01 NSTimer造成的内存泄漏问题?
1.1 什么是内存泄漏?
一个对象在引用计数变为0时,系统会回收内存。如果一个本应该被回收的内存,没有被回收(引用计数>0),那么就会造成内存泄漏。
以下代码将造成内存泄漏:
@interface ViewController ()
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSTimer *timer;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(timerTest) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
}
- (void)timerTest
{
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
// 该ViewController将不会释放
- (void)dealloc
{
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
[self.timer invalidate];
}1.2 分析如下:
NSTimer的scheduledTimerWith
TimeInterval方法会传进去一个target,NSTimer内部实现会有一个对象强引用传入的对象例如(伪代码如下,示意图如下):
// 伪代码@interface NSTimer ()@property (strong, nonatomic) id target;@end // 强引用该对象self.target = target
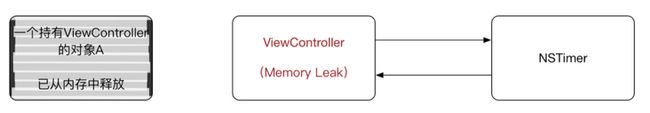
ViewController和NSTimer互相引用,此刻ViewController的引用计数为2
当一个对象的引用计数变为0时,系统将回收这块内存。
假设对象A在某一时刻需要从内存中释放,那么理应他引用的ViewController也应该释放,但是由于ViewController内部的NSTimer对其有个强引用,最终导致ViewController不能释放,从而导致内存泄漏。如图所示:
对象A释放,ViewController的引用计数变为1,原本应该引用计数变为0,从而ViewController内存泄漏
1.3 如何解决?
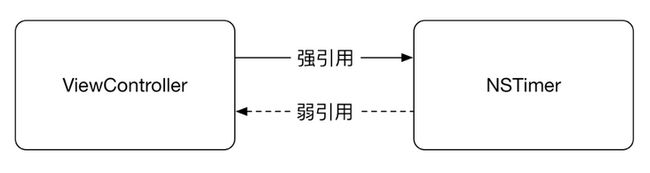
按照分析,那应该打破ViewController和NSTimer双方的强引用。使用弱引用(弱引用不增加对象的引用计数)。
方案1
使用系统代码Block块的方法破除循环引用
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; __weak typedef(self) weakSelf = self; self.timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1.0 repeats:YES block:^(NSTimer * _Nonnull timer) { [weakSelf timerTest]; }];}
NSTimer弱引用ViewController,在ViewController释放时,NSTimer也获得释放,循环链条断开
方案2
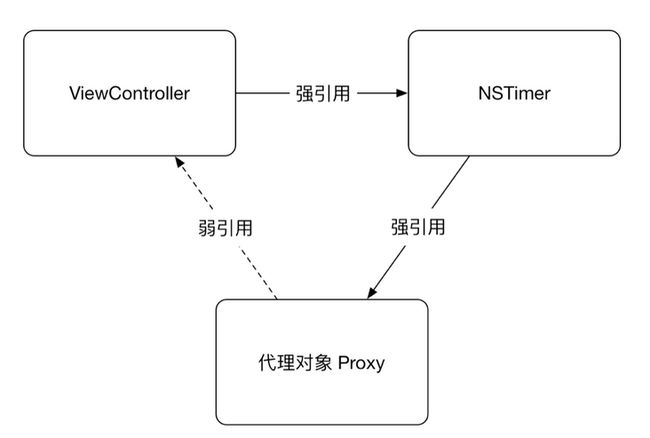
使用中间代理层来解决循环引用
// 代理类@interface Proxy : NSObject+ (instancetype)proxyWithTarget:(id)target;// 弱引用target@property (weak, nonatomic) id target;@end@implementation Proxy+ (instancetype)proxyWithTarget:(id)target { Proxy *proxy = [[MJProxy1 alloc] init]; proxy.target = target; return proxy;}- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { return self.target;}@end@interface ViewController ()@property (nonatomic, strong) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation ViewController- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; self.timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:[Proxy proxyWithTarget:self] selector:@selector(timerTest) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];}- (void)timerTest{ NSLog(@"%s", __func__);}// 该ViewController将不会释放- (void)dealloc{ NSLog(@"%s", __func__); [self.timer invalidate];}
如下图所示,ViewController需要强引用NSTimer,NSTimer内部需要强引用一个target对象,所以可以创建一个代理类来处理这个问题,所以proxy内部有一个弱引用的target对象,ViewController调用proxyWithTarget把self传入时不会强持有self。
三方之间没有循环引用,最终可以释放对象
02浅析Android的焦点机制
焦点是一个很宽泛的概念,中文释义是比喻问题的关键所在或争论的集中点,在物理学、数学、生活中都有广泛的使用。那么Android中的焦点是什么呢?
2.1 Android焦点概念
焦点在Android中也就是Focus,称为Focus机制。focus在英文中的释义是:
"the main or central point of something, especially of attention or interest",和中文语义相同。
回到我们Android开发中,我们手机屏幕可以同时显示多种多样的内容,那么你的焦点或者说你的注意力在哪个内容上?系统又该如何判断呢?举个例子,当屏幕界面中同时存在多个EditText(输入框)时,你的键盘输入会显示在哪个输入框内呢?亦或是同时显示在所有输入框中?这显然是不合理的,而这时焦点机制就体现了它的意义。对于EditText控件来说,获取到焦点,则意味着激活了和用户的交互,键盘输入的内容会输入到这个EditText上面。
2.2 焦点处理
焦点的处理包含获取焦点、分发焦点、清除焦点等。
2.2.1 获取焦点
让一个View获取焦点直接调用View#requestFocus方法,最终会调用到View#requestFocusNoSearch方法,其通过多个条件判断该View是否允许获取焦点,包括是否可见、是否可获取焦点、是否可用,以及在触屏设备中是否允许获取焦点等。
private boolean requestFocusNoSearch(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
// need to be focusable
if (!canTakeFocus()) {
return false;
}
// need to be focusable in touch mode if in touch mode
if (isInTouchMode() &&
(FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE != (mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE))) {
return false;
}
// need to not have any parents blocking us
if (hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus()) {
return false;
}
if (!isLayoutValid()) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_WANTS_FOCUS;
} else {
clearParentsWantFocus();
}
handleFocusGainInternal(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
return true;
}2.2.2 获取焦点的模式
获取焦点有两种模式,分别是:
普通模式(focusable):允许有普通获取焦点的能力(比如物理键、电视、手表等非触摸的输入方式)
触摸模式(focusableInTouchMode):允许有触摸获取焦点的能力。
需要注意的是,在设置允许触摸模式时会默认开启普通模式,注意同时设置这两个属性时不要冲突。
并且由此我们可以得到一条关于焦点的特性:
- 并不是所有View都可以获取焦点。获取焦点的前提是视图必需要有获取焦点的资格。
2.2.3 分发焦点
上述View在获取焦点时,需要逐级通知它的父View进行焦点处理,清除旧焦点信息并保存新焦点信息,参见ViewGroup#requestChildFocus。
通过ViewGroup中mFocused(View类型)这个成员来保存具有焦点的子View,并且一直递归下去,为父View判断是否包含焦点(hasFocus)和查找焦点(findFocus)提供了便利。
举例:某个根View A包含B、C两个子View,C下又包含C1、C2两个子View,且C2具有焦点,则C中mFocused保存的是C2,根View A中mFocused保存的则是C。
另外ViewGroup也可以获取焦点,参见ViewGroup#requestFocus,与View获取焦点逻辑不同,ViewGroup获取焦点受策略控制,如下:
FOCUS\_BLOCK\_DESCENDANTS:This view will block any of its descendants from getting focus, even if they are focusable.
FOCUS\_BEFORE\_DESCENDANTS:This view will get focus before any of its descendants.
FOCUS\_AFTER\_DESCENDANTS:This view will get focus only if none of its descendants want it.
public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
// ...省略
int descendantFocusability = getDescendantFocusability();
boolean result;
switch (descendantFocusability) {
case FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS:
result = super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
break;
case FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS: {
final boolean took = super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
result = took ? took : onRequestFocusInDescendants(direction,
previouslyFocusedRect);
break;
}
case FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS: {
final boolean took = onRequestFocusInDescendants(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
result = took ? took : super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
break;
}
default:
// ...省略
}
if (result && !isLayoutValid() && ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_WANTS_FOCUS) == 0)) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_WANTS_FOCUS;
}
return result;
}由此我们也能得到另一些关于焦点的特性:
- 一个窗口内最多只有一个View具有焦点,或者无焦点。上述在递归分发焦点时,当有View获取焦点后则会退出递归。
- 根View没有焦点不能说明子View一定没有焦点。子View具有焦点,根View能够感知。
2.2.4 清除焦点
需要我们主动清除焦点的场景其实较少,我们可以通过clearFocus来清除焦点,View和ViewGroup的清除逻辑有细微差异,ViewGroup会同时清除上诉分发焦点过程中所记录的状态(需区分当前焦点是自己还是子View),最终都会调用View#clearFocusInternal进行真正的清除操作,后面会继续提到焦点清除的问题。
/**
* Clears focus from the view, optionally propagating the change up through
* the parent hierarchy and requesting that the root view place new focus.
*
* @param propagate whether to propagate the change up through the parent
* hierarchy
* @param refocus when propagate is true, specifies whether to request the
* root view place new focus
*/
void clearFocusInternal(View focused, boolean propagate, boolean refocus) {
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FOCUSED;
clearParentsWantFocus();
if (propagate && mParent != null) {
mParent.clearChildFocus(this);
}
onFocusChanged(false, 0, null);
refreshDrawableState();
if (propagate && (!refocus || !rootViewRequestFocus())) {
notifyGlobalFocusCleared(this);
}
}
}问题1:错误启用获取焦点能力导致点击失效
以EditText为例,我们在点击时即会获取焦点,输入框中会显示光标,弹出输入法等。但像Button、TextView等控件,默认触摸不会获取焦点,如果对此类控件设置了focusableInTouchMode=true,就会发现第一次触摸无法响应点击事件,第二次点击才会响应,这是为什么呢?从事件分发机制中寻找线索,看View#onTouchEvent中对MotionEvent.ACTION\_UP的处理,可以清晰看到UP事件的处理会优先处理焦点获取,只有在无焦点变化时才会如我们所想的开始分发点击事件。所以我们在第一次点击时收到的是onFocusChange事件,第二次点击收到的才是onClick事件。
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// ...省略
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
// ...省略
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
// ...省略
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClickInternal();
}
}
}
}
}问题2:clearFocus“无效”?
在之前我们了解了清除焦点的机制,但为什么有时候会碰到调用clearFocus时"无效"呢?我们对比一下我们可以主动调用的clearFocus方法和系统内部调用的unFocus方法。
void unFocus(View focused) {
clearFocusInternal(focused, false, false);
}发现一处可疑点,propagate和refocus的值决定了rootViewRequestFocus是否被调用,由于&&和||的短路作用,当propagate和refocus均为true时,才会执行rootViewRequestFocus,而在rootViewRequestFocus中会触发root的获取焦点逻辑。
boolean rootViewRequestFocus() {
final View root = getRootView();
return root != null && root.requestFocus();
}因此clearFocus看似“无效”,其实是焦点被清除后又立马被设置上了。那该如何解决呢?回顾之前提到的焦点分发逻辑,当父View抢先获取了焦点就能够解决,因此,让父view自动获取焦点是很好的解决方法。这里我们可以回忆上面分发焦点中所提及的三种焦点分发策略,我们希望父View先于子View获取焦点,很明显这符合FOCUS\_BEFORE\_DESCENDANTS策略,但我们好像并没有手动配置过这个策略,那FOCUS\_BEFORE\_DESCENDANTS策略是否是ViewGroup的默认策略呢?我们查看ViewGroup源码发现在initViewGroup中确实有默认的设置,如下:
private void initViewGroup() {
// ...省略
setDescendantFocusability(FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS);
// ...省略
}举一反三,如果我们想让子View先于父View获取焦点或者禁止子View获取焦点,即可通过setDescendantFocusability方法来设置。
另外感兴趣的同学可以继续探究refocus的取值逻辑。
问题3:焦点抢占
在问题2中,我们通过焦点抢占解决了一些问题,但有时候View错误的获取焦点会带来一些意料外的问题。比如EditText自动获取了焦点导致自动弹起输入法。又比如RecyclerView在嵌套时子View抢占了焦点导致列表发生预期外的移动等等,这是个有趣的问题,感兴趣的同学可以查看RecyclerView#requestChildFocus方法,其中执行的requestChildRectangleOnScreen方法会为你解决这个疑惑。碰到这些问题时,我们可以考虑禁止不需要获取焦点的View的焦点获取能力,或者让其父View先获取焦点来解决问题。
2.3 总结
Android中的焦点机制是一个很有趣的内容,很多疑难问题的答案都藏在源码中,理解了焦点的机制后,相关问题都将变得有迹可循。
03Android中Cookie
3.1 首先什么是Cookie:
Cookie是服务器保存在浏览器的一小段文本信息,每个 Cookie 的大小一般不能超过4KB。浏览器每次向服务器发出请求,就会自动附上这段信息。
3.2 Webview的Cookie存储:
WebView是基于 webkit 内核的UI控件,相当于一个浏览器客户端。
它会在本地维护每次会话的cookie( 保存在 data/data/package\_name/app\_WebView/Cookies.db )
导出后可见:
3.3 Cookie属性:
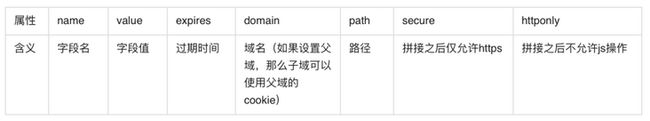
Set-Cookie:name=value [ ;expires=date][ ;max-age=time][ ;domain=domain][ ;path=path][ ;secure][ ;httponly]
例:
Set-Cookie: TEST=1234567890; Expires=Wed, 21 Oct 2022 07:28:00 GMT; Domain=baidu.com; Path=/test;Secure; HttpOnly3.4 Cookie的设置
Android中的WebKit为我们提供了CookieManager,它是一个单例,我们可以利用它进行Cookie的读取和存储,例如
CookieManager.getInstance().setCookie(url, cookie); CookieManager.getInstance().getCookie(url);
3.5 Cookie在请求中携带:
3.5.1 Request的Header:
WebView中H5的请求:
在WebView的H5中发送请求时,同浏览器一样,每次向服务器发出请求(domain&path与cookie中设置一致),就会自动附上这段信息。
客户端Native发请求:
由客户端发送,包含在HTTP请求的头部中。注意,Native发送请求时,需要网络库主动addHeader,所以建议封装网络库时,Native仿照浏览器自动携带Cookie的机制。如:
// 简单写了个意思,具体实现需要遍历拼接等判断,大家明白就好CookieManager cookieManager = CookieManager.getInstance();String webviewCookies = cookieManager.getCookie(url);httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("Cookie", webviewCookies);
3.5.2 Response的Set-Header:
WebView中H5的请求响应:
在WebView的H5中接收到服务端响应时,同浏览器一样,会响应response的set-header自动为内核种上cookie。
客户端Native请求响应:
由客户端接收到response后,需要注意的是系统并不会自动为内核种上cookie,建议封装网络库时,Native仿照浏览器响应response的set-header自动为内核种上Cookie。如:
// 简单写了个意思,具体实现需要添加安全性的判断,大家明白就好
Map> responseHeaderMap = httpURLConnection.getHeaderFields();
List cookieList = responseHeaderMap.get("Set-Cookie");
CookieSyncManager.createInstance(context);
CookieManager cookieManager = CookieManager.getInstance();
cookieManager.setAcceptCookie(true);
for (String cookie : cookieList) {
List httpCookieList = HttpCookie.parse(cookie);
HttpCookie httpCookie = httpCookieList.get(0);
String relCookie = buildCookie(httpCookie.getDomain(), httpCookie.getName(),
httpCookie.getValue(), System.currentTimeMillis() + httpCookie.getMaxAge() * 1000,
httpCookie.getSecure());
cookieManager.setCookie(domain, relCookie);
}其他额外知识:
Cookie多进程使用及同步:https://iluhcm.com/2018/04/27...
推荐阅读: