多传感器融合定位-常用辅助调试工具总结
多传感器融合定位-常用辅助调试工具总结
前言:多传感器融合定位调试过程中,会用到很多调试方法,诸如open3d可视化,matplotlib波形可视化,本章节进行汇众,持续更新~
调试方法汇总
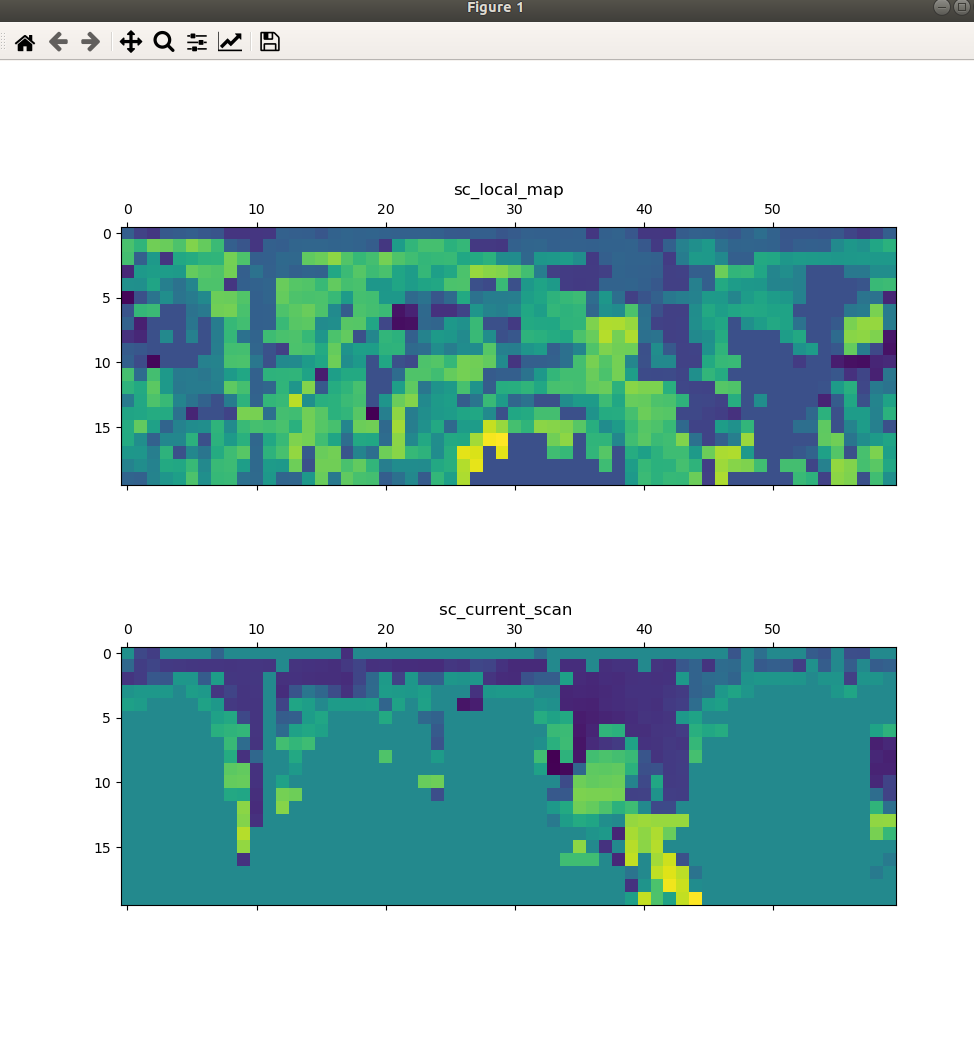
1. mamtplotlib可视化scan_context矩阵
存储scan_context 矩阵都txt文件中
#include
#include 调用方法:
Eigen::MatrixXf sc_matrix(query_scan_context.rows(), query_scan_context.cols()); // 将sc存到sc_matrix 中
for(int did = 0; did < query_scan_context.rows(); ++ did){
for(int sid = 0; sid < query_scan_context.cols(); ++sid){
sc_matrix(did,sid) = query_scan_context(did,sid);
}
}
CreateFile(sc_local_map, sc_local_map_path); // 创建文件夹
WriteText(sc_local_map, sc_matrix); // 把 sc_matrxi_local_map 写进文件夹中
python matplotlib 读取sc_matrix 并可视化矩阵
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
sc_matrix_cur_scan = np.loadtxt("sc_matrix_cur_scan.txt")
sc_matrix_lcoal_map = np.loadtxt("sc_matrix_local_map.txt")
def samplemat(mat):
"""Make a matrix with all zeros and increasing elements on the diagonal"""
sector = mat.shape[0] # x
ring = mat.shape[1] # y
aa = np.zeros((sector,ring))
for i in range(sector):
for j in range(ring):
if(mat[i,j]):
aa[i,j] = 1 #mat[i,j]
else:
aa[i, j] = mat[i,j]
return aa
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2,1,1) # 2*1 分布,第1个
# Display matrix
#ax1.matshow(samplemat(sc_matrix_lcoal_map)) #,cmap = plt.cm.gray
ax1.matshow(sc_matrix_lcoal_map) #,cmap = plt.cm.gray
plt.title("sc_local_map");
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2,1,2) # 2*1 分布,第2个
#ax2.matshow(samplemat(sc_matrix_cur_scan)) #,cmap = plt.cm.gray
ax2.matshow(sc_matrix_cur_scan) #,cmap = plt.cm.gray
plt.title("sc_current_scan ");
plt.show()
2. open3d可视化点云
存储点云为pcd
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("/home/kaho/catkin2_ws/visual_sc_matrix/pcd/cur_scan.pcd",*transformed_scan_.cloud_ptr );
//save pcd
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("/home/kaho/catkin2_ws/visual_sc_matrix/pcd/local_map.pcd",*local_map_ptr_ );
python open3d 可视化
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
local_map_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("pcd/local_map.pcd")
cur_scan_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("pcd/cur_scan.pcd")
local_map_points = np.asarray(local_map_pcd.points)
cur_scan_points = np.asarray(cur_scan_pcd.points)
# print(local_map_pcd)#输出点云点的个数
# print(cur_scan_pcd)#输出点云点的个数
#
print(local_map_points)#输出点的三维坐标
# print(cur_scan_points)#输出点的三维坐标
#
# print('给所有的点上一个统一的颜色,颜色是在RGB空间得[0,1]范围内得值')
local_map_pcd.paint_uniform_color([0.9, 0.9, 0.9]) # blue
cur_scan_pcd.paint_uniform_color([1, 0, 0]) # red
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([local_map_pcd,cur_scan_pcd])
3. evo 格式存储 pose
FILE:catkin_ws/src/imu_integration/src/evo_evaluate/evaluate.cpp
使用evo工具进行精度评估,evo format 使用TUM格式,参考了eamo 助教的GitHub写法,为了方便后续调用,将保存文件格式写成ROS Node的方式,通过订阅:
/sim/sensor/imu /pose/ground_truth 两个话题,存储到对应格式的文件中,进行 evo 评估。
evo的使用方式可参考:
SLAM轨迹精度评估工具evo使用方法
evo测评TUM数据集
evo安装、evo使用方法详细介绍使用教程,SLAM轨迹精度评估工具,如何用来评估ORB-SLAM2生成的轨迹精度,评估激光雷达SLAM与视觉SLAM的轨迹精度,量化SLAM的误差
3.1 evo TUM格式存储
常用的evo KITTI pose format是美誉timestamp的,通过固定序列数来进行精度评估比较,TUM 数据集 format中有时间戳,通过时间戳来比较,会比较准,所以本次存储的evo数据格式为TUM
evo TUM需要pose 存储格式为 timestamp x y z q_x q_y q_z q_w ;具体参考evo 官档Formats
存储写法
/* write2txt format TUM*/
void WriteText(std::ofstream& ofs, pose data){
ofs << std::fixed << data.timestamp << " " << data.pos.x() << " " << data.pos.y() << " " << data.pos.z() << " "
<< data.q.x() << " " << data.q.y() <<" " << data.q.z() << " " << data.q.w() << std::endl;
}
3.2 TUM timestamps时间对齐
一开始,给gt.txt 和 ins.txt 中写上timestamps时,时间戳都是各自的ROS topic的时间戳,运行evo_rpe 分段评估时,报错,找不到两个文件中时间戳相差0.01s的数据,经过观察,因为estimate imu惯性解算节点是先通过订阅imu_sim topic 数据才进行解算,会比groundtruth topic 时间戳显示慢一点,因此将各自当前时间戳减去第一帧的数据时间戳,就可以对齐各自的时间。
if(flag_ins){
stamp_ins_init = msg->header.stamp.toSec();
flag_ins = 0;
}
pose_ins.timestamp = msg->header.stamp.toSec() - stamp_ins_init; //把时间戳转化成浮点型格式
/******************************************************************************************************/
if(flag_gt){
stamp_gt_init = msg->header.stamp.toSec();
flag_gt = 0;
}
pose_gt.timestamp = msg->header.stamp.toSec() - stamp_gt_init;
3.3 evo TUM ROS_Node 完整实现
FILE:catkin_ws/src/imu_integration/src/evo_evaluate/evaluate.cpp
#include
#include 4.Mapviz 做GPS 里程计可视化
主要参考博客:
代凯哥的知乎博客:
惯性导航系统INS570D测试
Mapviz来做GPS+里程计+LiDAR可视化
4.1.mapviz 安装
参考 : 使用Mapviz、中科图新 进行机器人GPS轨迹卫星地图绘制
4.2.mapviz 调用天地图api
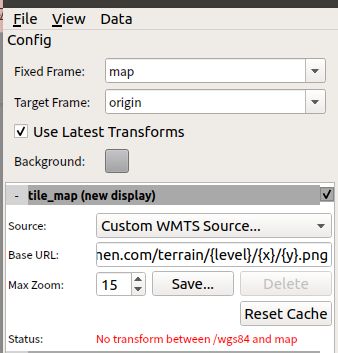
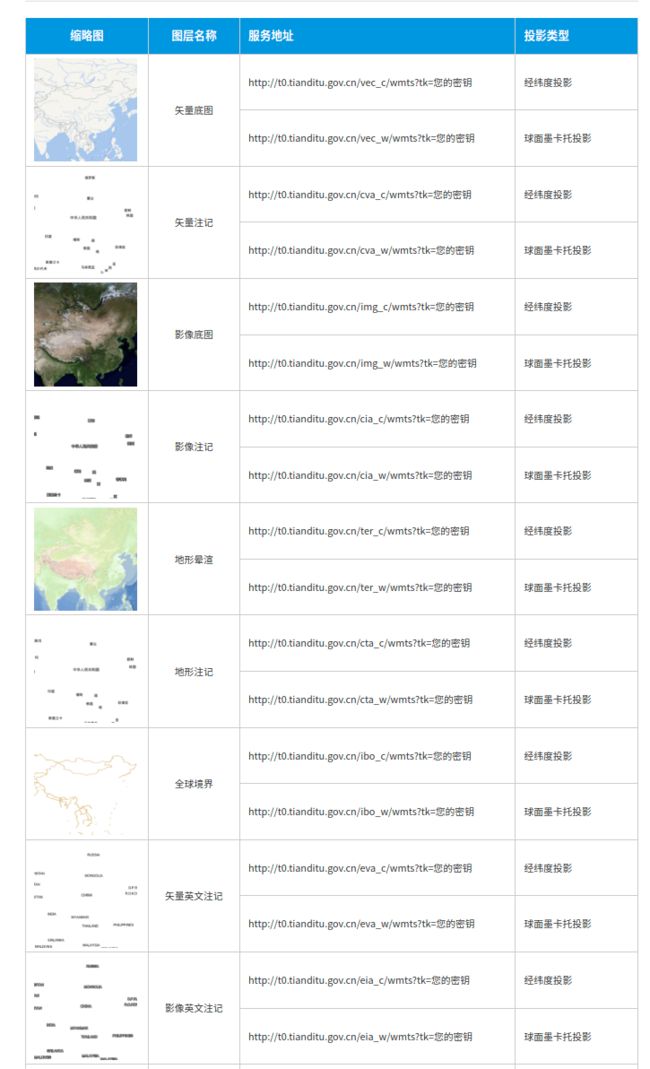
因为mapviz默认加载的地图为Stamen的地图,为外国网站,所以加载很慢,在代凯博士的指点下,选择使用天地图的WMTS-api,进行切片地图的显示,并在上面显示轨迹
4.2.1申请天地图API key 个人密钥
需要先申请天地图API KEY,注意申请时,选择的应用类型为:服务端,提交后就能生成自己的tk 密钥。
4.2.2地图瓦片获取格式
按照地图API的格式,写入你的密钥
格式:
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/img_w/wmts?SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={z}&TILEROW={x}&TILECOL={y}&tk=您的密钥
需要注意的是: 如下图所示,mapviz中,在tile_map 中,添加的Base URL 格式为
http://tile.stamen.com/terrain/{level}/{x}/{y}.png # level x y 分别表示 高经纬
所以需要将天地图api调取格式中的 z 变量改为 level 变量,mapviz才能识别到,修改后的天地图api调取格式为
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/img_w/wmts?SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={x}&TILECOL={y}&tk=您的密钥
矢量底图
经纬度投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/vec_c/wmts?SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
球面墨卡托投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/vec_w/wmts?
SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
矢量注记
经纬度投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/cva_c/wmts?SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
球面墨卡托投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/cva_w/wmts?
SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
影像底图
经纬度投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/img_c/wmts?
SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
球面墨卡托投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/img_w/wmts?
SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
地形晕渲
经纬度投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/ter_c/wmts?
SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
球面墨卡托投影
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/ter_w/wmts?
SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
三维地形影像底图
https://[ t0-t7 ].tianditu.gov.cn/mapservice/swdx?
SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
4.3.使用
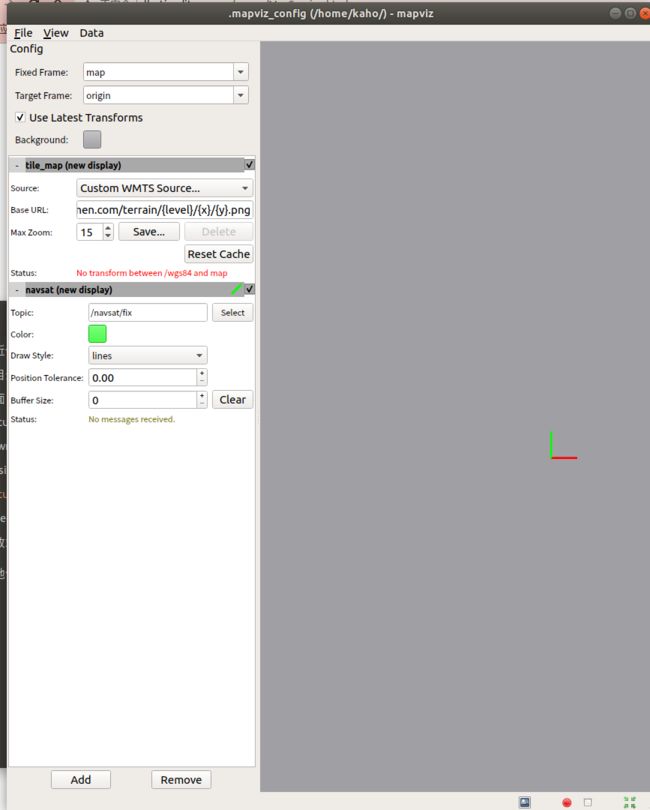
4.3.1 添加 Custom WMTS Source
例如,使用 影像底图-球面墨卡托投影,往Base URL 里添加天地图URL+密钥,Max zoom 选择99 ,加大分辨率
http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/img_w/wmts?SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMATRIX={level}&TILEROW={y}&TILECOL={x}&tk=您的密钥
4.3.2 添加 navsat 路径display
选择/navsat/fix 话题和适当的颜色,即可在卫星地图上绘制路径
注意,mapviz中要先添加tile_map 再 添加 navsat(new display)
4.3.3 播放数据集
3.3.4 最后效果
如下图所示,红色轨迹为在广场的轨迹路线图
edited by kaho 12.5