A*算法(超级详细讲解,附有举例的详细手写步骤)
背景:项目需要接触此算法,以下是一些自学成果,如有不足之处,欢迎指出,必虚心接受。做了一份PPT来汇报,此处直接使用自己PPT的截图。部分图片来源网络,如有侵权立马删除,以下博文仅作为学习笔记。后期又新增了完整PPT。A*算法完整PTT_dujuancao11的博客-CSDN博客
目录
A*寻路算法
A*算法解决什么问题
A*算法的基本原理
A*算法的详细原理
A*算法的详细原理之定义
A*算法的详细原理之初始设定
A*算法的详细原理之寻路原理
A*算法的详细原理之结束条件
A*算法的寻路详细步骤
A*算法的举例说明
A*算法的伪代码
A*算法的定义伪代码 (C++)
A*算法的寻路伪代码(C++)
Python+PyQt代码实现
代码内容(可运行)
运行结果
可执行文件
拓展
Dijkstra算法和A*算法的比较
A*寻路算法
A*算法解决什么问题
A*算法的基本原理
A*算法的详细原理
A*算法的详细原理之定义
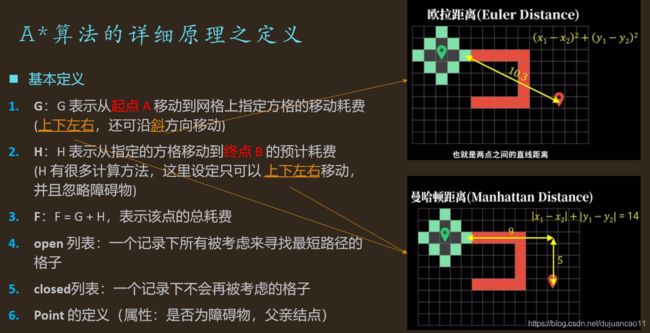 A*算法的详细原理之初始设定
A*算法的详细原理之初始设定
 A*算法的详细原理之寻路原理
A*算法的详细原理之寻路原理
A*算法的详细原理之结束条件
A*算法的寻路详细步骤
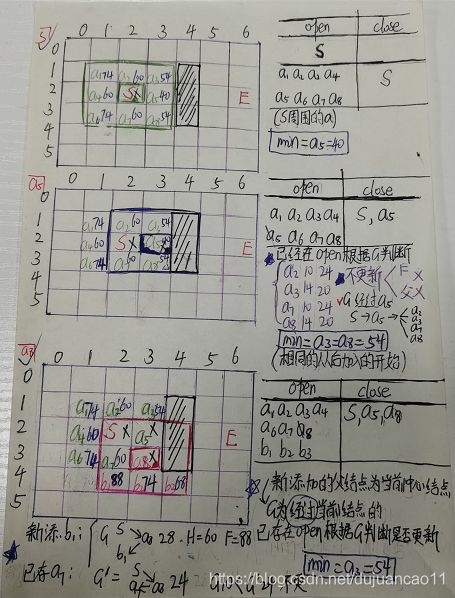
S(start)起点 E(End)终点
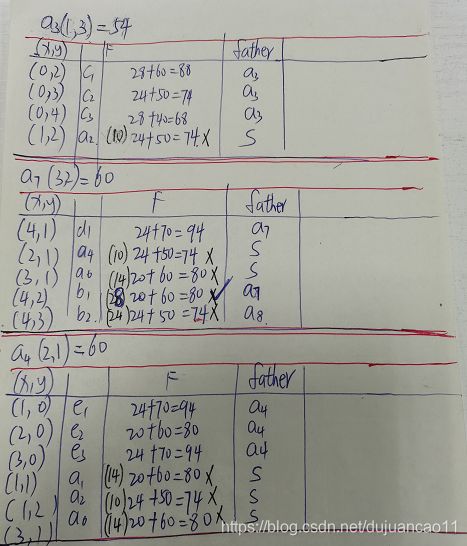
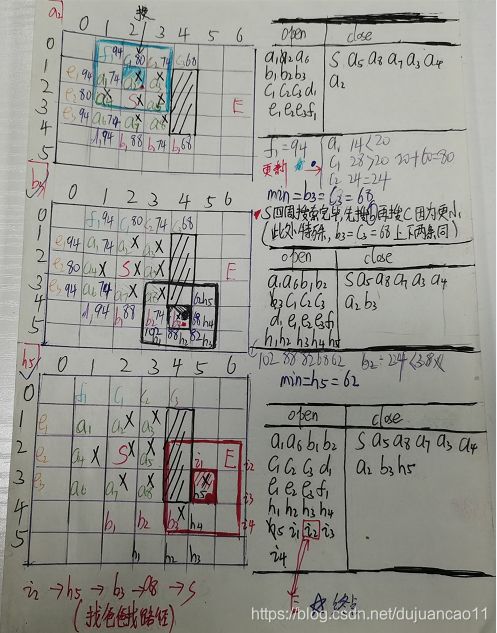
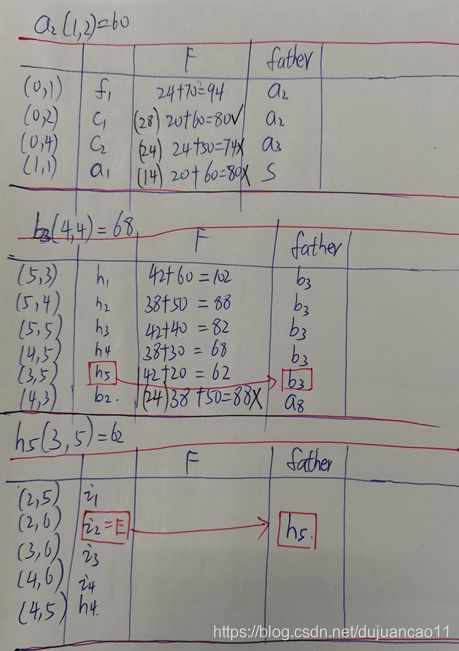
A*算法的举例说明
如果还不懂的话,可以参考我手写的计算步骤,再不懂可以私信我。(手稿字有点丑)
A*算法的伪代码
A*算法的定义伪代码 (C++)
int open_list;//一个记录下所有被考虑来寻找最短路径的格子
int close_list; //一个记录下不会再被考虑的格子
typedef struct point{
bool Is_Wall;
struct point* father;//父节点
int G;// 表示从起点 A 移动到网格上指定方格的移动耗费 (上下左右,还可沿斜方向移动)
int old_G;//旧G 第一次:从起点 A 直接移动到 A 四周方格的移动耗费 ;上次更新得到的G
int new_G; //新G 从起点 A 经过当前搜索中心点到其四周指定点的移动耗费
int H;//表示从指定的方格移动到终点 B 的预计耗费 (H 有很多计算方法, 这里我们设定只可以上下左右移动)
int F=G+H;//表示该点的总耗费
}Point;
point* start_point;
point* end_point;
point* min_point;
point* now_point; A*算法的寻路伪代码(C++)
//FindPath
do{
//确定中心搜索点,上一个中心点关闭,新的中心点开启
查找:Find the minimumm "point" of "F" from the "open_list" center;
"now_point" = "min_point";//minimumm point
"now_point"添加到"close_list";
//新中心点的周围点开启,新中心点关闭
循环遍历:"now_point"相邻的周围8格"s_now_point"中的每一个;
//这一块它指的就是now_point周围8点当前搜索点 s_now_point,为了简单直接用它表示
if (它不可通过||它已经在"close_list"中){
什么也不做;
} else if (它不在开启列表中){
把它添加进"open_list";
把"now_point"作为这它的"father",计算它的"F","G","H";
}else if (它已经在开启列表中){//通过G来判断是否需要更新
if (new_G < old_G){
更新它的"father"为当前中心搜索点"now_point";
更新它的"G"与"F" ;
} else{
不更新,保持原来的"father", "G"与"F" ;
}
}
} while(目标格"end_point"已经在"open_list"||"open_list"==NULL)
//存在路径:目标格"end_point"已经在"open_list"
//不存在路径: "open_list"==NULL,搜索了所有可能的点
Python+PyQt代码实现
代码内容(可运行)
import time,sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QDialogButtonBox,QDialog,QMainWindow,QGridLayout,QTextEdit,QLineEdit,QWidget, QMessageBox, QApplication,QLabel,QPushButton,QHBoxLayout,QVBoxLayout
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt,QTimer,QObject,pyqtSignal,QBasicTimer
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter, QColor, QFont,QPen
import json
class config:
WIDTH=20#地图列数
HEIGHT=20#地图行数
blockLength=30#绘制画面时每一个节点方块的边长
class point:#点类(每一个唯一坐标只有对应的一个实例)
_list=[]#储存所有的point类实例
_tag=True#标记最新创建的实例是否为_list中的已有的实例,True表示不是已有实例
def __new__(cls,x,y):#重写new方法实现对于同样的坐标只有唯一的一个实例
for i in point._list:
if i.x==x and i.y==y:
point._tag=False
return i
nt=super(point,cls).__new__(cls)
point._list.append(nt)
return nt
def __init__(self,x,y):
if point._tag:
self.x=x
self.y=y
self.father=None
self.F=0#当前点的评分 F=G+H
self.G=0#起点到当前节点所花费的消耗
self.cost=0#父节点到此节点的消耗
else:
point._tag=True
@classmethod
def clear(cls):#clear方法,每次搜索结束后,将所有点数据清除,以便进行下一次搜索的时候点数据不会冲突。
point._list=[]
def __eq__(self,T):#重写==运算以便实现point类的in运算
if type(self)==type(T):
return (self.x,self.y)==(T.x,T.y)
else:
return False
def __str__(self):
return'(%d,%d)[F=%d,G=%d,cost=%d][father:(%s)]'%(self.x,self.y,self.F,self.G,self.cost,str((self.father.x,self.father.y)) if self.father!=None else 'null')
class A_Search:#核心部分,寻路类
def __init__(self,arg_start,arg_end,arg_map):
self.start=arg_start#储存此次搜索的开始点
self.end=arg_end#储存此次搜索的目的点
self.Map=arg_map#一个二维数组,为此次搜索的地图引用
self.open=[]#开放列表:储存即将被搜索的节点
self.close=[]#关闭列表:储存已经搜索过的节点
self.result=[]#当计算完成后,将最终得到的路径写入到此属性中
self.count=0#记录此次搜索所搜索过的节点数
self.useTime=0#记录此次搜索花费的时间--在此演示中无意义,因为process方法变成了一个逐步处理的生成器,统计时间无意义。
#开始进行初始数据处理
self.open.append(arg_start)
def cal_F(self,loc):
print('计算值:',loc)
G=loc.father.G+loc.cost
H=self.getEstimate(loc)
F=G+H
print("F=%d G=%d H=%d"%(F,G,H))
return {'G':G,'H':H,'F':F}
def F_Min(self):#搜索open列表中F值最小的点并将其返回,同时判断open列表是否为空,为空则代表搜索失败
if len(self.open)<=0:
return None
t=self.open[0]
for i in self.open:
if i.F=config.HEIGHT or i[1]<0 or i[1]>=config.WIDTH:
l.remove(i)
nl=[]
for i in l:
if self.Map[i[0]][i[1]]==0:
nt=point(i[0],i[1])
nt.cost=i[2]
nl.append(nt)
return nl
def addToOpen(self,l,father):#此次判断的点周围的可通行点加入到open列表中,如此点已经在open列表中则对其进行判断,如果此次路径得到的F值较之之前的F值更小,则将其父节点更新为此次判断的点,同时更新F、G值。
for i in l:
if i not in self.open:
if i not in self.close:
i.father=father
self.open.append(i)
r=self.cal_F(i)
i.G=r['G']
i.F=r['F']
else:
tf=i.father
i.father=father
r=self.cal_F(i)
if i.F>r['F']:
i.G=r['G']
i.F=r['F']
# i.father=father
else:
i.father=tf
def getEstimate(self,loc):#H :从点loc移动到终点的预估花费
return (abs(loc.x-self.end.x)+abs(loc.y-self.end.y))*10
def DisplayPath(self):#在此演示中无意义
print('搜索花费的时间:%.2fs.迭代次数%d,路径长度:%d'%(self.useTime,self.count,len(self.result)))
if self.result!=None:
for i in self.result:
self.Map[i.x][i.y]=8
for i in self.Map:
for j in i:
if j==0:
print('%s'%'□',end='')
elif j==1:
print('%s'%'▽',end='')
elif j==8:
print('%s'%'★',end='')
print('')
else:
print('搜索失败,无可通行路径')
def process(self):#使用yield将process方法变成一个生成器,可以逐步的对搜索过程进行处理并返回关键数据
while True:
self.count+=1
tar=self.F_Min()#先获取open列表中F值最低的点tar
if tar==None:
self.result=None
self.count=-1
break
else:
aroundP=self.getAroundPoint(tar)#获取tar周围的可用点列表aroundP
self.addToOpen(aroundP,tar)#把aroundP加入到open列表中并更新F值以及设定父节点
self.open.remove(tar)#将tar从open列表中移除
self.close.append(tar)#已经迭代过的节点tar放入close列表中
if self.end in self.open:#判断终点是否已经处于open列表中
e=self.end
self.result.append(e)
while True:
e=e.father
if e==None:
break
self.result.append(e)
yield (tar,self.open,self.close)
break
# self.repaint()
# print('返回')
yield (tar,self.open,self.close)
time.sleep(5)#暂停
self.useTime=time2-time1
class GameBoard(QMainWindow):#可视化类,pyqt5进行编写。
def __init__(self):
print('初始化地图...')
self.Map=[]
for i in range(config.HEIGHT):
col=[]
for j in range(config.WIDTH):
col.append(0)
self.Map.append(col)
self.startPoint=None
self.endPoint=None
self.search=None
self.centerTimer=None
self.yi=None
self.special=None
self.displayFlush=False
super().__init__()
print('初始化UI...')
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
#开始初始化UI部分
#创建UI控件
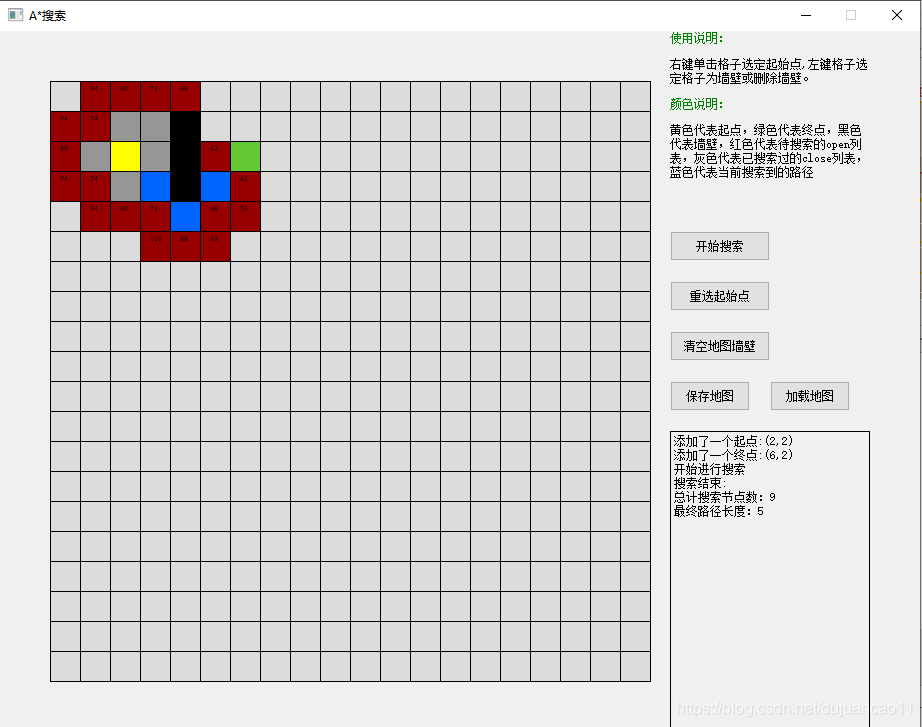
self.label_tips=QLabel("使用说明:
右键单击格子选定起始点,左键格子选定格子为墙壁或删除墙壁。\n颜色说明:
\n黄色代表起点,绿色代表终点,黑色代表墙壁,红色代表待搜索的open列表,灰色代表已搜索过的close列表,蓝色代表当前搜索到的路径",self)
self.label_display=QLabel("",self)
self.button_start=QPushButton("开始搜索",self)
self.button_clearSE=QPushButton("重选起始点",self)
self.button_clearWall=QPushButton("清空地图墙壁",self)
self.button_saveMap=QPushButton("保存地图",self)
self.button_loadMap=QPushButton("加载地图",self)
#设置控件属性
self.label_tips.setWordWrap(True)
self.label_display.setWordWrap(True)
#设置控件样式
self.label_display.setStyleSheet("border:1px solid black")
self.label_display.setAlignment(Qt.AlignLeft)
self.label_display.setAlignment(Qt.AlignTop)
#设置控件的尺寸和位置
self.label_tips.resize(200,150)
self.button_saveMap.resize(80,30)
self.button_loadMap.resize(80,30)
self.label_display.resize(200,300)
self.label_tips.move(100+(config.WIDTH-1)*config.blockLength,0)
self.label_display.move(100+(config.WIDTH-1)*config.blockLength,400)
self.button_start.move(100+(config.WIDTH-1)*config.blockLength,200)
self.button_clearSE.move(100+(config.WIDTH-1)*config.blockLength,250)
self.button_clearWall.move(100+(config.WIDTH-1)*config.blockLength,300)
self.button_saveMap.move(100+(config.WIDTH-1)*config.blockLength,350)
self.button_loadMap.move(200+(config.WIDTH-1)*config.blockLength,350)
#给控件绑定事件
self.button_start.clicked.connect(self.button_StartEvent)
self.button_clearSE.clicked.connect(self.button_Clear)
self.button_clearWall.clicked.connect(self.button_Clear)
self.button_saveMap.clicked.connect(self.button_SaveMap)
self.button_loadMap.clicked.connect(self.button_LoadMap)
#UI初始化完成
self.setGeometry(0, 0, 150+(config.WIDTH*config.blockLength-config.blockLength)+200, 150+(config.HEIGHT*config.blockLength-config.blockLength))
self.setMinimumSize(150+(config.WIDTH*config.blockLength-config.blockLength)+200, 150+(config.HEIGHT*config.blockLength-config.blockLength))
self.setMaximumSize(150+(config.WIDTH*config.blockLength-config.blockLength)+200, 150+(config.HEIGHT*config.blockLength-config.blockLength))
self.setWindowTitle('A*搜索')
self.show()
def addDisplayText(self,text):
if self.displayFlush:
self.label_display.setText(text+'\n')
self.displayFlush=False
else:
self.label_display.setText(self.label_display.text()+text+'\n')
def mousePressEvent(self,event):
x,y=event.x()-50,event.y()-50
x=x//config.blockLength
y=y//config.blockLength
if x>=0 and x=0 and ymap.txt')
# else:
# self.addDisplayText('地图保存失败')
def button_LoadMap(self):
try:
with open('map.txt','r') as f:
self.Map=json.loads(f.read())
config.HEIGHT=len(self.Map)
config.WIDTH=len(self.Map[0])
self.addDisplayText('地图加载成功')
self.repaint()
except Exception as e:
print('失败',e,type(e))
if type(e)==FileNotFoundError:
self.addDisplayText('地图加载失败:地图文件不存在')
elif type(e)==json.decoder.JSONDecodeError:
self.addDisplayText('地图加载失败:错误的地图文件')
def button_Clear(self):
sender=self.sender()
print(self.button_clearSE,type(self.button_clearSE))
if sender==self.button_clearSE:
self.startPoint=None
self.endPoint=None
self.repaint()
self.addDisplayText('清空起始点')
elif sender==self.button_clearWall:
for i in range(len(self.Map)):
for j in range(len(self.Map[i])):
self.Map[i][j]=0
self.repaint()
self.addDisplayText('清空所有墙壁')
def paintEvent(self, event):
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawBoard(event,qp)
qp.end()
def drawBoard(self, event, qp):
self.drawMap(qp)
def drawMap(self,qp):#画面绘制方法,每次地图有所改动都将重绘
time1=time.time()
if self.search!=None:
if self.special!=None:
e=self.special[0]
path=[e]
while True:
e=e.father
if e!=None:
path.append(e)
else:
break
else:
path=None
pen=QPen(QColor(0,0,0),1,Qt.SolidLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
for i in range(len(self.Map)):
for j in range(len(self.Map[i])):
wordTag=False
if i==self.search.start.x and j==self.search.start.y:
qp.setBrush(QColor(255,255,0))
elif i==self.search.end.x and j==self.search.end.y:
qp.setBrush(QColor(100,200,50))
else:
if self.Map[i][j]==0:
tagx=True
if path:
for k in path:
if k.x==i and k.y==j:
tagx=False
qp.setBrush(QColor(0,100,255))
if tagx:
if self.special!=None:
if i==self.special[0].x and j==self.special[0].y:
qp.setBrush(QColor(0,255,0))
else:
tag=True
for k in self.special[1]:
if k.x==i and k.y==j:
tag=False
wordTag=True
word=str(k.F)
qp.setBrush(QColor(150,0,0))
break
else:
qp.setBrush(QColor(220,220,220))
if tag:
for k in self.special[2]:
if k.x==i and k.y==j:
qp.setBrush(QColor(150,150,150))
break
else:
qp.setBrush(QColor(220,220,220))
else:
qp.setBrush(QColor(220,220,220))
elif self.Map[i][j]==1:
qp.setBrush(QColor(0,0,0))
else:
qp.setBrush(QColor(255,0,0))
qp.drawRect(50+j*config.blockLength,50+i*config.blockLength,config.blockLength,config.blockLength)
if wordTag:
qp.setFont(QFont('楷体',5,QFont.Light))
qp.drawText(50+10+j*config.blockLength,50+10+i*config.blockLength,word)
wordTag=False
#time.sleep(20)
else:
for i in range(len(self.Map)):
for j in range(len(self.Map[i])):
if (j,i)==self.startPoint:
qp.setBrush(QColor(255,255,0))
elif (j,i)==self.endPoint:
qp.setBrush(QColor(100,200,50))
else:
if self.Map[i][j]==0:
qp.setBrush(QColor(220,220,220))
elif self.Map[i][j]==1:
qp.setBrush(QColor(0,0,0))
else:
qp.setBrush(QColor(255,0,0))
qp.drawRect(50+j*config.blockLength,50+i*config.blockLength,config.blockLength,config.blockLength)
time2=time.time()
#time.sleep(20)
# print('绘制时间:',time2-time1)
def timerEvent(self,e):
try:
data=next(self.yi)
except Exception as e:
self.addDisplayText('搜索结束:')
print('搜索结束!')
if self.search.result==None:
self.addDisplayText('未找到可行路径')
print('搜索结束!')
else:
self.addDisplayText('总计搜索节点数:%d'%self.search.count)
self.addDisplayText('最终路径长度:%d'%len(self.search.result))
self.centerTimer.stop()
self.search=None
self.yi=None
self.special=None
point.clear()
self.button_start.setEnabled(True)
self.button_clearSE.setEnabled(True)
self.button_clearWall.setEnabled(True)
self.displayFlush=True
else:
self.special=data
self.repaint()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = GameBoard()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
注意:代码运行可以设置动态遍历的时候暂停时间(大概在145行的time.sleep(5)语句)
运行结果
输出每次计算的每个点的F和父结点,直接看图吧!
详细列表
初始化地图...
初始化UI...
计算值: (2,3)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((2, 2))]
F=40 G=10 H=30
计算值: (3,3)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((2, 2))]
F=54 G=14 H=40
计算值: (3,2)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((2, 2))]
F=60 G=10 H=50
计算值: (3,1)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((2, 2))]
F=74 G=14 H=60
计算值: (2,1)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((2, 2))]
F=60 G=10 H=50
计算值: (1,1)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((2, 2))]
F=74 G=14 H=60
计算值: (1,2)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((2, 2))]
F=60 G=10 H=50
计算值: (1,3)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((2, 2))]
F=54 G=14 H=40
计算值: (3,3)[F=54,G=14,cost=10][father:((2, 3))]
F=60 G=20 H=40
计算值: (3,2)[F=60,G=10,cost=14][father:((2, 3))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (1,2)[F=60,G=10,cost=14][father:((2, 3))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (1,3)[F=54,G=14,cost=10][father:((2, 3))]
F=60 G=20 H=40
计算值: (4,4)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((3, 3))]
F=68 G=28 H=40
计算值: (4,3)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((3, 3))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (4,2)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((3, 3))]
F=88 G=28 H=60
计算值: (3,2)[F=60,G=10,cost=10][father:((3, 3))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (1,2)[F=60,G=10,cost=10][father:((1, 3))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (0,2)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((1, 3))]
F=88 G=28 H=60
计算值: (0,3)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((1, 3))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (0,4)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((1, 3))]
F=68 G=28 H=40
计算值: (4,3)[F=74,G=24,cost=14][father:((3, 2))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (4,2)[F=88,G=28,cost=10][father:((3, 2))]
F=80 G=20 H=60
计算值: (4,1)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((3, 2))]
F=94 G=24 H=70
计算值: (3,1)[F=74,G=14,cost=10][father:((3, 2))]
F=80 G=20 H=60
计算值: (2,1)[F=60,G=10,cost=14][father:((3, 2))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (3,1)[F=74,G=14,cost=10][father:((2, 1))]
F=80 G=20 H=60
计算值: (3,0)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((2, 1))]
F=94 G=24 H=70
计算值: (2,0)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((2, 1))]
F=80 G=20 H=60
计算值: (1,0)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((2, 1))]
F=94 G=24 H=70
计算值: (1,1)[F=74,G=14,cost=10][father:((2, 1))]
F=80 G=20 H=60
计算值: (1,2)[F=60,G=10,cost=14][father:((2, 1))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (1,1)[F=74,G=14,cost=10][father:((1, 2))]
F=80 G=20 H=60
计算值: (0,1)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((1, 2))]
F=94 G=24 H=70
计算值: (0,2)[F=88,G=28,cost=10][father:((1, 2))]
F=80 G=20 H=60
计算值: (0,3)[F=74,G=24,cost=14][father:((1, 2))]
F=74 G=24 H=50
计算值: (4,5)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((4, 4))]
F=68 G=38 H=30
计算值: (5,5)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((4, 4))]
F=82 G=42 H=40
计算值: (5,4)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((4, 4))]
F=88 G=38 H=50
计算值: (5,3)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((4, 4))]
F=102 G=42 H=60
计算值: (4,3)[F=74,G=24,cost=10][father:((4, 4))]
F=88 G=38 H=50
计算值: (3,5)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((4, 4))]
F=62 G=42 H=20
计算值: (3,6)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((3, 5))]
F=62 G=52 H=10
计算值: (4,6)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((3, 5))]
F=76 G=56 H=20
计算值: (4,5)[F=68,G=38,cost=10][father:((3, 5))]
F=82 G=52 H=30
计算值: (2,5)[F=0,G=0,cost=10][father:((3, 5))]
F=62 G=52 H=10
计算值: (2,6)[F=0,G=0,cost=14][father:((3, 5))]
F=56 G=56 H=0
搜索结束! 可执行文件
已经将程序打包成exe可执行文件,点击即可用,不需要py环境。
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UqvI5vtoxwXu0PPUFHfxdg
提取码:fwwm
复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
拓展
Dijkstra算法和A*算法的比较
Dijkstra算法和A*都是最短路径问题的常用算法,下面就对这两种算法的特点进行一下比较。
1.Dijkstra算法计算源点到其他所有点的最短路径长度,A*关注点到点的最短路径(包括具体路径)。
2.Dijkstra算法建立在较为抽象的图论层面,A*算法可以更轻松地用在诸如游戏地图寻路中。
3.Dijkstra算法的实质是广度优先搜索,是一种发散式的搜索,所以空间复杂度和时间复杂度都比较高。对路径上的当前点,A*算法不但记录其到源点的代价,还计算当前点到目标点的期望代价,是一种启发式算法,也可以认为是一种深度优先的算法。
4.由第一点,当目标点很多时,A*算法会带入大量重复数据和复杂的估价函数,所以如果不要求获得具体路径而只比较路径长度时,Dijkstra算法会成为更好的选择。参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42382758/article/details/88840581