Android日常开发中,总是离不开Activity;说起Activity那就避不开Activity启动模式(launchMode)。
Activity的四种启动模式:
- standard:
- singleTop:
- singleTask:
- singleInstance:
我们都知道2,3,4这几种情况,如果Activity栈中有相应的实例,则直接重用该实例而不需要new。重用时会调用该实例的onNewIntent(),让该实例回到栈顶,并将其上面的其他实例退出栈。
我们从源码角度来看一下onNewIntent():
/**
* This is called for activities that set launchMode to "singleTop" in
* their package, or if a client used the {@link Intent#FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP}
* flag when calling {@link #startActivity}. In either case, when the
* activity is re-launched while at the top of the activity stack instead
* of a new instance of the activity being started, onNewIntent() will be
* called on the existing instance with the Intent that was used to
* re-launch it.
*
* An activity will always be paused before receiving a new intent, so
* you can count on {@link #onResume} being called after this method.
*
*
Note that {@link #getIntent} still returns the original Intent. You
* can use {@link #setIntent} to update it to this new Intent.
*
* @param intent The new intent that was started for the activity.
*
* @see #getIntent
* @see #setIntent
* @see #onResume
*/
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
}
It's clear that 该方法的注释是关键,初级英语你可以的...
下面来谈一下过程:
- 如果Activity第一次启动,则执行序列:
onCreate() ---> onStart() --->onResume() ....and so on...
- 如果Activity栈有该实例(启动模式2,3,4),则执行序列:
onNewIntent() ---> onRestart() ---> onStart() ---> onResume...
- 如果android系统由于内存不足把已存在Activity释放掉,则只能重新启动Activity,即执行:
onCreate() ---> onStart() ---> onResume() ... and so on...
注意事项
- 当我们把当前Activity置于后台(不启动其他Activity),再切换至前台,其执行序列为:
onRestart() ---> onStart() ---> onResume()...
- 当我们在当前Activity,弹出对话框orToast,将不会对Activity的生命周期产生任何影响。下面是源码中AlertDialog的show()的实现:
/**
* Start the dialog and display it on screen. The window is placed in the
* application layer and opaque. Note that you should not override this
* method to do initialization when the dialog is shown, instead implement
* that in {@link #onStart}.
*/
public void show() {
if (mShowing) {
if (mDecor != null) {
if (mWindow.hasFeature(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) {
mWindow.invalidatePanelMenu(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
return;
}
mCanceled = false;
if (!mCreated) {
dispatchOnCreate(null);
} else {
// Fill the DecorView in on any configuration changes that
// may have occured while it was removed from the WindowManager.
final Configuration config = mContext.getResources().getConfiguration();
mWindow.getDecorView().dispatchConfigurationChanged(config);
}
onStart();
/**mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);*/
mDecor = mWindow.getDecorView();
if (mActionBar == null && mWindow.hasFeature(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) {
final ApplicationInfo info = mContext.getApplicationInfo();
mWindow.setDefaultIcon(info.icon);
mWindow.setDefaultLogo(info.logo);
mActionBar = new WindowDecorActionBar(this);
}
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = mWindow.getAttributes();
if ((l.softInputMode
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION) == 0) {
WindowManager.LayoutParams nl = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
nl.copyFrom(l);
nl.softInputMode |=
WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION;
l = nl;
}
/**这句话是关键,AlertDialog的本质就是:
* windowManager.addView(mWindow.getDecorView(),mWindow.getAttribute())
*/
mWindowManager.addView(mDecor, l);
mShowing = true;
/**通过发送Message,通知Handler来做相应处理**/
sendShowMessage();
}
通过上述的Source Code,We will be find that AlertDialog的本质就是通过WindowManager.addView()来实现的,所以对Activity的生命周期有毛的影响...
如果你此时对Activity Lifecycle产生了质疑,Please click here,我还是怕没人点啊。
onPause() --- Called when the system is about to start resuming a previous activity(当系统将要开始显示另一个Activity时调用).
立帖为证,回头写个Dialog的源码分析...
总结
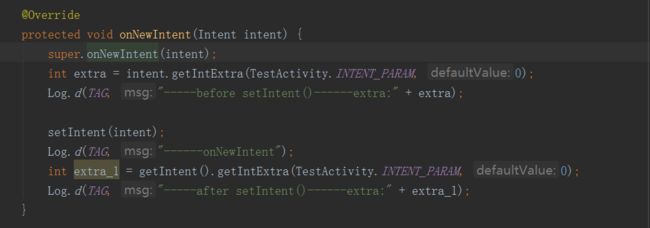
- 除了startand模式外,无论采用什么模式,只有activity时同一个实例,且Intent发生了变化,即启动了其他Activity,才会触发onNewIntent()方法。
- 使用onNewIntent()方法时,需要在onNewIntent()中使用setIntent(intent)赋值给Activity的Intent,否则,我们只能得到以前的Intent.(详见onNewIntent()源码的注释)
经测试会发现,onNewIntent()的参数intent是最新的Intent,我们如果不调用setIntent,就需要本地自己维护该Activity的Intent啦。(推荐使用onNewIntent())
3.无意中测试发现,AlertDialog和Toast将不会影响Activity的Lifecycle。(实践是检验真理的唯一标准...)
欢迎留言...期待指导...