邻接表实现有向图BFS、DFS、拓扑排序
图的大家族
常用图的存储结构有两种:邻接矩阵,邻接表。一个数组,一个链表,可见复杂的数据结构是建立在基础结构之上的,在这里选择邻接表存储,边比较少时省空间。
图按照有无方向,有无权重,分为四类
- 无向无权:无向图
- 无向有权:无向网
- 有向无权:有向图
- 有向有权:有向网
可见带有权重称为网,否则称为图。
图可以看成边权均为1,所以是特殊网。因此掌握了网,也就顺带会了图
由于无向图均有对称性,所以大多问题较好处理。而有向图无对称性,情况多变,且生活中的应用也较多,所以这里选择有向图处理
因此,本文用邻接表存储有向图,并实现深度、广度优先搜索和拓扑排序
数据结构
依次定义以下数据结构
边->表头->邻接表->图
typedef struct VNode{
int adjvex;
struct VNode* nextarc;
}VNode;//边
typedef struct Adj{
int data;
VNode* firstarc;
}Adj,AdjList[MAX_VEXNUM];//表头
typedef struct{
int n,m;
AdjList vertices;//邻接表
}Graph;//图
bool visited[MAX_VEXNUM];//访问数组,遍历时的核心;全局变量
工具–队列 (可参考队列实现)
//队列基本操作:初始化->入队->判空->获取队头->出队->遍历测试
typedef struct QNode{
int data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue{
QNode* front;
QNode* rear;
}Queue;
实现步骤
首先得建立图,然后实现查找指定点的第一个邻接点和下一个邻接点,这是实现两种遍历的核心,最后利用队列和入度表即可实现拓扑排序
建图
采取文件输入,比较方便
文件有向图.txt内容(第一行为顶点,边个数;余下为三元组(u,v,w)u,v为两个顶点,w为权值)
6 8
1 2 1 1 3 1 1 4 1
3 2 1 3 5 1
4 5 1
6 4 1 6 5 1
//文件读取数据建立有向图/网
void CreateGraph(Graph &G)
{
fstream inFile("有向图.txt",ios::in);
if(!inFile)cout<<"Fail to open file!"<<endl;
inFile>>G.n>>G.m;
int n=G.n,m=G.m;cout<<n<<" "<<m<<endl;
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){//初始化
G.vertices[i].data = i;
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
int u,v,w;
VNode* p;
// Adj pfst;//链表头 注意指针使用,传值还是传址
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
inFile>>u>>v>>w;//cout<
u--;v--;//输入从1开始,而存储从0开始
p = (VNode*)malloc(sizeof(VNode));
p->adjvex = v;
p->nextarc = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
G.vertices[u].firstarc = p;
}
inFile.close();
//输出调试
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
// pfst = G.vertices[i];
p = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while(p != NULL){
cout<<p->adjvex<<" ";
p = p->nextarc;
}cout<<endl;
}
}
第一个邻接点
查找到第一个未访问过的顶点立刻返回;若不存在,返回-1
//返回u的第一个邻接点
int FirstAdjvex(Graph G,int u)
{
VNode* p = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
while(p != NULL){
if(visited[p->adjvex])p = p->nextarc;//跳过访问过的
else return p->adjvex;
}
return -1;//表示未找到邻接点
}
下一个邻接点
先找到邻接点v的位置,从他的后一位再开始查找第一个邻接点
//返回相对于邻接点u后的邻接点
int NextAdjvex(Graph G,int u,int v)
{
VNode* p = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
//先找到v
while(p != NULL){
if(p->adjvex == v)break;
else p = p->nextarc;
}
p = p->nextarc;
while(p != NULL){//查找下一个邻接点
if(visited[p->adjvex])p = p->nextarc;
else return p->adjvex;
}
return -1;//表示无下一邻接点
}
DFS
深度优先搜索,类似于树的先序遍历
//一次只能遍历一个连通分支
void DFS(Graph G,int u)
{
visited[u] = true;
cout<<u+1<<" ";
for(int v = FirstAdjvex(G,u); v >= 0; v = NextAdjvex(G,u,v)){//寻求下一个邻接点,为了回退时准备
if(!visited[v])DFS(G,v);
}
}
//总函数,可处理非连通图
void DFSTraverse(Graph G)
{
for(int i = 0; i < G.n; i++){
visited[i] = false;
}
//考虑到非连通图,才写循环
for(int v = 0; v < G.n; v++){//可计算连通分支数
if(!visited[v]){
DFS(G,v);
cout<<endl;
}
}
}
BFS
广度优先:类似于树的层次遍历,队列实现
二者区别在于,图必须先访问再入队,否则会出现重复访问一个点;而树无所谓
//一次只能遍历一个连通分支
void BFS(Graph G,int u)
{
Queue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
//先访问再入队
visited[u] = true;
cout<<u+1<<" ";
EnQueue(Q,u);
while(!IsEmpty(Q)){//队非空
u = GetTop(Q)->data;
DeQueue(Q);
for(int v = FirstAdjvex(G,u); v >= 0; v = NextAdjvex(G,u,v)){//出队元素u 的所有相邻点入队
if(!visited[v]){
visited[v] = true;
EnQueue(Q,v);
cout<<v+1<<" ";
}
}
}
}
//广度优先遍历
void BFSTraverse(Graph G)
{
//访问数组初始化
for(int i = 0; i < G.n; i++){
visited[i] = false;
}
//不一定是连通图
for(int i = 0; i < G.n; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
BFS(G,i);
cout<<endl;
}
}
}
拓扑排序
拓扑排序,同样用队列实现,并且和图一样,先访问,再入队,不过需要维护一个入度表,每次出队记得更新入度表
void TopologicalSort(Graph G)
{
int n=G.n,m=G.m;//方便用
int indegree[n];//入度表
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){//入度表初始化
indegree[i] = 0;
}
//=========计算每个点的入度=========
for(int i =0; i < n; i++){
VNode* pcur = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while(pcur != NULL){
indegree[pcur->adjvex]++;
pcur = pcur->nextarc;
}
}
Queue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
//初始化拓扑排序,寻找第一届入度为0的点
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(indegree[i] == 0){
EnQueue(Q,i);
indegree[i] = -1;//表示已访问
cout<<i+1<<" ";
}
}
while(!IsEmpty(Q)){
int u = GetTop(Q)->data;
DeQueue(Q);
VNode* p = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
while(p != NULL){//出队的元素所有边(仅有出边)都要删除,所以将与其相邻的点的入度-1
if(indegree[p->adjvex] != -1)indegree[p->adjvex]--;
p = p->nextarc;
}
//扫描剩余点的入度,为0则标记且入队
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(indegree[i] != -1 && indegree[i] == 0){
EnQueue(Q,i);
indegree[i] = -1;
cout<<i+1<<" ";
}
}
}
}
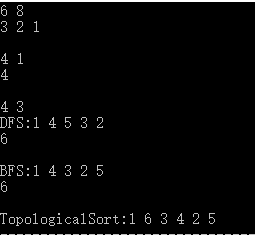
测试结果
小收获
- 学而时习之,果然不是盖的,这学期伊始,编写这些算法还觉得有些难度,现在第二次在来编写,哗啦啦一下就成功啦,果然实践出真知,哈哈哈哈h~
- 最近刚好在复习数据结构,正好将过去学的知识整理总结下,加深系统理解,记录下来以便日后复习用,就像写日记般
完整Code
#includedata<<" ";
// DeQueue(Q);
// }
}
//文件读取数据建立有向图/网
void CreateGraph(Graph &G)
{
fstream inFile("有向图.txt",ios::in);
if(!inFile)cout<<"Fail to open file!"<<endl;
inFile>>G.n>>G.m;
int n=G.n,m=G.m;cout<<n<<" "<<m<<endl;
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){//初始化
G.vertices[i].data = i;
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
int u,v,w;
VNode* p;
// Adj pfst;//链表头 注意指针使用,传值还是传址
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
inFile>>u>>v>>w;//cout<
u--;v--;//输入从1开始,而存储从0开始
p = (VNode*)malloc(sizeof(VNode));
p->adjvex = v;
p->nextarc = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
G.vertices[u].firstarc = p;
}
inFile.close();
//输出调试
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
// pfst = G.vertices[i];
p = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while(p != NULL){
cout<<p->adjvex<<" ";
p = p->nextarc;
}cout<<endl;
}
}
//返回u的第一个邻接点
int FirstAdjvex(Graph G,int u)
{
VNode* p = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
while(p != NULL){
if(visited[p->adjvex])p = p->nextarc;//跳过访问过的
else return p->adjvex;
}
return -1;//表示未找到邻接点
}
//返回相对于邻接点u后的邻接点
int NextAdjvex(Graph G,int u,int v)
{
VNode* p = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
//先找到v
while(p != NULL){
if(p->adjvex == v)break;
else p = p->nextarc;
}
p = p->nextarc;
while(p != NULL){//查找下一个邻接点
if(visited[p->adjvex])p = p->nextarc;
else return p->adjvex;
}
return -1;//表示无下一邻接点
}
//深度优先搜索,类似于树的先序遍历
void DFS(Graph G,int u)
{
visited[u] = true;
cout<<u+1<<" ";
for(int v = FirstAdjvex(G,u); v >= 0; v = NextAdjvex(G,u,v)){//寻求下一个邻接点,为了回退时准备
if(!visited[v])DFS(G,v);
}
}
//
void DFSTraverse(Graph G)
{
for(int i = 0; i < G.n; i++){
visited[i] = false;
}
//考虑到非连通图,才写循环
for(int v = 0; v < G.n; v++){//可计算连通分支数
if(!visited[v]){
DFS(G,v);
cout<<endl;
}
}
}
//广度优先:类似于树的层次遍历,队列实现
//二者区别在于,图必须先访问再入队,否则会出现重复访问一个点;而树无所谓
void BFS(Graph G,int u)
{
Queue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
//先访问再入队
visited[u] = true;
cout<<u+1<<" ";
EnQueue(Q,u);
while(!IsEmpty(Q)){//队非空
u = GetTop(Q)->data;
DeQueue(Q);
for(int v = FirstAdjvex(G,u); v >= 0; v = NextAdjvex(G,u,v)){//出队元素u 的所有相邻点入队
if(!visited[v]){
visited[v] = true;
EnQueue(Q,v);
cout<<v+1<<" ";
}
}
}
}
//广度优先遍历
void BFSTraverse(Graph G)
{
//访问数组初始化
for(int i = 0; i < G.n; i++){
visited[i] = false;
}
//不一定是连通图
for(int i = 0; i < G.n; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
BFS(G,i);
cout<<endl;
}
}
}
//拓扑排序,同样用队列实现,并且和图一样,先访问,再入队,
//不过需要维护一个入度表,每次出队记得更新入度表
void TopologicalSort(Graph G)
{
int n=G.n,m=G.m;//方便用
int indegree[n];//入度表
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){//入度表初始化
indegree[i] = 0;
}
//=========计算每个点的入度=========
for(int i =0; i < n; i++){
VNode* pcur = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while(pcur != NULL){
indegree[pcur->adjvex]++;
pcur = pcur->nextarc;
}
}
Queue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
//初始化拓扑排序,寻找第一届入度为0的点
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(indegree[i] == 0){
EnQueue(Q,i);
indegree[i] = -1;//表示已访问
cout<<i+1<<" ";
}
}
while(!IsEmpty(Q)){
int u = GetTop(Q)->data;
DeQueue(Q);
VNode* p = G.vertices[u].firstarc;
while(p != NULL){//出队的元素所有边(仅有出边)都要删除,所以将与其相邻的点的入度-1
if(indegree[p->adjvex] != -1)indegree[p->adjvex]--;
p = p->nextarc;
}
//扫描剩余点的入度,为0则标记且入队
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(indegree[i] != -1 && indegree[i] == 0){
EnQueue(Q,i);
indegree[i] = -1;
cout<<i+1<<" ";
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Graph G;
CreateGraph(G);
cout<<"DFS:";DFSTraverse(G);
cout<<endl<<"BFS:";BFSTraverse(G);
cout<<endl<<"TopologicalSort:";TopologicalSort(G);
return 0;
}