计算机视觉——第二章 图像局部描述符 :SIFT特征匹配
图像局部描述符 :SIFT特征匹配
- 1.SIFT特征提取与检索原理
-
- 1.1 SIFT特征和Harris特征点匹配处理结果对比
- 2.特征匹配
-
- 2.1 Harris特征匹配处理
- 2.2 sift特征匹配处理
- 2.3 两种特征匹配处理结果对比分析
- 3.地理标记图像匹配
- 总结
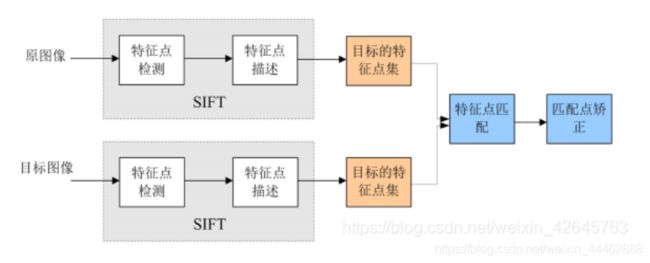
1.SIFT特征提取与检索原理
SIFT算法的实质可以归为在不同尺度空间上查找特征点(关键点)的问题。
关键点(特征点)
这些点是一些十分突出的点不会因光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消 失,比如角点、边缘点、暗区域的亮点以及亮区域的暗点。既然两幅图像中 有相同的景物,那么使用某种方法分别提取各自的稳定点,这些点之间会有 相互对应的匹配点。
尺度空间(scale space )
尺度空间理论最早于1962年提出,其主要思想是通过 对原始图像进行尺度变换,获得图像多尺度下的空间表示。 从而实现边缘、角点检测和不同分辨率上的特征提取,以 满足特征点的尺度不变性。
尺度空间中各尺度图像的 模糊程度逐渐变大,能够模拟 人在距离目标由近到远时目标 在视网膜上的形成过程。 尺度越大图像越模糊。
SIFT是尺度不变特征变换,其过程包括兴趣点的采集和描述子。SIFT的描述子具有很强的稳健性,这也是SIFT特征成功和流行的主要原因。
SIFT具体可以分为以下几个步骤。
1.使用高斯差分函数来定位兴趣点:
Gσ是二维高斯核,Iσ是Gσ模糊的灰度图像,K是决定相差尺度的常数。兴趣点是在图像位置和尺度变化下D(x,σ)的最大值和最小值点。
SIFT描述子在兴趣点附近选取子区域网格,在每个区域内计算图像梯度方向直方图,每个子区域的直方图拼接起来组成描述子向量。SIFT描述子的标准设置使用4x4的子区域,每个子区域使用8个小区间的方向直方图,共计产生128个小区间直方图。最终确定特征方向。
具体原理参照
1.1 SIFT特征和Harris特征点匹配处理结果对比
运行代码:
#*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\SimSun.ttc", size=14)
imname = 'D:\\pycharmProject\\大三下课程(Anaconda)\\计算机视觉\\实验三(第二章)\\sift特征匹配图片\\14.jpg'
im = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L'))
sift.process_image(imname, '21.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('21.sift')
figure()
gray()
subplot(131)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=False)
title(u'SIFT特征',fontproperties=font)
subplot(132)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=True)
title(u'用圆圈表示SIFT特征尺度',fontproperties=font)
#检测harris角点
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im)
subplot(133)
filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, 0.1)
imshow(im)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
title(u'Harris角点',fontproperties=font)
show()
运行结果:

结果分析:
从结果中我们可以明显的看出SIFT特征的识别要强于Harris角点,例如图中建筑物中部的轮廓和空中的鳞云SIFT能够很好的识别而Harris脚点却无法识别。这正是由于算法的原理不同而导致了结果的不同,Harris脚点检测主要依据Harris矩阵的特征值为依据进行脚点的检测,在一定区域内像素差别不大的情况下不能够很好的进行脚点检测; 而SIFT特征通过在不同的尺度空间中寻找极值点(特征点,关键点)的精确定位和主方向,构建关键点描述符来提取特征。在不同尺度空间的变换很好地解决了小区域的识别不清问题。
2.特征匹配
2.1 Harris特征匹配处理
#*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
from PCV.tools.imtools import imresize
"""
This is the Harris point matching example in Figure 2-2.
"""
im1 = array(Image.open("D:\\pycharmProject\\大三下课程(Anaconda)\\计算机视觉\\实验三(第二章)\\sift特征匹配图片\\2.jpg").convert("L"))
im2 = array(Image.open("D:\\pycharmProject\\大三下课程(Anaconda)\\计算机视觉\\实验三(第二章)\\sift特征匹配图片\\22.jpg").convert("L"))
#resize加快匹配速度
im1 = imresize(im1, (int(im1.shape[1]/2), int(im1.shape[0]/2)))
im2 = imresize(im2, (int(im2.shape[1]/2), int(im2.shape[0]/2)))
wid = 5
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d1 = harris.get_descriptors(im1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d2 = harris.get_descriptors(im2, filtered_coords2, wid)
print ('starting matching')
matches = harris.match_twosided(d1, d2)
figure()
gray()
harris.plot_matches(im1, im2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
2.2 sift特征匹配处理
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
import sys
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
im1f = r'D:\pycharmProject\大三下课程(Anaconda)\计算机视觉\实验三(第二章)\sift特征匹配图片\2.jpg'
im2f = r'D:\pycharmProject\大三下课程(Anaconda)\计算机视觉\实验三(第二章)\sift特征匹配图片\22.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
#matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print ('{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
2.3 两种特征匹配处理结果对比分析
通过对比两个实验运行结果可以很明显看出,sift特征匹配优于Harris特征匹配,此次两张实验图片是相似的,但是角度和尺度有点不大一样,SIFT提取的关键点具有尺度不变性、旋转不变性,且在亮度差异较大的情况也能够很好的进行特征匹配,Harris的算法则比较容易产生误差。
3.地理标记图像匹配
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import json
import os
import urllib
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
if __name__ == '__main__':
download_path = "D:\\image3"
path = "D:\\image3\\"
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
# 可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('D:\\image3\\jmu.png')
运行结果:
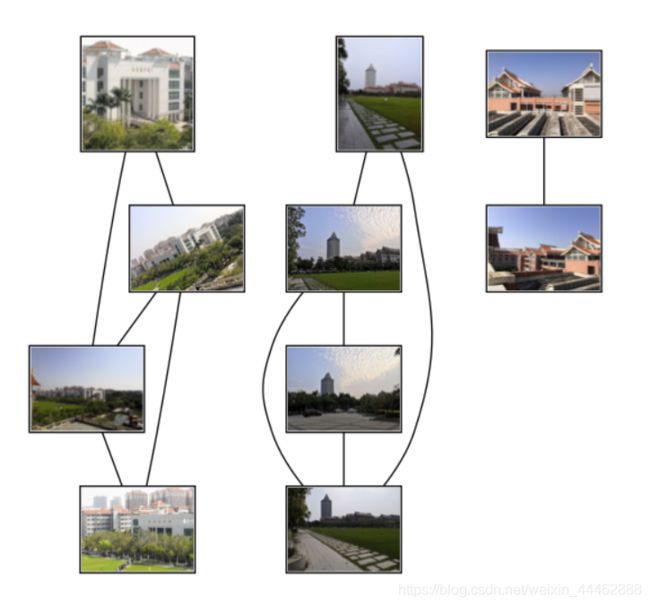

结果分析:
图片2.jpg是旋转二维的方向,图片集中1.jpg与10.jpg是对从不同拍摄角度拍摄,虽然SIFT对二维的图片旋转能够很好地进行匹配,但是通过不同角度拍摄得到的图片经过三维旋转并不能够准确的进行匹配。
图552.jpg与图8.jpg显然是不同场景拍摄的,但是由于灰色的地板砖占图片内容挺多的,所以会出现匹配成功的错误。
图13.jpg和图8.jpg显然是同一个方向拍摄的图片,但是由于是白天和夜晚的光线原因,sift不能很好的识别匹配特征点。
总结
此次实验验证sift的尺度不变性、旋转不变性,且在亮度差异较大的情况也能够很好的进行特征匹配,但是也从中发现三维方向的变化和亮度差距极大时sift还是会出现错误的。
此次实验有出现一些错误,其中之一地理匹配标记时可视化的代码要保存成png,要是保存成jpg时运行结果的连接图片无法展示出来,是空白的。
备注:用于测试的图片全部来自福建省厦门市集美大学,觉得集美大学长得不错的可以点个赞。
