数据结构与算法作业2——双向链表
第二次作业:
习题1 双向链表
双向链表的知识点:
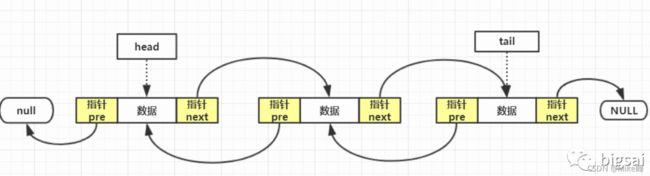
同单链表相比,双链表仅是各节点多了一个用于指向直接前驱的指针域。因此,我们可以在单链表的基础轻松实现对双链表的创建。
与单链表不同,双链表创建过程中,每创建一个新节点,都要与其前驱节点建立两次联系,分别是:
将新节点的 prior 指针指向直接前驱节点;
将直接前驱节点的 next 指针指向新节点。
双向链表的创建 2021/9/26
Doubly Linked List | Set 1 (Introduction and Insertion) - GeeksforGeeks![]() https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/doubly-linked-list/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/doubly-linked-list/
先定义Node of DLL
struct和typedef struct彻底明白了 - bingo~ - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)![]() https://www.cnblogs.com/qyaizs/articles/2039101.htmltypedef struct {
https://www.cnblogs.com/qyaizs/articles/2039101.htmltypedef struct {
int data = 0;
下一个节点*;//指向DLL
Node* prev中下一个节点的指针;//指向DLL中前一个节点的指针
}Node;
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list
and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* 1. allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* 2. put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* 4. change prev of head node to new node */
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
/* 5. move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
**想在函数中改变指针名本身所表示的地址的话(就像头指针head_prev,它的指向会随着我们的头节点的改变而变化),那么就需要使用指针的指针作为函数的输入,这样就可以在函数中改变指针本身。
做插入操作的时候,要注意:
(1)是否插入的前后有NULL,要用if加上这种情况的处理办法。
(2)先为这个新的node分配空间,然后赋予其data。
(2)双链表插入要进行四次改指针指向。(要注意修改的顺序,否则可能出现死循环)
(3)注意修改是否会修改了该链表的指示指针(如head、ending),如果改了的话,还可能用到“指针的指针”对原来的指示指针值(也就是该指针表示的位置)进行修改。
习题1题目:
请你实现一种数据结构,该结构中包含一个双向链表BL和一个指向链表节点的指针P。
初始时,BL只有一个头节点,头节点的值为0;P指向头节点。
该结构需要实现下列8种方法,它们均不需要返回值
a. insert_right():在P的右边插入一个新节点,新节点的值为0。
b. insert_left():在P的左边插入一个新节点,新节点的值为0。
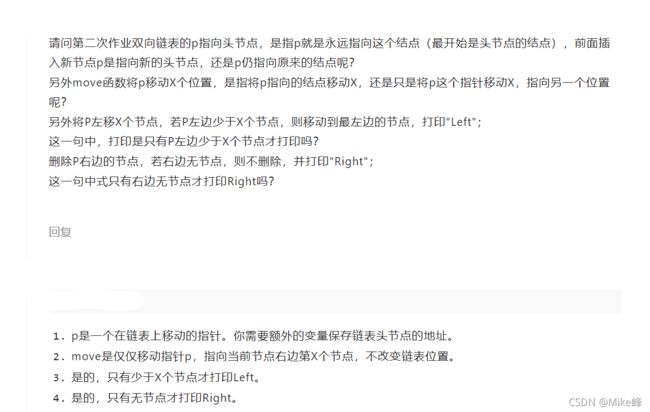
c. move_left(int X):将P左移X个节点,若P左边少于X个节点,则移动到最左边的节点,打印"Left"。
d. move_right(int X):将P右移X个节点,若右边少于X个节点,则移动到最右边的节点,打印"Right"。
e. remove_right():删除P右边的节点,若右边无节点,则不删除,并打印"Right"。
f. remove_left():删除P左边的节点,若左边无节点,则不删除,并打印"Left"。
g. set(int X):将P指向的节点的值改为X。
h. show():打印P指向的节点的值。
双向链表节点类型定义(供参考):
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *left, *right;
};
我自己的思路:
(1)先构造结点typedef
//define a node
typedef struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* left;
struct ListNode* right;
} ListNode;(2)主函数中构造head、p
int main()
{
//define the head_node and let p points to it
ListNode* head = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
head->val = 0;
head->left = NULL;
head->right = NULL;
ListNode* p = head;
}(3)按照题中条件构造各个函数
- insert_right()
//define a function to insert node on the right
void insert_right(ListNode* p)
{
ListNode* new_node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
new_node->val = 0;
new_node->right = p->right;
p->right->left = new_node;
p->right = new_node;
new_node->left = p;
}- insert_left()
//define a function to insert node on the left
void insert_left(ListNode* p)
{
ListNode* new_node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
new_node->val = 0;
new_node->left = p->left;
p->left->right = new_node;
p->left = new_node;
new_node->right = p;
}-
move_right(int X)
//move the p to the right by X
void move_right(int X, ListNode* p)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < X; i++)
{
if (p->right != NULL)
{
p = p->right;
}
else
{
printf("Right");
break;
}
}
}-
move_left(int X)
//move the p to the left by X
void move_left(int X, ListNode* p)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < X; i++)
{
if (p->left != NULL)
{
p = p->left;
}
else
{
printf("Left");
break;
}
}
}
-
remove_right()
//delete the node on the right of p
void remove_right(ListNode* p)
{
if(p->right != NULL)
{
p->right->right->left = p;
p->right = p->right->right;
}
else printf("Right");
}-
remove_left()
//delete the node on the left of p
void remove_left(ListNode* p)
{
if(p->left != NULL)
{
p->left->left->right = p;
p->left = p->left->left;
}
else printf("Left");
}-
set(int X)
//change the val of the node(p points to) to X
void set(int X, ListNode* p)
{
p->val = X;
}-
show()
//show the value of the node which p points to
void show(ListNode* p)
{
printf("%d", p->val);
}到了这里,我发现我的程序难以运行,因为其中当然出现了问题(滑稽),于是在dev c++这个破玩意上调试了半天,发现调试系统不好使,于是下载了 codeblocks 。记住下载带mingw的!要不然没法运行!然后设置debugger、compiler。
之后发现cb的debugger比dev好太多!
debug发现在insert_left的函数处停住,经过分析发现当指针为NULL时,根本没法指向left, right。于是我将NULL的情况用if 进行了改进
//define a function to insert node on the right
void insert_right(ListNode* p)
{
ListNode* new_node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
new_node->val = 0;
new_node->right = p->right;
if(p->right != NULL)
{
p->right->left = new_node;
}
p->right = new_node;
new_node->left = p;
}
//define a function to insert node on the left
void insert_left(ListNode* p)
{
ListNode* new_node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
new_node->val = 0;
new_node->left = p->left;
if(p->left != NULL)
{
p->left->right = new_node; //这里p->left如果为NULL,那么就无法指向right
}
p->left = new_node;
new_node->right = p;
}这回可以运行了,我安装、调试、在StackOverflow上问总共花了三个小时吧,连我的程序项目名字(在cb上新建的)都用的 "dontcry". 现在可是好多了,风雨过后见彩虹,虽然我明天英语课作文还没写呢,看来得通宵了。
下面的Stackoverflow 上的问题是我问的,大概就是一个经历,我好好珍惜吧。
c - Why doesn't my compiler show my input operation about the linked list and with returned value 3221225477? - Stack Overflow![]() https://stackoverflow.com/questions/69361883/why-doesnt-my-compiler-show-my-input-operation-about-the-linked-list-and-with-r/69362860#69362860里面有个大佬说的很好:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/69361883/why-doesnt-my-compiler-show-my-input-operation-about-the-linked-list-and-with-r/69362860#69362860里面有个大佬说的很好:
There is a problem of the first call of insert_left(p); as head->left = NULL; and, in insert_left() a NULL pointer is used in p->left->right = new_node;.
I suggest to use debugger and go line by line and check weather the variables follows your simple test data. It is very difficult to investigate memory overwriting in C or C++. It is important to always check that a pointer is NULL or not. There is one exception: if you checked before.
—— Adrian Mole & Attila Biró
这句话说的很好 It is important to always check that a pointer is NULL or not. There is one exception: if you checked before.
一定要时刻注意指针是不是NULL!!!
总代码上传至本人Gitee:
code(二级指针) · Mike Wang/c doubly linked list - 码云 - 开源中国 (gitee.com)![]() https://gitee.com/cs_wangfeng/c-doubly-linked-list/blob/master/code%EF%BC%88%E4%BA%8C%E7%BA%A7%E6%8C%87%E9%92%88%EF%BC%89
https://gitee.com/cs_wangfeng/c-doubly-linked-list/blob/master/code%EF%BC%88%E4%BA%8C%E7%BA%A7%E6%8C%87%E9%92%88%EF%BC%89
code(无二级指针) · Mike Wang/c doubly linked list - 码云 - 开源中国 (gitee.com)![]() https://gitee.com/cs_wangfeng/c-doubly-linked-list/blob/master/code%EF%BC%88%E6%97%A0%E4%BA%8C%E7%BA%A7%E6%8C%87%E9%92%88%EF%BC%89突然感觉又有问题:到底为什么不用二级指针还可以呢?
https://gitee.com/cs_wangfeng/c-doubly-linked-list/blob/master/code%EF%BC%88%E6%97%A0%E4%BA%8C%E7%BA%A7%E6%8C%87%E9%92%88%EF%BC%89突然感觉又有问题:到底为什么不用二级指针还可以呢?
经过一番询问,YSY同学给出了原因:
其实这个无二级指针的是错的,但是我在这个move函数中就进行了打印的任务,因此在函数内部这个形参确实是改变了,但是在函数外面并没有改变实参,所以当我添加
set(p);
insert_left(p);
move_left(1,p);
show(p);时,打印出的是5,说明p根本呆在原地没动弹,所以使用二级指针是必要的。
最后发现,按照题目的要求,其实这些函数都没有p的输入,于是我使用了全局指针,在前面加上static ListNode* p = NULL即可,这样,二级指针也不用了。
以下关于全局变量定义位置:
全局变量可以定义在任何位置, 只要不被包含在任何函数内即可.
理论上作用域是整个项目.
但如果不做声明情况下, 作用域为定义位置到所在文件尾.
每增加一个声明, 作用域会扩展从声明位置到该文件尾范围.
全文代码:
#include
#include
//define a node
typedef struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* left;
struct ListNode* right;
} ListNode;
static ListNode* p = NULL;
//define a function to insert node on the right
void insert_right()
{
ListNode* new_node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
new_node->val = 0;
new_node->right = p->right;
if(p->right != NULL)
{
p->right->left = new_node;
}
p->right = new_node;
new_node->left = p;
}
//define a function to insert node on the left
void insert_left()
{
ListNode* new_node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
new_node->val = 0;
new_node->left = p->left;
if(p->left != NULL)
{
p->left->right = new_node; //这里p->left如果为NULL,那么就无法指向right
}
p->left = new_node;
new_node->right = p;
}
//move the p to the right by X
void move_right(int X)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < X; i++)
{
if (p->right != NULL)
{
p= p->right;
}
else
{
printf("Right");
break;
}
}
}
//move the p to the left by X
void move_left(int X)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < X; i++)
{
if (p->left != NULL)
{
p = p->left;
}
else
{
printf("Left");
break;
}
}
}
//delete the node on the right of p
void remove_right()
{
if(p->right != NULL)
{
p->right->right->left = p;
p->right = p->right->right;
}
else printf("Right");
}
//delete the node on the left of p
void remove_left()
{
if(p->left != NULL)
{
p->left->left->right = p;
p->left = p->left->left;
}
else printf("Left");
}
//change the val of the node(p points to) to X
void set(int X)
{
p->val = X;
}
//show the value of the node which p points to
void show()
{
printf("%d", p->val);
}
int main()
{
int i;
//define the head_node and let p points to it
ListNode* head = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
head->val = 0;
head->left = NULL;
head->right = NULL;
p = head;
for(i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
insert_left();
}
for(i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
insert_right();
}
move_left(20);
show();
move_right(30);
show();
set(5);
insert_left();
move_left(0);
show();
}