第3章 函数
第3章 函数
函数定义
函数:定义好的可重用的功能模块
定义函数:将一个模块的算法用C++描述出来
函数的参数:计算所需要的数据和条件
函数的返回值:需要返回的计算结果
函数定义的语法形式
类型标识符 函数名(形式参数表){
语句序列
}
函数调用
例3-1
调用函数前需要先声明函数原型
函数原型
类型标识符 被调用函数名(含类型说明的形参表)
函数调用形式
函数名(实参列表)
函数调用:
嵌套调用:在一个函数的函数体中,调用另一函数
递归调用:函数直接或间接调用自身
例3-1编写一个求x的n次方的函数
#include
using namespace std;
double power(double x, int n) {
double val = 1.0;
while (n--)
val *= x;
return val;
}
int main() {
double pow;
pow = power(5, 2);
cout << "5 to the power 2 is " << pow << endl;
return 0;
}
例3-2
数制转换
输入一个8位二进制数,将其转换为十进制数输出
#include
using namespace std;
double power(double x, int n);
int main() {
double value = 0;
cout << "Enter an 8 bit binary number ";
for (int i = 7; i >= 0; i--) {
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '1')
value += static_cast(power(2, i));
}
cout << "Decimal value is " << value << endl;
return 0;
}
double power(double x, int n) {
double val = 1.0;
while (n--)
val *= x;
return val;
}
Enter an 8 bit binary number 01101001
Decimal value is 105
例3-3
编写程序求 π \pi π的值 π \pi π的计算公式如下:
π = 16 a r c t a n ( 1 5 ) − 4 a r c t a n ( 1 239 ) \pi =16arctan(\frac{1}{5})-4arctan(\frac{1}{239}) π=16arctan(51)−4arctan(2391)
其中arctan用如下形式的级数计算:
a r c t a n x = x − x 3 3 + x 5 5 − x 7 7 + ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ arctanx=x-\frac{x^{3}}{3}+\frac{x^{5}}{5}-\frac{x^{7}}{7}+\cdot \cdot \cdot arctanx=x−3x3+5x5−7x7+⋅⋅⋅
直到级数某项绝对值不大于 1 0 − 15 10^{-15} 10−15为止; π \pi π和x均为double型
#include
using namespace std;
double arctan(double x) {
double sqr = x * x;
double e = x;
double r = 0;
int i = 1;
while (e / i > 1e-15) {
double f = e / i;
r = (i % 4 == 1) ? r + f : r - f;
e = e * sqr;
i += 2;
}
return r;
}
int main() {
double a = 16.0 * arctan(1/5.0);
double b = 4.0 * arctan(1/239.0);
cout << "PI = " << a - b << endl;
return 0;
}
PI = 3.14159
例3-4
寻找并输出11~999之间的数m
它满足m、 m 2 m^{2} m2和 m 3 m^{3} m3均为回文数
回文:各位数字左右对称的整数
例如:11满足上述条件
1 1 2 = 121 11^{2}=121 112=121, 1 1 3 = 1331 11^{3}=1331 113=1331
#include
using namespace std;
bool symm(unsigned n) {
unsigned i = n;
unsigned m = 0;
while (i > 0){
m = m * 10 + i % 10;
i /= 10;
}
return m == n;
}
int main() {
for(unsigned m = 11;m < 1000;m++)
if (symm(m) && symm(m * m) && symm(m * m * m)) {
cout << "m = " << m;
cout << " m * m = " << m * m;
cout << " m * m * m = " << m * m * m << endl;
}
return 0;
}
例3-5
计算下面公式,并输出结果:
k = { s i n 2 r + s i n 2 s 当 r 2 ≤ s 2 1 2 s i n ( r s ) 当 r 2 > s 2 k=\begin{cases}\sqrt{sin^{2}r+sin^{2}s} & \text{ 当 } r^{2}\leq s^{2} \\ \frac{1}{2}sin(rs) & \text{ 当 } r^{2} > s^{2} \end{cases} k={sin2r+sin2s21sin(rs) 当 r2≤s2 当 r2>s2
其中r、s的值由键盘输入
sinx的近似值按如下公式计算,计算精度为 1 0 − 10 10^{-10} 10−10:
s i n x = x 1 ! − x 3 3 ! + x 5 5 ! − x 7 7 ! + ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ = ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( − 1 ) n − 1 x 2 n − 1 ( 2 n − 1 ) ! sinx=\frac{x}{1!}-\frac{x^{3}}{3!}+\frac{x^{5}}{5!}-\frac{x^{7}}{7!}+\cdot \cdot \cdot=\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }(-1)^{n-1}\frac{x^{2n-1}}{(2n-1)!} sinx=1!x−3!x3+5!x5−7!x7+⋅⋅⋅=n=1∑∞(−1)n−1(2n−1)!x2n−1
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const double TINY_VALUE = 1e-10;
double tsin(double x) {
double g = 0;
double t = x;
int n = 1;
do {
g += t;
n++;
t = -t * x * x / ((2 * n - 1) * (2 * n - 2));
} while (fabs(t) >= TINY_VALUE);
return g;
}
int main() {
double k, r, s;
cout << "r = ";
cin >> r;
cout << "s = ";
cin >> s;
if (r * r <= s * s)
k = sqrt(tsin(r) * tsin(r) + tsin(s) * tsin(s));
else
k = tsin(r * s) / 2;
cout << k << endl;
return 0;
}
r = 5
s = 8
1.37781
例3-6
投骰子的随机游戏
每个骰子有六面,点数分别为1、2、3、4、5、6
游戏者在程序开始时输入一个无符号整数,作为产生随机数的种子
每轮投两次骰子,第一轮如果和数为7或11则为胜,游戏结束;
和数为2、3或12则为负,游戏结束;
和数为其他值则将此值作为自己的点数,继续第二轮、第三轮
直到某轮的和数等于点数则取胜则取胜,若在此前出现和数为7则为负
rand函数
函数原型:int rand(void);
所需头文件:
功能和返回值:求出并返回一个伪随机数
原型:void srand(unsigned int seed)
参数:seed产生随机数的种子
所需头文件:
功能:为使rand()产生一序列伪随机整数而设置起始点。使用1作为seed参数,可以重新初化rand()
#include
#include
using namespace std;
enum GameStatus{WIN, LOSE, PLAYING};
int main() {
int sum, myPoint;
GameStatus status;
unsigned seed;
int rollDice();
cout << "Please enter an unsigned integer: ";
cin >> seed;
srand(seed);
sum = rollDice();
switch (sum) {
case 7:
case 11:
status = WIN;
break;
case 2:
case 3:
case 12:
status = LOSE;
break;
default:
status = PLAYING;
myPoint = sum;
cout << "point is " << myPoint << endl;
break;
}
while (status == PLAYING) {
sum = rollDice();
if (sum = myPoint)
status = WIN;
else if (sum == 7)
status = LOSE;
}
if (status == WIN)
cout << "player wins" << endl;
else
cout << "player loses" << endl;
return 0;
}
int rollDice() {
int die1 = 1 + rand() % 6;
int die2 = 1 + rand() % 6;
int sum = die1 + die2;
cout << "play rolled " << die1 << " + " << die2 << " = " << sum << endl;
return sum;
}
Please enter an unsigned integer: 23
play rolled 6 + 3 = 9
point is 9
play rolled 5 + 4 = 9
player wins
嵌套与递归
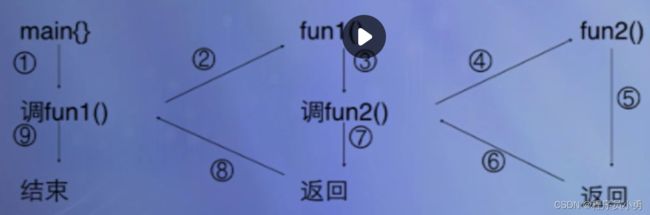
函数的嵌套调用(例3-7)
嵌套调用
例3-7 输入两个整数,求平方和。
#include
using namespace std;
int fun2(int m)
{
return m * m;
}
int fun1(int x, int y)
{
return fun2(x) + fun2(y);
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
cout << "Please enter two integers(a and b): ";
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "The sum of square of a and b: "
<< fun1(a, b) << endl;
return 0;
}
Please enter two integers(a and b):3 5
The sum of square of a and b: 34
函数的递归调用(例3-8)
函数直接或间接地调用自身,称为递归调用
例:计算n!
公式1:n!=n×(n-1)×(n-2)×(n-3)×…×2×1
公式2: n ! = { 1 ( n = 0 ) n ( n − 1 ) ( n > 0 ) n!=\begin{cases} 1 & \text{ } (n=0) \\ n(n-1) & \text{ } (n>0) \end{cases} n!={1n(n−1) (n=0) (n>0)
例3-8 实现如下递归公式,求n!
n ! = { 1 ( n = 0 ) n ( n − 1 ) ( n > 0 ) n!=\begin{cases} 1 & \text{ } (n=0) \\ n(n-1) & \text{ } (n>0) \end{cases} n!={1n(n−1) (n=0) (n>0)
#include
using namespace std;
unsigned fac(int n)
{
unsigned f;
if(n == 0)
f = 1;
else
f = fac(n - 1) * n;
return f;
}
int main()
{
unsigned n;
cout << "Enter a positive integer:";
cin >> n;
unsigned y = fac(n);
cout << n << "! = " << y < Enter a positive integer:8
8! = 40320
例3-9
例3-9:用递归法计算从n个人中选择k个人组成一个委员会的不同组合数
分析:
- 由n个人里选k个人的组合数=由n-1个人里选k个人的组合数+由n-1个人里选k-1个人的组合数
- 当n=k或k=0时,组合数为1
#include
using namespace std;
int comm(int n, int k)
{
if(k > n)
return 0;
else if(n == k || k == 0)
return 1;
else
return comm(n - 1, k) + comm(n - 1, k - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n, k;
cout << "Please enter two integers n and k: ";
cin >> n >> k;
cout << "C(n, k) = " << comm(n, k) << endl;
return 0;
}
Please enter two integers n and k:18 5
C(n, k) = 8568
例3-10
有三根针A、B、C。A针上有N个盘子,大的在下,小的在上
要求把这N个盘子从A针移到C针,在移动过程中可以借助B针
每次只允许移动一个盘,且在移动过程中
在三根针上都保持大盘在下,小盘在上
将N个盘子从A针移到B针上可以分解为三个步骤
①将A上n-1个盘子移到B针上(借助C针)
②把A针上剩下的一个盘子移到C针上
③将n-1个盘子从B针移到C针上(借助A针)
#include
using namespace std;
void move(char src, char dest)
{
cout << src << "-->" << dest <> m;
cout << "the steps to moving " << m << " diskes:" < Enter the number of diskes:3
the steps to moving 3 diskes:
A-->C
A-->B
C-->B
A-->C
B-->A
B-->C
A-->C
函数的参数传递
- 在函数被调用时才分配形参的存储单元
- 实参可以是常量、变量或表达式
- 实参类型必须与形参相符
- 值传递是传递参数值,即单向传递
- 引用传递可以实现双向传递
- 常引用作参数可以保障实参数据的安全
引用类型
-
引用(&)是标识符的别名
-
定义一个引用时,必须同时对它初始化,使它指向一个已存在的对象
-
例如:
int i, j; int &ri = i;//定义int引用ri,并初始化为变量i的引用 j = 10; ri = j;//相当于i = j -
一旦一个引用被初始化后,就不能改为其他对象
-
引用可以作为形参
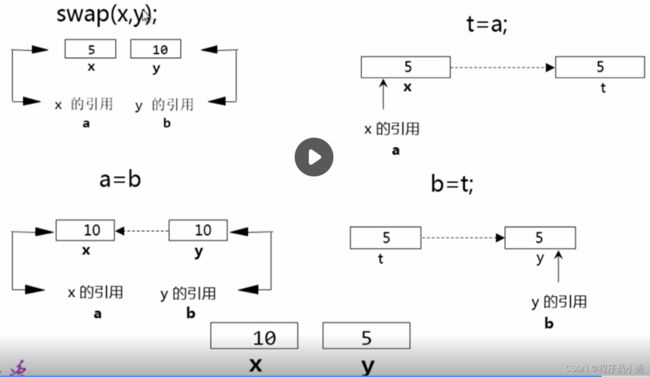
例3-11 输入两个整数并交换(值传递)
#include
using namespace std;
void swap(int a, int b){
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
int main(){
int x = 5, y = 10;
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
swap(x, y);
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
return 0;
}
x = 5 y = 10x = 5 y = 10
#include
using namespace std;
void swap(int& a, int& b){
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
int main(){
int x = 5, y = 10;
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
swap(x, y);
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
return 0;
}
x = 5 y = 10
x = 10 y = 5
含有可变参数的函数
-
C++标准中提供了两种主要的方法
- 如果所有的实参类型相同,可以传递一个名为initializer_list的标准库类型
- 如果实参的类型不同,我们可以编写可变形参的模板(第9章)
-
initializer_list
-
initializer_list是一种标准库类型,用于表示某种特定类型的值的数组
该类型定义在同名的头文件中
-
initializer_list提供的操作
initializer_list的使用方法
-
initializer_list是一个类模板(第9章详细介绍模板)
-
使用模板时,我们需要在模板名字后面跟一对尖括号,括号内给出类型参数。
例如:
initializer_listls//initializer_list的元素类型是string initializer_listli//initializer_list的元素类型是int
-
initializer_list比较特殊的一点是,其对象中的元素永远是常量值
我们无法改变initializer_list对象中的元素值
-
含有initializer_list形参的函数也可以同时拥有其他形参
initializer_list使用举例
- 在编写代码输出程序产生的错误信息时,最好统一用一个函数实现该功能,使得对所有i错误的处理能够整齐划一。然而错误信息的种类不同,调用错误信息输出函数时传递的参数也会各不相同。
- 使用initializer_list编写一个错误信息输出函数,使其可以作用于可变数量的形参。
内联函数
内联函数声明时使用关键字inline
编译时在调用处用函数体进行替换
节省了参数传递
控制转移等开销
注意:
- 内联函数体内不能有循环语句和switch语句
- 内联函数的定义必须出现在内联函数第一次被调用之前
- 对内联函数不能进行异常接口声明
例3-14 内联函数应用举例
#include
using namespace std;
const double PI = 3.14159265358979;
inline double calArea(double radius){
return PI * radius * radius;
}
int main(){
double r = 3.0;
double area = calArea(r);
cout << area << endl;
return 0;
}
constexpr函数
constexpr函数语法规定
- constexpr修饰的函数
在其所有参数都是constexpr时一定返回constexpr
constexpr函数举例
constexpr int get_size(){return 20;}constexpr int foo = get_size();//正确:foo是一个常量表达式
带默认参数值的函数
带默认参数值的函数
可以预先设置默认的参数值,调用时如给出实参,则采用实参值,否则采用预先设置的默认参数值。
例:
int add(int x = 5, int y = 6){
return x + y;
}
int main(){
add(10, 20);//10 + 20
add(10);//10 + 6
add();//5 + 6
}
默认参数值的说明次序
-
有默认参数的形参必须列在形参列表的最右,即默认参数值的右面不能有无默认值的参数;
-
调用时实参与形参的结合次序是从左向右。
-
例;
int add(int x, int y = 5; int z = 6);//正确 int add(int x = 1, int y = 5, int z);//错误 int add(int x = 1, int y, int z = 6);//错误
默认参数值与函数的调用位置
-
如果一个函数有原型声明,且原型声明在定义之前,则默认参数值应在函数原型声明中给出;
如果只有函数的定义,或函数定义在前,
则默认参数值可以在函数定义中给出。
-
例:
int add(int x = 5, int y = 6); //原型声明在前 int main(){ add(); } int add(int x, int y){ //此处不能再指定默认值 return x + y;; }int add(int x = 5, int y = 6); //定义在调用在前 int main(){ add(); }
默认参数值例(3-15)
例3-15计算长方体的体积
-
函数getVolume计算体积
-
有三个形参:length(长)、width(宽)、height(高)
其中width和height带有默认值2和3
-
-
主函数中以不同形式调用getVolume函数
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int getVolume(int length, int width = 2, int height = 3);
int main(){
const int X = 10, Y = 12, Z = 15;
cout << "Some box data is ";
cout << getVolume(X, Y, Z) << endl;
cout << "Some box data is ";
cout << getVolume(X, Y) << endl;
cout << "Some box data is ";
cout << getVolume(X) << endl;
return 0;
}
int getVolume(int length, int width, int height){
cout << setw(5) << length << setw(5) << width << setw(5)
<< height <<'\t';
return length * width * height;
}
函数重载
int abs(int x){
return x < 0 ? -x : x;
}
double abs(double x){
return x < 0 ? -x : x;
}
C++允许功能相近的函数在相同的作用域内以相同函数名声明,从而形成重载。方便使用,便于记忆。
注意事项
- 重载函数的形参必须不同:个数不同或类型不同。
- 编译程序将根据实参和形参的类型及个数的最佳匹配来选择调用哪一个函数。
- 不要将不同功能的函数声明为重载函数,以免出现调用结果的误解、混淆。这样不好:
例3-16重载函数应用举例
编写两个名为sumOfSquare的重载函数,分别求两整数的平方和及两实数的平方和。
#include
using namespace std;
int sumOfSquare(int a, int b){
return a * a + b * b;
}
double sumOfSquare(double a, double b){
return a * a + b * b;
}
int main(){
int m, n;
cout << "Enter two integer: ";
cin >> m >> n;
cout << "Their sum of square: " << sumOfSquare(m, n) <> x >> y;
cout << "Their sum of square: " << sumOfSquare(x, y) < Enter two integer:3 5
Their sum of square: 34
Enter two real number:2.3 5.8
Their sum of square: 38.93
C++系统函数
- C++的系统库中提供了几百个函数可供程序员使用,例如:
- 求平方根函数(sqrt)
- 求绝对值函数(abs)
- 使用系统函数时要包含相应的头文件,例如:
- cmath
例3-17 系统函数应用举例
-
题目:
从键盘输入一个角度值,求出该角度的正弦值、余弦值和正切值。
-
分析:
系统函数中提供了求正弦值、余弦值和正切值的函数:sin()、cos()、tan(),函数的声明在头文件cmath中。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const double PI = 3.1415926535;
int main(){
double angle;
cout << "Please enter an angle: ";
cin >> angle;
double radian = angle * PI /180;
cout << "sin(" << angle << ") = " << sin(radian) <#include
using namespace std;
float Convert(float F){
float C;
C = (F - 32) * 5/9;
return C;
}
int main(){
float F;
cout << "Please input the temperature in fahrenheit: \n";
cin >> F;
cout << "Convert the temperature in celsius:\n";
cout << Convert(F);
return 0;
}
Please input the temperature in fahrenheit:
100
Convert the temperature in celsius:
37.7778
例题二
编写递归函数int fib(int n),在主程序中输入n的值,调用fib函数计算Fibonacci级数。
公式为:
fib(n) = fib(n-1) + fib(n-2), n>2;
fib(1) = fib(2) = 1。
#include
using namespace std;
int fib(int n);
int main(){
int n, answer;
cout << "Enter number: ";
cin >> n;
cout << "\n\n";
answer = fib(n);
cout << answer << "is the " << n << "th Fibonacci number\n";
return 0;
}
int fib(int n){
cout << "Processing fib(" << n << ")...";
if(n < 3){
cout << "Return 1!\n";
return(1);
}else{
cout << "Call fib(" << n - 2 << " and fib(" << n - 1 <<").\n";
return (fib(n - 2) + fib(n - 1));
}
}
Processing fib(2)...Return 1!
1 is the 2th Fibonacci number
Enter number:4
Processing fib(4)...Call fib(2 and fib(3).
Processing fib(2)...Return 1!
Processing fib(3)...Call fib(1 and fib(2).
Processing fib(1)...Return 1!
Processing fib(2)...Return 1!
3 is the 4th Fibonacci number
实验三(下)函数的应用
例题一
分别编写四个同名函数max1,实现函数重载:
可分别求取两个整数,三个整数,两个双精度数,三个双精度数的最大值。
在main()函数中测试函数功能。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int max1(int x, int y);
int max1(int x, int y, int z);
double max1(double x, double y);
double max1(double x, double y, double z);
int main(){
int a, b, c;
double m, n, l;
cout << "Enter int a: ";
cin >> a;
cout << "Enter int b: ";
cin >> b;
cout << "Enter int c: ";
cin >> c;
cout << "\n";
cout << "max of " << a << " and " << b << " is " << max1(a, b) << endl;
cout << "max of " << a << " , " << b <<" and " << c << " is " << max1(a, b, c) << endl;
cout << "\n\n";
cout << "Enter double m: ";
cin >> m;
cout << "Enter double n: ";
cin >> n;
cout << "Enter double l: ";
cin >> l;
cout << "\n";
cout << "max of " << m << " and " << n << " is " << max1(m, n) << endl;
cout << "max of " << m << " , " << n <<" and " << l << " is " << max1(m, n, l) << endl;
}
int max1(int x, int y){
if(x == y) return 0;
else if(x >= y)
return x;
else
return y;
}
int max1(int x, int y, int z){
return max1(max1(x, y),z);
}
double max1(double x, double y){
if(abs(x - y) < 1e-10) return x;
else if(x >= y)
return x;
else
return y;
}
double max1(double x, double y, double z){
return max1(max1(x, y),z);
}
Enter int a:2022
Enter int b:3
Enter int c:13
max of 2022 and 3 is 2022
max of 2022 , 3 and 13 is 2022
Enter double m:2022.0
Enter double n:3.1
Enter double l:13.2
max of 2022 and 3.1 is 2022
max of 2022 , 3.1 and 13.2 is 2022
例题二
在main()函数中提示输入两个整数x、y,使用cin语句得到x、y的值,调用pow(x,y)函数计算x的y次幂的结果,再显示出来。
注意:包含cmath库
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int x, y;
cout << "Enter int x: ";
cin >> x;
cout << "Enter int y: ";
cin >> y;
cout << "\n";
cout << "x = " << x << '\t';
cout << "y = " << y << '\n';
cout << "pow(x, y)= " << pow(x, y);
return 0;
}
Enter int x:9
Enter int y:3
x = 9 y = 3
pow(x, y)= 729