[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换
0. 往期内容
[一]深度学习Pytorch-张量定义与张量创建
[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换
[三]深度学习Pytorch-张量数学运算
[四]深度学习Pytorch-线性回归
[五]深度学习Pytorch-计算图与动态图机制
[六]深度学习Pytorch-autograd与逻辑回归
[七]深度学习Pytorch-DataLoader与Dataset(含人民币二分类实战)
[八]深度学习Pytorch-图像预处理transforms
[九]深度学习Pytorch-transforms图像增强(剪裁、翻转、旋转)
[十]深度学习Pytorch-transforms图像操作及自定义方法
深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换
- 0. 往期内容
- 1. 张量拼接
-
- 1.1 torch.cat(tensors, dim=0)
- 1.2 torch.stack(tensors, dim=0)
- 2. 张量切分
-
- 2.1 torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0)
- 2.4 torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
- 3. 张量索引
-
- 3.1 torch.index_select(input, dim, index)
- 3.2 torch.masked_select(input, mask)
- 4. 张量变换
-
- 4.1 torch.reshape(input, shape)
- 4.2 torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1)
- 4.3 torch.t(input)
- 4.4 torch.squeeze(input)
- 4.5 torch.unsqueeze(input, dim)
1. 张量拼接
1.1 torch.cat(tensors, dim=0)
torch.cat(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
(1)功能:将张量在第dim个维度上进行拼接;
(2)参数:
tensors: 张量序列;
dim: 要拼接的维度;
(3)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 1 =======================================
# torch.cat
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.ones((2, 3)) #创建一个2*3的张量
#dim=0表示在第0个维度上进行拼接,输出为4*3张量,因为2+2=4,拼接的第0个维度:2
t_0 = torch.cat([t, t], dim=0)
#dim=1表示在第1个维度上进行拼接,输出为2*6的张量,因为3+3=6,拼接的是第1个维度:3
t_1 = torch.cat([t, t, t], dim=1)
#dim=1表示在第1个维度上进行拼接,输出为2*9的张量,因为3+3+3=9,拼接的是第1个维度:3
t_2 = torch.cat([t, t, t], dim=1)
print("t_0:{} shape:{}\nt_1:{} shape:{}".format(t_0, t_0.shape, t_1, t_1.shape))
>>> x = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.6580, -1.0969, -0.4614],
[-0.1034, -0.5790, 0.1497]])
>>> torch.cat((x, x, x), 0)
tensor([[ 0.6580, -1.0969, -0.4614],
[-0.1034, -0.5790, 0.1497],
[ 0.6580, -1.0969, -0.4614],
[-0.1034, -0.5790, 0.1497],
[ 0.6580, -1.0969, -0.4614],
[-0.1034, -0.5790, 0.1497]])
>>> torch.cat((x, x, x), 1)
tensor([[ 0.6580, -1.0969, -0.4614, 0.6580, -1.0969, -0.4614, 0.6580,
-1.0969, -0.4614],
[-0.1034, -0.5790, 0.1497, -0.1034, -0.5790, 0.1497, -0.1034,
-0.5790, 0.1497]])
1.2 torch.stack(tensors, dim=0)
torch.stack(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
(1)功能:将张量在新创建的dim维度上进行拼接;
(2)参数:
tensors: 张量序列;
dim: 新创建的维度,如果维度已经存在,则其他维度顺移;
(3)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 2 =======================================
# torch.stack
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.ones((2, 3))
#在新的维度上进行拼接,dim=2,由于t只有0、1维,因此会创建第2个维度,并在第二个维度进行拼接。
#输出为2*3*2的张量,最后一个2是新创建的。
t_stack = torch.stack([t, t], dim=2)
#由于t中已经存在0维,因此会重新创建第0维,原先的维度顺移(原来的第0维移为第1维,第1维移为第2维)
#输出为2*2*3,第一个2是新创建的。
t_stack = torch.stack([t, t], dim=0)
#由于t中已经存在0维,因此会重新创建第0维,原先的维度顺移(原来的第0维移为第1维,第1维移为第2维)
#输出为3*2*3,第一个2是新创建的。
t_stack = torch.stack([t, t, t], dim=0)
print("\nt_stack:{} shape:{}".format(t_stack, t_stack.shape))
2. 张量切分
2.1 torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0)
torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0)
(1)功能:将张量在第dim维度上进行平均切分;
(2)返回值:张量列表;
(3)参数:
input: 要进行切分的张量;
chunks: 要切分的份数;
dim: 要切分的维度;
(4)注意事项:
若不能整除,最后一份张量小于其他张量;
(5)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 3 =======================================
# torch.chunk
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
a = torch.ones((2, 5)) #创建2*5的张量
list_of_tensors = torch.chunk(a, dim=1, chunks=2) #在第1个维度(5)进行切分,并分为2份。
for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
#第1个张量:2*3,第二个张量:2*2,这是因为不能整除时,最后一个张量的尺寸会比前面的小,5/2向上取整=3
print("第{}个张量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1, t, t.shape))
a = torch.ones((2, 7)) #创建2*7的张量
list_of_tensors = torch.chunk(a, dim=1, chunks=3) #在第1个维度(7)进行切分,并分为3份。
for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
#第1个张量:2*3,第二个张量:2*3,第三个张量:2*1,这是因为不能整除时,最后一个张量的尺寸会比前面的小,7/3向上取整=3
print("第{}个张量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1, t, t.shape))
>>> torch.arange(11).chunk(6)
(tensor([0, 1]),
tensor([2, 3]),
tensor([4, 5]),
tensor([6, 7]),
tensor([8, 9]),
tensor([10]))
>>> torch.arange(12).chunk(6)
(tensor([0, 1]),
tensor([2, 3]),
tensor([4, 5]),
tensor([6, 7]),
tensor([8, 9]),
tensor([10, 11]))
>>> torch.arange(13).chunk(6)
(tensor([0, 1, 2]),
tensor([3, 4, 5]),
tensor([6, 7, 8]),
tensor([ 9, 10, 11]),
tensor([12]))
2.4 torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
(1)功能:将张量在第dim维度上进行切分;
(2)返回值:张量列表;
(3)参数:
input: 要进行切分的张量;
split_size_or_sections: 为int时,表示每一份的长度;为list时,按照list中的元素进行切分;
dim: 要切分的维度;
(4)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 4 =======================================
# torch.split
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.ones((2, 5))
#把张量t在第一个维度(5)上切成每份长度为2的张量,2+2+1=5
#第一个张量:2*2,第二个张量:2*2,第三个张量:2*1
list_of_tensors = torch.split(t, 2, dim=1)
for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}个张量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1, t, t.shape))
#根据list来决定每份的长度,因此第一个张量长度为2,第二个为1,第三个为2,2+1+2=5,即list的元素之和一定等于要切维度的大小,否则会报错。
#第一个张量:2*2,第二个张量:2*1,第三个张量:2*2
list_of_tensors = torch.split(t, [2, 1, 2], dim=1)
for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}个张量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx, t, t.shape))
>>> a = torch.arange(10).reshape(5,2)
>>> a
tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7],
[8, 9]])
>>> torch.split(a, [1,4])
(tensor([[0, 1]]),
tensor([[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7],
[8, 9]]))
3. 张量索引
3.1 torch.index_select(input, dim, index)
torch.index_select(input, dim, index, out=None)
(1)功能:在维度dim上,按照index索引数据;
(2)返回值:根据index索引数据拼接成的张量;
(3)参数:
input: 要索引的张量;
dim: 要索引的维度;
index: 要索引数据的序号;
(4)注意事项:索引的数据类型必须是torch.long;
(5)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 5 =======================================
# torch.index_select
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3)) #生成数值为[0,9)均匀分布的整数,大小为3*3的张量
#t=[[4,5,0], [5,7,1], [2,5,8]]
idx = torch.tensor([0, 2], dtype=torch.long) # 生成[0,2]张量,索引的数据类型必须是torch.long
#在第0个维度上找idx(第0个、第2个)的张量,输出为[[4,5,0],[2,5,8]]
t_select = torch.index_select(t, dim=0, index=idx)
print("t:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}".format(t, t_select))
>>> x = torch.randn(3, 4)
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.1427, 0.0231, -0.5414, -1.0009],
[-0.4664, 0.2647, -0.1228, -1.1068],
[-1.1734, -0.6571, 0.7230, -0.6004]])
>>> indices = torch.tensor([0, 2])
>>> torch.index_select(x, 0, indices)
tensor([[ 0.1427, 0.0231, -0.5414, -1.0009],
[-1.1734, -0.6571, 0.7230, -0.6004]])
>>> torch.index_select(x, 1, indices)
tensor([[ 0.1427, -0.5414],
[-0.4664, -0.1228],
[-1.1734, 0.7230]])
3.2 torch.masked_select(input, mask)
torch.masked_select(input, mask, out=None)
(1)功能:按照mask中的True来索引元素;
(2)返回值:一维张量;
(3)参数:
input: 要索引的张量;
mask: 与input同形状的布尔型张量;
(4)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 6 =======================================
# torch.masked_select
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3)) #t=[[4,5,0], [5,7,1], [2,5,8]]
#ge大于等于,gt大于,le小于等于,lt小于
mask = t.ge(5) #d大于等于5返回True,小于5返回False
#mask=[[False, True, False],[True, True, False],[False, True, True]]
t_select = torch.masked_select(t, mask)
print("t:\n{}\nmask:\n{}\nt_select:\n{} ".format(t, mask, t_select))
#t_select=[5,5,7,5,8]
>>> x = torch.randn(3, 4)
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.3552, -2.3825, -0.8297, 0.3477],
[-1.2035, 1.2252, 0.5002, 0.6248],
[ 0.1307, -2.0608, 0.1244, 2.0139]])
>>> mask = x.ge(0.5)
>>> mask
tensor([[False, False, False, False],
[False, True, True, True],
[False, False, False, True]])
>>> torch.masked_select(x, mask)
tensor([ 1.2252, 0.5002, 0.6248, 2.0139])
4. 张量变换
4.1 torch.reshape(input, shape)
torch.reshape(input, shape)
(1)功能:变换张量的形状;
(2)注意事项:当张量在内存中是连续时,新张量与input共享数据内存;
(3)参数:
input: 要变换的张量;
shape: 新张量的形状;
(4)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 7 =======================================
# torch.reshape
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.randperm(8) #生成从0到7的随机数列
#t为张量[5,4,2,6,7,3,1,0]
t_reshape = torch.reshape(t, (2, 4)) #重新形状为2*4的张量
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t, t_reshape))
#t_reshape为张量[[5,4,2,6],[7,3,1,0]]
#重新形状为第0维*4的张量,第0维的数值自动计算,第0维=8/4=2
t_reshape = torch.reshape(t, (-1, 4))
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t, t_reshape))
#t_reshape为张量[[5,4,2,6],[7,3,1,0]]
#重新形状为第0维*2*2的张量,第0维的数值自动计算,第0维=8/2/2=2
t_reshape = torch.reshape(t, (-1, 2, 2))
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t, t_reshape))
#输出为[[[5,4],[2,6]],[[7,3],[1,0]]]
t[0] = 1024 #t的第0个数值改为1024
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t, t_reshape))
#t为张量[1024,4,2,6,7,3,1,0]
#输出为[[[1024,4],[2,6]],[[7,3],[1,0]]]
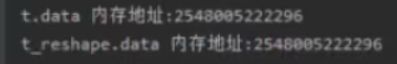
#两者的内存地址一样,是共享的
print("t.data 内存地址:{}".format(id(t.data)))
print("t_reshape.data 内存地址:{}".format(id(t_reshape.data)))
>>> a = torch.arange(4.)
>>> torch.reshape(a, (2, 2))
tensor([[ 0., 1.],
[ 2., 3.]])
>>> b = torch.tensor([[0, 1], [2, 3]])
>>> torch.reshape(b, (-1,))
tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3])
4.2 torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1)
torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1)
(1)功能:交换张量的两个维度;
(2)*参数:
input: 要交换的张量;
dim0: 要交换的维度;
dim1: 要交换的维度;
(3)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 8 =======================================
# torch.transpose
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
# torch.transpose
t = torch.rand((2, 3, 4)) #数值为(0,1)均匀分布,大小为2*3*4的张量
#输出为2*4*3,交换第一维和第二维
t_transpose = torch.transpose(t, dim0=1, dim1=2)
print("t shape:{}\nt_transpose shape: {}".format(t.shape, t_transpose.shape))
>>> x = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> x
tensor([[ 1.0028, -0.9893, 0.5809],
[-0.1669, 0.7299, 0.4942]])
>>> torch.transpose(x, 0, 1)
tensor([[ 1.0028, -0.1669],
[-0.9893, 0.7299],
[ 0.5809, 0.4942]])
4.3 torch.t(input)
torch.t(input)
(1)功能:用于2维张量转置,等价于torch.transpose(input, 0, 1);
(2)代码示例:
>>> x = torch.randn(())
>>> x
tensor(0.1995)
>>> torch.t(x)
tensor(0.1995)
>>> x = torch.randn(3)
>>> x
tensor([ 2.4320, -0.4608, 0.7702])
>>> torch.t(x)
tensor([ 2.4320, -0.4608, 0.7702])
>>> x = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.4875, 0.9158, -0.5872],
[ 0.3938, -0.6929, 0.6932]])
>>> torch.t(x)
tensor([[ 0.4875, 0.3938],
[ 0.9158, -0.6929],
[-0.5872, 0.6932]])
4.4 torch.squeeze(input)
torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None)
(1)功能:移除长度为1的维度(轴);
(2)*参数:
dim: 若dim=None,则移除所有长度为1的轴;若指定dim,当且仅当该轴长度为1时,移除对应的dim;
(3)代码示例:
# ======================================= example 9 =======================================
# torch.squeeze
# flag = True
flag = False
if flag:
t = torch.rand((1, 2, 3, 1)) #创建1*2*3*1的张量
t_sq = torch.squeeze(t) #dim=None,所以移除所有长度为1的轴,输出为2*3
t_0 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=0) #第0维为1维则移除第0维,输出为2*3*1
t_1 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=1) #第1为不是1维则不移除,输出为1*2*3*1
print(t.shape)
print(t_sq.shape)
print(t_0.shape)
print(t_1.shape)
>>> x = torch.zeros(2, 1, 2, 1, 2)
>>> x.size()
torch.Size([2, 1, 2, 1, 2])
>>> y = torch.squeeze(x)
>>> y.size()
torch.Size([2, 2, 2])
>>> y = torch.squeeze(x, 0)
>>> y.size()
torch.Size([2, 1, 2, 1, 2])
>>> y = torch.squeeze(x, 1)
>>> y.size()
torch.Size([2, 2, 1, 2])
4.5 torch.unsqueeze(input, dim)
torch.unsqueeze(input, dim)
(1)功能:根据dim扩展维度;
(2)*参数:
dim: 要扩展的维度;
(3)代码示例:
>>> x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> torch.unsqueeze(x, 0)
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3, 4]])
>>> torch.unsqueeze(x, 1)
tensor([[ 1],
[ 2],
[ 3],
[ 4]])
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/cc7d2bc0f7b14df7968d695b2db502c7.jpg)

![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/82d2c925b86142aaa738082cb3dc67fb.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7f732fcaa18e44d2b22d2e5fd30d0153.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3e731461459f4f5bbe484c066f1228f8.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/63bd58b66df446dbb367fa8903b72094.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/dd5089a173c343c697d0f00f05916c64.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b5f3c6a4c8394ca58e57704a619255bb.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/305bc5daeffe4b4ca966aeb1a706c6af.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/332f84ac5b7d4cc08bb0e5872c007e2e.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/eb160d206e5f4546bf2cd17e6bc0bc21.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/5fc1991abf704daca2a6a4ba187f0421.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第12张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/eebda0f7e3e74967b9b11deea2db2916.jpg)

![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第13张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ad37476b159b4fc38d3027b4a1e3fffd.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第14张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c25d19d38d0b442e897fe1f1c0c54513.jpg)
![[二]深度学习Pytorch-张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换_第15张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/94d45058380146a7a0e168b1e40cde67.jpg)