【JAVA百炼成仙】渡劫篇 下——Map集合(HashMap、TreeMap)
这里是JAVA成仙路,关注我学习JAVA不迷路
如果对你有帮助,给博主一个免费的点赞以示鼓励
欢迎各位点赞评论收藏⭐️
前言:本章具体介绍了HashMap、TreeMap两种集合的基本使用方法和区别,图解穿插代码实现。
JAVA成仙路从基础开始讲,后续会讲到JAVA高级,中间会穿插面试题和项目实战,希望能给大家带来帮助!
文章目录
- Map
-
- HashMap
-
- 创建HashMap
- 添加元素
- 访问元素
- 删除元素
- TreeMap
-
- 创建TreeMap
- 添加元素
- 访问元素
- 删除元素
- HashMap、TreeMap区别
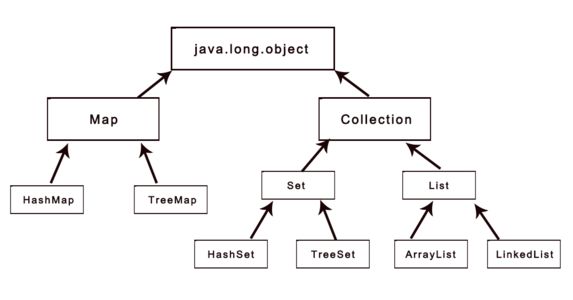
Map
Map接口储存一组成对的键-值对象,提供key(键)到value(值)的映射,Map中的key不要求有序,不允许重复。value同样不要求有序,但可以重复。最常见的Map实现类是HashMap,他的储存方式是哈希表,优点是查询指定元素效率高。
Map接口被HashMap和TreeMap两个类实现。
HashMap
HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。
HashMap 实现了 Map 接口,根据键的 HashCode 值存储数据,具有很快的访问速度,最多允许一条记录的键为 null,不支持线程同步。
HashMap 是无序的,即不会记录插入的顺序。
HashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了 Map、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable 接口。
HashMap 的 key 与 value 类型可以相同也可以不同,可以是字符串(String)类型的 key 和 value,也可以是整型(Integer)的 key 和字符串(String)类型的 value。
简单介绍一下HashMap的简单使用
创建HashMap
以下实例创建一个 HashMap 对象 Sites, 整型(Integer)的 key 和字符串(String)类型的 value:
HashMap<Integer, String> Sites = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
添加元素
HashMap 类提供了很多有用的方法,添加键值对(key-value)可以使用 put() 方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 HashMap 对象 Sites
HashMap<Integer, String> Sites = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 添加键值对
Sites.put(1, "Google");
Sites.put(2, "Runoob");
Sites.put(3, "Taobao");
Sites.put(4, "Zhihu");
System.out.println(Sites);
}
访问元素
我们可以使用 get(key) 方法来获取 key 对应的 value:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 HashMap 对象 Sites
HashMap<Integer, String> Sites = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 添加键值对
Sites.put(1, "Google");
Sites.put(2, "Runoob");
Sites.put(3, "Taobao");
Sites.put(4, "Zhihu");
System.out.println(Sites.get(3));
}
![]()
删除元素
我们可以使用 remove(key) 方法来删除 key 对应的键值对(key-value):
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 HashMap 对象 Sites
HashMap<Integer, String> Sites = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 添加键值对
Sites.put(1, "Google");
Sites.put(2, "Runoob");
Sites.put(3, "Taobao");
Sites.put(4, "Zhihu");
Sites.remove(4);
System.out.println(Sites);
}
![]()
TreeMap
在Map集合框架中,除了HashMap以外,TreeMap也是常用到的集合对象之一。
与HashMap相比,TreeMap是一个能比较元素大小的Map集合,会对传入的key进行了大小排序。其中,可以使用元素的自然顺序,也可以使用集合中自定义的比较器来进行排序;
不同于HashMap的哈希映射,TreeMap实现了红黑树的结构,形成了一颗二叉树。
TreeMap具有如下特点:
不允许出现重复的key;
可以插入null键,null值;
可以对元素进行排序;
无序集合(插入和遍历顺序不一致);
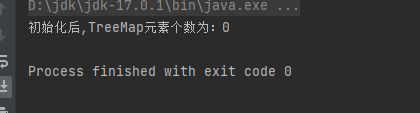
创建TreeMap
TreeMap<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
System.out.println("初始化后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
添加元素
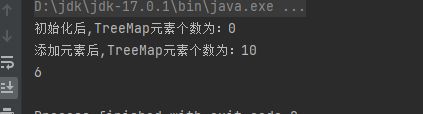
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
System.out.println("初始化后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
treeMap.put("hello", 1);
treeMap.put("world", 2);
treeMap.put("my", 3);
treeMap.put("name", 4);
treeMap.put("is", 5);
treeMap.put("huangqiuping", 6);
treeMap.put("i", 6);
treeMap.put("am", 6);
treeMap.put("a", 6);
treeMap.put("developer", 6);
System.out.println("添加元素后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
}
访问元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
System.out.println("初始化后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
treeMap.put("hello", 1);
treeMap.put("world", 2);
treeMap.put("my", 3);
treeMap.put("name", 4);
treeMap.put("is", 5);
treeMap.put("huangqiuping", 6);
treeMap.put("i", 6);
treeMap.put("am", 6);
treeMap.put("a", 6);
treeMap.put("developer", 6);
System.out.println("添加元素后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
//访问元素
System.out.println(treeMap.get("a"));
}
删除元素
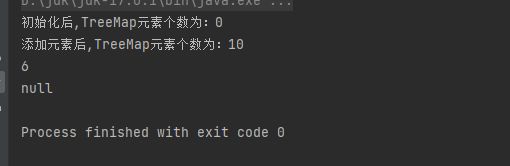
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
System.out.println("初始化后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
treeMap.put("hello", 1);
treeMap.put("world", 2);
treeMap.put("my", 3);
treeMap.put("name", 4);
treeMap.put("is", 5);
treeMap.put("huangqiuping", 6);
treeMap.put("i", 6);
treeMap.put("am", 6);
treeMap.put("a", 6);
treeMap.put("developer", 6);
System.out.println("添加元素后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
//访问元素
System.out.println(treeMap.get("a"));
//删除元素
treeMap.remove("a");
System.out.println(treeMap.get("a"));
}
HashMap、TreeMap区别
HashMap:适用于在Map中插入、删除和定位元素。
Treemap:适用于按自然顺序或自定义顺序遍历键(key)。
HashMap通常比TreeMap快一点(树和哈希表的数据结构使然),建议多使用HashMap,在需要排序的Map时候才用TreeMap。