SSM---MyBatis
文章目录
- Mybatis
-
- 一、MyBatis入门
-
- 1、MyBatis介绍
- 2、入门案例
-
- (1)准备数据库
- (2)创建maven项目
- (3)定义User类
- (4)创建mapper文件
- (5)创建mybatis配置文件
- (6)加载主配置文件进行测试
- 3、增删改查
-
- (1)增
-
- ① 自增主键
- ② uuid做主键
- (2)删
- (3)改
- (4)查
- 4、MyBatis架构介绍
- 5、引入Mapper
- 二、全局配置
-
- 1、properties
- 2、settings
- 3、typeAliases
-
- (1)MyBatis自带的别名
- (2)自定义别名
- 4、Mapper
- 三、Mapper映射文件
-
- 1、parameterType
-
- (1)'$'和'#'
- (2)简单类型
- (3)对象参数
- 2、resultType
- 3、resultMap
- 四、动态SQL
-
- 1、if
- 2、where
- 3、foreach
- 4、sql片段
- 5、set
- 五、查询进阶
-
- 1、一对一查询
-
- (1)懒加载
- 2、一对多查询
- 3、查询缓存
- 4、逆向工程
说明:MyBatis的学习是参考江南一点雨的教程(安利这个公众号),教程原文。
Mybatis
一、MyBatis入门
1、MyBatis介绍
MyBatis是一个持久层框架,它对jdbc的操作数据库的过程进行封装,使开发者只需要关注sql本身,而不需要花费精力去处理例如注册驱动、创建Connection、创建Statement、手动设置参数、结果集检索等jdbc复杂的过程代码。MyBatis通过xml或注解的方式将要执行的各种statement配置起来,并通过java对象和statement中的sql进行映射生成最终执行的sql语句,最后由MyBatis框架执行sql并将结果映射为java对象并返回。
2、入门案例
(1)准备数据库
CREATE DATABASE test01;
USE `test01`;/*Table structure for table `user` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `user` */
insert into `user`(`id`,`username`,`address`) values (1,'javaboy123','www.javaboy.org'),(3,'javaboy','spring.javaboy.org'),(4,'张三','深圳'),(5,'李四','广州'),(6,'王五','北京');
(2)创建maven项目
并在pom.xml中引入mybatis依赖和数据库连接驱动。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>3.4.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>6.0.6version>
dependency>
dependencies>
(3)定义User类
package org.luyangsyi.test01.bean;
/**
* Created by luyangsiyi on 2020/2/11
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
(4)创建mapper文件
在main—resources中定义UserMapper.xml:
编写一个简单的select语句,其中id表示查询方法的唯一标识符,resultType定义了返回值的类型,#{id}表示这个位置用来接收外部传进来的参数。
<mapper namespace="org.luyangsiyi.mymapper">
<select id="getUserById" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user where id = #{id};
select>
mapper>
(5)创建mybatis配置文件
在main—resources下添加myatis-config.xml文件:
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
(6)加载主配置文件进行测试
可以写在test–java中。
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Created by luyangsiyi on 2020/2/11
*/
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));//导入配置文件
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();//sqlSession中封装了对数据库的操作
User user = (User) sqlSession.selectOne("org.luyangsiyi.mymapper.getUserById", 3);//进行查询并传入参数id
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
3、增删改查
(1)增
① 自增主键
在mapper中插入sql语句:
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
insert into user (username,address) values(#{username},#{address});
insert>
编写测试方法:
//2.增
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("赵六");
user.setAddress("北京");
int insert = sqlSession.insert("org.luyangsiyi.mymapper.addUser",user);
System.out.println(insert);
sqlSession.commit();//sql插入提交后一定要commit
sqlSession.close();
② uuid做主键
使用mysql自带的uuid函数生成uuid。
首先调用mysql中的uuid函数,获取到一个uuid,然后将这个uuid赋值给User对象的id属性,然后再去进行SQL插入操作,在插入时使用这个uuid。
需要实现将数据的id类型改为varchar
<insert id="addUser2" parameterType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
<selectKey resultType="java.lang.String" keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE">
select uuid();
selectKey>
insert into user (id,username,address) values (#{id},#{username},#{address});
insert>
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("赵六");
user.setAddress("北京");
int insert = sqlSession.insert("org.luyangsiyi.mymapper.addUser2",user);
System.out.println(insert);
sqlSession.commit();//sql插入提交后一定要commit
sqlSession.close();
(2)删
<delete id="deleteById">
delete from user where id=#{id};
delete>
//3.删
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
int delete = sqlSession.delete("org.luyangsiyi.mymapper.deleteById",8);
System.out.println(delete);
sqlSession.commit();//sql插入提交后一定要commit
sqlSession.close();
(3)改
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
update user set username=#{username} where id=#{id};
update>
//4.改
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("javaboy");
int update = sqlSession.update("org.luyangsiyi.mymapper.updateUser",user);
System.out.println(update);
sqlSession.commit();//sql插入提交后一定要commit
sqlSession.close();
(4)查
<select id="selectAll" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user;
select>
//5.查
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("org.luyangsiyi.mymapper.selectAll");
System.out.println(list);
sqlSession.close();
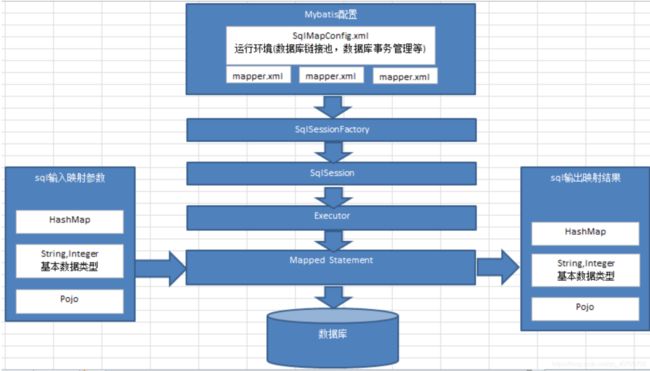
4、MyBatis架构介绍
- mybatis 配置:mybatis-config.xml,此文件作为 mybatis 的全局配置文件,配置了 mybatis 的运行环境等信息。另一个 mapper.xml 文件即 sql 映射文件,文件中配置了操作数据库的 sql 语句。此文件需要在 mybatis-config.xml 中加载。
- 通过 mybatis 环境等配置信息构造 SqlSessionFactory 即会话工厂
- 由会话工厂创建 sqlSession 即会话,操作数据库需要通过 sqlSession 进行。
- mybatis 底层自定义了 Executor 执行器接口操作数据库,Executor 接口有两个实现,一个是基本执行器、一个是缓存执行器。
- Mapped Statement 也是 mybatis 一个底层封装对象,它包装了 mybatis 配置信息及 sql 映射信息等。mapper.xml 文件中一个 sql 对应一个 Mapped Statement 对象,sql 的 id 即是Mapped statement 的 id。
- Mapped Statement 对 sql 执行输入参数进行定义,包括 HashMap、基本类型、pojo,Executor 通过 Mapped Statement 在执行 sql 前将输入的 java 对象映射至 sql 中,输入参数映射就是 jdbc 编程中对 preparedStatement 设置参数。
- Mapped Statement 对 sql 执行输出结果进行定义,包括 HashMap、基本类型、pojo,Executor 通过 Mapped Statement 在执行 sql 后将输出结果映射至 java 对象中,输出结果映射过程相当于 jdbc 编程中对结果的解析处理过程。
5、引入Mapper
UserDao.java:
package org.luyangsiyi.test01.dao;
import org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by luyangsiyi on 2020/2/11
*/
public interface UserDao {
User getUserById(Integer id);
Integer addUser(User user);
Integer addUser2(User user);
Integer deleteUserById(Integer id);
Integer updateUser(User user);
List<User> getAllUser();
}
UserMapper.xml:
<mapper namespace="org.luyangsiyi.test01.dao.UserDao">
<select id="getUserById" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user where id = #{id};
select>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
insert into user (username,address) values(#{username},#{address});
insert>
<delete id="deleteById">
delete from user where id=#{id};
delete>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
update user set username=#{username} where id=#{id};
update>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user;
select>
mapper>
mybatis-config.xml:
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="wawj6241"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<package name="mapper"/>
mappers>
configuration>
二、全局配置
1、properties
引入数据库的配置文件,在resources目录下添加一个jdbc.properties文件作为数据库的配置文件:
db.username=root
db.password=123456
db.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01
然后在mybatis-config.xml中做修改,而不是直接写死数据库相关信息:
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbc.properties">properties>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${db.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${db.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${db.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${db.password}"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<package name="mapper"/>
mappers>
configuration>
2、settings
常用设置:mapUnderscoreToCamelCase(驼峰命名法)
3、typeAliases
(1)MyBatis自带的别名
本来,在Mapper中定义数据类型时,需要写全路径,如下:
<select id="getUserCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(*) from user;
select>
此时可以使用类型别名来替代(有对应的映射表)
<select id="getUserCount" resultType="java.lang.int">
select count(*) from user;
select>
(2)自定义别名
自己的对象,在Mapper定义的时候,也需要写全路径:
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user;
select>
为了避免写全路径,我们可以给User对象取一个别名,在mybatis-config.xml中添加typeAliases节点:
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User" alias="User"/>
typeAliases>
则此时的mapper可以为:
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="User">
select * from user;
select>
由于一个个去修改别名很麻烦,所以我们可以批量操作(建议这种方式):
<typeAliases>
<package name="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean"/>
typeAliases>
默认别名为类名但是首字母小写:
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="user">
select * from user;
select>
4、Mapper
Mapper配置的几种方式:
<mappers>
<package name="mapper"/>
mappers>
三、Mapper映射文件
1、parameterType
表示输入的参数类型。
(1)’$‘和’#’
在mapper引用变量时,默认使用的是’#’,如:
<select id="getUserById" resultType="user">
select * from user where id = #{id};
select>
除了’#‘之外,也可以用’$'来引用,即:
<select id="getUserById" resultType="user">
select * from user where id = ${id};
select>
在最新的mybatis中,无论是’KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '#' at position 5: '还是'#̲'只有一个参数可以不用别名@P…‘相当于参数拼接的方式,而’#'相当于占位符的方式。
‘#’ 对应PreparedStatement预编译的情况,’$'对应Statement的情况。
(2)简单类型
多个参数添加@Param来指定参数名,可以在mapper文件中直接使用。
Integer updateUsernameById(@Param("username") String username, @Param("id") Integer id);
<update id="updateUsernameById">
update user set username = #{username} where id=#{id};
update>
(3)对象参数
如果存在多个对象,那么我们也需要对对象添加@Param注解,此时再mapper中引用对象的属性会有所改变,如从username变为user.username(@Param(“user”))
2、resultType
resultType 是返回类型,在实际开发中,如果返回的数据类型比较复杂,一般我们使用 resultMap,但是,对于一些简单的返回,使用 resultType 就够用了。
resultType 返回的类型可以是简单类型,可以是对象,可以是集合,也可以是一个 hashmap,如果是 hashmap,map 中的 key 就是字段名,value 就是字段的值。
3、resultMap
在实际开发中,resultMap 是使用较多的返回数据类型配置。因为实际项目中,一般的返回数据类型比较丰富,要么字段和属性对不上,要么是一对一、一对多的查询,等等,这些需求,单纯的使用 resultType 是无法满足的,因此我们还需要使用 resultMap,也就是自己定义映射的结果集。
可以在mapper.xml中定义一个resultMap:
<resultMap id="MyResultMap" type="org.javaboy.mybatis.model.User">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
resultMap>
id用来描述主键,column是数据库查询出来的列名,property是对象中的属性名。
在查询结果中,可以直接使用这个ResultMap:
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="MyResultMap">
select * from user where id=#{id};
select>
四、动态SQL
可以解决类似查询条件不确定、批量插入等需求。
1、if
if是一个判断节点,如果满足某个条件,节点中的SQL就会生效。例如分页查询,要传递两个参数,页码和查询的记录数,如果这两个参数都为null,那么查询所有。
接口方法:
List<User> getUserByPage(@Param("start") Integer start, @Param("count") Integer count);
xml中定义sql:
<select id="getUserByPage" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user
<if test="start != null and count != null">
if>
select>
if节点中,test表示判断条件,如果结果为true,则if节点中的sql会生效,否则不会生效。
2、where
用where节点将所有的查询条件包起来,如果有满足的条件,where节点会自动加上,如果没有,where节点将不存在,在有满足条件的情况下,where还会自动处理and关键字。
接口:
List<User> getUserByUsernameAndId(@Param("id") Integer id, @Param("name") String name);
xml中定义sql:
<select id="getUserByUsernameAndId" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
and id>#{id}
if>
<if test="name!=null">
and username like concat('%',#{name},'%')
if>
where>
select>
3、foreach
foreach用来处理数组/集合参数。
List<User> getUserByIds(@Param("ids")Integer[] ids);
<select id="getUserByIds" resultType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
select * from user where id in
<foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
foreach>
select>
在mapper中,通过foreach节点来遍历数组,collection表示数组变量,open表示循环结束后左边的符号,close表示循环结束后右边的符号,item表示循环时候的单个变量,separator表示循环的元素之间的分隔符。
4、sql片段
每次查询都需要把字段名列出来,可以使用SQL片段来解决这问题。
<sql id="Base_Column">
id,username,address
sql>
则可以在其它SQL中,引用该变量;
5、set
set关键词一般用在更新中。大部分情况下,更新的字段可能不确定,如果对象中存在该字段的值,就更新该字段,否则不更新。
Integer updateUser(User user);
现在,这个方法的需求,是根据用户id来更新用户的其他属性,所以,user对象中一定存在id,其他属性则不确定,如果其他属性有值,就更新,没值就不处理该字段。
<update id"updateUser" parameterType="org.luyangsiyi.test01.bean.User">
update user
<set>
<if test="username!=null">
username = #{username},
if>
<if test="address!=null">
address = #{address},
if>
set>
where id=#{id};
update>
五、查询进阶
1、一对一查询
定义一个书本类,包含作者类。
public class Book{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Author author;
//省略getter、setter、toString方法
......
}
public class Auther{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
//省略getter、setter、toString方法
......
}
对应添加两张表,书的属性为id、name、aid,作者的属性为id、name、age。
定义一个接口方法,实现根据id查询书,同时需要范围Auther的信息:
public interface BookMapper{
Book getBookById(Integer id);
}
相应的BookMapper.xml为:
<resultMap id="BookWithAuthor" type="....bean.Book">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<association property="author" javaType="...bean.Auther">
<id column="aid" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
association>
resultMap>
<select id="getBookById" resultMap="BookWithAuther">
select book.*, author.age, auther.id, author.name, author.age from book, author where book.aid=author.id and book.id = #{id};
select>
在实际项目中,每次返回的数据类型可能有部分是相同的,所以可以抽取相同的部分做成公共的模板,然后被其他resultMap继承:
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="...bean.Book">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
resusltMap>
<resultMap id="BookWithAuthor" type="....bean.Book" extends="BaseResultMap">
<association property="author" javaType="...bean.Auther">
<id column="aid" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
association>
resultMap>
(1)懒加载
如果一对一的属性使用不是很频繁,可能偶尔用一下,则可以启用懒加载。
懒加载,就是先查询book,在查询的过程中不去查询author,当用户第一次调用了book中的author属性后,再去查询author。
需在配置中开启:
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
settings>
定义一个Book的查询方法:
Book getBookById(Integer id);
Author getAuthorById(Integer id);
在mapper中定义相应的SQL:
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="...bean.Book">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
resusltMap>
<resultMap id="BookWithAuthor" type="....bean.Book" extends="BaseResultMap">
<association property="author" javaType="...bean.Auther">
select="...BookMapper.getAuthorById" column="aid" fetchType="lazy"/>
association>
resultMap>
<select id="getBookById" resultMap="BookWithAuther">
select * from book where id = #{id};
select>
<select id="getAuthorById" resultMap="...bean.Author">
select * from author where id=#{aid};
select>
这里定义association的时候,不直接指定映射的字段,而是指定要执行的方法,通过select字段来指定,column表示执行方法时传递的参数字段,最后的fetchType表示开启懒加载。
2、一对多查询
用户和角色的关系表:
role表:id、name、nameZh;user表:id、username、password、enabled、locked;user_role表:id、uid、rid。
新建两个实体类:
public class User{
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private List<Role> roles;
.....
}
public class Role{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String nameZh;
.....
}
定义接口方法:
User getUserById(Integer id);
定义该方法的实现:
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="password" property="password"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="...bean.Role">
<id property="id" column="rid"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="nameZh" property="nameZh"/>
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="UserWithRole">
select user.*, role.id, role.name, role.nameZh from user, role,user_role where user.id=user_role.uid and role.id=user_role.rid and user.id=#{id};
select>
3、查询缓存
MyBatis一级缓存的作用域是同一个SqlSession,在同一个sqlSession中两次执行相同的sql语句,第一次执行完毕后会将数据库中查询的数据写到缓存,第二次会从缓存中获取数据,从而提高效率。当一个sqlSession结束后一次缓存也不存在了。MyBatis默认开启一级缓存。
MyBatis二级缓存是多个sqlSession共享的,其作用域是mapper的同一个namespace,不同的sqlSession两次执行相同 namespace下的sql语句且向sql语句中传递参数也相同,第一次执行完毕后会将结果写入到缓存,第二次直接读取缓存中的结果,需要在settings中配置开启二级缓存。
4、逆向工程
在pom.xml中添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generatorgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-coreartifactId>
<version>1.3.7version>
dependency>
新增generatorConfig.xml文件:
<generatorConfiguration>
<context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<commentGenerator>
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="true"/>
commentGenerator>
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/e3mall"
userId="root"
password="111">
jdbcConnection>
<javaTypeResolver >
<property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" />
javaTypeResolver>
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="cn.e3mall.pojo" targetProject=".\src">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
<property name="trimStrings" value="true" />
javaModelGenerator>
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="cn.e3mall.mapper" targetProject=".\src">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
sqlMapGenerator>
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="cn.e3mall.mapper" targetProject=".\src">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
javaClientGenerator>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_content">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_content_category">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_cat">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_desc">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_param">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_param_item">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_order">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_order_item">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_order_shipping">table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_user">table>
context>
generatorConfiguration>
使用java代码生成:
import java.io.File;
import java.util.*;
import org.mybatis.generator.api.MyBatisGenerator;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.Configuration;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.xml.ConfigurationParser;
import org.mybatis.generator.internal.DefaultShellCallback;
public class GeneratorSqlmap {
public void generator() throws Exception {
List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<String>();
boolean overwrite = true;
// 指定配置文件
File configFile = new File("generatorConfig.xml的路径");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config, callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
}
// 执行main方法以生成代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
GeneratorSqlmap generatorSqlmap = new GeneratorSqlmap();
generatorSqlmap.generator();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}