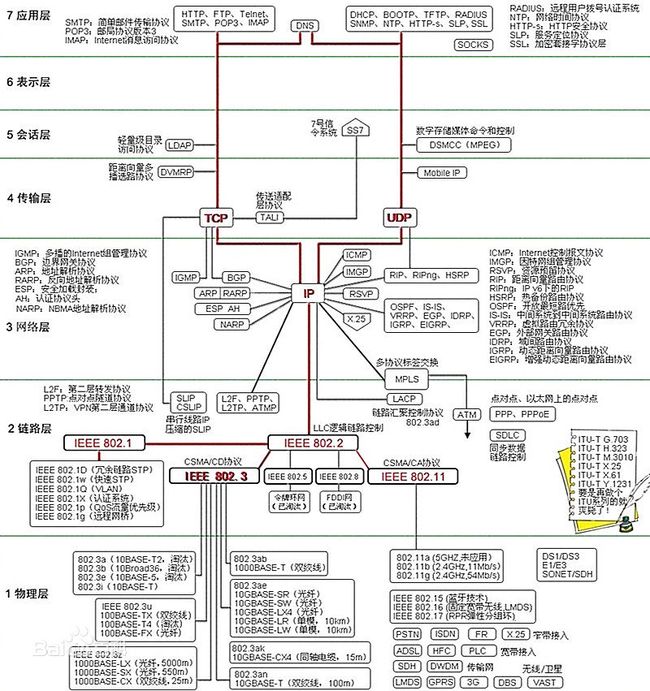
首先回顾7层网络模型
由上面socket类型所知,socket主要是传输层的概念,主要也就是udp,和tcp两种情况。(另外一种暂不讨论)
先看下api
实例代码:
try {
new Socket("127.0.0.1",80);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
1.常用构造器
public Socket(InetAddress address, int port) throws IOException {
this(address != null ? new InetSocketAddress(address, port) : null,
(SocketAddress) null, true);
}
private Socket(SocketAddress address, SocketAddress localAddr,
boolean stream) throws IOException {
setImpl();
// backward compatibility
if (address == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
try {
createImpl(stream);
if (localAddr != null)
bind(localAddr);
connect(address);
} catch (IOException | IllegalArgumentException | SecurityException e) {
try {
close();
} catch (IOException ce) {
e.addSuppressed(ce);
}
throw e;
}
}
1.以上构造器创建了一个IP Socket Address ,基于ip协议的SocketAddress(IP address + port number)
public InetSocketAddress(InetAddress addr, int port) {
holder = new InetSocketAddressHolder(
null,
addr == null ? InetAddress.anyLocalAddress() : addr,
checkPort(port));
}
2.创建SocksSocketImpl
void setImpl() {
if (factory != null) {
impl = factory.createSocketImpl();
checkOldImpl();
} else {
// No need to do a checkOldImpl() here, we know it's an up to date
// SocketImpl!
impl = new SocksSocketImpl();
}
if (impl != null)
impl.setSocket(this);
}
- createImpl 即SocksSocketImpl::createImpl
SocksSocketImpl是AbstractPlainSocketImpl的子类,最终看AbstractPlainSocketImpl的createImpl。由代码可知,最终的socket创建是由AbstractPlainSocketImpl创建的。如果是tcp,create(boolean stream)参数为true;如果是udp,参数为false。
/**
* Creates a socket with a boolean that specifies whether this
* is a stream socket (true) or an unconnected UDP socket (false).
*/
protected synchronized void create(boolean stream) throws IOException {
this.stream = stream;
if (!stream) {
ResourceManager.beforeUdpCreate();
// only create the fd after we know we will be able to create the socket
fd = new FileDescriptor();
try {
socketCreate(false);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ResourceManager.afterUdpClose();
fd = null;
throw ioe;
}
} else {
fd = new FileDescriptor();
socketCreate(true);//子类PlainSocketImpl调用native void socketCreate(boolean isServer) throws IOException;
}
if (socket != null)
socket.setCreated();
//这里的socket,即开始new 的socket(“127.0.0.1”,80)对象
if (serverSocket != null)
serverSocket.setCreated();
}
3.在接着回到开始创建socket的代码:创建完socket,接着校验地址是否是IP4或ip6格式,校验端口是否有权限(如果端口不允许访问,会抛异常SecurityException),接着就开始bind远程地址,并开始connect。
if (localAddr != null)
bind(localAddr);
connect(address);
bind最终调用的是SocksSocketImpl,即PlainSocketImpl的本地方法
getImpl().bind (addr, port);
protected synchronized void bind(InetAddress address, int lport)
throws IOException
{
synchronized (fdLock) {
if (!closePending && (socket == null || !socket.isBound())) {
NetHooks.beforeTcpBind(fd, address, lport);
}
}
socketBind(address, lport);//PlainSocketImpl 的native void socketBind(InetAddress address, int port)
throws IOException;
if (socket != null)
socket.setBound();
if (serverSocket != null)
serverSocket.setBound();
}
接着看connect
public void connect(SocketAddress endpoint) throws IOException {
connect(endpoint, 0);
}
//关键代码
//再次校验ip地址等
.....
else if (timeout == 0) {
if (epoint.isUnresolved())
impl.connect(addr.getHostName(), port);
else
impl.connect(addr, port);
} else
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("SocketImpl.connect(addr, timeout)");
connected = true;
bound = true;
上面连接的流程,默认timeout为0,直接连接,不支持超时。
改过程为阻塞的。( The connection will then block until established or an error occurs.)
protected void connect(String host, int port)
throws UnknownHostException, IOException
{
boolean connected = false;
try {
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName(host);
this.port = port;
this.address = address;
connectToAddress(address, port, timeout);
connected = true;
} finally {
if (!connected) {
try {
close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
/* Do nothing. If connect threw an exception then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
}
最终也是AbstractPlainSocketImpl调用子类PlainSocketImpl的本地方法socketConnect,来连接。
4.服务端socket创建, ServerSocket和Socket是完全相干的两个类。
但是他们的初始化,共同点:如果指定端口,都会在初始化的时候尝试bind本地端口,并判断该端口是否有权限。区别:Socket如果初始化指定了(IP,port)除了bind外,会多一步connect的操作。
new ServerSocket(80);
public
class ServerSocket implements java.io.Closeable
public ServerSocket(int port) throws IOException {
this(port, 50, null);
}
ServerSocket(port)默认队列大小50.当超过50的连接会被拒绝。
getImpl().bind(epoint.getAddress(), epoint.getPort());
getImpl().listen(backlog);
bound = true;
结下来看,accept():阻塞的,除非接收到一个连接。
步骤:创建一个unconnected Socket,并调用implAccept(s)
* Listens for a connection to be made to this socket and accepts
* it. The method blocks until a connection is made.
*
* A new Socket {@code s} is created and, if there
* is a security manager,
* the security manager's {@code checkAccept} method is called
* with {@code s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()} and
* {@code s.getPort()}
* as its arguments to ensure the operation is allowed.
* This could result in a SecurityException.
*
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs when waiting for a
* connection.
* @exception SecurityException if a security manager exists and its
* {@code checkAccept} method doesn't allow the operation.
* @exception SocketTimeoutException if a timeout was previously set with setSoTimeout and
* the timeout has been reached.
* @exception java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException
* if this socket has an associated channel, the channel is in
* non-blocking mode, and there is no connection ready to be
* accepted
public Socket accept() throws IOException {
if (isClosed())
throw new SocketException("Socket is closed");
if (!isBound())
throw new SocketException("Socket is not bound yet");
Socket s = new Socket((SocketImpl) null);
implAccept(s);
return s;
}
接下来,和客户端socket一样,默认新建SocksSocketImpl对象,并添加新的InetAddress对象
protected final void implAccept(Socket s) throws IOException {
SocketImpl si = null;
try {
if (s.impl == null)
s.setImpl();
else {
s.impl.reset();
}
si = s.impl;
s.impl = null;
si.address = new InetAddress();
si.fd = new FileDescriptor();
getImpl().accept(si);
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkAccept(si.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(),
si.getPort());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (si != null)
si.reset();
s.impl = si;
throw e;
} catch (SecurityException e) {
if (si != null)
si.reset();
s.impl = si;
throw e;
}
s.impl = si;
s.postAccept();
}
/**
* Constructor for the Socket.accept() method.
* This creates an empty InetAddress, which is filled in by
* the accept() method. This InetAddress, however, is not
* put in the address cache, since it is not created by name.
*/
InetAddress() {
holder = new InetAddressHolder();
}
调用新建SocksSocketImpl的accept,即AbstractPlainSocketImpl的accept,如下:
/**
* Accepts connections.
* @param s the connection
*/
protected void accept(SocketImpl s) throws IOException {
acquireFD();
try {
socketAccept(s);//子类PlainSocketImpl的本地方法 native void socketAccept(SocketImpl s) throws IOException;
} finally {
releaseFD();//释放fd
}
}
/*
* "Release" the FileDescriptor for this impl.
*
* If the use count goes to -1 then the socket is closed.
*/
void releaseFD() {
synchronized (fdLock) {
fdUseCount--;
if (fdUseCount == -1) {
if (fd != null) {
try {
socketClose();
} catch (IOException e) {
} finally {
fd = null;
}
}
}
}
}
题外话:
socket体系这里面涉及到了工厂的设计模式。方便内容的扩展。如果设置了factory,就按照自己设置的factory去实现
SocketImpl。代码如下:
/**
* Sets impl to the system-default type of SocketImpl.
* @since 1.4
*/
void setImpl() {
if (factory != null) {
impl = factory.createSocketImpl();
checkOldImpl();
} else {
// No need to do a checkOldImpl() here, we know it's an up to date
// SocketImpl!
impl = new SocksSocketImpl();
}
if (impl != null)
impl.setSocket(this);
}
public
interface SocketImplFactory {
/**
* Creates a new {@code SocketImpl} instance.
*
* @return a new instance of {@code SocketImpl}.
* @see java.net.SocketImpl
*/
SocketImpl createSocketImpl();
}
public static synchronized void setSocketImplFactory(SocketImplFactory fac)
throws IOException
{
if (factory != null) {
throw new SocketException("factory already defined");
}
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkSetFactory();
}
factory = fac;
}