SIFT地理特征匹配——计算机视觉实验二
SIFT地理特征匹配——计算机视觉实验二
- 局部图像特征描述子
-
- 角点
- Harris角点检测
- Harris角点检测程序
- 结果分析
- 非极大值抑制
- 图像间寻找对应点
-
- 图像特征匹配
- 欧式距离
- NCC
- SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)
-
- 高斯金字塔
- DoG(Difference of Gaussian)高斯差分金字塔
- 关键点方向分配
- 关键点描述符
- SIFT检测关键点代码
- SIFT图像匹配
-
- 程序代码
- 地理特征匹配
-
- 测试图片
- 程序代码
- 运行结果
- 结果分析
局部图像特征描述子
图像特征描述是图片局部特征的表达,反映了图片局部的特性,常用用图片的特征匹配等应用。特征的分类有角点、梯度特征点等,特征点必须具有不变性。角点的检测常用Harris算子,梯度特征点的检测常用SIFT算子。
角点
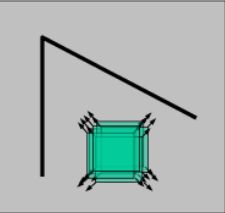
在图像局部做一个小的窗口,当窗口沿着各个方向移动,窗口内的灰度发生了明显的变化点称作角点,如图1;如果窗口沿着各个方向移动,窗口内的灰度均没有有明显的变化,则是平坦的,如图2;如果窗口沿着某个直线方向移动灰度没有明显的变化,但是沿着其他方向灰度有明显的变化,则该点处于边缘,如下图3


Harris角点检测
既然知道了什么是角点,那么如何去检测角点呢?常用的检测算法就是Harris算子。下面我们来看看如何用数学来表达Harris算子。
- 灰度变化函数E(u, v)

E(u, v)表示局部窗口在x轴方向移动了u,在y轴方向移动了v,产生的灰度变化。w(x, y)表示一个窗口函数,I(x+u, y+v)表示窗口移动的灰度值,I(x, y)表示窗口移动前的灰度值 - 求解E(u ,v)和 I(x+u, y+v)
求解I(x+u, y+v)这里用到了高数的知识——泰勒展开式,学过高数的都知道,f(x) 在 x=x0 处的泰勒展开式如下面这个式子
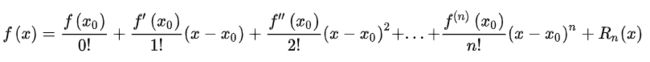
由一元的泰勒展开,我们就可以联想到二元函数在(x0, y0)处的泰勒展开如下。因为在二阶导及其之后的项可以算是高阶无穷小,因此可以忽略不计。
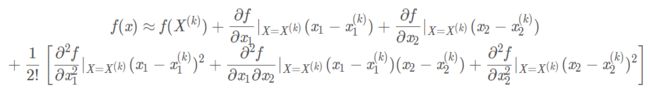
借助二元泰勒展开的式子,我们将I(x+u, y+v) 在(x, y)处展开到二阶。得到了下面的式子

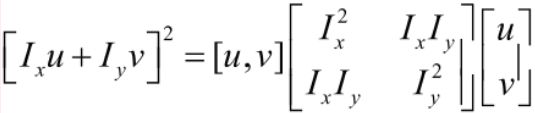
所以E(u ,v)可以等价的转换成下面的公式,其中M是一个2×2的矩阵。而众所周知,2×2的行列式矩阵有两个特征值λ1、λ2。通过λ1、λ2我们可以定义角点响应函数R=λ1λ2 - k(λ1+λ2)^2,用角点响应函数R来判断一个点是否是角点。其中k的值一般0.04~0.06。如果R>0,则该点是个角点,如果R=0,则是平坦的,如果R<0,则是边缘区域。
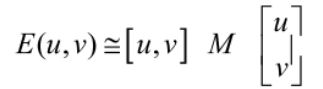
Harris角点检测程序
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
# 读入图像
im = array(Image.open('img/jmu01.jpg').convert('L'))
# 检测harris角点
'''
compute_harris_response函数是在在一幅灰度图像中,
对每个像素计算harris角点检测器响应函数,返回像数值为Harris响应值的一幅图像
'''
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im)
# Harris响应函数
harrisim1 = 255 - harrisim
figure()
gray()
#画出Harris响应图
subplot(141)
imshow(harrisim1)
axis('off')
axis('equal')
# 阈值
threshold = [0.01, 0.05, 0.1]
for i, thres in enumerate(threshold):
filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, thres)
subplot(1, 4, i+2)
imshow(im)
print(im.shape)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
show()
结果分析
从程序运行的结果可以发现,角点周围也有很多响应值很大的角点,使得角点比较密集,这是因为角点周围的点的角点响应函数值一般也会比较大,这样角点周围也会有很多点被当作是角点,就会像上面角点检测程序得到的结果一样,检测的角点很密集。如果要留下一个角点,可以用非极大值抑制的方法。
非极大值抑制
非极大值抑制就是用一个模板,以该模板的中心点为准,计算该点的角点响应值R,如果该点的响应值R比周围的响应值都大,则周围的响应值变为0,如果该点的响应值R比周围的响应值都笑,则该点的响应值变为0
图像间寻找对应点
图像特征匹配
图像特征匹配主要说明三种方法:欧式距离、NCC(Normalized Cross Correlation)、SIFT。主要详细讲解SIFT
欧式距离
两幅图像检测到了特征点后,可以提取特征点周围的图像块,构造特征描述符,特征描述符是一个特征向量。即每一个特征点都会有一个特征向量来描述它,如下图的X和Y。将图A的特征向量X(1)和B图肿的所有特征点Y(i)相减做欧式距离,距离越小,则特征点越相似

NCC
- NCC算法用来匹配两幅图像的相似程度,它将图像进行归一化处理,然后两个图像的对应值相乘,得到的结果如果越大,则对应点越匹配。
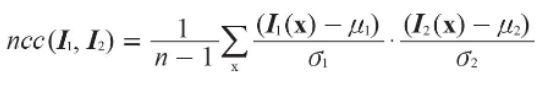
- ncc图像匹配存在一些问题,如果两幅图像中目标的大小不一致,那么窗口内的像素内容就会不一致,导致归一化效果不好,或者如果目标有形变、改变光照等,也会导致匹配不精确
SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)
SIFT算子是对前人技术的一个总结的一项技术。在前面说的两种图像特征匹配算子都不能够很好的解决图像尺度变换、角度旋转、曝光程度不一致、部分目标遮挡、杂物场景、噪声等问题。
如果两幅图像曝光程度差别很大,那么做欧式距离,得到的差值也会比较大;再如,两幅图像中目标的尺度一个较大、一个较小,那么NCC算法归一化的效果就不会很好,但是SIFT能够解决上述为题。
显然SIFT要解决上述的问题,那么SIFT要找的特征点应该是那些十分突出、不会因为光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消失的点,它希望选出的关键点(或特征点)应该具有尺度不变性、方向不变性、位移不变性、光照不变性,例如角点、边缘点、暗区域的亮点、亮区域的暗点等。下面介绍SIFT的匹配过程
高斯金字塔
- 高斯金字塔模拟的是我们人眼看图像的效果,人眼看近处的图像的时候尺度是大的,且比较清晰;当人眼看远处的图像的时候尺度是小的,且模糊。
- 高斯金字塔用来解决的是尺度不变性的问题。图像在高斯金字塔上被分成很多组(Octave[i],八度),每一组中有3~5层(一般为5层),每组图像的尺度都是一样的,但是每一组的尺度是逐渐减小的。
- 先将图像放大一倍作为金字塔第一组的第一层,然后以方差σ对这一层图像进行高斯滤波(用高斯滤波不会对图像带来额外的噪声),经过高斯滤波后,图像变得模糊,将得到的图像作为第一组的第二层。然后再对第二层的图像以方差 kσ 进行高斯滤波得到第三层,以此类推。当完成第一组图像的构建后,要对第一组导数第三层图像进行降采样(图像宽高各缩小一般),来得到第二组第一层的图像,第二组图像是第一组图像尺度的一半。
- 依此类推就模拟了人眼看近图大而清晰,看远图小而模糊的效果,需要注意的是,每一层的方差是前一层的k倍
DoG(Difference of Gaussian)高斯差分金字塔
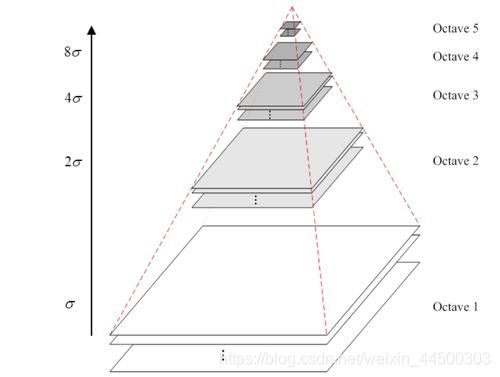
- 将高斯金字塔同一组的相邻图像进行相减,就得到了高斯差分金字塔,如果一组有5层,那得到的高斯差分金字塔的一组就有4层。构建高斯金字塔的目的就是为了构建DoG金字塔,因为SIFT特征的提取是在DoG金字塔上进行的
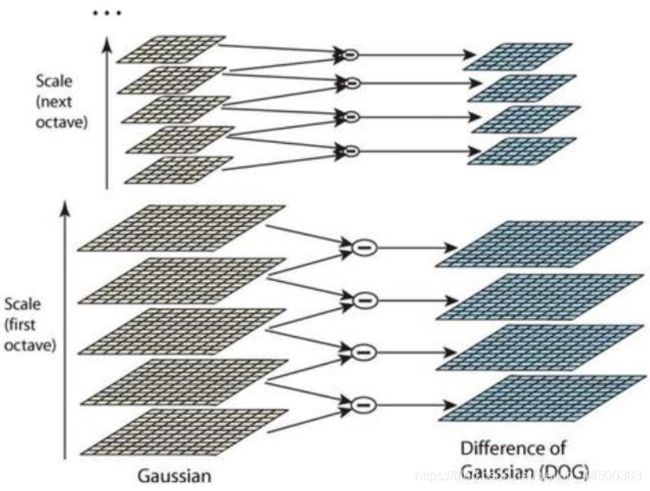
- 通过高斯差分图像可以看出图像上的像素值变化情况,如果没有变化就没有特征,特征变化必须是必须尽可能多的点。特征点由DoG空间的局部极值点组成,要找到DoG图像的局部极值,就要对图像上的点进行求导,求导需要用到x、y、z三个方向(z方向即为尺度轴),所以DoG金字塔的每一组图像只有中间两层可以求导,而组内最上面一层或最下面一层z轴方向没有图像,所以无法求导,不能找极值点
关键点方向分配
- 关键点方向分配,用来解决旋转角度问题。首先要了解图像的梯度幅值和梯度方向
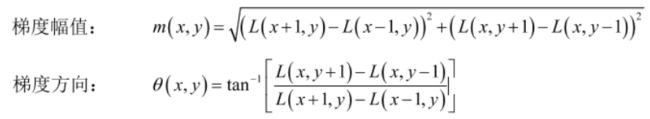
- 要确定关键点的主方向,首先以关键点为圆心,以该关键点所在高斯图像的尺度的1.5倍为半径的作圆,统计圆内的所有的像素的梯度方向,及其梯度幅值,并做1.5σ的高斯滤波。像素的梯度方向会在[0, 2π]分布,因此将2π分成8个方向,并统计梯度方向落在每个方向上的数量,统计直方图,数量最多的定为关键点的主方向。如果梯度方向直方图中存在一个主峰值80%的峰值时,则认为这个点是关键点的辅方向
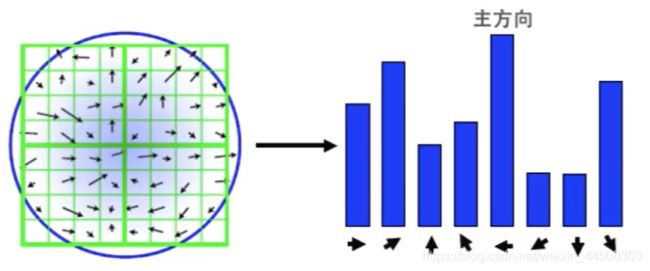
关键点描述符
- 每个关键点都有描述符。要匹配两张图片,就要将两张图片所有关键点的描述符拿来进行匹配,计算欧式距离,如果距离小就可能是相同的特征点。下面简单说明如何构建关键点描述符
- 首先周围像素分成2×2=4个子区域,每个子区域都是一个4×4的像素大小,因此每个子区域都会有不同方向的梯度方向和梯度幅值,将这些方向分类成[0, 2π]内的8个方向,相同方向上的赋值进行累加。因此一个子区域就会有8维的特征描述符,每一维的数值为对应方向上的幅值,总的4个区域就会有32维的特征描述符。
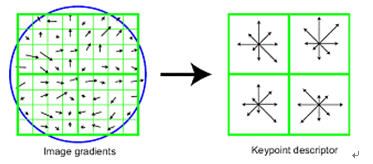
- 实验证明,128维的向量表征效果最优,即分成4×4=16个子区域
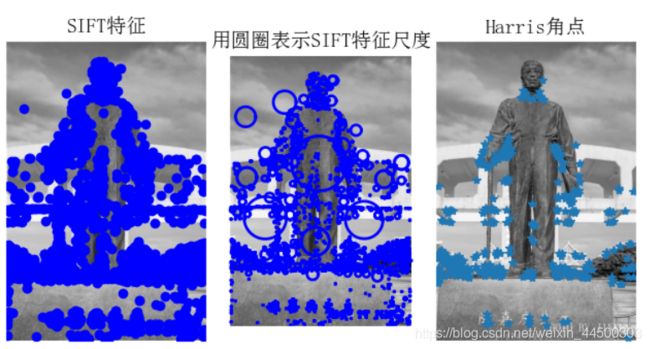
SIFT检测关键点代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
# 添加中文字体支持
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\SimSun.ttc", size=14)
imname = 'img/jmu01.jpg'
im = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L'))
sift.process_image(imname, 'img/jmu01.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('img/jmu01.sift')
figure()
gray()
subplot(131)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=False)
title(u'SIFT特征',fontproperties=font)
subplot(132)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=True)
title(u'用圆圈表示SIFT特征尺度',fontproperties=font)
# 检测harris角点
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im)
subplot(133)
filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, 0.1)
imshow(im)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
title(u'Harris角点',fontproperties=font)
show()
SIFT图像匹配
程序代码
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
import sys
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
im1f = 'D:/pythonProjects/sift/img/jmu13.jpg'
im2f = 'D:/pythonProjects/sift/img/jmu14.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
#matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print('{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
运行结果


结果分析
从上面的结果看出SIFT特征匹配能够比较好的处理尺度变换、角度旋转问题,即使目标发生了大小变化和形变,也能够较好的匹配到两幅相似的图像。
地理特征匹配
测试图片
程序代码
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
download_path = "D:\\pythonProjects\\sift\\img" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "D:\\pythonProjects\\sift\\img\\" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print("The match scores is: \n", matchscores)
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
#可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('jmu.png')
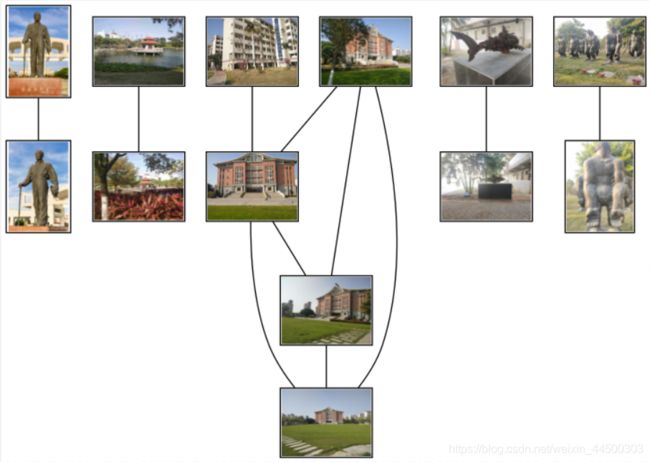
运行结果
结果分析
从结果看到测试用了17张图片,但是出来了是13张,其中有4张没有匹配出来。因为在上面代码的第42行设定了阈值theshhold=2,而有些图片特征点匹配的数量小于等于2,使得在可视化图片匹配的时候没有显示出来。
对于同一场景的相同目标,即使发生了形变、尺度的变化,有些光照程度也不一致,或是目标被部分遮挡,但是SIFT算子还是能够找到这些目标,从而较准确的匹配到。说明SIFT算子具有旋转、缩放、平移不变性的优点,并且光照影响小,目标遮挡影响小。因为SIFT使用的是高斯滤波,因此噪声对算法的影响也是比较小的。
上面显示的结果出现了一个问题,那就是jmu05和jmu06这两张图片实际上拍摄的是引桐楼,但是jmu06却和中山纪念馆匹配在了一起。jmu05没有和jmu06相匹配因为拍摄的角度发生了较大的改变,导致两幅图像没有相同的特征目标,相匹配的特征点小于或等于2。但是jmu06这张引桐楼的照片却和中山纪念馆匹配到了一起,观察图片应该是因为jmu06引桐楼的表面上的纹理和中山纪念正面表面的纹理比较相似,所以jmu06引桐楼和jmu12正面中山纪念馆的近照匹配到了一起。
另外鲨鱼的三张图片只匹配了两张出来,应该也是应该角度变换过多的问题,导致特征点消失。而猩猩看天的4张图片,只匹配出了jmu16和jmu17,因为jmu17中明显包含了jmu16这只猩猩,有相同的目标,而SIFT能够解决尺度旋转问题,所以匹配出了这两张图片,但是其他两张图片没有匹配出来,因为角度旋转过多,导致目标的特征点消失,从而无法匹配出来。
从上面的实验结果,可以得到一些SIFT的不足之处,其一,如果存在外表很像的两幅图像,有可能会被误判为相同的图像;其二,如果两幅图像没有相同的特征目标,那么这两幅图像可能不会被匹配在一起;其三,如果两幅图像因为角度旋转的问题导致了特征点消失,那么这两幅图像也不会被匹配在一起。
使用代码进行SIFT特征匹配的时候,最好把图片改成一样的宽度和高度,不然可能会报出图片维度不一致的错误