求2个字符串的最长公共子序列和最长公共子字符串
一. 最长公共子序列
定义:
一个数列S,如果分别是两个或多个已知数列的子序列,且是所有符合此条件序列中最长的,则 S 称为已知序列的最长公共子序列。
例如:输入两个字符串BDCABA和 ABCBDAB,字符串 BCBA和BDAB 都是是它们的最长公共子序列,则输出它们的长度4,并打印任意一个子序列. (Note: 不要求连续)
判断字符串相似度的方法之一 - 最长公共子序列越长,越相似。
思路:
穷举方法:
穷举法是解决最长公共子序列问题最容易想到的方法,即对S的每一个子序列,检查是否为T的子序列,从而确定它是否为S和T的公共子序列,并且选出最长的公共子序列。
S和T的所有子序列都检查过后即可求出S和T的最长公共子序列。S的一个子序列相应于下标序列1,2,...,n的一个子序列。因此,S共有2^n个子序列。当然,T也有2^m个子序列。
因此,蛮力法的时间复杂度为O(2^n * 2^m),这是指数级别。
动态规划方法:
最优子结构性质:
设序列 X= 和 Y= 的一个最长公共子序列 Z=,则:
-
若
xm = yn,则zk = xm = yn则Zk-1是Xm-1和Yn-1的最长公共子序列;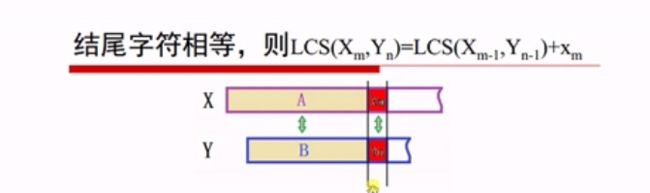 image
image 若
xm ≠ yn, 要么Z是Xm-1和Y的最长公共子序列,要么Z是X和Yn-1的最长公共子序列。
若
xm ≠ yn且zk≠xm,则Z是Xm-1和Y的最长公共子序列;若
xm ≠ yn 且 zk ≠yn,则Z是X和Yn-1的最长公共子序列。
综合一下:就是求二者的大者
递归结构容易看到最长公共子序列问题具有子问题重叠性质。例如,在计算 X 和Y 的最长公共子序列时,可能要计算出 X 和 Yn-1 及 Xm-1 和 Y 的最长公共子序列。而这两个子问题都包含一个公共子问题,即计算 Xm-1 和 Yn-1 的最长公共子序列。
计算最优值:
子问题空间中,总共只有O(m*n)个不同的子问题,因此,用动态规划算法自底向上地计算最优值能提高算法的效率。
长度表C 和 方向变量B:
实现代码:
/**
找出 两个 字符串 的公共 子序列(动态规划)
@param str1 字符串1
@param str2 字符串2
*/
void maxPublicSubSequence(char *str1, char *str2) {
assert(str1 != NULL && str2 != NULL);
// 字符串 1 长度
int str1Length = strlen(str1);
// 字符串 2 长度
int str2Length = strlen(str2);
// 开辟 二维 存储 数组 (并初始化 值为:0)
int **postionArray = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * (str1Length + 1));
for (int i = 0; i <= str1Length; i ++) {
postionArray[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (str2Length + 1));
}
for (int i = 0; i <= str1Length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= str2Length; j++) {
postionArray[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 循环 遍历
for(int i = 1; i <= str1Length; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= str2Length; j ++) {
// 如果 两个字符 相同
if (str1[i - 1] == str2[j - 1]) {
postionArray[i][j] = postionArray[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
// 如果 两个 字符 不同
else {
postionArray[i][j] = (postionArray[i - 1][j] > postionArray[i][j - 1]) ? postionArray[i - 1][j] : postionArray[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < str1Length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < str2Length; j++) {
printf("%d ", postionArray[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int i, j ;
for (i = str1Length, j = str2Length; i >= 1 && j >= 1;) {
if (str1[i - 1] == str2[j - 1]) {
printf("%c ", str1[i - 1]);
i --;
j --;
}
else {
if (postionArray[i][j - 1] > postionArray[i - 1][j]) {
j--;
}
else {
i --;
}
}
}
// 释放开辟数组
for (int i = 0; i < str1Length; i++) {
free(postionArray[i]);
}
free(postionArray);
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
maxPublicSubSequenceTwo("ABCBDAB" , "BDCABA");
}
return 0;
}
二: 最长公共子串
题目:
给定两个字符串,求出它们之间
最长的相同子字符串的长度。
思路:
穷举法:
给定两个字符串A和B,我们可以通过从A的第一个字符开始与B对应的每一个字符进行对比的方式找到最长的公共字串。如果此时没有找到匹的字母,则移动到A的第二个字符处,然后从B的第一个字符处进行对比,以此类推。
实现代码:
#import
/**
找出 两个 字符串 的 最长 公共 子串 (穷举法)
@param str1 字符串1
@param str2 字符串2
*/
void maxPublicSubStringOne(char *str1, char *str2) {
assert(str1 != NULL && str2 != NULL);
// 起始 位置
int startPosition = 0;
// 公共 子串 长度
int maxStringLength = 0;
// 循环 遍历 所有 子字符串
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str1); i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < strlen(str2); j++) {
// 如果 两个 字符 相等
if(str1[i] == str2[j]) {
// 继续 比较 后面的字符
int k = 1;
while (str1[i + k] == str2[j + k] && str1[i + k] != '\0' && str2[j + k] != '\0') {
k ++;
}
// 如果 k 大于 最长 字符串
if (k > maxStringLength) {
// 公共 子串 长度
maxStringLength = k;
// 起始位置
startPosition = i;
}
}
}
}
if(maxStringLength > 0) {
for (int i = startPosition; i <= maxStringLength; i++) {
printf("%c ", str1[i]);
}
}
}
动态规划-空间换时间
采用一个二维矩阵来记录中间结果,矩阵的横坐标为字符串1的各个字符,矩阵的纵坐标为字符串2的各个字符。
举例说明:假设两个字符串分别为"bab"和"caba" (当然我们现在一眼就可以看出来最长公共子串是"ba"或"ab")
b a b
c 0 0 0
a 0 1 0
b 1 0 1
a 0 1 0
可以看出,矩阵的斜对角线最长的那个就对应着两个字符串的最长公共子串。
不过在二维矩阵上找最长的由1组成的斜对角线也是件麻烦费时的事,可以用下面的方法改进:当要在矩阵是填1时让它等于其左上角元素加1。
b a b
c 0 0 0
a 0 1 0
b 1 0 2
a 0 2 0
这样矩阵中的最大元素就是最长公共子串的长度。另外,在构造这个二维矩阵的过程中由于得出矩阵的某一行后其上一行就没用了,所以实际上在程序中可以用一维数组来代替这个矩阵。
实现代码:
/**
找出 两个 字符串 的公共 子串(动态规划)
@param str1 字符串1
@param str2 字符串2
*/
void maxPublicSubStringTwo(char *str1, char *str2) {
assert(str1 != NULL && str2 != NULL);
// 起始 位置
int startPosition = 0;
// 公共 子串 长度
int maxStringLength = 0;
// 字符串 1 长度
int str1Length = strlen(str1);
// 字符串 2 长度
int str2Length = strlen(str2);
// 开辟 二维 存储 数组 (并初始化 值为:0)
int **postionArray = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * str1Length);
for (int i = 0; i < str1Length; i ++) {
postionArray[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * str2Length);
}
for (int i = 0; i < str1Length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < str2Length; j++) {
postionArray[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 循环 遍历
for(int i = 0; i < str1Length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < str2Length; j ++) {
// 如果 两个字符 相同
if (str1[i] == str2[j]) {
// 判断 释放 是 边界 情况
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
// 边界 情况
postionArray[i][j] = 1;
}
// 非边界 情况
else {
postionArray[i][j] = postionArray[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
if (postionArray[i][j] > maxStringLength) {
maxStringLength = postionArray[i][j];
startPosition = i - postionArray[i][j] + 1;
}
}
}
}
// 打印 字符串
if(maxStringLength > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i <= maxStringLength; i++) {
printf("%c ", str1[startPosition + i]);
}
}
// 释放开辟数组
for (int i = 0; i < str1Length; i++) {
free(postionArray[i]);
}
free(postionArray);
}
9人点赞
算法题学习