【重温SSM框架系列】4 - Spring集成web环境(三层结构和配置监听器)
Spring集成web环境
- 三层架构环境搭建
-
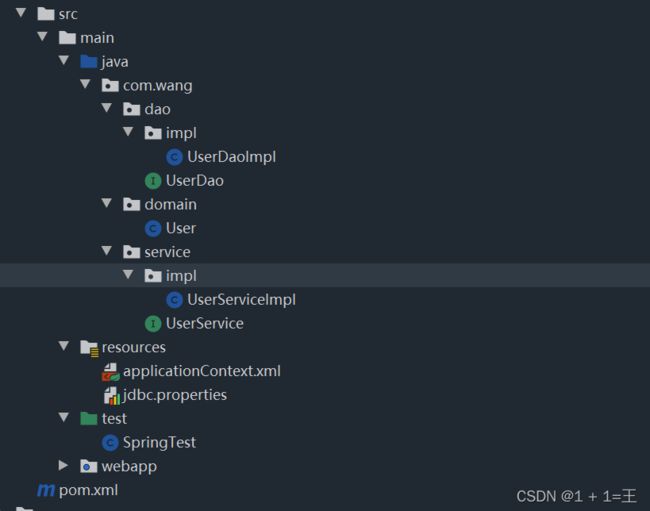
- 目前的项目结构
- 搭建web层
-
- 1. 引入servlet和jsp依赖
- 2. 创建UserServlet类
- 3. 配置Tomcat并启动测试
- 三层架构基本项目结构
- 设置获取applicationContext.xml的监听器
-
- 在web.xml中配置核心配置文件的位置
- 创建一个ContextLoaderListener类
- 在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器
- 修改UserServlet,使用监听器获取ApplicationContext
- 使用Spring集成ContextLoaderListener监听器
-
- 引入spring-web包
- 修改web.xml配置Spring的ContextLoaderListener监听器
- 使用Spring工具获得应用上下文对象
大家好,我是【1+1=王】, 热爱java的计算机(人工智能)渣硕研究生在读。
如果你也对java、人工智能等技术感兴趣,欢迎关注,抱团交流进大厂!!!
Good better best, never let it rest, until good is better, and better best.近期会重新温习一下SSM的相关知识,相应的博客会更新至专栏【SSM框架】中,欢迎大家关注!
SSM专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43598687/category_11652306.html
三层架构环境搭建
在前面Spring核心配置文件以及数据源配置的讲解中,主要是在dao层和service层,现在我们就把web层环境也给他集成进来。
目前的项目结构
搭建web层
1. 引入servlet和jsp依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-apiartifactId>
<version>2.2.1version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
2. 创建UserServlet类
@WebServlet("/userServlet")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) application.getBean("userService");
userService.save();
}
}
3. 配置Tomcat并启动测试

启动Tomcat并访问/UserServlet,控制台打印如下,三层架构基本环境搭建成功。
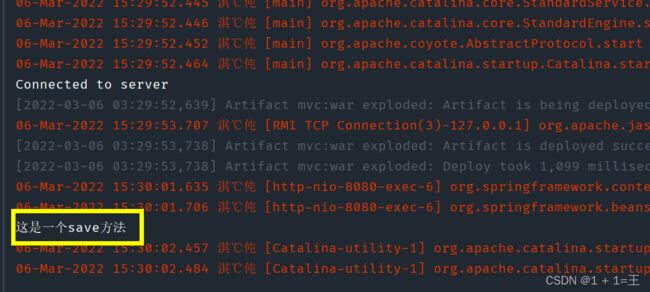
三层架构基本项目结构
设置获取applicationContext.xml的监听器
现在出现了一个问题:每次从容器中获得Bean时,都需要ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”),当配置文件多次加载时,就会创建很多个ApplicationContext对象,造成资源的浪费。
在Web项目中,我们运用监听器的特性,创建一个配置文件加载的监听器,在应用启动的时候就加载Spring的配置文件,并创建ApplicationContext 对象;当要使用时,直接从域中获取即可,达到一处加载处处使用的效果。
在web.xml中配置核心配置文件的位置
<context-param>
<param-name>applicationContextLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
创建一个ContextLoaderListener类
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
ServletContextEvent sce;
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
// 读取web.xml中配置的Spring核心配置文件的位置
String applicationContextLocation = servletContext.getInitParameter("applicationContextLocation");
// 创建ApplicationContext上下文对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(applicationContextLocation);
// 将ApplicationContext对象存到域中
servletContext.setAttribute("applicationContext",applicationContext);
System.out.println("创建ApplicationContext对象成功:" + applicationContext);
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
}
}
在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器
<listener>
<listener-class>com.wang.listener.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
启动Tomcat,查看控制台打印,发现ApplicationContext对象在Tomcat启动时被创建:

修改UserServlet,使用监听器获取ApplicationContext
@WebServlet("/userServlet")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ApplicationContext application = (ApplicationContext) req.getServletContext().getAttribute("applicationContext");
UserService userService = (UserService) application.getBean("userService");
userService.save();
}
}
使用Spring集成ContextLoaderListener监听器
上面通过自定义监听器的方式实现了在应用启动的时候就加载Spring的配置文件,并创建ApplicationContext 对象。但是这个过程还是比较复杂,可以使用Spring提供获取应用上下文的工具直接获取上下文对象。
引入spring-web包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webartifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
修改web.xml配置Spring的ContextLoaderListener监听器
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
使用Spring工具获得应用上下文对象
@WebServlet("/userServlet")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// ApplicationContext application = (ApplicationContext) req.getServletContext().getAttribute("applicationContext");
ApplicationContext application = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(req.getServletContext());
UserService userService = (UserService) application.getBean("userService");
userService.save();
}
}