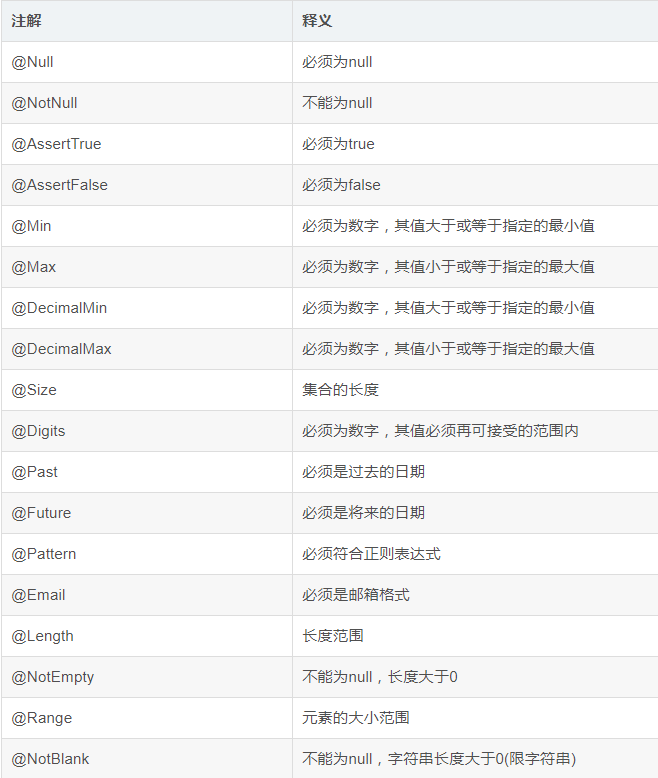
hibernate validator 校验操作小结
@Override
public Result> getCalendarList(@Validated({ calendar.class }) @RequestBody GroupDTO dto)}...
在controller 的方法定义中加上 @Validated({ calendar.class }) 注解
(calendar.class 为校验分组 ),那么按照该分组的规则校验前端传过来的值是否满足定义的校验规则。
同一个dto可能会在多个handler的方法中使用,但是可能会要按照不同的校验规则分组,如insert的controller需要这个对象的属性都非空,但是删除的controller只需要id非空即可。那么在dto定义的校验规则就需要分组:
@NotNull(message="{ProductEmpty}",groups = {deleteGroup.class, addPriceList.class, addPriceWeeks.class,calendarPrice.class})
private Integer productId;
@NotNull(message="{MenuEmpty}",groups = {deleteGroup.class, addPriceList.class,addPriceWeeks.class,calendarPrice.class })
private Integer menuId;
如上所示在校验注解中有groups属性可以定义这个校验是属于哪个分组的,而属性的值只是一个空的接口,在controller方法的参数前使用@Validated({ calendar.class }) 即指定了这个方法使用哪组校验,那么就只会校验该dto下groups中有该组的属性。
message中返回的是校验失败的信息 可以直接写字符串如 “****不能为空” 也可以如上所示在定义一个properties文件统一每个返回信息。
可以看到这个文件名字中有zh_CN,这个其实是jar包中自带的中文返回信息配置,我们同样可以在hibernate-validator的jar包下找到英文的配置文件 配置它 这样方便国际化。
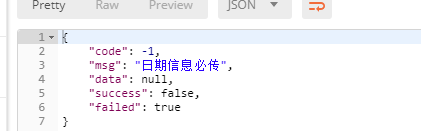
DateEmpty=\u65E5\u671F\u4FE1\u606F\u5FC5\u4F20
ProductEmpty=\u4EA7\u54C1\u4FE1\u606F\u4E0D\u5168
具体配置中是这样的 配置信息被转码
配置的好处是有一个地方统一管理了返回信息,方便修改。
校验规则制定
1 普通校验
把该注解的属性填好 加到被校验对象的字段上就可以了 注意一定要类型 匹配 如@MIN加到string头上 运行就会报错
2 复合校验
如果说 我的对象里有对象属性 ,对象的属性里又有对象 那么对这种深层次的校验应该这么做:
@Override
public Result> getCalendarList(@Validated({ calendar.class }) @RequestBody GroupDTO dto
) {....
方法定义这里不用变
dto校验规则中
@NotEmpty(message="价格信息必传",groups = { addPriceList.class,addPriceWeeks.class })
private List<@Valid PriceInfo> priceInfos;
首先在校验的属性对象前加上@validate注解
然后定义这个对象的校验规则,即对priceInfo中各个属性加上校验注解当然想要在这里被校验的字段的校验分组要和外面一直为addPriceList.class 或另一个。
3 自定义校验
如果说框架提供给我的校验不能满足我的场景需求 那么我们可以自定义校验
属性单独校验
如果我们要定义一个对单独属性的校验类型:
package admtic.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.Payload;
import admtic.validator.IsNumValidator;
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = IsNumValidator.class)
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface IsNum {
/*
* 用于验证的注解下列这三个方法必须要,这是Hibernate Validation框架要求的,否则程序再在调用的时候会报错
* default用于对属性给定默认值
* 如果不给定默认值,则在使用注解的时候必须给属性指定属性值,否则报错
* 给定默认值时,在使用注解的时候可以不用指定属性值
*/
String message() default "不是数字!";
Class[] groups() default {};
Class[] payload() default {};
// 非必须属性
// // 没加default给定默认值,使用注解的时候该属性必须赋值,否则报错
// String regex();
// // value属性,加上了default "mercy" 使得该属性在使用注解的时候可以不用输入也不会报错
// String value() default "mercy";
}
先自定义一个校验注解 然后再实现一个校验器
package admtic.validator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
import admtic.annotation.IsNum;
/**
* 泛型中一个是枚举类一个是校验支持的数据类型
* @author spf
* @version 2019年5月8日 下午3:46:35
*
*/
public class IsNumValidator implements ConstraintValidator {
// private String regex;
/**
* 通过initialize()可以获取注解里的属性值
*/
// @Override
// public void initialize(IsNum constraintAnnotation) {
// ConstraintValidator.super.initialize(constraintAnnotation);
// regex = constraintAnnotation.regex();
// }
/**
* 强行return true hahahhah
*/
@Override
public boolean isValid(Integer s, ConstraintValidatorContext arg1) {
if(s == -1){
}
return false;
}
}
需要注意的是 该校验器泛型定义中 第一个是校验注解的名字 第二个是校验属性的类型 isvalid返回是否校验成功。
属性联合校验
如果我们要定义一个对对象的联合校验,比如说如果有一个flag属性,如果flag属性为特殊值的话那么这个对象就不用校验其他属性了,或者说另一种场景前端输入的密码和重复密码,我后端这里要校验一下这两个属性的值是否相同,不相同就定义校验失败,不能操作。这种多个属性之间联合起来一起影响校验结果的联合校验需要我们这样定义:
由于校验注解是自定义的 我们可以把它定义到类头上 然后校验器里获取到这个类对象再做联合校验
如
@Target({TYPE, ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = FieldMatchValidator.class)
@Documented
public @interface FieldMatch
{
String message() default "{constraints.fieldmatch}";
Class[] groups() default {};
Class[] payload() default {};
// /**
// * Defines several @FieldMatch annotations on the same element
// *
// * @see FieldMatch
// */
// @Target({TYPE, ANNOTATION_TYPE})
// @Retention(RUNTIME)
// @Documented
// @interface List
// {
// FieldMatch[] value();
// }
//只能有string 类型的参数 获取后再转
String priceTypeId();
String costPrice();
String sellPrice();
String stock();
String flag();
}
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
import admtic.annotation.FieldMatch;
//校验注解 也可以用于dto整个类 注意这里的泛型 前面的时自定义的注解,后面那个时被校验的字段类型 这个用于对象属性的联合校验 所以用object
public class FieldMatchValidator implements ConstraintValidator {
// 只能有string 类型的参数
private String priceTypeId;
private String costPrice;
private String sellPrice;
private String stock;
private String flag;
@Override
public void initialize(final FieldMatch constraintAnnotation) {
priceTypeId = constraintAnnotation.priceTypeId();
costPrice = constraintAnnotation.costPrice();
sellPrice = constraintAnnotation.sellPrice();
stock = constraintAnnotation.stock();
flag = constraintAnnotation.flag();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(final Object value, final ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
try {
List fields = Arrays.asList(value.getClass().getDeclaredFields());
Integer priceTypeIdValue = null;
Double sellPriceValue = null;
Double costPriceValue = null;
Integer stockValue = null;
Integer flagValue = null;
fields.forEach(e->e.setAccessible(true));
Map> group =
fields.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Field::getName));
priceTypeIdValue = (Integer) group.get(priceTypeId).get(0).get(value);
if(priceTypeIdValue == null || priceTypeIdValue < 1){
return false;
}
flagValue = (Integer) group.get(flag).get(0).get(value);
if(flagValue == -1){
return true;
}
sellPriceValue = (Double) group.get(sellPrice).get(0).get(value);
costPriceValue = (Double) group.get(costPrice).get(0).get(value);
stockValue=(Integer) group.get(stock).get(0).get(value);
// System.out.println("######");
// System.out.println(priceTypeIdValue);
// System.out.println(sellPriceValue);
// System.out.println(costPriceValue);
// System.out.println(stockValue);
// System.out.println(flagValue);
if(sellPriceValue == null || costPriceValue == null || stockValue == null || priceTypeIdValue == null){
return false;
}
} catch (final Exception ignore) {
ignore.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
在校验器中反射获取属性值 并进行校验处理
校验结果的处理
立即返回和全部校验
对一个对象校验时,比如说我们要校验10个字段,第3个字段没有通过,此时我们可以选择马上返回前端失败,也可以选择把后面的字段全部校验,拿到所有字段的校验结果后再返回。
对于第一种快速失败的配置如下:
@Configuration
public class ValidatorConfiguration {
@Bean
public Validator validator(){
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.byProvider( HibernateValidator.class )
.configure()
.failFast( true )
.buildValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
return validator;
}
}
或
//failFast: true 快速失败返回模式,false 普通模式
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.byProvider( HibernateValidator.class )
.configure()
.failFast( true )
.buildValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
或
//hibernate.validator.fail_fast: true 快速失败返回模式,false 普通模式
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.byProvider( HibernateValidator.class )
.configure()
.addProperty( "hibernate.validator.fail_fast", "true" )
.buildValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
1 handler 单独处理
在每个controller方法中可以获取校验失败后的错误信息 进行处理 如:
@Override
public Result addMenuOne(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody @Validated MenuDTO dto,
BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
for (ObjectError error : result.getAllErrors()) {
return Result.failed(error.getDefaultMessage());
}
}
2 全局处理
每个方法都加这个处理太麻烦了 我们可以把这个错误跑出来 再全局处理
方法:
@Override
public Result> getCalendarList(@Validated({ calendar.class }) @RequestBody GroupDTO dto
) {
// if (result.hasErrors()) {
// for (ObjectError error : result.getAllErrors()) {
// return Result.failed(error.getDefaultMessage());
// }
// }
List months = groupService.getDefaultCalendar(dto);
return Result.success(months);
}
我们把bindingResult 去掉不做处理 之后 全局定义一个错误处理器:
package org.dmc.b.admtic.config;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MissingPathVariableException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.ServletRequestBindingException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.dmc.common.utils.Result;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GloableExceptionHandler {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GloableExceptionHandler.class);
@ExceptionHandler({ ConstraintViolationException.class,
MethodArgumentNotValidException.class,
ServletRequestBindingException.class,
BindException.class })
@ResponseBody
public Result handleValidationException(Exception e) {
String msg = "";
if (e instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) {
MethodArgumentNotValidException t = (MethodArgumentNotValidException) e;
msg = t.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().stream().map(DefaultMessageSourceResolvable::getDefaultMessage)
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
} else if (e instanceof BindException) {
BindException t = (BindException) e;
msg = t.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().stream().map(DefaultMessageSourceResolvable::getDefaultMessage)
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
} else if (e instanceof ConstraintViolationException) {
ConstraintViolationException t = (ConstraintViolationException) e;
msg = t.getConstraintViolations().stream().map(ConstraintViolation::getMessage)
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
} else if (e instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException) {
MissingServletRequestParameterException t = (MissingServletRequestParameterException) e;
msg = t.getParameterName() + " 不能为空";
} else if (e instanceof MissingPathVariableException) {
MissingPathVariableException t = (MissingPathVariableException) e;
msg = t.getVariableName() + " 不能为空";
} else {
msg = "必填参数缺失";
}
log.warn("=========================**********=====================参数校验不通过,msg: {}", msg);
return Result.failed(msg);
}
}
可以达到同样的效果 但是又少些了很多代码
返回前端
用到的注解
@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice 注解,spring3.2提供的新注解,控制器增强,全局增强可以用于定义@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder、@ModelAttribute,并应用到所有@RequestMapping中
使用 @ControllerAdvice,不用任何的配置,只要把这个类放在项目中,Spring能扫描到的地方。就可以实现全局异常的回调。
该注解使用@Component注解,这样的话当我们使用
仅仅从命名上来看 advice就是通知,猜想它就是依赖一个aop实现。
这个后面有时间探究。
如:
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyControllerAdvice {
/**
* 应用到所有@RequestMapping注解方法,在其执行之前初始化数据绑定器
* @param binder
*/
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) {
//可以对日期的统一处理
binder.addCustomFormatter(new DateFormatter("yyyy-MM-dd"));
//也可以添加对数据的校验
//binder.setValidator();
}
/**
* 把值绑定到Model中,使全局@RequestMapping可以获取到该值
* @param model
*/
@ModelAttribute
public void addAttributes(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("author", "Magical Sam");
}
/**
* 全局异常捕捉处理
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public Map errorHandler(Exception ex) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("code", 100);
map.put("msg", ex.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
启动应用后,上述三个方法都会作用在 被 @RequestMapping 注解的方法上
@controllerAdvice源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface ControllerAdvice {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class[] basePackageClasses() default {};
Class[] assignableTypes() default {};
Class[] annotations() default {};
}
我们可以传递basePackage,声明的类(是一个数组)指定的Annotation参数
@ControllerAdvice是一个@Component,用于定义@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder和@ModelAttribute方法,适用于所有使用@RequestMapping方法。
Spring4之前,@ControllerAdvice在同一调度的Servlet中协助所有控制器。Spring4已经改变:@ControllerAdvice支持配置控制器的子集,而默认的行为仍然可以利用。
在Spring4中, @ControllerAdvice通过annotations(), basePackageClasses(), basePackages() 方法定制用于选择控制器子集。
ControllerAdvice定义的Class是有作用范围的,默认情况下,什么参数都不指定时它的作用范围是所有的范围。ControllerAdvice提供了一些可以缩小它的处理范围的参数。
value:数组类型,用来指定可以作用的基包,即将对指定的包下面的Controller及其子包下面的Controller起作用。
basePackages:数组类型,等价于value。
basePackageClasses:数组类型,此时的基包将以指定的Class所在的包为准。
assignableTypes:数组类型,用来指定具体的Controller类型,它可以是一个共同的接口或父类等。
annotations:数组类型,用来指定Class上拥有指定的注解的Controller。
下面的ControllerAdvice将对定义在com.elim.app.mvc.controller包及其子包中的Controller起作用。
@ControllerAdvice(value="com.elim.app.mvc.controller")
下面的ControllerAdvice也将对定义在com.elim.app.mvc.controller包及其子包中的Controller起作用。
@ControllerAdvice(basePackages="com.elim.app.mvc.controller")
下面的ControllerAdvice也将对定义在com.elim.app.mvc.controller包及其子包中的Controller起作用。它通过basePackageClasses指定了需要作为基包的Class,此时基包将以basePackageClasses指定的Class所在的包为准,即com.elim.app.mvc.controller。
@ControllerAdvice(basePackageClasses=com.elim.app.mvc.controller.Package.class)
面的ControllerAdvice将对FooController及其子类型的Controller起作用。
@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes=FooController.class)
下面的ControllerAdvice将对所有Class上使用了RestController注解标注的Controller起作用。
@ControllerAdvice(annotations=RestController.class)
也可以同时指定多个属性,比如下面的ControllerAdvice将对FooController及其子类型的Controller起作用,同时也将对com.elim.app.mvc.controller包及其子包下面的Controller起作用。
@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes=FooController.class, basePackages="com.elim.app.m
@ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler 拦截了异常,我们可以通过该注解实现自定义异常处理。其中,@ExceptionHandler 配置的 value 指定需要拦截的异常类型。
需要注意的是使用@ExceptionHandler注解传入的参数可以一个数组,且使用该注解时,传入的参数不能相同,也就是不能使用两个@ExceptionHandler去处理同一个异常。如果传入参数相同,则初始化ExceptionHandler时会失败
当一个Controller中有方法加了@ExceptionHandler之后,这个Controller其他方法中没有捕获的异常就会以参数的形式传入加了@ExceptionHandler注解的那个方法中
除了全局增强捕获所有Controller中抛出的异常,我们也可以使用接口的默认方法(1.8)
public interface DataExceptionSolver {
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseBody
default Object exceptionHandler(Exception e){
try {
throw e;
} catch (SystemException systemException) {
systemException.printStackTrace();
return WebResult.buildResult().status(systemException.getCode())
.msg(systemException.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e1){
e1.printStackTrace();
return WebResult.buildResult().status(Config.FAIL)
.msg("系统错误");
}
}
}
但这种方法即依赖1.8 又需要controller实现接口 不如全局爽。
还有更加偷鸡的方法时直接定义到handler中 @ExceptionHandler这个只会是在当前的Controller里面起作用
当一个Controller中有多个@ExceptionHandler注解出现时,那么异常被哪个方法捕捉呢?这就存在一个优先级的问题,@ExceptionHandler的优先级是:在异常的体系结构中,哪个异常与目标方法抛出的异常血缘关系越紧密,就会被哪个捕捉到
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "exception")
public class ExceptionHandlerController {
@ExceptionHandler({ ArithmeticException.class })
public String handleArithmeticException(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "error";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "e/{id}", method = {RequestMethod.GET })
@ResponseBody
public String testExceptionHandle(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) {
System.out.println(10 / id);
return id.toString();
}
}
当访问exception/e/0的时候,会抛出ArithmeticException异常,@ExceptionHandler就会处理并响应error.jsp
@ResponseStatus
这里还有一个注解@ResponseStatus 可以将某种异常映射为HTTP状态码
如:
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "status")
public class ResponseStatusController {
/**
* ResponseStatus修饰目标方法,无论它执行方法过程中有没有异常产生,用户都会得到异常的界面。而目标方法正常执行
* @param id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "e2/{id}", method = { RequestMethod.GET })
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.BAD_GATEWAY)
@ResponseBody
public String status2(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) {
System.out.println(10 / id);
return id.toString();
}
}
这样前端即使请求成功了也会返回 502的状态码
那么 将这个注解也放入controller增强的代码中
/**
* 捕获CustomException
* @param e
* @return json格式类型
*/
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler({CustomException.class}) //指定拦截异常的类型
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) //自定义浏览器返回状态码
public Map customExceptionHandler(CustomException e) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", e.getCode());
map.put("msg", e.getMsg());
return map;
}
/**
* 捕获CustomException
* @param e
* @return 视图
*/
// @ExceptionHandler({CustomException.class})
// public ModelAndView customModelAndViewExceptionHandler(CustomException e) {
// Map map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put("code", e.getCode());
// map.put("msg", e.getMsg());
// ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// modelAndView.setViewName("error");
// modelAndView.addObject(map);
// return modelAndView;
// }
那么单独多定义几个处理方法 即可控制返回的错误码