注意:本文内容基于JDK11,不同版本会有差异
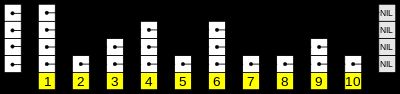
ConcurrentSkipListMap的结构
ConcurrentSkipListMap是以链表(自然排序)的形式进行数据存储的。即在类中通过定义Node内部类来存储单个节点的数据,通过Node中的next属性,来记录链表的下一个节点。同时会对Node中记录的数据创建多级索引。结构总体如图所示:
源码解析
本文以put方法来对ConcurrentSkipListMap进行解析。
ConcurrentSkipListMap会在put方法里调用doPut方法。所以doPut()才是最终的实现
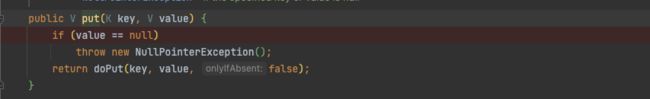
以下动图为doPut方法的动态演示:

对于doPut方法的理解,可以通过调用ConcurrentSkipListMap的put方法。断点调试,配合说明进行理解加深
关键代码说明:
/**
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param onlyIfAbsent 如果已经存在,是否不进行插入(false就是进行插入,true就是不进行插入)
* @return
*/
private V doPut(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent){
if(key == null){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//比较器
Comparator cmp = comparator;
for(;;){
//头索引
Index h;
Node b;
//禁止重排序
VarHandle.acquireFence();
//级别
int levels = 0;
/**
* 在第一次进行put方法时,会对head进行一个初始化操作。head是ConcurrentSkipListMap类的入口。
* 因为是链表结构,所以所有的操作都需要从head开始
* 这里定义了一个null的Node节点,并且把这个Node赋值给Index(Index可以通过查看源码的内部类),即当前索引所对应的节点就是该Node节点
* 这里定义的Node不存储数据,仅仅是作为整个链表的开始,可以配合结构图进行理解
* compareAndSet 原子操作,保证高并发下的原子性。
*/
if( (h = head) == null){
//第一次初始化操作时会进入到这个if里
Node base = new Node(null, null, null);
h = new Index(base, null, null);
b = HEAD.compareAndSet(this, null, h) ? base : null;
}
else{
/**
* 这里包含了两个循环
* while循环是对索引的横向查找,一直找到right为空或者需要插入的key小于已存在的key的索引的位置
* for循环则是进行纵向查找,即查找到多层索引中的最底层索引
* cpr()方法是对两个key的自然排序比较。本质上使用的是compareTo方法进行比较
*/
for (Index q = h, r, d;;){
//通过while循环查找合适的索引位置横行查找
while((r = q.right) != null){
Node p;
K k;
if((p = r.node) == null || (k = p.key) == null || p.val == null){
RIGHT.compareAndSet();
}
else if(cpr(cmp, key, k) > 0){
q = r;
}
else{
break;
}
}
if(( d = q.down) != null){
++levels;
q = d;
}
else{
b = q.node;
break;
}
}
}
if(b != null){
Node z = null;
/**
* 这里通过for循环来查找插入点,即key的值需要大于插入点之前Node的key的值且小于插入点之后Node的key的值
*/
for (;;){
Node n, p;
K k;
V v;
int c;
if( (n = b.next) == null){
if(b.key == null){
cpr(cmp, key, key);
}
c = -1;
}
else if((k = n.key) == null){
break;
}
else if((v = n.val) == null){
c = 1;
}
else if((c = cpr(cmp, key, k)) > 0){
//如果key > k
//那么将n对应的node赋值给b。也就是重置b,将下一个Node的对象赋值到当前的b上
//同时将1赋值给c,然后进入下一次循环
b = n;
}
else {
c = 1;
}
//具体的插入操作就是在这实现的
if(c < 0 && NEXT.compareAndSet(b, n, p = new Node(key, value, n))){
z = p;
//跳出本次循环
break;
}
}
if(z != null){
//源码中使用ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed()方法。
// 但是我们无法使用,所以用这个临时替代。保证不报错
int lr = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt();
//1/4的概率添加索引
if((lr & 0x3) == 0 ){
int hr = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt();
long rnd = hr << 32 | lr & 0xffffffffL;
//添加之前级别需要下降
int skips = levels;
Index x = null;
//for循环表示,当前节点如果需要生成索引,那么需要根据索引的层级来判断生产多少层的索引
for(;;){
x = new Index(z, x,null);
if (rnd >= 0L || --skips < 0){
break;
}
else{
rnd <<= 1;
}
}
//addIndices是具体索引生成的方法
//该方法返回boolean类型的数据,如果索引生成成功,那么返回true,如果索引插入失败,那么返回false。
//这个if判断是代表如果当前索引生成成功,那么在当前索引的基础上再生成上一级索引(对索引再生成一层索引)。
if(addIndices(h, skips, x, cmp) && skips < 0 && head == h){
Index hx = new Index(z, x, null);
//生成头索引
Index nh = new Index(h.node, h, hx);
HEAD.compareAndSet(this, h, nh);
}
if (z.val == null){
}
}
//元素技术进行+1操作
addCount(1L);
return null;
}
}
}
}