总结任务的作用:是做依稀周期性的任务,在生产中的主要用来定期备份数据
crond : 这个守护进程是为了周期性执行任务或者处理器等待事件而存在
任务调度芬两种,系统任务调度,用户任务调度
计划任务的安排芬两种
一种是定时性的,也即是例行,就是每隔一段时间的周期就要重复来的做这个事情
一种是突发性的,就是这次做完了这个事,就没有下一次了,临时决定,只执行一次的任务
at 和crontab 着两个买那个了
at : 它是一个可以处理仅执行一次的就结束的指令
crontab : 它是会把你指定的工作或者任务, 比如脚本等,按照你设定的周期一直循环下去
16.1。1 at 计划任务的使用
语法格式: at 时间 ; 服务 :atd
1) systemctl start atd 开启atd 服务
2) systemctl status atd 查看atd 服务状态
3) systemctl is-enabled atd 查看是否开启开机服务,如果弹出enabled 说明开机启动此服务
[root@xueshen65 ~]# date
2020年 04月 04日 星期六 06:57:30 CST
1)
[root@xueshen65 ~]# date
2020年 04月 04日 星期六 06:58:25 CST
2)
[root@xueshen65 ~]# at 07:23
at> mkdir /tem/xuegod
at> touch /te^C[root@xueshen65 ~]#
[root@xueshen65 ~]# at 07:23
at> mkdir /tmp/xuegod 输入你要执行的命令
at> touch /tmp/xuegod/a.txt
at>
3)at>
job 2 at Sat Apr 4 07:23:00 2020 按下ctrl +D 退出
[root@xueshen65 ~]# ls /tmp/xuegod/ 发现有了文件
a.txt
[root@xueshen65 ~]#
at -l 查看计划任务
atq # 查看计划任务
16.1.2 查看和删除at 要执行的任务计划
这个查看,只能看到还没执行的,如果这个任务开始执行或者执行完成了,是看不到的
[root@xueshen65 ~]# at -l
2 Sat Apr 4 07:23:00 2020 a root
1) [root@xueshen65 ~]# atq
2 Sat Apr 4 07:23:00 2020 a root
2)
[root@xueshen65 ~]# at -c 2
这些文件存在
3) [root@xueshen65 ~]# ls /var/spool/at/
a000020193545b spool
4) 查看最后5行
[root@xueshen65 ~]# tail -5 /var/spool/at/a000020193545b
mkdir /tmp/xuegod
touch /tmp/xuegod/a.txt
marcinDELIMITER22bf3731
at 计划任务的特殊写法
at 20:00 2020-10-1 在某一天
at now + 10min 在10分钟后执行
at 17:00 tomorrow 明天下午5点执行
at 6:00 pm 3+days 在3天以后的下午6点执行
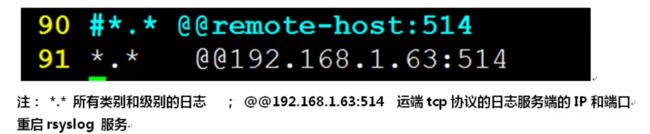
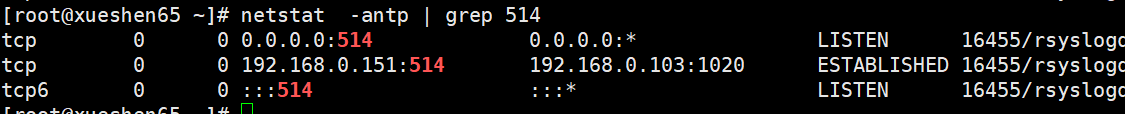
at 23:00 语法:atrm 任务编号 [root@xueshen65 ~]# atq 4 Sat Apr 4 07:35:00 2020 a root [root@xueshen65 ~]# atrm 4 [root@xueshen65 ~]# at -l crond 命令定期检查是否要指定的工作,如果有要执行的工作便会执行该工作 cron 是一个linux下的定时执行工具,可以在无需人工干预的情况下运行作业 linux任务调度的工作主要分为以下两类 系统执行的工作,系统周期性所要执行的工作,如要新whatis 数据库, updatedb 数据库 收集系统找他信息, /tmp 定期清理 1)[root@xueshen65 ~]# systemctl start crond 启动cron服务 2)[root@xueshen65 ~]# systemctl enable crond 默认开机启动 16.1.4 cron 命令参数介绍 crontab 的参数 crontab -u hr 指定hr 用户的cron服务 crontab -l 列出当前用户下的cron 服务的详细内容 crontab -u centos -l 列出执行用户centos 下的cron 服务的详细内容 crontab -r 删除cron 服务 crontab -e 编辑cron 服务 例如: crontab -u root -l #root 查看自己的cron 计划任务 crontab -u san -r # roor 想删除san的cron 计划任务 例子1. 创建计划任务, 每天2点1分 开始备份数据 crontab -e 类似于vim 打开一个文件一样 [root@xueshen65 ~]# crontab -e no crontab for root - using an empty one crontab: installing new crontab 分钟 小时 几号 月 星期 [root@xueshen65 ~]# crontab -l 查看 1 2 * * * tar zcvf /opt/grub2.tar.gz /boot/grub2 例子2 : 黑客;以非root 用户添加计划任务,最好使用已经存在系统用户添加,这里使用bin用户来添加 1 )crontab -u bin -e 2) 1 * * * * echo aaaaa >> /tmp/bin.txt 使用crontab -u bin -l 来排查 3 )[root@xueshen65 ~]# crontab -u bin -l 1 * * * * echo aaaaa >> /tmp/bin.txt 4)[root@xueshen65 ~]# ll /var/spool/cron/ 总用量 8 -rw-------. 1 root root 49 4月 4 08:20 bin -rw-------. 1 root root 58 4月 4 08:09 root 5)[root@xueshen65 ~]# cd !$ 6) [root@xueshen65 cron]# ls bin root [root@xueshen65 cron]# cat root 1 2 * * * tar zcvf /opt/grub2.tar.gz /boot/grub2 [root@xueshen65 cron]# crontab -l 1 2 * * * tar zcvf /opt/grub2.tar.gz /boot/grub2 [root@xueshen65 cron]# crontab -l -u root 1 2 * * * tar zcvf /opt/grub2.tar.gz /boot/grub2 做黑客要有扎实的基础,还要有很好的基础 所以后期可以使用者一招来排查,黑客是否在你的机器中安装了定时任务 系统级别德计划任务 [root@xueshen65 cron]# ll /etc/crontab -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 451 6月 10 2014 /etc/crontab 这个是系统任务调度的配置文件 [root@xueshen65 cron]# vim /etc/crontab [root@xueshen65 cron]# tail !$ tail /etc/crontab SHELL=/bin/bash # 指定操作系统使用哪个shell PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin 系统执行命令的搜索路径 MAILTO=root # 将执行任务的信息通过邮件发送给xx用户 # Example of job definition: # .---------------- minute (0 - 59) # | .------------- hour (0 - 23) # | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31) # | | | .------- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ... # | | | | .---- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat # | | | | | # * * * * * user-name command to be executed * * * * 5 root /bin/back.sh 1) [root@xueshen65 cron]# ls /etc/cron cron.d/ 是系统自动定期需要做的任务,但是不是按小时,按天,按星期,按月来执行的,那么放在这些目录下 cron.deny 控制用户是否能做计划任务的文件 cron.daily/ #每天执行的脚本 cron.hourly/ 每小时执行的脚本 cron.monthly/ 每月执行的脚本 crontab 主配置文件,也可以添加 cron.weekly/ 每周执行的脚本 [root@xueshen65 cron]# ls /etc/cron.daily/ logrotate man-db.cron mlocate 打开这个shell脚本 添加echo naaaaaaaaa 2 )[root@xueshen65 cron]# vim /etc/cron.daily/logrotate 3) [root@xueshen65 cron]# find /etc/cron* -type f /etc/cron.d/0hourly /etc/cron.d/raid-check /etc/cron.d/sysstat /etc/cron.daily/man-db.cron /etc/cron.daily/mlocate /etc/cron.daily/logrotate /etc/cron.deny /etc/cron.hourly/0anacron /etc/cron.hourly/mcelog.cron /etc/crontab 互动: crontab 不支持没秒,没2秒执行一次脚本,怎么写 在脚本的死循环里面,添加sleep2 ,指定30次自动退出,然后计划任务 mkdir /tmp/backup tar zcf etc.tar.gz /etc find /tmp/back -name "tar.gz" -mtime +3 -exec rm -rf {}\ 注意 : 工作中备份的文件不要放到/tmp 中,因为过一段时间,系统会清空/tmp 目录 在cento7 中,系统日志消息有两个负责处理,systemd-journald 和rsyslog 16.2.1 常见的日志文件的作用 系统日志文件概述 :/var/log 目录下保管由 rsyslog 维护的,里面存放的一些特定于系统和服务的日志文件 日志文件 用途 /var/log/message 大多数日志消息记录在此处,也有例外的,如与身份验证,电子邮件处理相关的定期作业任务等 /var/log/secure 安全和身份验证相关的消息和登录失败的日志文件,ssh 远程连接产生的日志 /var/log/maillog 邮件服务器相关的消息日志 / var/log/cron 与定期执行任务相关的日志文件 /var/log/boot.log 与日志启动相关的消息记录 /var/log/dmesg 与日志启动相关的消息记录 例子1 : 查看那个IP地址经常暴力破解用户密码 1) [root@xueshen65 ~]# ssh [email protected] 2) [root@xueshen65 ~]# vim /var/log/secure 3) [root@xueshen65 ~]# grep Failed /var/lo local/ lock/ log/ [root@xueshen65 ~]# grep Failed /var/log/secure Apr 4 09:55:49 xueshen65 sshd[21367]: Failed password for root from 192.168.0.151 port 46572 ssh2 Apr 4 09:55:52 xueshen65 sshd[21367]: Failed password for root from 192.168.0.151 port 46572 ssh2 Apr 4 09:56:06 xueshen65 sshd[21367]: Failed password for root from 192.168.0.151 port 46572 ssh2 4) [root@xueshen65 ~]# grep Failed /var/log/secure | awk '{print $11}' uniq 去掉重复的 192.168.0.151 192.168.0.151 192.168.0.151 5) [root@xueshen65 ~]# grep Failed /var/log/secure | awk '{print $11}' | uniq 192.168.0.151 注意: AWK ‘{print $11 }’ # 空格作为分隔符,打印第11列的数据 uniq 命令用于报考或忽略文件中的重复行,-c 或connt 在每行旁边显示该行重复出现的次数 /var/log/wtmp 也是一个二进制文件,记录每个用户的登录次数和持续时间等信息 可以用last 命令输出当中的内容 显示成功登录的用户的记录 1) last root pts/2 192.168.0.103 Sat Apr 4 09:49 still logged in root pts/5 192.168.0.103 Sat Apr 4 04:08 - 06:09 (02:00) root pts/5 192.168.0.103 Sat Apr 4 03:02 - 03:25 (00:23) 或者 [root@xueshen65 ~]# last -f /var/log/wtmp /var/log/btmp 文件记录错误登录系统的日志,如果发现/var/log/btmp 日志文件比较大,就说明很多人在暴力破解ssh服务,此日志需要使用lastb 程序查看 1 )[root@xueshen65 ~]# ll -h /var/log/btmp -rw-------. 1 root utmp 6.0K 3月 24 10:50 /var/log/btmp 2 )[root@xueshen65 ~]# lastb root ssh:notty 192.168.0.104 Tue Mar 24 10:50 - 10:50 (00:00) root ssh:notty 192.168.0.104 Tue Mar 24 10:50 - 10:50 (00:00) 3 ) 发现后,使用防火墙,拒绝掉, 命令如下 [root@xueshen65 ~]# iptables -A INPUT -i ens33 -s IP地址-j DROP 4) 也可以通过这种命令去查看 [root@xueshen65 ~]# lastb | awk '{print $3}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -n 1 1 Sun 解决问题后 ,向清空日志 方法1 /var/log/btmp 方法2 rm -rf /var/log/btmp && touch /var/log/btmp 两个的区别 分类-> 级别 -> 日志的种类 daemon 后天进程相关的 kern 内核产生的信息 lpr 打印系统产生的 authpriv 安全认证 cron 定死相关的 mail 邮件相关的 syslog 日志服务本身的 news 新闻系统 local0 ~7 自定义的日志设备 local 0-1local 7 8个系统保留的类,供其他的程序使用 或者使用户定义 日志的级别: 轻 - > 重 16.2.3 rsyslog 日志服务 rhel5 -> 服务名称,syslog -> 配置文件。/etc/syslog.conf rhel57 -> 服务名称,rsyslog -> 配置文件。/etc/sryslog.conf 我们来查看一下日志的配置文件信息 编辑配置文件, vim /etc/rsyslog.conf 16.2.5 实战-自定义ssh 服务的日志类型和存储位置 1 ) 打开 、vim /var/log/rsyslog.conf 2) 3) [root@xueshen65 ~]# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config 4) 5 ) systemctl restart rsyslog 6) [root@xueshen65 ~]# systemctl restart sshd 7) [root@xueshen65 ~]# ls /var/log/sshd.log /var/log/sshd.log 8) [root@xueshen65 ~]# cat /var/log/sshd.log Apr 5 14:49:35 xueshen65 sshd[12141]: Server listening on 0.0.0.0 port 22. Apr 5 14:49:35 xueshen65 sshd[12141]: Server listening on :: port 22. 上面对就的信息, 时间 主机 服务 进程ID 相关的信息 互动如何防治日志删除 1 )打开 [root@xueshen65 ~]# vim /etc/cron.daily/logrotate 2) 3) [root@xueshen65 ~]# vim /etc/logrotate.conf 4) [root@xueshen65 ~]# ls /etc/logrotate.d bootlog chrony cups httpd iscsiuiolog libvirtd libvirtd.qemu named numad ppp psacct samba syslog wpa_supplicant yum 说明 (全局参数) weekly : 每周之星回滚,或者说每周执行一次日志回滚 rotate 表示日志切割后历史文件最多保留到现在的多少分 create 指定新创建的文件的权限与所属主与群主 dateext 使用日期最后缀的回滚文件, 可以去 /var/log 目录下 5)[root@xueshen65 ~]# ll /var/log/btmp -rw-------. 1 root utmp 0 4月 5 12:10 /var/log/btmp 6 )[root@xueshen65 ~]# ls /var/log/yum* /var/log/yum.log ss日志存储在 /var/log/sshd 的基础上执行的 1 ) [root@xueshen65 ~]# vim /etc/logrotate.d/sshd 创建一个配置文件 2) 插入以下内容, /var/log/sshd.log{ missingok weekly create 0600 root root minsize 1M rotate 3 最多保留3份,不包含当前的那份 }~ 3) [root@xueshen65 ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog 启动服务日志 测试一下 可以查看它的大小 [root@xueshen65 ~]# cd /var/log/ [root@xueshen65 log]# ll sshd.log -h -rw-------. 1 root root 247 4月 5 16:31 sshd.log 4 )[root@xueshen65 ~]# logrotate -d /etc/logrotate.d/sshd [root@xueshen65 ~]# logrotate -d /etc/logrotate.d/sshd reading config file /etc/logrotate.d/sshd Allocating hash table for state file, size 15360 B Handling 1 logs rotating pattern: /var/log/sshd.log weekly (3 rotations) empty log files are rotated, only log files >= 1048576 bytes are rotated, old logs are removed considering log /var/log/sshd.log log does not need rotating (log has been already rotated)[root@xueshen65 ~]# 强行执行过程 5)[root@xueshen65 ~]# logrotate -vf /etc/logrotate.d/sshd 强制轮训,就是说即是不满足条件,也可以通过-f 让logrotate 轮循日志文件 -v 显示指令执行过程 -f 强制执行 发现有了数据 6) [root@xueshen65 log]# ll sshd.* -rw-------. 1 root root 0 4月 5 17:08 sshd.log -rw-------. 1 root root 247 4月 5 16:31 sshd.log.1 16.3.4 配置远程日志服务器,实现日志集中的管理 1 )[root@xueshen65 ~]# vim /etc/rsyslog.conf 2 ) 把19 行的注释去掉 启动日志服务 4 ) 监听端口514 端口 [root@xueshen65 ~]# netstat -anlpt | grep 514 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:514 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 16455/rsyslogd tcp6 0 0 :::514 :::* LISTEN 16455/rsyslogd 5 ) 同样打开客户端 [root@xueshen65 ~]# vim /etc/rsyslog.conf 把第90行改为服务端的IP地址 再次启动服务日志 6) oot@localhost ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog 7 ) [root@xueshen65 ~]# iptables -F 清空防火墙 8)systemctl restart rsyslog 再次启动日志 9) 发现已经有了日志 服务端验证 在服务端关闭selinux 和防火墙 10)tail -f /var/log/messages 11) [root@localhost ~]# logger "aaaa" 发现 后端出现了aaaa 的字样 能监听到 删除计划任务
16.1.3 crontab 定时任务的使用
16.1.6 系统级别的计划任务
计划任务常见的写法
16.2 日志的种类和记录的方式-自定义ssh 服务日志类型和存储位置
例2 : /var/log/wtmp 文件的作用
例3 : 使用/var/log/btmp 文件查看暴力破解系统的用户
16.2.2 日志的记录方式
16.3.3 实战-使用logrotate 进行ssh 日志分割
例子2: 实战-使用logrotate 进行nginx 日志分割
3) [root@xueshen65 ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog