libtorch学习笔记(11)- 保存和加载训练结果
保存和加载训练结果
libtorch/pytorch提供了很好的serialize操作,可以很容把训练结果保存起来,最初我认为训练结果包括网络拓补结构,权重和偏置量等,后来发现应该只包含权重和偏置量,这样一来就需要在这个训练结果中存储一些扩展值,用于下一次重构网络。
保存网络权重和偏置量
torch::nn:Module提供了一个方法save方法,我们构建的网络一般会继承这个类,所以可以调用此方法存储网络权重和偏置量。
torch::serialize::OutputArchive archive;
save(archive);
archive.save_to(szTrainSetStateFilePath);保存其他网络信息
只保存网络权重和偏置量是不够的,下次加载训练结果之前,还是需要先将Module注册好,然后再将网络权重和偏置量加载到当前网络的各个module中。比如对于VGG网络,需要保存哪种类型的VGG网络,需不需要在各个卷积层后面添加batchnorm层,是否需要使用32x32的小图片输入,还是224x224的大图片输入,以及最后输出多少个classes,当然也需要保存当前网络的所支持图片分类的标签。
从下面的代码可以看到如何将这些信息保存到训练结果中:
| 存储的关键字 | 存储内容 |
|---|---|
| VGG_labels | VGG支持的网络标签,比如0: 猫;1:狗 |
| VGG_num_of_class | 最后输出的分类数,缺省是1000 |
| VGG_config | VGG网络类型,每个类型包含两个子类,带batchnorm和不带batchnorm |
| VGG_use_32x32_input | 使用32x32的小图片输入,还是224x224的大图片输入 |
int VGGNet::savenet(const char* szTrainSetStateFilePath)
{
// Save the net state to xxxx.pt and save the labels to xxxx.pt.label
char szLabel[MAX_LABEL_NAME] = { 0 };
try
{
torch::serialize::OutputArchive archive;
// Add nested archive here
c10::List<std::string> label_list;
for (size_t i = 0; i < m_image_labels.size(); i++)
{
memset(szLabel, 0, sizeof(szLabel));
WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0,
m_image_labels[i].c_str(), -1, szLabel, MAX_LABEL_NAME, NULL, NULL);
label_list.emplace_back((const char*)szLabel);
}
torch::IValue value(label_list);
archive.write("VGG_labels", label_list);
// also save the current network configuration
torch::IValue valNumClass(m_num_classes);
archive.write("VGG_num_of_class", valNumClass);
torch::IValue valNetConfig((int64_t)m_VGG_config);
archive.write("VGG_config", valNetConfig);
torch::IValue valUseSmallSize(m_use_32x32_input);
archive.write("VGG_use_32x32_input", valUseSmallSize);
save(archive);
archive.save_to(szTrainSetStateFilePath);
}
catch (...)
{
printf("Failed to save the trained VGG net state.\n");
return -1;
}
printf("Save the training result to %s.\n", szTrainSetStateFilePath);
return 0;
}加载训练结果
从指定的预训练结果文档中,首先把分类标签载入,这就是当前训练好的网络所支持的多少种图像的分类,然后加载网络类型,这个主要用来构建网络拓补图,注册网络层模块,然后就是一些小的配置参数, 比如小图片还是大图片输入,网路最后输入的类数目等等。等到这些信息读取完毕后,就开始加载网络了,当网络的拓补结构,权重和偏置量张量都构建完毕后,再通过torch:nn::Module::load方法加载网络权重和偏置张量到网络各权重层中,这样一来网络就能恢复中训练后的状态,可以做分类、测试,甚至能基于之前训练结果再接着训练。
下面这段代码就是加载和还原上面保存下来的网络:
int VGGNet::loadnet(const char* szPreTrainSetStateFilePath)
{
wchar_t szLabel[MAX_LABEL_NAME] = { 0 };
try
{
torch::serialize::InputArchive archive;
archive.load_from(szPreTrainSetStateFilePath);
torch::IValue value;
if (archive.try_read("VGG_labels", value) && value.isList())
{
auto& label_list = value.toListRef();
for (size_t i = 0; i < label_list.size(); i++)
{
#ifdef _UNICODE
if (MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0,
label_list[i].toStringRef().c_str(), -1, szLabel, MAX_LABEL_NAME) <= 0)
m_image_labels.push_back(_T("Unknown"));
else
m_image_labels.push_back(szLabel);
#else
m_image_labels.push_back(label_list.get(i).toStringRef());
#endif
}
}
archive.read("VGG_num_of_class", value);
m_num_classes = (int)value.toInt();
archive.read("VGG_config", value);
m_VGG_config = (VGG_CONFIG)value.toInt();
m_bEnableBatchNorm = IS_BATCHNORM_ENABLED(m_VGG_config);
archive.read("VGG_use_32x32_input", value);
m_use_32x32_input = value.toBool();
m_imageprocessor.Init(m_use_32x32_input ? 32 : VGG_INPUT_IMG_WIDTH,
m_use_32x32_input ? 32 : VGG_INPUT_IMG_HEIGHT);
// Construct network layout,weight layers and so on
if (_Init() < 0)
{
printf("Failed to initialize VGG network {num_of_classes: %d, VGG config: %d, use_32x32_input: %s}.\n",
m_num_classes, m_VGG_config, m_use_32x32_input?"yes":"no");
return -1;
}
// Load the network state into the constructed neutral network
load(archive);
}
catch (...)
{
printf("Failed to load the pre-trained VGG net state.\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}其他需要注意点
如果要接着之前的网络继续训练,这个时候需要检查之前网络训练结果和当前网络配置是否一致,如果不一致的话,需要停止训练,或者删除之前的训练结果重新训练网络。
代码和测试
对应的测试代码已经放到GitHub,这是一些基本用法:
- 查看训练结构网络状态
VGGNet.exe state I:\catdog.pt
- 训练网络,训练结构存放到I:\catdog.pt,如果已经存在在其基础上继续训练
VGGNet.exe train I:\CatDog I:\catdog.pt --bn -b 64 -l 0.0001 --showloss 10
- 加载网络训练结构,验证测试集,得到准确率
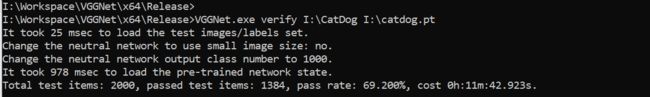
VGGNet.exe verify I:\CatDog I:\catdog.pt
- 网上下来一些图片,加载之前训练的网络,随机测试这个图片类型
VGGNet.exe classify I:\catdog.pt I:\test.png