【深入分析Map接口】HashMap LinkHashMap TreeMap
❤写在前面
❤博客主页:努力的小鳴人
❤系列专栏:JavaSE超详总结
❤欢迎小伙伴们,点赞关注收藏一起学习!
❤如有错误的地方,还请小伙伴们指正!
对于【10章Java集合】几张脑图带你进入Java集合的头脑风暴的拓展分析

文章目录
- 一、HashMap
- 二、LinkHashMap
-
- 基本结构
- 快速存取
- 扩容
- 三、TreeMap
-
- 数据结构
- 核心方法
一、HashMap
请看传送门 >>> 深入分析 HashMap
二、LinkHashMap
HashMap是无序的,迭代HashMap所得到的元素顺序并不是它们最初放置到HashMap时的顺序,这一缺点会造成诸多不便,在很多情景中,需要用到一个可以保持插入顺序的Map,JDK解决了这个问题,为HashMap提供了一个子类>>> LinkedHashMap,通过维护运行于所有条目的双向链表,LinkedHashMap保证了元素迭代的顺序,该迭代顺序可以是插入顺序或访问顺序
实际上,LinkedHashMap就是HashMap加双向链表,是将所有Entry节点链入一个双向链表双向链表的HashMap,put的Entry放在哈希表中,也会放在一个以head为头结点的双向链表中(设定迭代顺序),如图
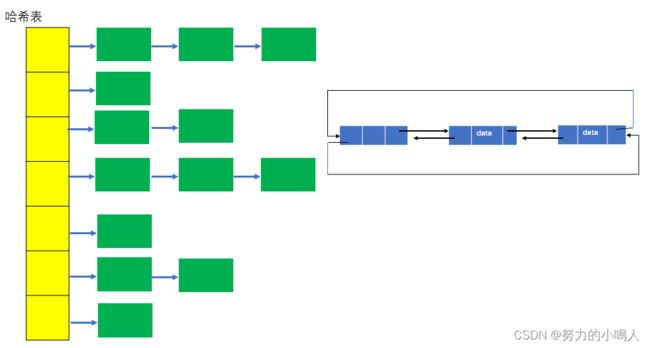
基本结构
- 类
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V> {
...
}
- 成员变量
增加了两个变量,双向链表头结点header 和 标志位accessOrder (值为true时,表示按照访问顺序迭代;值为false时,表示按照插入顺序迭代)
/**
* The head of the doubly linked list.
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> header; // 双向链表的表头元素
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: true
* for access-order, false for insertion-order.
*
* @serial
*/
private final boolean accessOrder; //true表示按照访问顺序迭代,false时表示按照插入顺序
- 构造方法
这些构造方法默认都采用插入顺序来维持取出键值对的次序,所有构造方法都是通过调用父类的构造方法来创建对象的
// 构造方法1,构造一个指定初始容量和负载因子的、按照插入顺序的LinkedList
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
// 构造方法2,构造一个指定初始容量的LinkedHashMap,取得键值对的顺序是插入顺序
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
// 构造方法3,用默认的初始化容量和负载因子创建一个LinkedHashMap,取得键值对的顺序是插入顺序
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
// 构造方法4,通过传入的map创建一个LinkedHashMap,容量为默认容量(16)和(map.zise()/DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTORY)+1的较大者,装载因子为默认值
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super(m);
accessOrder = false;
}
// 构造方法5,根据指定容量、装载因子和键值对保持顺序创建一个LinkedHashMap
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
- Entry
LinkHashMap重新定义了Entry,LinkedHashMap中的Entry增加了两个指针 before 和 after,它们分别用于维护双向链接列表。特别需要注意的是,next用于维护HashMap各个桶中Entry的连接顺序,before、after用于维护Entry插入的先后顺序的
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
...
}
快速存取
put(Key,Value) 和 get(Key)
LinkedHashMap完全继承了HashMap的 put(Key,Value) 方法
LinkedHashMap则直接重写了get(Key)方法
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or null if there was no mapping for key.
* Note that a null return can also indicate that the map previously associated null with key.
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
//当key为null时,调用putForNullKey方法,并将该键值对保存到table的第一个位置
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//根据key的hashCode计算hash值
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
//计算该键值对在数组中的存储位置(哪个桶)
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//在table的第i个桶上进行迭代,寻找 key 保存的位置
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//判断该条链上是否存在hash值相同且key值相等的映射,若存在,则直接覆盖 value,并返回旧value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this); // LinkedHashMap重写了Entry中的recordAccess方法--- (1)
return oldValue; // 返回旧值
}
}
modCount++; //修改次数增加1,快速失败机制
//原Map中无该映射,将该添加至该链的链头
addEntry(hash, key, value, i); // LinkedHashMap重写了HashMap中的createEntry方法 ---- (2)
return null;
}
上面是LinkedHashMap和HashMap保存数据的过程,在LinkedHashMap中重写了addEntry方法和Entry的recordAccess方法,LinkedHashMap 和HashMap的addEntry方法的对比来了解其实现:
LinkedHashMap是维护了插入的先后顺序
/**
* This override alters behavior of superclass put method. It causes newly
* allocated entry to get inserted at the end of the linked list and
* removes the eldest entry if appropriate.
*
* LinkedHashMap中的addEntry方法
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//创建新的Entry,并插入到LinkedHashMap中
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); // 重写了HashMap中的createEntry方法
//双向链表的第一个有效节点(header后的那个节点)为最近最少使用的节点,这是用来支持LRU算法的
Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after;
//如果有必要,则删除掉该近期最少使用的节点,
//这要看对removeEldestEntry的覆写,由于默认为false,因此默认是不做任何处理的。
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
} else {
//扩容到原来的2倍
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
}
******************************************************************************
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*
* HashMap中的addEntry方法
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//获取bucketIndex处的Entry
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
//将新创建的 Entry 放入 bucketIndex 索引处,并让新的 Entry 指向原来的 Entry
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
//若HashMap中元素的个数超过极限了,则容量扩大两倍
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
看一下重写的createEntry方法:
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 向哈希表中插入Entry,这点与HashMap中相同
//创建新的Entry并将其链入到数组对应桶的链表的头结点处,
HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
//在每次向哈希表插入Entry的同时,都会将其插入到双向链表的尾部,
//这样就按照Entry插入LinkedHashMap的先后顺序来迭代元素(LinkedHashMap根据双向链表重写了迭代器)
//同时,新put进来的Entry是最近访问的Entry,把其放在链表末尾 ,也符合LRU算法的实现
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
addBefore方法源码:
是一个双向链表的插入操作
//在双向链表中,将当前的Entry插入到existingEntry(header)的前面
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
扩容
resize()
随着HashMap中元素的数量越来越多,发生碰撞的概率将越来越大,所产生的子链长度就会越来越长,这样势必会影响HashMap的存取速度。为了保证HashMap的效率,系统必须要在某个临界点进行扩容处理,该临界点就是HashMap中元素的数量在数值上等于threshold(table数组长度*加载因子)。但是,不得不说,扩容是一个非常耗时的过程,因为它需要重新计算这些元素在新table数组中的位置并进行复制处理。所以,如果我们能够提前预知HashMap 中元素的个数,那么在构造HashMap时预设元素的个数能够有效的提高HashMap的性能
- resize()方法源码:
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
// 若 oldCapacity 已达到最大值,直接将 threshold 设为 Integer.MAX_VALUE
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return; // 直接返回
}
// 否则,创建一个更大的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//将每条Entry重新哈希到新的数组中
transfer(newTable); //LinkedHashMap对它所调用的transfer方法进行了重写
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); // 重新设定 threshold
}
LinkedHashMap完全继承了HashMap的resize()方法,Map扩容操作的核心在于重哈希,是指重新计算原HashMap中的元素在新table数组中的位置并进行复制处理的过程,LinkedHashMap对重哈希过程(transfer方法)进行了重写
源码如下:
/**
* Transfers all entries to new table array. This method is called
* by superclass resize. It is overridden for performance, as it is
* faster to iterate using our linked list.
*/
void transfer(HashMap.Entry[] newTable) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
// 与HashMap相比,借助于双向链表的特点进行重哈希使得代码更加简洁
for (Entry<K,V> e = header.after; e != header; e = e.after) {
int index = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); // 计算每个Entry所在的桶
// 将其链入桶中的链表
e.next = newTable[index];
newTable[index] = e;
}
}
LinkedHashMap借助于自身维护的双向链表轻松地实现了重哈希操作
三、TreeMap
TreeMap是有序的
- 属性
//比较器,因为TreeMap是有序的,通过comparator接口我们可以对TreeMap的内部排序进行精密的控制
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//TreeMap红-黑节点,为TreeMap的内部类
private transient Entry<K,V> root = null;
//容器大小
private transient int size = 0;
//TreeMap修改次数
private transient int modCount = 0;
//红黑树的节点颜色--红色
private static final boolean RED = false;
//红黑树的节点颜色--黑色
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
- 叶子节点Entry是TreeMap的内部类,其属性:
//键
K key;
//值
V value;
//左孩子
Entry<K,V> left = null;
//右孩子
Entry<K,V> right = null;
//父亲
Entry<K,V> parent;
//颜色
boolean color = BLACK;
数据结构
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
TreeMap继承AbstractMap,实现NavigableMap、Cloneable、Serializable三个接口。其中AbstractMap表明TreeMap为一个Map即支持key-value的集合
核心方法
put()
put方法的代码实现:
public V put(K key, V value) {
//用t表示二叉树的当前节点
Entry<K,V> t = root;
//t为null表示一个空树,即TreeMap中没有任何元素,直接插入
if (t == null) {
//比较key值,个人觉得这句代码没有任何意义,空树还需要比较、排序?
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
//将新的key-value键值对创建为一个Entry节点,并将该节点赋予给root
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
//容器的size = 1,表示TreeMap集合中存在一个元素
size = 1;
//修改次数 + 1
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp; //cmp表示key排序的返回结果
Entry<K,V> parent; //父节点
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; //指定的排序算法
//如果cpr不为空,则采用既定的排序算法进行创建TreeMap集合
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t; //parent指向上次循环后的t
//比较新增节点的key和当前节点key的大小
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
//cmp返回值小于0,表示新增节点的key小于当前节点的key,则以当前节点的左子节点作为新的当前节点
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
//cmp返回值大于0,表示新增节点的key大于当前节点的key,则以当前节点的右子节点作为新的当前节点
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
//cmp返回值等于0,表示两个key值相等,则新值覆盖旧值,并返回新值
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//如果cpr为空,则采用默认的排序算法进行创建TreeMap集合
else {
if (key == null) //key值为空抛出异常
throw new NullPointerException();
/* 下面处理过程和上面一样 */
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//将新增节点当做parent的子节点
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
//如果新增节点的key小于parent的key,则当做左子节点
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
//如果新增节点的key大于parent的key,则当做右子节点
else
parent.right = e;
/*
* 上面已经完成了排序二叉树的的构建,将新增节点插入该树中的合适位置
* 下面fixAfterInsertion()方法就是对这棵树进行调整、平衡,具体过程参考上面的五种情况
*/
fixAfterInsertion(e);
//TreeMap元素数量 + 1
size++;
//TreeMap容器修改次数 + 1
modCount++;
return null;
}
- 获取根节点,根节点为空,产生一个根节点,着色为黑色,退出余下流程
- 获取比较器,如传入的Comparator接口不为空,使用传入的Comparator接口实现类进行比较;如传入的Comparator接口为空,将Key强转为Comparable接口进行比较
- 从根节点开始一一依照规定的排序算法进行比较,取比较值temp,如temp=0,表示插入的Key已存在;如temp>0,取当前节点的右子节点;如temp<0,取当前节点的左子节点
- 排除插入的Key已存在的情况,第(3)步的比较一直比较到当前节点t的左子节点或右子节点为null,此时t就是我们寻找到的节点,temp>0则准备往t的右子节点插入新节点,temp<0则准备往t的左子节点插入新节点
- new出一个新节点,默认为黑色,根据cmp的值向t的左边或者右边进行插入
- 插入之后进行修复,包括左旋、右旋、重新着色这些操作,让树保持平衡性第1~第5步都没有什么问题,红黑树最核心的应当是第6步插入数据之后进行的修复工作,对应的Java代码是TreeMap中的fixAfterInsertion方法
总结:也不知道是不是深入分析反正用了我的不少头发和不少时间
作者算是一名Java初学者,文章如有错误,欢迎评论私信指正,一起学习~~
如果文章对小伙伴们来说有用的话,点赞关注收藏就是我的最大动力!
不积跬步,无以至千里,书接下回,欢迎再见
