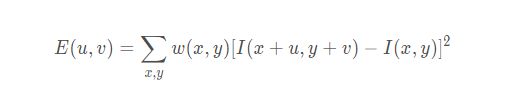计算机视觉学习02:局部图像描述子:Harris角点检测及匹配,以及地理标记的匹配
计算机视觉学习02:局部图像描述子:Harris角点检测及匹配以及地理标记
文章目录
- 计算机视觉学习02:局部图像描述子:Harris角点检测及匹配以及地理标记
-
-
- 1. Harris角点检测器
-
- 1.1 算法基础思想
- 1.2 检测算法的数学公式
- 1.3 检测算法代码
- 2.寻找地理标记图像
-
1. Harris角点检测器
1.1 算法基础思想
算法思想:通过图像局部小窗口观察图像特征,并通过窗口向任意方向移动都会导致图像灰度明显变化的像素窗口内的像素点即为角点。
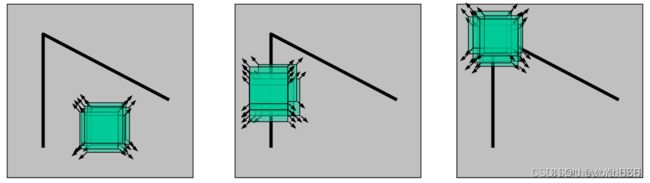
如上图所示,左边的图像在任意方向进行微小的局部平移并不会导致灰度明显的变化,因此可以判断该局部窗口所属区域为平坦区域;中间的图像在上下移动时并不会产生明显的灰度变化,而在左右移动时会产生较大的变化,因此可以判断该局部窗口区域处于一个竖直的边缘;右边的图像在往任意方向进行移动时都会导致图像灰度明显变化,判断局部窗口内的像素点为角点。
1.2 检测算法的数学公式
Harris角点检测思想中很重要的一步是去计算局部窗口滑动前后的像素点灰度变化。因此首先需要了解窗口像素灰度变化的描述表达,如下公式:
1.3 检测算法代码
上述的数学表达中可以看出我们的计算对象是矩阵M,因此代码的第一步是通过高斯滤波对X轴方向和Y轴方向进行一系列的图像导数提取(图像导数可以表示灰度变化)。再进行响应函数的计算。
# 在一幅灰度图像中,对每个函数计算Harris角点检测相应函数
def compute_harris_response(img, sigma = 3):
# 计算导数
imx = zeros(img.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(img, (sigma,sigma),(0,1), imx)
imy = zeros(img.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(img, (sigma,sigma),(1,0), imy)
# 可视化原图
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.title('灰度图')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(img, plt.cm.gray)
# 可视化x方向导数图像
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.title('x方向导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imx, plt.cm.gray)
# 可视化y方向导数图像
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.title('y方向导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imy, plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.title('x方向二阶导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imx * imx, plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.title('x/y方向二阶导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imx * imy, plt.cm.gray)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
plt.title('y方向二阶导数')
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(imy * imy, plt.cm.gray)
plt.show()
# 计算Harris矩阵的分量
Wxx = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imx,sigma)
Wxy = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imy,sigma)
Wyy = filters.gaussian_filter(imy*imy,sigma)
# 计算特征值和迹
# 矩阵特征值的积等于行列式的值
Wdet = Wxx * Wyy - Wxy ** 2
# 主对角线上元素的和称为矩阵的迹,也是特征值的和
Wtr = Wxx + Wyy
return Wdet / Wtr
# 从一幅Harris响应图像中返回角点。min_dist为分割角点和图像边界的最少像素数目
def get_harris_points(harrisim, min_dist = 10, threshold = 0.1):
# 寻找高于阈值的候选角点
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
#print(corner_threshold)
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
plt.imshow(harrisim_t, plt.cm.gray)
# 得到候选点的坐标(取出是角点的坐标)
coords = array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
#print(coords.shape)
# 以及它们的Harris响应值
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0],c[1]] for c in coords]
# 对候选点按照Harris响应值进行排序
index = argsort(candidate_values)
# 将可行点的位置保存到数组中
allowed_location = zeros(harrisim.shape)
# 相当于把外面一圈有响应值的点先舍去(匹配主体在中心)
allowed_location[min_dist:-min_dist, min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# 按照min_distance原则,选择最佳的Harris角点
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_location[coords[i,0],coords[i,1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_location[(coords[i,0] - min_dist):(coords[i,0] + min_dist), (coords[i,1] - min_dist):(coords[i,1] + min_dist)] = 0
return filtered_coords
# 绘制图像中检测到的角点
def plot_harris_point(image, filtered_coords):
figure()
gray()
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords],[p[0] for p in filtered_coords],'*')
axis('off')
show()
if "__main__" == __name__:
# 打开灰度图convert('L')
img = array(Image.open("harris/test1.jpg").convert('L'))
harrisim = compute_harris_response(img)
# harrisim1 = 255 - harrisim
# img1 = Image.fromarray(harrisim1)
# figure()
# gray()
# imshow(img1)
# show()
filtered_coords = get_harris_points(harrisim,6)
plot_harris_point(img, filtered_coords)
# 获得角点的特征描述(划分以角点为中心的5*5区域)
def get_descriptors(image, filtered_coords, wid = 5):
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0] - wid:coords[0] + wid + 1, coords[1] - wid:coords[1] + wid + 1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
# 归一化互相关获得得分
def match(desc1, desc2, threshold = 0.5):
n = len(desc1[0])
d = -ones((len(desc1),len(desc2)))
for i in tqdm(range(len(desc1))):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n-1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i,j] = ncc_value
ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:,0]
return matchscores
# 进行两边对称版本的匹配
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2, threshold = 0.5):
matches_12 = match(desc1,desc2,threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2,desc1,threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 >= 0)[0]
# 筛去不匹配的点
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12[n]] != n:
matches_12[n] = -1
return matches_12
def appendimages(img1,img2):
rows1 = img1.shape[0]
rows2 = img2.shape[0]
if rows1 < rows2:
img1 = concatenate((img1, zeros((rows2 - rows1, img1.shape[1]))),axis = 0)
elif rows1 > rows2:
img2 = concatenate((img2, zeros((rows1 - rows2, img2.shape[1]))),axis = 0)
return concatenate((img1,img2), axis = 1)
def plot_matches(img1, img2, locs1, locs2, matchscores, show_below = False):
img3 = appendimages(img1, img2)
if show_below:
img3 = vstack((img3,img3))
imshow(img3)
cols1 = img1.shape[1]
for i,m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m > 0:
plot([locs1[i][1],locs2[m][1] + cols1],[locs1[i][0],locs2[m][0]],'c')
axis('off')
if "__main__" == __name__:
# 打开灰度图convert('L')
img1 = array(Image.open("harris/test1.jpg").convert('L'))
img2 = array(Image.open("harris/test2.jpg").convert('L'))
wid = 5
harrisim = compute_harris_response(img1,5)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisim, wid + 1)
d1 = get_descriptors(img1,filtered_coords1,wid)
harrisim = compute_harris_response(img2,5)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisim, wid + 1)
d2 = get_descriptors(img2,filtered_coords2,wid)
print("starting matching")
matches = match_twosided(d1,d2)
figure()
gray()
plot_matches(img1,img2,filtered_coords1,filtered_coords2,matches)
show()
效果如下:
2.寻找地理标记图像
代码:
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
""" This is the example graph illustration of matching images from Figure 2-10.
To download the images, see ch2_download_panoramio.py."""
#download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
#path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
download_path = "C:\\Users\lianx\PycharmProjects\\untitled2\zsjng" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "C:\\Users\lianx\PycharmProjects\\untitled2\zsjng" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print("The match scores is: \n", matchscores)
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
#可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('jmu.png')
效果:
效果看起来还不错,但是这样的匹配对于照片的清晰度是有一定要求的。
temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor=‘transparent’, shape=‘rectangle’, image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png(‘jmu.png’)
效果:
[外链图片转存中...(img-qKnENDdc-1648653636052)]
效果看起来还不错,但是这样的匹配对于照片的清晰度是有一定要求的。