Onehot_encode与Word2vec词向量训练
Onehot_encode与Word2vec词向量训练
1.编写onehot_encode函数
使用:
class sklearn.preprocessing.OneHotEncoder(*, categories='auto', drop=None, sparse=True, dtype=<class 'numpy.float64'>, handle_unknown='error')
categories中指定含有的类别[[a,b,c],[1,2,3]]一个大数组表示所有的特征,里面的每一个小数组表示每个特征含有的具体表现有什么,特征的种类数决定了使用多少位进行编码,比如有三个特征使用3位编码,2个特征使用2位编码,独热编码有几位就用几位编码,默认为auto,根据数据中出现多少种同样可以进行转化.
实现
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
def onehot_encode(x):
# categories中指定含有的类别[[a,b,c],[1,2,3]]一个大数组表示所有的特征,里面的每一个小数组表示每个特征
# 含有的具体表现有什么,特征的种类数决定了使用多少位进行编码,比如有三个特征使用3位编码,2个特征使用2位编码
# 独热编码有几位就用几位编码
# 默认为auto,根据数据中出现多少种同样可以进行转化
enc = OneHotEncoder(categories=[x],sparse = False)#(sparse = False) ,
to_encode=[[one]for one in x] #转化成每一个实例,表示为[[],[]]
ans = enc.fit_transform(to_encode)
# print('begin--')
# print(ans)
# 输出结果
rnt={}
for one,encoded in zip(x,ans):
print(one,':',encoded)
# print(rnt) # 输出 [[ 1. 0. 1. ..., 0. 0. 1.]
# [ 0. 1. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0.]
# [ 1. 0. 0. ..., 1. 0. 0.]
# [ 0. 1. 1. ..., 0. 1. 0.]]
x=['体育', '军事', '娱乐', '教育', '文化', '时尚', '科技', '财经']
print(x)
onehot_encode(x)
sparse=true作用:
体育 : (0, 0) 1.0
军事 : (0, 1) 1.0
娱乐 : (0, 2) 1.0
教育 : (0, 3) 1.0
文化 : (0, 4) 1.0
时尚 : (0, 5) 1.0
科技 : (0, 6) 1.0
财经 : (0, 7) 1.0
结果只是输出为1的位置,不会全部输出0/1值。
输出所有类别enc.categories_
print(enc.categories_)
>>[array(['体育', '军事', '娱乐', '教育', '文化', '时尚', '科技
', '财经'], dtype=object)]
通过编码反推对应种类enc.inverse_transform
print(enc.inverse_transform([[0,0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]]))
# >>[['财经']]
获得某个特征的所有名称enc.get_feature_names()
print(enc.get_feature_names())
# >>['group_体育' 'group_军事' 'group_娱乐' 'group_教育' 'group_文化' 'group_时尚'
# 'group_科技' 'group_财经']
# >>不加名称:['x0_体育' 'x0_军事' 'x0_娱乐' 'x0_教育' 'x0_文化' 'x0_时尚' 'x0_科技' 'x0_财经']
输出结果
2.Word2vec词向量训练
-
预处理:包括繁体->简体转换,分词,去除非中文词等主要步骤。
-
训练词向量:使用gensim训练并保存model。
-
加载模型并测试效果:如查看词汇的词向量,获取与某词汇最相关的n个词。
将XML的Wiki数据转换为text格式
classgensim.corpora.WikiCorpus(fname, processes=None, lemmatize=True, dictionary=None, filter_namespaces=('0', ))
get_texts() |
Iterate over the dump, returning text version of each article as a list of tokens |
|---|
得到xml里面的text文本;
#数据处理部分
from gensim.corpora import WikiCorpus
from gensim.models import word2vec
import zhconv #繁体字简体字转换
import jieba
import re
import multiprocessing
input_file_name = 'zhwiki-latest-pages-articles.xml.bz2'
output_file_name = 'corpus_cn.txt'
#加载数据
input_file = WikiCorpus(input_file_name, lemmatize=False, dictionary={})
#将lemmatize设置为False的主要目的是不使用pattern模块来进行英文单词的词干化处理,无论你的电脑#是否已经安装了pattern,因为使用pattern会严重影响这个处理过程,变得很慢
with open(output_file_name, 'w', encoding="utf8") as output_file:
#使用WikiCorpus类中的get_texts()方法读取文件,每篇文章转换为一行文本,并去掉标签符号等内容
count = 0
for text in input_file.get_texts():
output_file.write(' '.join(text) + '\n')
count = count + 1
if count % 10000 == 0:
print('已处理%d条数据' % count)
print('处理完成!')
#查看处理结果
with open('corpus_cn.txt',"r",encoding="utf8") as f:
print(f.readlines()[:1])
注意该方法为并行,因此实验代码必须放在__name__=='__main__'中;使用这种方法得到的数据既有繁体字又有简体字。
Wiki数据预处理
中文繁体替换成简体
使用opencc转化,下载c++版本,配置环境变量,使用命令行,将转化成简体:
opencc -i corpus_cn.txt -o corpus_cn_spl_seg.txt -c F:/t2s.json
使用的json文件要用绝对路径得到。
环境配置:
结巴分词
使用5w/10w/33w条数据:
if __name__ == '__main__':
f = codecs.open('corpus_cn_spl.txt', 'r', encoding='utf8')
target = codecs.open('corpus_cn_spl_seg.txt', 'w', encoding='utf8')
print ('open files.')
lineNum = 1
line = f.readline()
while line:
if lineNum==50000:#控制数量
break
if lineNum%10000==0:
print ('---processing ',lineNum,' article---')
seg_list = jieba.cut(line,cut_all=False)
line_seg = ' '.join(seg_list)
target.writelines(line_seg)
lineNum = lineNum + 1
line = f.readline()
print ('well done.')
f.close()
target.close()
这里使用了5W数据。
Word2Vec模型训练
#使用gensim word2vec训练脚本获取词向量 env nlppy36
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(action='ignore', category=UserWarning, module='gensim')# 忽略警告
import logging
import os.path
import sys
import multiprocessing
from gensim.corpora import WikiCorpus
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
from gensim.models.word2vec import LineSentence
if __name__ == '__main__':
program = os.path.basename(sys.argv[0])
logger = logging.getLogger(program)
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s: %(levelname)s: %(message)s',level=logging.INFO)
logger.info("running %s" % ' '.join(sys.argv))
# inp为输入语料, outp1 为输出模型, outp2为原始c版本word2vec的vector格式的模型
fdir = './'
inp = fdir + 'corpus_cn_spl_seg.txt'
outp1 = fdir + 'wiki.zh.text.model'
outp2 = fdir + 'wiki.zh.text.vector'
# 训练skip-gram模型
model = Word2Vec(LineSentence(inp), vector_size=400, window=5, min_count=5,
workers=multiprocessing.cpu_count())
# 保存模型
model.save(outp1)#保存模型
model.wv.save_word2vec_format(outp2, binary=False)#保存词向量
训练好的模型可以增加训练语料继续训练:
loaded_model = Word2Vec.load('word2vec.model') # 加载模型
loaded_model.train([["hello", "world"]], total_examples=1, epochs=1)
直接调用Word2Vec函数,训练得到模型,保存模型或者只保存词向量用于后续任务。
gensim.models.word2vec可选择两种训练模式,CBOW和skip-gram,分别对应从周围的词预测中间和从中间词预测周围的词是什么,通过这种方式训练后得到词向量矩阵。使用sg参数控制算法选择。
查看函数对应的各个参数
gensim.models.word2vec.Word2Vec(句子=None , corpus_file=None , vector_size=100 , alpha=0.025 , window=5 , min_count=5 , max_vocab_size=None , sample=0.001 , seed=1 , workers=3 , min_alpha=0.0001 , sg=0 , hs =0 , negative=5 , ns_exponent=0.75 , cbow_mean=1 , hashfxn=<内置 函数 哈希> , epochs =5 , null_word=0 , trim_rule=None ,sorted_vocab=1, batch_words=10000, compute_loss=False, callbacks=(), comment=None, max_final_vocab=None, shrink_windows=True )
- sg ( {0 , 1} , optional ) – 训练算法:1 表示 skip-gram;否则 CBOW。
- window ( int , optional ) – 句子中当前单词和预测单词之间的最大距离。
模型测试
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(action='ignore', category=UserWarning, module='gensim')# 忽略警告
import gensim
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = gensim.models.Word2Vec.load('wiki.zh.text.model')#调用模型
word = model.wv.most_similar(u"自然语言")#topn=100 可选择展示多少相近单词
for t in word:
print (t[0],t[1])
这里采用不同大小的数据集训练模型,训练数据集采用5w,10w和33w,给出不同大小 的数据集训练后给出的结果。找到某个单词最相近的几个单词。加载模型,然后选择应用函数。
查看存储词向量
输出某个词的词向量:“自然语言”
print('vector len:',len(wv['自然语言'])) #输出某个单词的词向量
vector len 词向量长度为: 400;
实验结果
输出对应的独热编码:
体育 : [1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
军事 : [0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
娱乐 : [0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
教育 : [0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
文化 : [0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
时尚 : [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
科技 : [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
财经 : [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]
训练:(https://github.com/AimeeLee77/wiki_zh_word2vec)
结果:
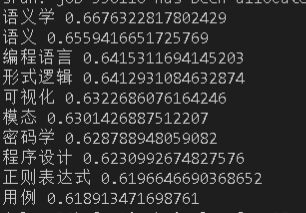
10w数据:
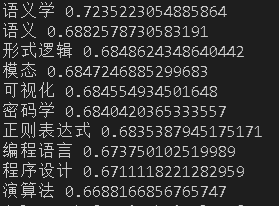
33w:
可以看到10w数据的时候,第一名仍然是语义学,第二名变成了语义而不是密码学,后续增加了形式逻辑、模态、可视化、密码学,相比与5w的密码学在第二位,语义在第三位,以及形式逻辑排名上升,去掉了数据结构、xml,总的来说结果有一定提升,给出的结果都与自然语言有比较强的相关性。
其他测试:
KeyError: "Key '计算机视觉' not present;KeyError: "Key 'computer vision' not present""
计算机 模型为 wiki.zh.text.model33w ;相近词语为:
计算器 0.6241149306297302
电脑 0.6170604825019836
电子计算机 0.6054976582527161
人工智能 0.6037363409996033
集成电路 0.5955638289451599
信号处理 0.5858120918273926
计算机科学 0.5816150903701782
个人电脑 0.5786007642745972
软件 0.5725179314613342
操作系统 0.571669340133667
计算机 模型为 wiki.zh.text.model10w ;相近词语为:
计算器 0.6530519127845764
人工智能 0.6474973559379578
电脑 0.6411188840866089
集成电路 0.619655191898346
电子计算机 0.6129189729690552
编程 0.6093308925628662
程序设计 0.603661835193634
电脑系统 0.5946774482727051
软件工程 0.5945618152618408
信号处理 0.5942318439483643
计算机 模型为 wiki.zh.text.model5w;相近词语为:
计算器 0.7061043977737427
人工智能 0.6994020342826843
电脑 0.6875249147415161
集成电路 0.6822654008865356
信号处理 0.6665181517601013
编程 0.6649145483970642
软件工程 0.6620650887489319
程序设计 0.6566900014877319
电子计算机 0.6523278951644897
建模 0.6512667536735535
通过计算机这个例子,可以更加明显看出使用全部语料U型训练的33w的模型结果中含有操作系统、个人电脑等词语,是5w和10w都不曾出现的,而且5/10w的词语相差不大,语料的大量增加导致结果大幅上升。