Stream流和Optional
| Lambda表达式和函数式接口 | https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45888932/article/details/122451124 |
目录
一、什么是Stream流
注意事项
二、快速体验
数据准备
数据跟踪
三、创建流
四、中间操作
五、终结操作
查找和匹配
reduce
六、Optional
安全获取值
一、什么是Stream流
使用函数式编程,用来对集合或者数组进行链状流式的操作
注意事项
- 流中没有终结操作,中间操作也是不会执行的
- 流是一次性的,在终结操作之后这个流不可以使用了
- 流中的操作对于原数据没有影响
二、快速体验
数据准备
pom.xml中添加依赖,这个依赖用于减少代码,快速开发
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.22
创建实体类
package com.righteye.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.List;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode // 用于去重
public class Author {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String intro;
private List books;
}
package com.righteye.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode // 用于去重
public class Book {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer score;
private String intro;
}
测试类
package com.righteye;
import com.righteye.domain.Author;
import com.righteye.domain.Book;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 删选出所有年龄大于18的作者,并对内容去重
List authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream() // 将List转换成stream流
.filter(author -> author.getAge() > 18)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author));
}
private static List getAuthors() {
Author author = new Author(1L, "青雉", 33, "海军大将", null);
Author author1 = new Author(2L, "赤犬", 35, "海军大将", null);
Author author2 = new Author(3L, "路飞", 18, "海贼", null);
Author author3 = new Author(3L, "路飞", 18, "海贼", null);
List books1 = new ArrayList<>();
List books2 = new ArrayList<>();
List books3 = new ArrayList<>();
books1.add(new Book(1L, "冰与火", 88, "11111"));
books1.add(new Book(2L, "冰与火2", 99, "111122221"));
books2.add(new Book(3L, "冰2", 99, "111122221"));
books2.add(new Book(4L, "火2", 91, "111122221"));
books2.add(new Book(4L, "火2", 91, "111122221"));
books3.add(new Book(5L, "海贼王", 91, "全集"));
books3.add(new Book(6L, "革命家", 91, "111122221"));
books3.add(new Book(6L, "革命家", 91, "111122221"));
author.setBooks(books1);
author1.setBooks(books2);
author2.setBooks(books3);
author3.setBooks(books3);
return new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(author, author1, author2, author3));
}
}
stream中提供了方法可以对集合中的元素进行筛选,方法中的参数很多都是函数式接口,使用lambda表达式,初学的时候按照参数要求直接创建相应的匿名内部类,然后 alt + enter自动转化成lambda表达式。
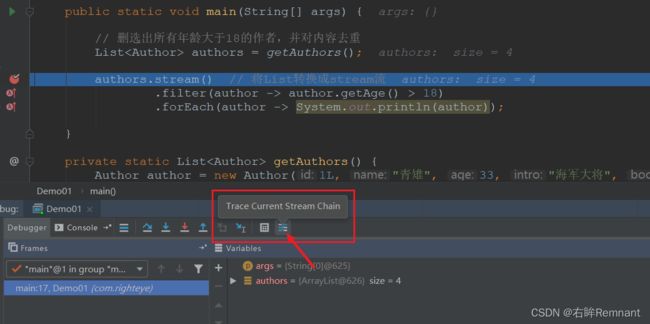
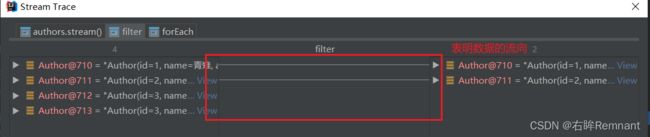
数据跟踪
对上面的例子进行debug调试,idea中提供了对于stream的跟踪操作
idea yyds,秒啊!
三、创建流
1.单列集合 集合.stream()
List authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream() // 将List转换成stream流
.filter(author -> author.getAge() > 18)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author)); 2.数组 Arrays.stream(args) 或者 Stream.of(args) 的方式
Integer[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Stream stream = Arrays.stream(arr);
Stream stream1 = Stream.of(arr); 3.双列集合 先转换成单列集合
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user1", 1);
map.put("user2", 2);
map.put("user3", 3);
// 先使用entrySet转换成单列集合
Stream> stream2 = map.entrySet().stream(); 四、中间操作
1.filter 对流中的数据进行过滤
// 对作者姓名长度 > 1的过滤
authors.stream()
.distinct() // 去重
.filter(author -> author.getName().length() > 1)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author));2.map 对流中的元素进行计算或转换
authors.stream()
// 匿名内部类形式:Function第一个参数为集合中的元素类型,第二个参数为转换后流中的元素
.map(new Function() {
@Override
public String apply(Author author) {
return author.getName();
}
})
.forEach(str -> System.out.println(str));
lambda优化:
authors.stream()
// 匿名内部类形式:Function第一个参数为集合中的元素类型,第二个参数为转换后流中的元素
.map(author -> author.getName())
.forEach(str -> System.out.println(str));3.distinct 对流中元素进行去重;使用distinct需要重写equals方法
4.sorted 对流中元素进行排序
当使用顺序排序的情况下,可以继续优化
// 对流中元素通过年龄降序排序,并进行去重
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Author::getAge))
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author));这里的lambda我直接alt + enter生成的,待我在往下学学;我现在只会下面这个
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((author1, author2) -> author1.getAge() - author2.getAge())
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author));
5.limit 限制流的长度,超出部分舍弃
// 对流中元素通过年龄降序排序,并进行去重 只打印前两个人
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((a1, a2) -> a2.getAge() - a2.getAge())
.limit(2)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author));
7.skip 跳过流中前n个元素,返回剩下的
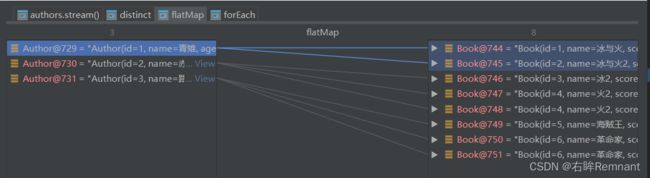
8.flatMap
map只能把一个对象转换成另一个对象作为流中的元素;而faltMap可以将一个对象转换成多个对象
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.flatMap(new Function>() {
@Override
public Stream apply(Author author) {
return author.getBooks().stream();
}
})
.forEach(book -> System.out.println(book)); 优化:
// 打印每名作者的书籍
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.flatMap((Function>) author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.forEach(book -> System.out.println(book)); debug追踪执行
五、终结操作
stream流中只有在最后调用终结操作,整个链式调用才能真正执行。
1.forEach 对流中的元素进行遍历。、
2.count 获取流中元素的个数
// 获取所有作家的所有书籍总数
long count = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.count();
System.out.println(count);count()没有参数,但是有个返回值接收结果
3.min&max 获取流中的最值
// 获取年级最大的作者
Optional max = authors.stream()
.max(((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge()));
System.out.println(max.get()); 4.collect 将流中的元素转换成集合
- 转换成list
// 获取作者的名字并封装成list
List list = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list); collect中的参数是Collector, 是个接口但不适合使用匿名内部类,这里使用工具类Collectors进行转换
- 转换成map
// 获取作者的名字和书籍并用map存储
final Map> authorMap = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(author -> author.getName(), author -> author.getBooks()));
for (Map.Entry> strName : authorMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(strName.getKey() + " " + strName.getValue());
} Collectors.toMap中的两个参数表示要将流中的元素分别转换到key和value所对应的类型
查找和匹配
一种条件判断,类似filter,但是filter是中间操作,而下面的方法是终结操作
1.anyMatch 判断是否存在一条数据满足条件
// 判断是否有年龄在44以上的人
boolean flag = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.anyMatch(author -> author.getAge() > 44);
System.out.println(flag);使用终结方法后流就停止了,不会再继续向下传递
2.allMatch 判断是否所有的元素都满足条件
3.noneMatch 判断是否都不符合条件
4.findAny 随机获取流中的一个元素
Optional res = authors.stream()
.findAny();
System.out.println(res.get()); 5.findFirst 获取流中第一个元素
reduce
用于将流中的元素通过定义的计算方法合并成一个结果并返回
内部实现:
res = initial;
public Integer apply(Integer res, Integer number) {
return (res, number)的具体计算关系;
}
res = apply(res, number);
测试实例:
// 计算所有作者的年龄之和
Integer res = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.map(author -> author.getAge()) // 将流中的元素转换成后面要计算的类型元素
// reduce 中第一个变量初始值,然后第二个参数是具体的实现逻辑
.reduce(0, (res1, number) -> res1 + number);
System.out.println(res);六、Optional
Optional用来避免程序中可能出现的空指针异常
传统使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
String author = getAuthorName();
if (author != null)
System.out.println(author);
}
private static String getAuthorName() {
Author author = new Author(1L, "青雉", 33, "海军大将", null);
return null;
}使用Optional后可以完全不考虑空指针的问题
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional author = getAuthorName();
author.ifPresent(name -> System.out.println(author.get().getName()));
}
private static Optional getAuthorName() {
Author author = new Author(1L, "青雉", 33, "海军大将", null);
return Optional.ofNullable(author);
} 实际上,在mybatis 3.5版本以上可以将返回的数据封装成Optional,这样可以省略自己封装的步骤,直接调用。
安全获取值
使用orElseGet()方法可以避免空指针异常的获取对象属性
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional author = getAuthorName();
Author res = author.orElseGet(() -> new Author(1L, "赤犬", 33, "海军大将", null));
System.out.println(res.getName());
}
private static Optional getAuthorName() {
Author author = new Author(1L, "青雉", 33, "海军大将", null);
return Optional.ofNullable(null);
} orElseThrow方法,当返回值为Null不存在的时候抛出异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional author = getAuthorName();
Author res = null;
try {
res = author.orElseThrow((Supplier) () -> new Exception());
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(res.getName());
}
private static Optional getAuthorName() {
Author author = new Author(1L, "青雉", 33, "海军大将", null);
return Optional.ofNullable(author);
} 对于抛出的异常,在spring当中可以进行异常的统一处理
七、Stream流的高级性质
基本数据类型优化
之前使用Stream流的时候使用泛型进行相应的操作,对于涉及的参数和返回值都是引用数据类型,但是在基本数据和包装类之间的关系时,由于自定装箱和拆箱也会造成额外的时间消耗,因此需要进行优化
long time1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.filter(age -> age > 18)
.max((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
}
long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time2 - time1); // 47时间消耗:422
使用mapToInt将流中的数据转换成int类型,不需要装箱和拆箱的操作
long time1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.mapToInt(author -> author.getAge())
.filter(age -> age > 18)
.max();
}
long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time2 - time1); 时间消耗:368
可以看到提示里流中数据类型
并行流
当流中的数据很多时候,可以使用并行流提高哦操作效率,通过开启多个线程共同完成这次操作;而使用Stream中提供的并行策略可以减少我们自己实现并发编程的困难和线程安全问题。
使用paraller()可以开启并行流
// 并行流
Stream stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
Optional optional = stream.parallel() // 开启并行流
.filter(num -> num > 5)
.map(num -> num + 5)
.peek(num -> System.out.println(num + ":" + Thread.currentThread().getName())) // 中间方法打印信息
.reduce((res, ele) -> res + ele);
optional.ifPresent(res -> System.out.println(res));
总结
记录下学习jdk8新特性的lambda表达式和Stream流相关知识
视频资源:b站搜索三更草堂,up小哥很棒的,支持!!