kubeadm部署kubernetes v1.23.5集群
kubeadm部署kubernetes v1.23.5集群
本示例中的安装部署Kubernetes集群将基于以下环境进行。
- OS: Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS (
红帽已停更CentOS 8,生产环境不再推荐使用CentOS发行版) - Kubernetes:v1.23.5
- Container Runtime: Containerd (
docker运行时已被弃用,不再推荐使用docker作为运行时)
前置要求:
- 至少2个CPU、2G内存
- 禁用swap交换分区
- 允许 iptables 检查桥接流量
本次使用kubeadm部署3节点的 Kubernetes集群,包含1个master节点及2个worker节点。
节点清单:
| HOSTNAME | IPADDRESS | CPU | Mem | Disk | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| master | 192.168.72.30 | 2C | 4G | 100G | Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS |
| worker1 | 192.168.72.31 | 2C | 4G | 100G | Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS |
| worker2 | 192.168.72.32 | 2C | 4G | 100G | Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS |
官方参考文档:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/container-runtimes/
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/install-kubeadm/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/create-cluster-kubeadm/
节点初始化
备注:以下操作在所有节点执行。
1、配置主机名
hostnamectl set-hostname master
hostnamectl set-hostname worker1
hostnamectl set-hostname worker2
2、配置hosts解析
cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF
192.168.72.30 master
192.168.72.31 worker1
192.168.72.32 worker2
EOF
3、更新系统
sudo apt update
sudo apt -y full-upgrade
4、关闭swap
swapoff -a
cp /etc/fstab{,.bak}
sed -e '/swap/ s/^#*/#/' -i /etc/fstab
swapon --show
5、禁用防火墙
ufw disable
ufw status
6、确认时间同步
apt install -y chrony
systemctl enable --now chronyd
chronyc sources && timedatectl
7、启用cgroupv2
sed -i -e 's/^GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=" systemd.unified_cgroup_hierarchy=1 "/' /etc/default/grub
sudo update-grub && reboot
grep cgroup /proc/filesystems
8、加载ipvs内核模块
参考:https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/master/pkg/proxy/ipvs
另外,针对Linux kernel 4.19以上的内核版本使用nf_conntrack 代替nf_conntrack_ipv4。
cat <<EOF | tee /etc/modules-load.d/ipvs.conf
# Load IPVS at boot
ip_vs
ip_vs_rr
ip_vs_wrr
ip_vs_sh
nf_conntrack
EOF
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack
#确认内核模块加载成功
lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack
#安装ipset和ipvsadm
apt install -y ipset ipvsadm
安装containerd
备注:以下操作在所有节点执行。
1、安装containerd容器运行时的前置条件
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/containerd.conf
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
# 设置必需的 sysctl 参数,这些参数在重新启动后仍然存在。
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/99-kubernetes-cri.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
EOF
# 应用 sysctl 参数而无需重新启动
sudo sysctl --system
2、安装containerd容器运行时,如果网络较差,建议使用浏览器下载到本地,在上传到服务器。
下载地址:https://github.com/containerd/nerdctl/releases
wget https://github.com/containerd/nerdctl/releases/download/v0.18.0/nerdctl-full-0.18.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar Cxzvvf /usr/local nerdctl-full-0.18.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
3、创建containerd配置文件
sudo mkdir -p /etc/containerd
containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.toml
4、配置使用 systemd cgroup 驱动程序
sed -i "s#SystemdCgroup = false#SystemdCgroup = true#g" /etc/containerd/config.toml
5、修改基础设施镜像
sed -i 's#k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.6#registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.6#g' /etc/containerd/config.toml
6、启动containerd服务
systemctl enable --now containerd
安装kubeadm
备注:以下操作在所有节点执行。
1、添加kubernetes源,使用阿里云apt源进行替换:
apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
curl https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | apt-key add -
cat <<EOF >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/apt/ kubernetes-xenial main
EOF
2、安装kubeadm、kubelet及kubectl
#查看可安装的版本
apt-cache madison kubectl | more
#指定版本进行安装
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet=1.23.5-00 kubeadm=1.23.5-00 kubectl=1.23.5-00
#锁定版本
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
3、启动kubelet服务
systemctl enable --now kubelet
部署master节点
备注:以下操作仅在master节点执行。
1、查看可安装的kubernetes版本
kubectl version --short
2、查看对应版本的容器镜像并提前拉取到本地
kubeadm config images list \
--kubernetes-version=v1.23.5 \
--image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
在所有节点执行以下命令,提前拉取镜像
kubeadm config images pull \
--kubernetes-version=v1.23.5 \
--image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
查看拉取的镜像
root@master:~# nerdctl -n k8s.io image
3、开始初始化master节点
如果后续扩展为高可用集群,则配置/etc/hosts将APIserver地址配置为DNS域名形式,所有节点都要执行:
echo "192.167.72.30 k8s-apiserver-lb.example.com" >> /etc/hosts
仅在master节点运行以下命令开始初始化master节点:
kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.23.5 \
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.72.30 \
--image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \
--pod-network-cidr=192.168.0.0/16 \
--control-plane-endpoint="k8s-apiserver-lb.example.com:6443" \
--upload-certs
参数说明:
- –apiserver-advertise-address kubeadm:kubernetes会使用默认网关所在的网络接口广播其主节点的 IP 地址,若需使用其他网络接口需要配置该参数
- –pod-network-cidr:Kubernetes 支持多种网络方案,不同网络方案对 --pod-network-cidr 有自己的要求,根据选择的 Pod 网络插件配置该参数,flannel设置为 10.244.0.0/16,calico设置为192.168.0.0/16
- –image-repository:Kubenetes默认registry地址是
k8s.gcr.io,国内无法访问,该参数将其指定为可访问的镜像地址,这里使用registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers - –control-plane-endpoint:如果计划后续将单控制平面集群升级为高可用集群,必须在初始化集群时配置该参数,否则不支持转换为高可用集群。该参数可以是负载均衡器的 DNS 名称或 IP 地址,推荐的做法是更新/etc/hosts文件并添加控制平面节点的 IP 地址和自定义 DNS 名称
- –kubernetes-version=v1.23.5:关闭版本探测,默认值是stable-1,会导致从
https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable-1.txt下载最新的版本号,可以将其指定为固定版本来跳过网络请求。
master节点初始化过程如下
root@master:~# kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.23.5 \
> --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.72.30 \
> --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \
> --pod-network-cidr=192.168.0.0/16 \
> --control-plane-endpoint="k8s-apiserver-lb.example.com:6443" \
> --upload-certs
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.23.5
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING SystemVerification]: missing optional cgroups: hugetlb
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-apiserver-lb.example.com kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.72.30]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master] and IPs [192.168.72.30 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master] and IPs [192.168.72.30 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[kubelet-check] Initial timeout of 40s passed.
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 135.015991 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.23" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
NOTE: The "kubelet-config-1.23" naming of the kubelet ConfigMap is deprecated. Once the UnversionedKubeletConfigMap feature gate graduates to Beta the default name will become just "kubelet-config". Kubeadm upgrade will handle this transition transparently.
[upload-certs] Storing the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[upload-certs] Using certificate key:
69ce81e92b717ec40ec97c7f073be779db97c73eb733975f6d156159ad132bc1
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: ycbz04.vnvwspu0vnvvcjqc
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of the control-plane node running the following command on each as root:
kubeadm join k8s-apiserver-lb.example.com:6443 --token ycbz04.vnvwspu0vnvvcjqc \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d1268d9fcfbe1ca264ce0a5f47314b48ada7ecdd75b91801b9d74e58ca8b6c4c \
--control-plane --certificate-key 69ce81e92b717ec40ec97c7f073be779db97c73eb733975f6d156159ad132bc1
Please note that the certificate-key gives access to cluster sensitive data, keep it secret!
As a safeguard, uploaded-certs will be deleted in two hours; If necessary, you can use
"kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs" to reload certs afterward.
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join k8s-apiserver-lb.example.com:6443 --token ycbz04.vnvwspu0vnvvcjqc \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d1268d9fcfbe1ca264ce0a5f47314b48ada7ecdd75b91801b9d74e58ca8b6c4c
4、master节点初始化完成后参考最后提示配置kubectl客户端连接
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
部署worker节点
备注:以下操作仅在worker节点执行。
参考master初始化提示信息,在worker1 和 worker12 节点上分别执行如下命令,将其注册到 Cluster 中:
kubeadm join k8s-apiserver-lb.example.com:6443 --token ycbz04.vnvwspu0vnvvcjqc \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d1268d9fcfbe1ca264ce0a5f47314b48ada7ecdd75b91801b9d74e58ca8b6c4c
在master节点查看节点当前运行状态,由于还未安装网络插件,此时节点状态为notready:
root@master:~# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master NotReady control-plane,master 9m53s v1.23.5
worker1 NotReady <none> 108s v1.23.5
worker2 NotReady <none> 105s v1.23.5
安装calico网络插件
参考:https://projectcalico.docs.tigera.io/getting-started/kubernetes/quickstart
1、在master节点执行以下操作,部署calico网络插件,等待calico相关pod完全启动
kubectl create -f https://projectcalico.docs.tigera.io/manifests/tigera-operator.yaml
kubectl create -f https://projectcalico.docs.tigera.io/manifests/custom-resources.yaml
2、查看节点状态全部为Ready
root@master:~# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master Ready control-plane,master 12h v1.23.5 192.168.72.30 <none> Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS 5.4.0-107-generic containerd://1.6.2
worker1 Ready <none> 12h v1.23.5 192.168.72.31 <none> Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS 5.4.0-107-generic containerd://1.6.2
worker2 Ready <none> 12h v1.23.5 192.168.72.32 <none> Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS 5.4.0-107-generic containerd://1.6.2
3、查看所有pod状态全部为Running
root@master:~# kubectl get pods -A -o wide
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
calico-apiserver calico-apiserver-7ffdf66697-jbq62 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.235.129 worker1 <none> <none>
calico-apiserver calico-apiserver-7ffdf66697-p48hx 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.189.68 worker2 <none> <none>
calico-system calico-kube-controllers-67f85d7449-5hpmz 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.189.66 worker2 <none> <none>
calico-system calico-node-d2znn 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.32 worker2 <none> <none>
calico-system calico-node-fz8qs 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.31 worker1 <none> <none>
calico-system calico-node-gkc6z 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.30 master <none> <none>
calico-system calico-typha-749477cf4-gdkfq 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.32 worker2 <none> <none>
calico-system calico-typha-749477cf4-xdhj2 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.31 worker1 <none> <none>
default nginx-85b98978db-48589 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.235.130 worker1 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-6d8c4cb4d-28n78 1/1 Running 0 12h 192.168.189.65 worker2 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-6d8c4cb4d-47qt9 1/1 Running 0 12h 192.168.189.67 worker2 <none> <none>
kube-system etcd-master 1/1 Running 0 12h 192.168.72.30 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-apiserver-master 1/1 Running 0 12h 192.168.72.30 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master 1/1 Running 0 12h 192.168.72.30 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-p7lmp 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.32 worker2 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-rg6kw 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.30 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-vmg46 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.31 worker1 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-scheduler-master 1/1 Running 0 12h 192.168.72.30 master <none> <none>
tigera-operator tigera-operator-b876f5799-rc5n7 1/1 Running 0 11h 192.168.72.31 worker1 <none> <none>
集群其他配置
1、在master节点执行以下操作,开启ipvs模式
修改kube-proxy configmap,添加mode:ipvs
kubectl -n kube-system get cm kube-proxy -o yaml | sed 's/mode: ""/mode: "ipvs"/g' | kubectl replace -f -
kubectl -n kube-system patch daemonset kube-proxy -p "{\"spec\":{\"template\":{\"metadata\":{\"annotations\":{\"date\":\"`date +'%s'`\"}}}}}"
验证工作模式
# curl 127.0.0.1:10249/proxyMode
ipvs
查看代理规则
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
2、master节点调度pod
默认情况下,出于安全原因,群集不会在master节点上调度pod,如果希望能够在master节点上调度pod,例如,对于用于开发的单机Kubernetes集群,请运行以下命令:
#master节点默认打了taints
[root@master ~]# kubectl describe nodes | grep Taints
Taints: node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule
#执行以下命令去掉taints污点
[root@master ~]# kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/master-
node/master untainted
#再次查看 taint字段为none
[root@master ~]# kubectl describe nodes | grep Taints
Taints: <none>
#如果要恢复Master Only状态,执行如下命令:
kubectl taint node k8s-master node-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoSchedule
部署应用验证集群
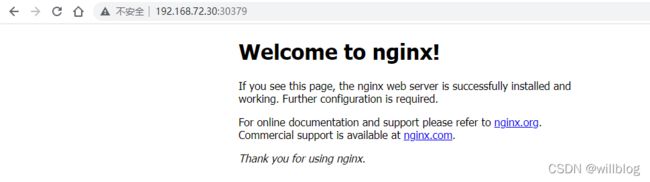
要检查是否可以成功创建 k8s 工作负载,请登录控制平面节点并使用 kubectl 命令创建名为 nginx 的新部署:
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx
公开 nginx pod 以通过互联网访问。为此目的创建一个新的服务节点端口:
kubectl create service nodeport nginx --tcp=80:80
使用下面给出的 kubectl 命令检查 nginx pod 和服务的状态:
root@master:~# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-85b98978db-48589 1/1 Running 0 11h
root@master:~# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 > 443/TCP 12h
nginx NodePort 10.96.166.220 > 80:30379/TCP 11h
清理集群
在所有节点执行以下操作:
kubeadm reset -f
ipvsadm --clear
ip link delete kube-ipvs0
rm -rf /etc/cni/
其他可选配置项
- 安装 Kubernetes dashboard 仪表板
- 安装 Metrics Server(用于检查 Pod 和节点资源使用情况)
- 部署 Prometheus / Grafana 监控
- 部署EFK、Grafana Loki日志系统
- 部署持久化存储,可选NFS、Rook-ceph、Openebs、Longhorn等
- 安装Ingress Controller、官方Ingress-Nginx、traefic、apache apisix等
- 安装负载均衡插件MetaLB、OpenELB等