前几天在生产环境上redis创建连接方面的故障,分析过程中对ServiceStack.Redis的连接创建和连接池机制有了进一步了解。问题分析结束后,通过此文系统的将学习到的知识点整理出来。
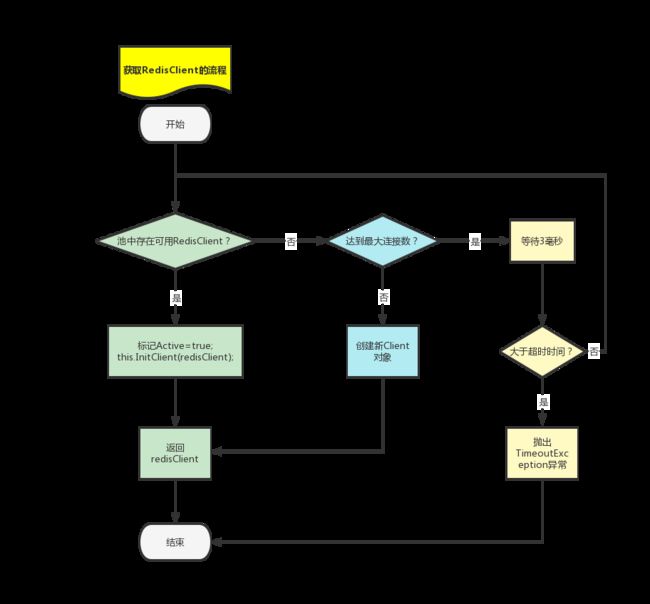
从连接池获取RedisClient的流程
public IRedisClient GetClient()
{
RedisClient redisClient = null;
DateTime now = DateTime.Now;
for (; ; )
{
if (!this.deactiveClientQueue.TryPop(out redisClient))
{
if (this.redisClientSize >= this.maxRedisClient)
{
Thread.Sleep(3);
if (this.PoolTimeout != null && (DateTime.Now - now).TotalMilliseconds >= (double)this.PoolTimeout.Value)
{
break;
}
}
else
{
redisClient = this.CreateRedisClient();
if (redisClient != null)
{
goto Block_5;
}
}
}
else
{
if (!redisClient.HadExceptions)
{
goto Block_6;
}
List obj = this.writeClients;
lock (obj)
{
this.writeClients.Remove(redisClient);
this.redisClientSize--;
}
RedisState.DisposeDeactivatedClient(redisClient);
}
}
bool flag2 = true;
if (flag2)
{
throw new TimeoutException("Redis Timeout expired. The timeout period elapsed prior to obtaining a connection from the pool. This may have occurred because all pooled connections were in use.");
}
return redisClient;
Block_5:
this.writeClients.Add(redisClient);
return redisClient;
Block_6:
redisClient.Active = true;
this.InitClient(redisClient);
return redisClient;
} 此方法的主体是死循环,主要实现了这几项功能:
- this.deactiveClientQueue代表空闲的Client集合,是ConcurrentStack
类型的。 - 当this.deactiveClientQueue能够Pop出redisClient时,则跳转到Block_6分支:标记redisClient.Active属性,并执行this.InitClient(redisClient),然后将redisClient实例返回。
- 当this.deactiveClientQueue没有可以Pop的元素时,首先执行Client数量上限的判断this.redisClientSize >= this.maxRedisClient;
- 如果未到达上限,则执行redisClient = this.CreateRedisClient();
- 如果达到上限,则先休眠3毫秒,然后判断是否超过连接池超时时间this.PoolTimeout,单位毫秒。超时的话直接break中断循环,不超时的话继续下一次for循环。
上述流程就是从连接池获取Client的主要流程,其中this.deactiveClientQueue相当于“Client池”。需要注意this.PoolTimeout的含义是当连接池耗尽时调用方等待的时间。
上述过程通过流程图表示为:
创建新Client的过程:CreateRedisClient()
源码如下:
private RedisClient CreateRedisClient()
{
if (this.redisClientSize >= this.maxRedisClient)
{
return null;
}
object obj = this.lckObj;
RedisClient result;
lock (obj)
{
if (this.redisClientSize >= this.maxRedisClient)
{
result = null;
}
else
{
Random random = new Random((int)DateTime.Now.Ticks);
RedisClient newClient = this.InitNewClient(this.RedisResolver.CreateMasterClient(random.Next(100)));
newClient.OnDispose += delegate()
{
if (!newClient.HadExceptions)
{
List obj2 = this.writeClients;
lock (obj2)
{
if (!newClient.HadExceptions)
{
try
{
this.deactiveClientQueue.Push(newClient);
return;
}
catch
{
this.writeClients.Remove(newClient);
this.redisClientSize--;
RedisState.DisposeDeactivatedClient(newClient);
}
}
}
}
this.writeClients.Remove(newClient);
this.redisClientSize--;
RedisState.DisposeDeactivatedClient(newClient);
};
this.redisClientSize++;
result = newClient;
}
}
return result;
} 基于并发的考虑,创建新Client的流程需要增加并发锁限制,即lock (obj)处。此时如果多个线程都进入CreateRedisClient()方法,则只有一个线程实际执行,其它线程阻塞等待锁释放。这个现象可以通过windbg的syncblk、clrstack命令分析查看。其余的部分就是继续调用this.InitNewClient(this.RedisResolver.CreateMasterClient(random.Next(100)))创建对象,并对newClient的OnDispose事件增加了处理逻辑。需要说明的是此处OnDispose事件并不是传统意义的析构,而是调用方用完此RedisClient对象后,用于将其回收到连接池的操作,即:newClient对象没有异常的前提下, 将其Push到this.deactiveClientQueue栈里,连接池就是此处回收扩充的。
this.InitNewClient()方法解读
此处是对新创建的RedisClient对象初始化,包括Id、Active等,并继续调用this.InitClient()进一步初始化。
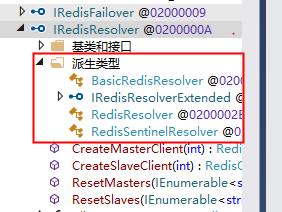
this.RedisResolver.CreateMasterClient()解读
this.redisResolver是IRedisResolver接口类型,源码中有三种实现,如下截图。此处以生产常见的哨兵模式为例进行分析。
RedisSentinelResolver类对应的就是哨兵模式,其相关操作源码如下:
public RedisClient CreateMasterClient(int desiredIndex)
{
return this.CreateRedisClient(this.GetReadWriteHost(desiredIndex), true);
}
public RedisEndpoint GetReadWriteHost(int desiredIndex)
{
return this.sentinel.GetMaster() ?? this.masters[desiredIndex % this.masters.Length];
}
public virtual RedisClient CreateRedisClient(RedisEndpoint config, bool master)
{
RedisClient result = this.ClientFactory(config);
if (master)
{
RedisServerRole redisServerRole = RedisServerRole.Unknown;
try
{
using (RedisClient redisClient = this.ClientFactory(config))
{
redisClient.ConnectTimeout = 5000;
redisClient.ReceiveTimeout = 5000;
redisServerRole = redisClient.GetServerRole();
if (redisServerRole == RedisServerRole.Master)
{
this.lastValidMasterFromSentinelAt = DateTime.UtcNow;
return result;
}
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalInvalidMasters);
using (RedisClient redisClient2 = this.ClientFactory(config))
{
redisClient2.ConnectTimeout = 5000;
redisClient2.ReceiveTimeout = 5000;
if (redisClient2.GetHostString() == this.lastInvalidMasterHost)
{
object obj = this.oLock;
lock (obj)
{
if (DateTime.UtcNow - this.lastValidMasterFromSentinelAt > this.sentinel.WaitBeforeForcingMasterFailover)
{
this.lastInvalidMasterHost = null;
this.lastValidMasterFromSentinelAt = DateTime.UtcNow;
RedisSentinelResolver.log.Error("Valid master was not found at '{0}' within '{1}'. Sending SENTINEL failover...".Fmt(redisClient2.GetHostString(), this.sentinel.WaitBeforeForcingMasterFailover), exception);
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalForcedMasterFailovers);
this.sentinel.ForceMasterFailover();
Thread.Sleep(this.sentinel.WaitBetweenFailedHosts);
redisServerRole = redisClient2.GetServerRole();
}
goto IL_16E;
}
}
this.lastInvalidMasterHost = redisClient2.GetHostString();
IL_16E:;
}
}
if (redisServerRole != RedisServerRole.Master && RedisConfig.VerifyMasterConnections)
{
try
{
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (;;)
{
try
{
RedisEndpoint master2 = this.sentinel.GetMaster();
using (RedisClient redisClient3 = this.ClientFactory(master2))
{
redisClient3.ReceiveTimeout = 5000;
redisClient3.ConnectTimeout = this.sentinel.SentinelWorkerConnectTimeoutMs;
if (redisClient3.GetServerRole() == RedisServerRole.Master)
{
this.lastValidMasterFromSentinelAt = DateTime.UtcNow;
return this.ClientFactory(master2);
}
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalInvalidMasters);
}
}
catch
{
}
if (stopwatch.Elapsed > this.sentinel.MaxWaitBetweenFailedHosts)
{
break;
}
Thread.Sleep(this.sentinel.WaitBetweenFailedHosts);
}
throw new TimeoutException("Max Wait Between Sentinel Lookups Elapsed: {0}".Fmt(this.sentinel.MaxWaitBetweenFailedHosts.ToString()));
}
catch (Exception exception2)
{
RedisSentinelResolver.log.Error("Redis Master Host '{0}' is {1}. Resetting allHosts...".Fmt(config.GetHostString(), redisServerRole), exception2);
List list = new List();
List list2 = new List();
RedisClient redisClient4 = null;
foreach (RedisEndpoint redisEndpoint in this.allHosts)
{
try
{
using (RedisClient redisClient5 = this.ClientFactory(redisEndpoint))
{
redisClient5.ReceiveTimeout = 5000;
redisClient5.ConnectTimeout = RedisConfig.HostLookupTimeoutMs;
RedisServerRole serverRole = redisClient5.GetServerRole();
if (serverRole != RedisServerRole.Master)
{
if (serverRole == RedisServerRole.Slave)
{
list2.Add(redisEndpoint);
}
}
else
{
list.Add(redisEndpoint);
if (redisClient4 == null)
{
redisClient4 = this.ClientFactory(redisEndpoint);
}
}
}
}
catch
{
}
}
if (redisClient4 == null)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalNoMastersFound);
string message = "No master found in: " + string.Join(", ", this.allHosts.Map((RedisEndpoint x) => x.GetHostString()));
RedisSentinelResolver.log.Error(message);
throw new Exception(message);
}
this.ResetMasters(list);
this.ResetSlaves(list2);
return redisClient4;
}
return result;
}
return result;
}
return result;
} 其中GetReadWriteHost()方法的逻辑是:优先使用this.sentinel.GetMaster()得到的主节点信息。如果GetMaster()失败,则从现有的主节点集合masters中随机选择一个进行连接。
然后进入CreateRedisClient()方法内:
- 首先通过this.ClientFactory()工厂创建对象redisClient,工厂内部实现了计数和new RedisClient()操作。没有太多内容。
- 然后是执行redisClient.GetServerRole(),代表向服务器核实当前连接的节点确实是Master角色。如果确认,则直接返回给调用方。【如果发送查询请求的过程出现异常,且符合一定条件,则会发起故障转移请求,即this.sentinel.ForceMasterFailover();】
- 如果当前连接的不是Master角色的节点,则多次调用this.sentinel.GetMaster()查询Master节点信息并重新实例化RedisClient对象;
- 如果超时仍然未能连接到Master节点,则会进入catch异常处理流程,遍历this.allHosts全部节点并更新对应的节点角色。
至此,通过上述的流程,最终能够得到master节点的RedisClient对象,并返回给调用方。
上述过程中,还有几处方法的实现比较重要和复杂,下面对其一一解释说明:
RedisSentinel类的GetMaster()实现原理解析
调用处很简单,但是此方法的实现操作挺多,RedisSentinel类 源码如下:
public RedisEndpoint GetMaster()
{
RedisSentinelWorker validSentinelWorker = this.GetValidSentinelWorker();
RedisSentinelWorker obj = validSentinelWorker;
RedisEndpoint result;
lock (obj)
{
string masterHost = validSentinelWorker.GetMasterHost(this.masterName);
if (this.ScanForOtherSentinels && DateTime.UtcNow - this.lastSentinelsRefresh > this.RefreshSentinelHostsAfter)
{
this.RefreshActiveSentinels();
}
result = ((masterHost != null) ? ((this.HostFilter != null) ? this.HostFilter(masterHost) : masterHost).ToRedisEndpoint(null) : null);
}
return result;
}
private RedisSentinelWorker GetValidSentinelWorker()
{
if (this.isDisposed)
{
throw new ObjectDisposedException(base.GetType().Name);
}
if (this.worker != null)
{
return this.worker;
}
RedisException innerException = null;
while (this.worker == null && this.ShouldRetry())
{
try
{
this.worker = this.GetNextSentinel();
this.GetSentinelInfo();
this.worker.BeginListeningForConfigurationChanges();
this.failures = 0;
return this.worker;
}
catch (RedisException ex)
{
if (this.OnWorkerError != null)
{
this.OnWorkerError(ex);
}
innerException = ex;
this.worker = null;
this.failures++;
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalFailedSentinelWorkers);
}
}
this.failures = 0;
Thread.Sleep(this.WaitBetweenFailedHosts);
throw new RedisException("No Redis Sentinels were available", innerException);
}
private RedisSentinelWorker GetNextSentinel()
{
object obj = this.oLock;
RedisSentinelWorker result;
lock (obj)
{
if (this.worker != null)
{
this.worker.Dispose();
this.worker = null;
}
int num = this.sentinelIndex + 1;
this.sentinelIndex = num;
if (num >= this.SentinelEndpoints.Length)
{
this.sentinelIndex = 0;
}
result = new RedisSentinelWorker(this, this.SentinelEndpoints[this.sentinelIndex])
{
OnSentinelError = new Action(this.OnSentinelError)
};
}
return result;
}
private void OnSentinelError(Exception ex)
{
if (this.worker != null)
{
RedisSentinel.Log.Error("Error on existing SentinelWorker, reconnecting...");
if (this.OnWorkerError != null)
{
this.OnWorkerError(ex);
}
this.worker = this.GetNextSentinel();
this.worker.BeginListeningForConfigurationChanges();
}
} 先通过GetValidSentinelWorker()获得RedisSentinelWorker对象。此方法的实现包含了重试机制的控制,最终是通过this.GetNextSentinel()方法给this.worker字段,即RedisSentinelWorker对象实例。
而GetNextSentinel()方法内部包含了同步锁、调用this.worker.Dispose()、随机选择哨兵节点、实例化RedisSentinelWorker对象等操作。
后面是对validSentinelWorker进行加锁,然后继续执行string masterHost = validSentinelWorker.GetMasterHost(this.masterName);
对应的RedisSentinelWorker类的代码如下:
internal string GetMasterHost(string masterName)
{
string result;
try
{
result = this.GetMasterHostInternal(masterName);
}
catch (Exception obj)
{
if (this.OnSentinelError != null)
{
this.OnSentinelError(obj);
}
result = null;
}
return result;
}
private string GetMasterHostInternal(string masterName)
{
List list = this.sentinelClient.SentinelGetMasterAddrByName(masterName);
if (list.Count <= 0)
{
return null;
}
return this.SanitizeMasterConfig(list);
}
public void Dispose()
{
new IDisposable[]
{
this.sentinelClient,
this.sentinePubSub
}.Dispose(RedisSentinelWorker.Log);
} 注意GetMasterHost()方法内:当发生异常时,会触发this对象的OnSentinelError事件,顾名思义这个事件用于哨兵异常的后续处理。通过源码搜索,只有GetNextSentinel()方法内对OnSentinelError事件增加了处理程序-->即RedisSentinel内的private void OnSentinelError(Exception ex)方法。而这个方法内部对打印日志和触发事件this.OnWorkerError后,又调用GetNextSentinel()重新给this.worker字段赋值。
需要注意:Dispose()方法实际是分别调用了this.sentinelClient和this.sentinePubSub的注销操作。
RedisNativeClient类的相关功能和实现
接着调用了RedisNativeClient类的SentinelGetMasterAddrByName()方法:
这个类里的几个方法的含义综合起来就是:将哨兵客户端的查询指令通过Socket发送到服务端,并将返回结果格式化为所需的RedisEndpoint类型。
在方法SendReceive()内还包含了Socket连接、重试、频率控制、超时控制等机制。
public List SentinelGetMasterAddrByName(string masterName)
{
List list = new List
{
Commands.Sentinel,
Commands.GetMasterAddrByName,
masterName.ToUtf8Bytes()
};
return this.SendExpectMultiData(list.ToArray()).ToStringList();
}
protected byte[][] SendExpectMultiData(params byte[][] cmdWithBinaryArgs)
{
return this.SendReceive(cmdWithBinaryArgs, new Func(this.ReadMultiData), (this.Pipeline != null) ? new Action>(this.Pipeline.CompleteMultiBytesQueuedCommand) : null, false) ?? TypeConstants.EmptyByteArrayArray;
}
protected T SendReceive(byte[][] cmdWithBinaryArgs, Func fn, Action> completePipelineFn = null, bool sendWithoutRead = false)
{
int num = 0;
Exception ex = null;
DateTime utcNow = DateTime.UtcNow;
T t;
for (;;)
{
try
{
this.TryConnectIfNeeded();
if (this.socket == null)
{
throw new RedisRetryableException("Socket is not connected");
}
if (num == 0)
{
this.WriteCommandToSendBuffer(cmdWithBinaryArgs);
}
if (this.Pipeline == null)
{
this.FlushSendBuffer();
}
else if (!sendWithoutRead)
{
if (completePipelineFn == null)
{
throw new NotSupportedException("Pipeline is not supported.");
}
completePipelineFn(fn);
t = default(T);
t = t;
break;
}
T t2 = default(T);
if (fn != null)
{
t2 = fn();
}
if (this.Pipeline == null)
{
this.ResetSendBuffer();
}
if (num > 0)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalRetrySuccess);
}
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalCommandsSent);
t = t2;
}
catch (Exception ex2)
{
RedisRetryableException ex3 = ex2 as RedisRetryableException;
if ((ex3 == null && ex2 is RedisException) || ex2 is LicenseException)
{
this.ResetSendBuffer();
throw;
}
Exception ex4 = ex3 ?? this.GetRetryableException(ex2);
if (ex4 == null)
{
throw this.CreateConnectionError(ex ?? ex2);
}
if (ex == null)
{
ex = ex4;
}
if (!(DateTime.UtcNow - utcNow < this.retryTimeout))
{
if (this.Pipeline == null)
{
this.ResetSendBuffer();
}
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalRetryTimedout);
throw this.CreateRetryTimeoutException(this.retryTimeout, ex);
}
Interlocked.Increment(ref RedisState.TotalRetryCount);
Thread.Sleep(RedisNativeClient.GetBackOffMultiplier(++num));
continue;
}
break;
}
return t;
} 总结
本文着重以Redis连接创建、获取为线索,对SDK内部的实现机制有了更深入的了解。在此基础上,分析生产环境Redis SDK相关故障时更加得心应手。