利用python进行数据分析—8.数据清洗与准备
文章目录
-
- 引言
- 8.1处理缺失值
-
- 8.1过滤缺失值
- 8.1.2补全缺失值
- 8.2数据转换
-
- 8.2.1删除重复值
- 7.2.2使用函数或者映射进行数据转换
- 8.2.3替代值
- 8.2.4重命名轴索引
- 8.2.5 离散化与分箱
- 8.2.6检测和过滤异常值
- 8.2.7随机排序与随机抽样
- 8.2.8计算指标/哑变量
- 8.3字符串操作
-
- 8.3.1python内建字符串对象方法
- 8.3.2正则表达式
- 8.3.3 pandas中的向量化字符串函数
引言
在进行数据分析与建模的过程中,大量的时间都花在数据的准备上:加载、清洗、转换与重新排列。
8.1处理缺失值
pandas中使用np.nan来表示缺失值,python内建None值在对象数组中也被当成缺失值。
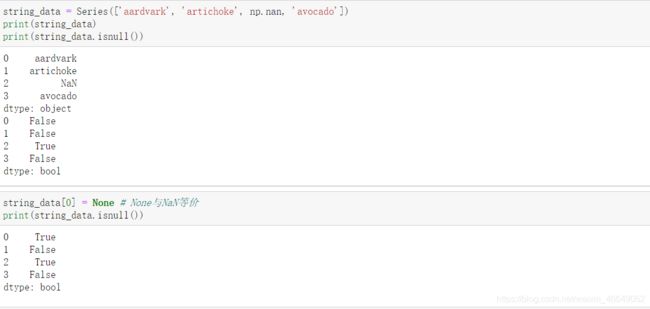
处理缺失值的处理方法:

8.1过滤缺失值
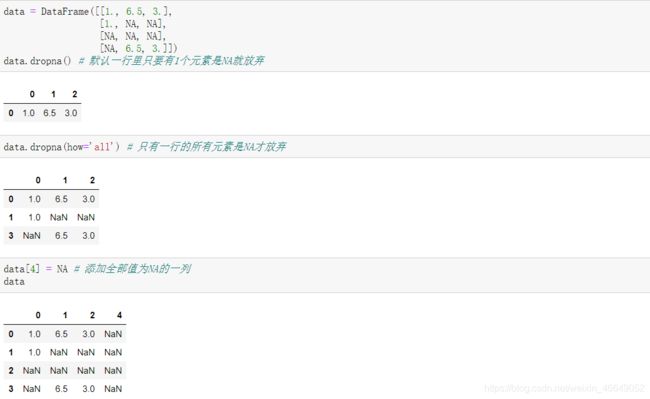
可以使用isnull()方法结合布尔值索引来手动过滤缺失值,同时,dropna在过滤缺失值中也是非常有用的。
在Series上使用dropna会返回Series中所有的非空数据及其索引值。
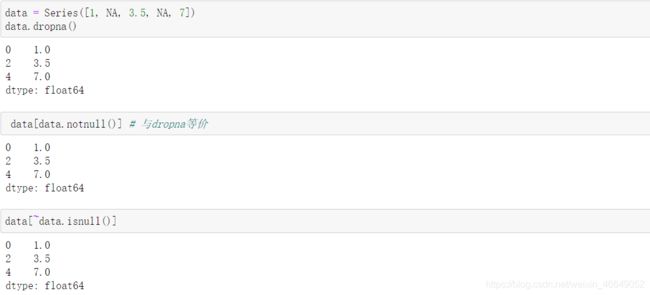
在DataFrame上使用dropna时,默认情况下会删除包含缺失值的行。该方法官方文档如下:
pd.DataFrame.dropna(
self,
axis=0,
how='any',
thresh=None,
subset=None,
inplace=False,
)
Docstring:
Remove missing values.
See the :ref:`User Guide <missing_data>` for more on which values are
considered missing, and how to work with missing data.
Parameters
----------
axis : {0 or 'index', 1 or 'columns'}, default 0
Determine if rows or columns which contain missing values are
removed.
* 0, or 'index' : Drop rows which contain missing values.
* 1, or 'columns' : Drop columns which contain missing value.
.. versionchanged:: 1.0.0
Pass tuple or list to drop on multiple axes.
Only a single axis is allowed.
how : {'any', 'all'}, default 'any'
Determine if row or column is removed from DataFrame, when we have
at least one NA or all NA.
* 'any' : If any NA values are present, drop that row or column.
* 'all' : If all values are NA, drop that row or column.
thresh : int, optional
Require that many non-NA values.
subset : array-like, optional
Labels along other axis to consider, e.g. if you are dropping rows
these would be a list of columns to include.
inplace : bool, default False
If True, do operation inplace and return None.
Returns
-------
DataFrame
DataFrame with NA entries dropped from it.
See Also
--------
DataFrame.isna: Indicate missing values.
DataFrame.notna : Indicate existing (non-missing) values.
DataFrame.fillna : Replace missing values.
Series.dropna : Drop missing values.
Index.dropna : Drop missing indices.
Examples
--------
>>> df = pd.DataFrame({"name": ['Alfred', 'Batman', 'Catwoman'],
... "toy": [np.nan, 'Batmobile', 'Bullwhip'],
... "born": [pd.NaT, pd.Timestamp("1940-04-25"),
... pd.NaT]})
>>> df
name toy born
0 Alfred NaN NaT
1 Batman Batmobile 1940-04-25
2 Catwoman Bullwhip NaT
Drop the rows where at least one element is missing.
>>> df.dropna()
name toy born
1 Batman Batmobile 1940-04-25
Drop the columns where at least one element is missing.
>>> df.dropna(axis='columns')
name
0 Alfred
1 Batman
2 Catwoman
Drop the rows where all elements are missing.
>>> df.dropna(how='all')
name toy born
0 Alfred NaN NaT
1 Batman Batmobile 1940-04-25
2 Catwoman Bullwhip NaT
Keep only the rows with at least 2 non-NA values.
>>> df.dropna(thresh=2)
name toy born
1 Batman Batmobile 1940-04-25
2 Catwoman Bullwhip NaT
Define in which columns to look for missing values.
>>> df.dropna(subset=['name', 'born'])
name toy born
1 Batman Batmobile 1940-04-25
Keep the DataFrame with valid entries in the same variable.
>>> df.dropna(inplace=True)
>>> df
name toy born
1 Batman Batmobile 1940-04-25
总结如下:
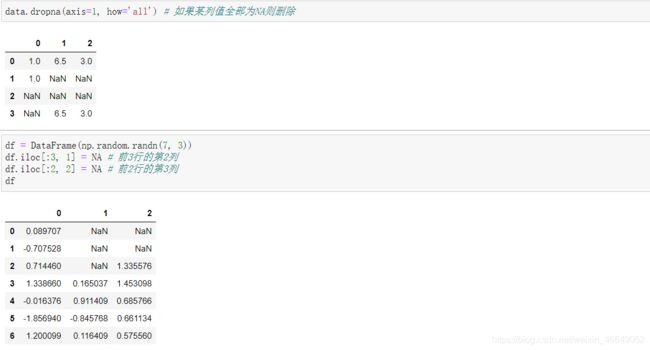
axis参数:axis=0时,删除的是行;axis=1时,删除的是列
how参数:how='any’时,行或列中有一个缺失值就删除;how=‘all’,行或列中都是缺失值才删除
thresh参数:保留至少有几个不为缺失值的行或列
subset参数:与axis参数对应的另一个轴的列表
inplace参数:如果为True,则就地执行操作并返回None
8.1.2补全缺失值
大多数情况下,主要使用fillna方法来补全缺失值。
pd.DataFrame.fillna(
self,
value=None,
method=None,
axis=None,
inplace=False,
limit=None,
downcast=None,
)
method=‘ffill’,前向填充
method=‘bfill’,后向填充
使用常数来填充缺失值

使用字典来填充缺失值,为不同的列设定不同的填充值

前向填充,填充范围为2

使用中值或者中位数来填充
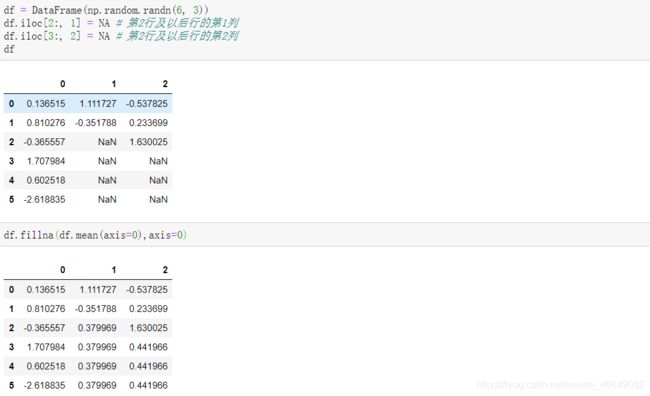

8.2数据转换
8.2.1删除重复值
由于各种原因,DataFrame中有时会出现重复行。这是要用到DataFrame中的两个方法duplicated()和drop_duplicates()方法。
pd.DataFrame.duplicated(
self,
subset: Union[Hashable, Sequence[Hashable], NoneType] = None,
keep: Union[str, bool] = 'first',
) -> 'Series'
Docstring:
Return boolean Series denoting duplicate rows.
Considering certain columns is optional.
Parameters
----------
subset : column label or sequence of labels, optional
Only consider certain columns for identifying duplicates, by
default use all of the columns.
keep : {'first', 'last', False}, default 'first'
Determines which duplicates (if any) to mark.
- ``first`` : Mark duplicates as ``True`` except for the first occurrence.
- ``last`` : Mark duplicates as ``True`` except for the last occurrence.
- False : Mark all duplicates as ``True``.
Returns
-------
Series
pd.DataFrame.drop_duplicates(
self,
subset: Union[Hashable, Sequence[Hashable], NoneType] = None,
keep: Union[str, bool] = 'first',
inplace: bool = False,
ignore_index: bool = False,
) -> Union[ForwardRef('DataFrame'), NoneType]
Docstring:
Return DataFrame with duplicate rows removed.
Considering certain columns is optional. Indexes, including time indexes
are ignored.
Parameters
----------
subset : column label or sequence of labels, optional
Only consider certain columns for identifying duplicates, by
default use all of the columns.
keep : {'first', 'last', False}, default 'first'
Determines which duplicates (if any) to keep.
- ``first`` : Drop duplicates except for the first occurrence.
- ``last`` : Drop duplicates except for the last occurrence.
- False : Drop all duplicates.
inplace : bool, default False
Whether to drop duplicates in place or to return a copy.
ignore_index : bool, default False
If True, the resulting axis will be labeled 0, 1, …, n - 1.
.. versionadded:: 1.0.0
Returns
-------
DataFrame
DataFrame with duplicates removed or None if ``inplace=True``.
duplicated()方法返回一个布尔值Series,这个布尔值Series反映每一行是否存在重复的情况。
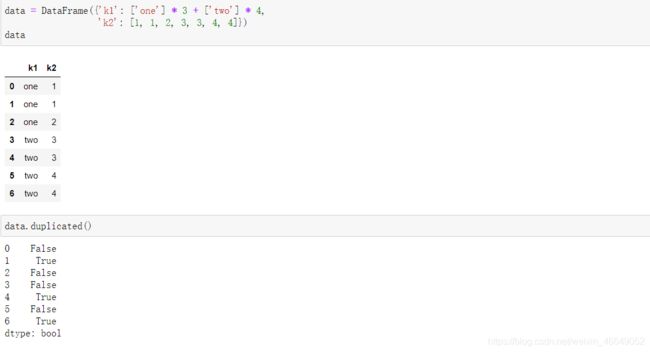
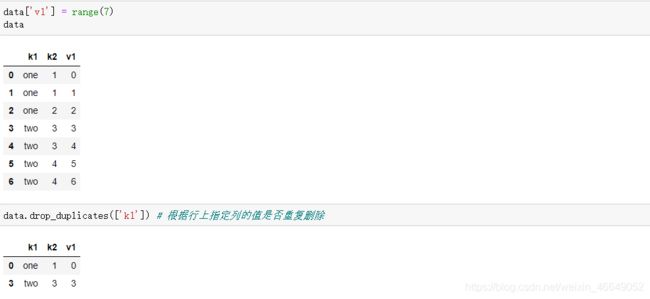
drop_duplicates()方法返回的是DataFrame,返回的是duplicated()方法中返回的布尔值Series中为False的部分。

subset参数为column label or sequence of labels,用来控制基于哪些列来操作
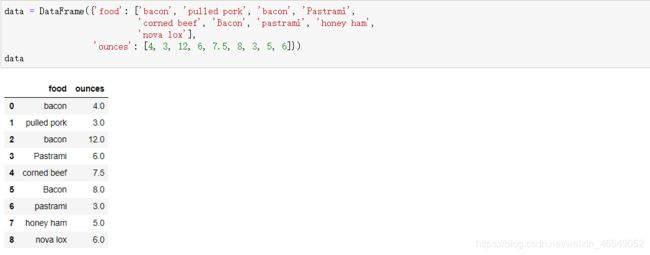
7.2.2使用函数或者映射进行数据转换
使用map方法可以便捷执行按元素转换及其他数据清洗相关操作。Series中的map方法接受一个函数或者一个包含映射关系的字典型对象。
map方法接受包含映射关系的字典型对象
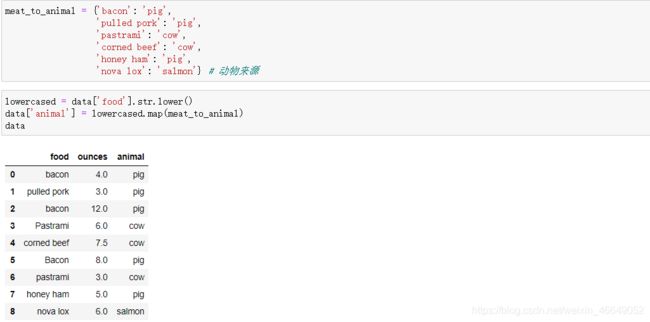
map方法接受函数
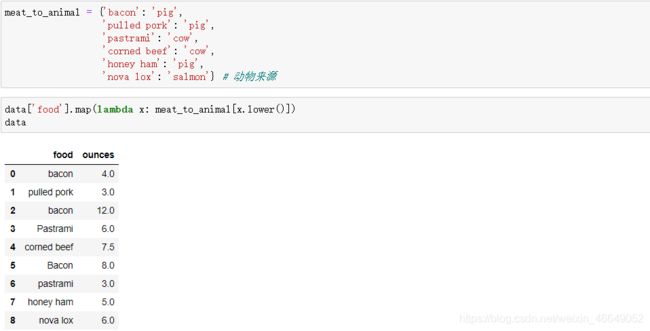
8.2.3替代值
replace方法用于动态的替换值
pd.DataFrame.replace(
self,
to_replace=None,
value=None,
inplace=False,
limit=None,
regex=False,
method='pad',
)
常用参数:
- 将to_replace 参数中的值替换为value参数中的值。
- limit参数指定向前或者向后填充的最大尺寸
- method参数指定填充的策略
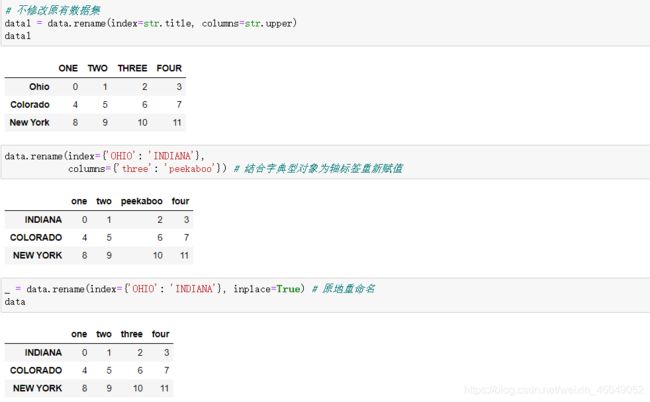
8.2.4重命名轴索引
与Series中的map方法一样,也可以通过函数或者字典映射对轴标签进行类似的转换,生成新的且带有不同标签的对象。还有rename方法使用更灵活
rename方法参数:
pd.DataFrame.rename(
self,
mapper=None,
index=None,
columns=None,
axis=None,
copy=True,
inplace=False,
level=None,
errors='ignore',
)
8.2.5 离散化与分箱
连续值经常需要离散化,或者分箱进行分析。其中会用到pd.cut方法,pd.qcut方法
pd.cut(
x,
bins,
right: bool = True,
labels=None,
retbins: bool = False,
precision: int = 3,
include_lowest: bool = False,
duplicates: str = 'raise',
)
参数描述:
x : 输入数组,维度必须是一维的
bins:
如果为int,则为等宽箱子的数量,“x”的范围在每一侧扩展了0.1%,以包括x的最小值和x的最大值
如果为sequence,则为箱子划分的显示箱边。[18, 25, 35, 60, 100] => [(18, 25] < (25, 35] < (35, 60] < (60, 100]]
如果为IntervalIndex,则类似于这个东西 [(18, 25] < (25, 35] < (35, 60] < (60, 100]]
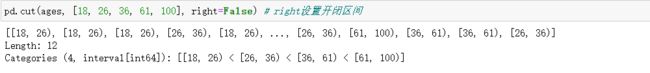
right:该参数控制左右区间哪侧是开的哪侧是闭的
labels:传递一个列表或者数组来自定义箱名
precision:用来限制十进制精度,precision=3,表示将十进制精度限制到3位
include_lowest:用来控制第一个区间是否包含左区间
duplicates : {default ‘raise’, ‘drop’}
如果bin边不是唯一的,引发ValueError或删除non-uniques

bins为int时,等距分箱
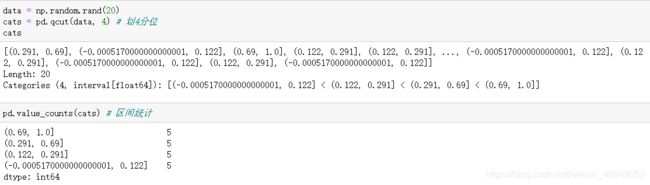
right参数控制哪一边是封闭的
label参数传递一个列表或者数组来自定义箱名

pd.qcut方法是一个与分箱模切相关的函数,它是基于样本分位数进行分箱,取决于数据的分布
pd.qcut方法可以获得等长的分箱

pd.qcut方法也可以传入自定义的分位数

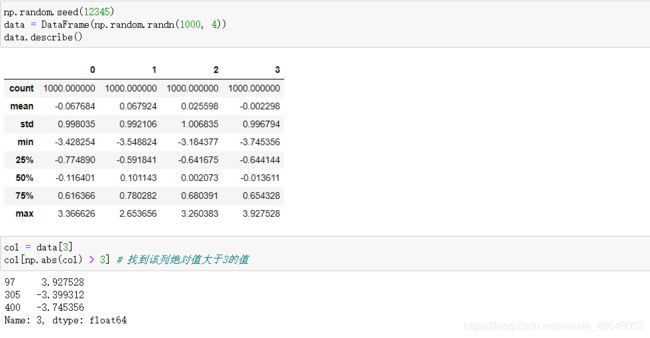
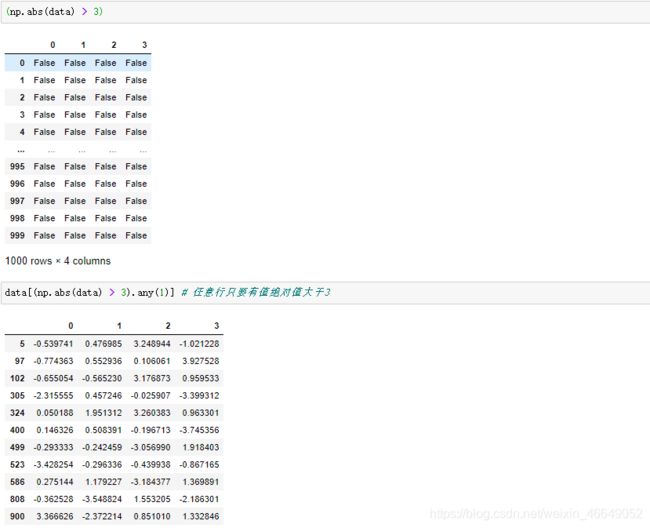
8.2.6检测和过滤异常值
np.sign(data)根据数据中的值的正负生成1和-1的数值
8.2.7随机排序与随机抽样
使用np.random.permutation对DataFrame中的Series或行进行随机排序,利用基于iloc索引或take函数进行随机抽样。np.random.permutation根据轴长度产生一个表示新顺序的整数数组。或者直接利用DataFrame.sample方法进行随机抽样。

8.2.8计算指标/哑变量
将类别型变量转换为哑变量是一种常见操作。即如果DataFrame中的一列有k个不同的值,则可以衍生k列值为0和1的矩阵
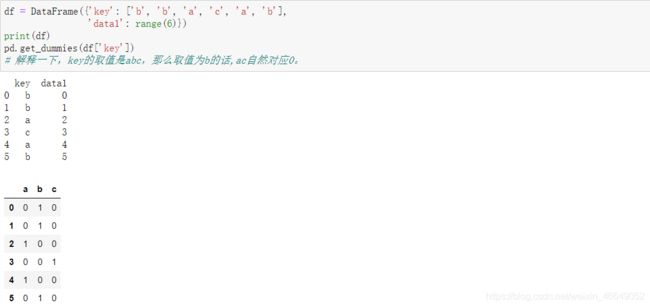
pd.get_dummies中有一个前缀参数prefix,可以在转换后的列上加上前缀

如果一行属于多个类别,则情况略微复杂,需要使用多成员构建指标变量

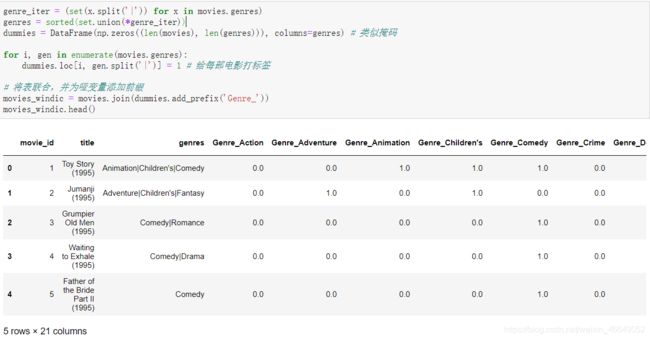
对于更大的数据,上面使用多成员构建指标变量并不是特别快的。
更好的方法是:写一个直接将数据写为Numpy的数组的底层函数,然后将结果封装进DataFrame中(不懂,有懂的麻烦评论区留言)
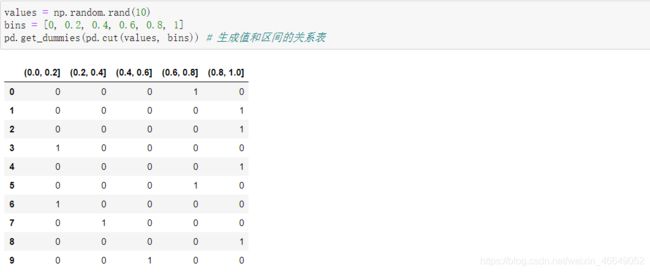
将pd.get_dummies与pd.cut结合使用,即将分箱后再哑编码
8.3字符串操作
pandas允许将字符串和正则表达式简洁地应用到整个数据数组上,此外还能处理缺失数据带来的困扰
8.3.1python内建字符串对象方法
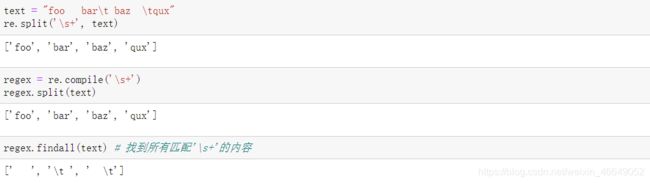
8.3.2正则表达式
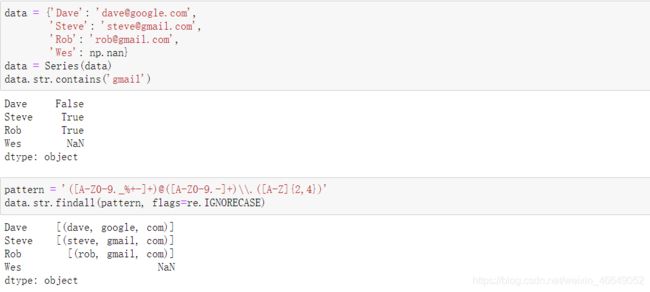
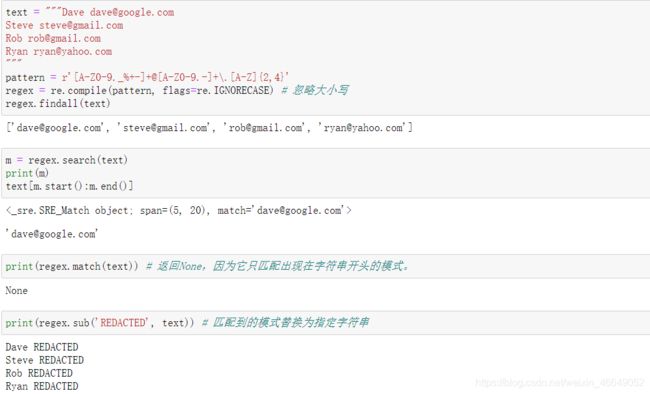
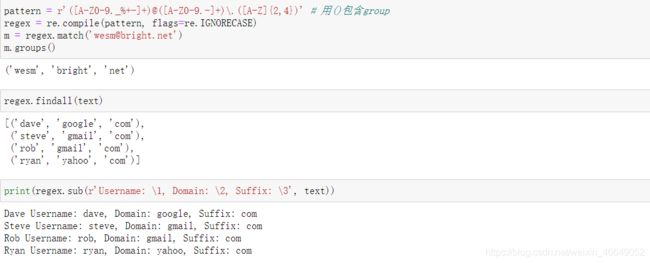
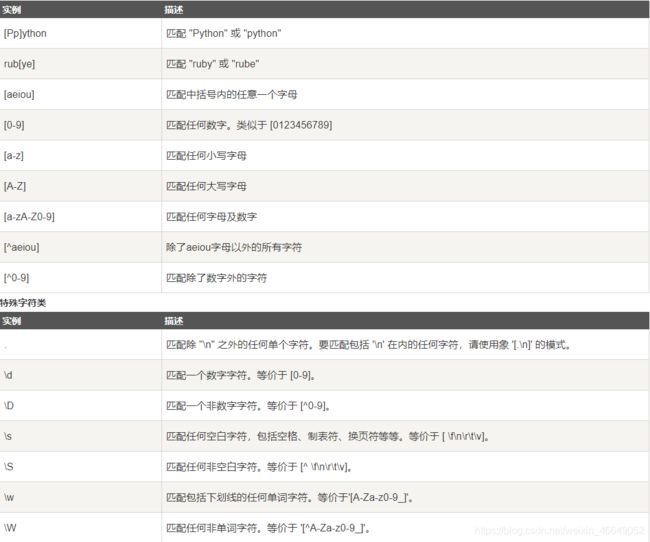
正则表达式提供了一种在文本中灵活查找或匹配的字符串模式的方法。python内建模块是将正则表达式应用于字符串上的库。
正则表达式方法:具体使用可参考这个网址

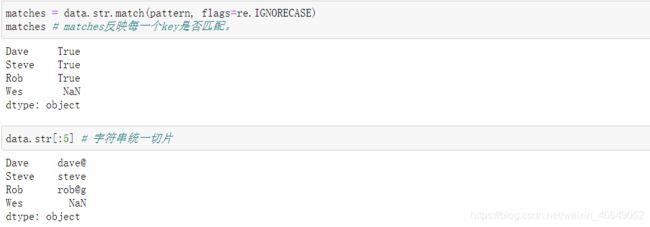
8.3.3 pandas中的向量化字符串函数
清理杂乱的数据集用于分析,通常需要大量的字符串处理和正则化,包含字符串的列有时会有缺失数据,使事情变得复杂。
向量化字符串列表有: