Linear Regression 线性回归sklearn python实现
示例说明
本示例是一个简单有趣的试验,是对天气变化的数据回归出一条预测线 出来,数据集非常简单,对应每一年二氧化碳的排放量,和每一年气温均值的变化,
编译环境是 jupyter notebook, 可以通过安装 Anaconda,导入 scikit-learn 库可以很容易实现,github示例代码数据集,有人上传视频到
Youtube Video ,也可以看看。
概述
linear_regression.ipynb代码中主要分为两个部分
- 2D 线性回归作用于一个简单二维数据集
challenge_dataset.txt[X, Y] - 3D 多元线性回归作用于气候变化数据集
global_co2.csvannul_temp.csv[Year, CO2 emissions, Global temperature].
Section 1: 2D 线性回归
首先导入各种需要用到的 packages
%matplotlib inline
# Imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import sklearn
import numpy as np
导入可视化二维数据
df = pd.read_csv('challenge_dataset.txt', names=['X','Y'])
sns.regplot(x='X', y='Y', data=df, fit_reg=False)
plt.show()
2D 线性回归及回归后的可视化结果
Section 2: 3D 线性回归
首先,对二氧化碳与气候变化数据集 global_co2.csv annul_temp.csv进行预处理,分别保留两个数据 1960 年以后的数据,得到
[Year, CO2 emissions], [Year, Global temperature] 两个数据集,然后合并,变为 [Year, CO2 emissions, Global temperature]
# Import data
co2_df = pd.read_csv('global_co2.csv')
temp_df = pd.read_csv('annual_temp.csv')
print(co2_df.head())
print(temp_df.head())
# Clean data
co2_df = co2_df.ix[:,:2] # Keep only total CO2
co2_df = co2_df.ix[co2_df['Year'] >= 1960] # Keep only 1960 - 2010
co2_df.columns=['Year','CO2'] # Rename columns
co2_df = co2_df.reset_index(drop=True) # Reset index
temp_df = temp_df[temp_df.Source != 'GISTEMP'] # Keep only one source
temp_df.drop('Source', inplace=True, axis=1) # Drop name of source
temp_df = temp_df.reindex(index=temp_df.index[::-1]) # Reset index
temp_df = temp_df.ix[temp_df['Year'] >= 1960].ix[temp_df['Year'] <= 2010] # Keep only 1960 - 2010
temp_df.columns=['Year','Temperature'] # Rename columns
temp_df = temp_df.reset_index(drop=True) # Reset index
print(co2_df.head())
print(temp_df.head())
# Concatenate
climate_change_df = pd.concat([co2_df, temp_df.Temperature], axis=1)
print(climate_change_df.head())
显示三维可视化数据
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
fig.set_size_inches(12.5, 7.5)
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(xs=climate_change_df['Year'], ys=climate_change_df['Temperature'], zs=climate_change_df['CO2'])
ax.set_ylabel('Relative tempature'); ax.set_xlabel('Year'); ax.set_zlabel('CO2 Emissions')
ax.view_init(10, -45)
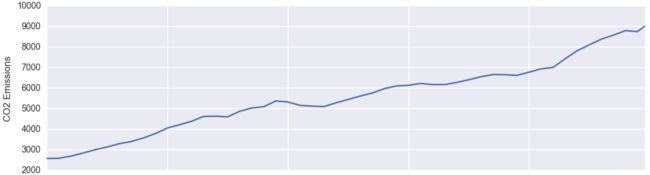
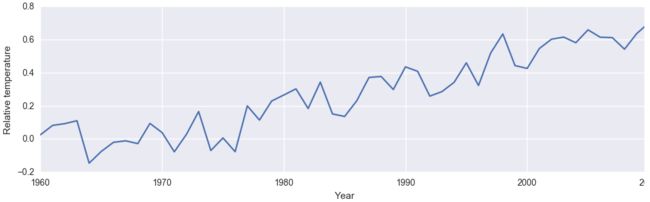
将二氧化碳排放和全球温度变化分别用二维显示
f, axarr = plt.subplots(2, sharex=True)
f.set_size_inches(12.5, 7.5)
axarr[0].plot(climate_change_df['Year'], climate_change_df['CO2'])
axarr[0].set_ylabel('CO2 Emissions')
axarr[1].plot(climate_change_df['Year'], climate_change_df['Temperature'])
axarr[1].set_xlabel('Year')
axarr[1].set_ylabel('Relative temperature')
3D线性回归并可视化结果
X = climate_change_df.as_matrix(['Year'])
Y = climate_change_df.as_matrix(['CO2', 'Temperature']).astype('float32')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = np.asarray(train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.1))
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
print('Score: ', reg.score(X_test.reshape(-1, 1), y_test))
x_line = np.arange(1960,2011).reshape(-1,1)
p = reg.predict(x_line).T
fig2 = plt.figure()
fig2.set_size_inches(12.5, 7.5)
ax = fig2.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(xs=climate_change_df['Year'], ys=climate_change_df['Temperature'], zs=climate_change_df['CO2'])
ax.set_ylabel('Relative tempature'); ax.set_xlabel('Year'); ax.set_zlabel('CO2 Emissions')
ax.plot(xs=x_line, ys=p[1], zs=p[0], color='green')
ax.view_init(10, -45)
将对二氧化碳和全球气温变化的预测分别在二维里面显示
f, axarr = plt.subplots(2, sharex=True)
f.set_size_inches(12.5, 7.5)
axarr[0].plot(climate_change_df['Year'], climate_change_df['CO2'])
axarr[0].plot(x_line, p[0])
axarr[0].set_ylabel('CO2 Emissions')
axarr[1].plot(climate_change_df['Year'], climate_change_df['Temperature'])
axarr[1].plot(x_line, p[1])
axarr[1].set_xlabel('Year')
axarr[1].set_ylabel('Relative temperature')
依赖的 packages
- matplotlib
- pandas
- numpy
- seaborn
others
- Email: [email protected]