shardingsphere之sharingjdbc
shardingsphere目前的定位已经远超过人们熟知分库分表的功能,其拥有自己的生态圈(sharingjdbc,sharingproxy,sidecar),未来宏图规划高大上,官方的一段定义:Apache ShardingSphere 是一套开源的分布式数据库增强计算引擎,其通过可插拔架构构建基于数据库之上的生态系统,实现包括数据分片、弹性伸缩、加密脱敏等功能为代表的增强能力。
shardingjdbc
shardingjdbc的主要功能在客户端进行数据分片和读写分离,通过shardingJDBC,应用可以使用jdbc访问已经分库分表、读写分离的多个数据源,而不用关心数据库数量和数据的分布
shardingjdbc中核心概念:
逻辑表:将一张表user水平拆分为两张表(user_1和user_2),此时user可以当做是逻辑表,总之,它是对真实存在的表的抽象。
真实表:user_1和user_2
分片键:可以理解为某一字段,应用需要操作某水平拆分后的多表时,shardingjdbc根据这个字段通过某种策略来计算数据应该落地到某张真实表,然后进行更新或者查询数据。
分片算法:以分片键为基础数据,实现某种算法,可以将数据落地到真实表,这种算法称之为分片算法
分片策略:分片键+分片算法=分片策略。shardingjdbc提供了inline,standard,complex,hint等默认分片策略,程序员可根据自己的需求实现自己的分片策略。
实战
环境搭建:基于上篇博客,mysql:两个节点(192.168.43.11和192.168.43.12),其中用于主从复制的数据库为mdemo,使用的表为user,用来测试读写分离;test数据库用于测试分片策略的,11和12分别包含user_1和user_2两张表。项目:基于spring boot框架,引入的maven包:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
com.alibaba
druid
1.2.8
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.5.1
org.apache.shardingsphere
sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter
4.1.1
mysql
mysql-connector-java
inline分片策略
配置文件:
#水平分表实战。inline分片策略:不支持范围查询,支持=查询
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1
# 配置数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.11:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123456
# 指定表的分布情况 配置表在哪个数据库里,表名是什么。水平分表,分两个表:m1.user_1,m1.user_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.actual-data-nodes=m1.user_$->{1..2}
# 指定表的主键生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
#雪花算法的一个可选参数
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
#使用自定义的主键生成策略
#spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=MyKey
#spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.props.mykey.offset=88
#指定分片策略 约定user_id值为偶数添加到user_1表。如果是奇数添加到user_2表。
# 指定分片键字段为user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
# 根据计算的字段算出对应的表名。
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=user_$->{user_id%2+1}
# 打开sql日志输出。
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true定义user实体类,包含四个字段:id,user_id,name,age,使用mybatis-plus实现UserMapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
@Select("select u.id,u.user_id,u.name,u.age,d.uvalue ustatus from user u left join t_dict d on u.ustatus=d.ustatus")
List findUsers();
}
编写测试类:
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private DictMapper dictMapper;
@Test
public void testUser() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(i);
user.setId(Long.valueOf(new Random().nextInt(100)));
user.setName("jjjj" + i);
userMapper.insert(user);
}
}
@Test
public void userQuery() {
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("user_id", 719929805809651713L);
// wrapper.between("user_id", 718855362370863104L, 718855362194702336L);
List users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(user -> {
System.out.println(user.toString());
});
}
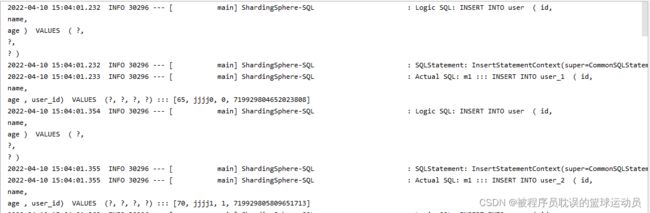
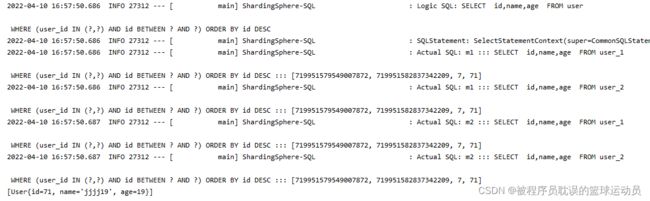
} 执行测试类testUser()插入用户:查看日志
从日志中可以看到逻辑sql使用的user,而真实执行的sql使用的是user_1或者user_2。
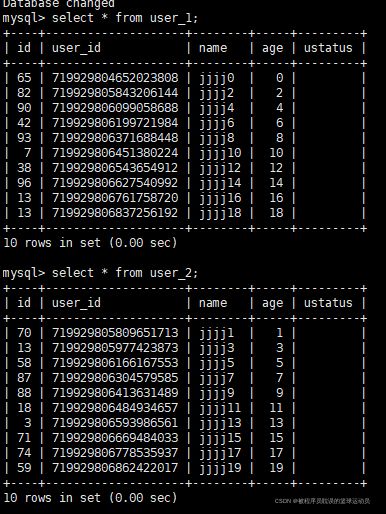
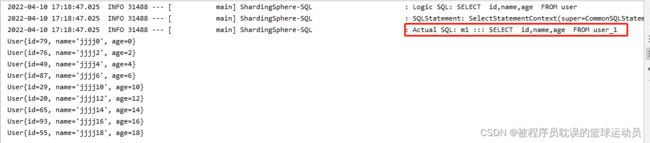
查看数据库和表
插入的20条数据被均匀分布在user_1和user_2中。
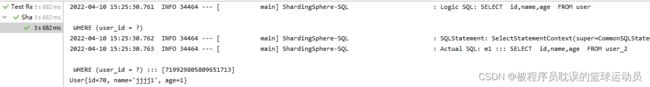
执行测试方法userQuery()查询用户:
inline分片策略只支持简单的分片键,无法支持多分片键、范围分片。
standard分片策略
inline是只支持=查询的分片策略,对于略微复杂的查询就束手无策,比如:between...and...范围查询和in查询,standard就支持范围查询
配置文件做如下修改:其中配置了两个数据源名称分别为m1,m2,真是表为m1.user_1和m1_user2,m2.user_1和m2_user_2
#standard分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2
# 配置第 1 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.11:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123456
# 配置第 2 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.12:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.user_$->{1..2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
#数据库策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.standard.range-algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.DBRangeShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.DBPreciseShardingAlgorithm
#表策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.standard.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.standard.range-algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.TableRangeShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.TablePreciseShardingAlgorithm
# 打开sql日志输出。
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true对于分片策略,这里分别对数据库和表配置了自定义的分片算法,为了让了数据更均匀的分布在两库四表中,数据库使用分片键对2取模,即奇数偶数分片键进行对半分离,而分配到同一数据库中的数据,为了让它们更均匀分布在两张表中,实现稍微复杂点的分片算法。
对于数据库范围查询的分片策略
/**
* 实现范围查询between..and..
*/
public class DBRangeShardingAlgorithm implements RangeShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public Collection doSharding(Collection collection, RangeShardingValue rangeShardingValue) {
// 获取查询范围的两端值
// rangeShardingValue.getValueRange().lowerEndpoint();
// rangeShardingValue.getValueRange().upperEndpoint();
return collection;
}
} 对于数据库精确的分片算法
@Log4j2
public class DBPreciseShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm {
/**
*
* @param collection 配置的数据库集合,如m1,m2
* @param preciseShardingValue 逻辑表名称,分片键和分片键的值
* @return
*/
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection collection, PreciseShardingValue preciseShardingValue) {
BigInteger value = BigInteger.valueOf(preciseShardingValue.getValue());
BigInteger dbValue = value.mod(new BigInteger("2")).add(new BigInteger("1"));
String key = "m"+ dbValue;
log.info("DBPreciseShardingAlgorithm logic, key: {}", key);
if (collection.contains(key)) {
return key;
}
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("unsupported key: " + key);
}
} 对于表的范围查询算法和精确的分片算法
public class TableRangeShardingAlgorithm implements RangeShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public Collection doSharding(Collection collection, RangeShardingValue rangeShardingValue) {
// rangeShardingValue.getValueRange().lowerEndpoint();
// rangeShardingValue.getValueRange().upperEndpoint();
return Arrays.asList(rangeShardingValue.getLogicTableName() + "_1", rangeShardingValue.getLogicTableName() + "_2");
}
} @Log4j2
public class TablePreciseShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection collection, PreciseShardingValue preciseShardingValue) {
BigInteger value = BigInteger.valueOf(preciseShardingValue.getValue());
String valueStr = value.toString();
//多库多表分配不均匀
// BigInteger add = value.mod(new BigInteger("2")).add(new BigInteger("1"));
// BigInteger add = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.valueOf(valueStr.substring(valueStr.length()-1)));
BigInteger add = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.valueOf(valueStr)).add(new BigInteger("1"));
//理论上应该对4取模,均匀的分部署,但是多次测试tableValue的值都是一样的。最后这里选择对3取模最终数据会不均匀的分布在各张表中。
BigInteger mod = add.mod(new BigInteger("3"));
BigInteger divide = mod.divide(new BigInteger("2"));
BigInteger tableValue = divide.add(new BigInteger("1"));
String key = preciseShardingValue.getLogicTableName() + "_" + tableValue;
log.info("TablePreciseShardingAlgorithm logic, key: {}", key);
if (collection.contains(key)) {
return key;
}
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("不支持的操作");
}
}
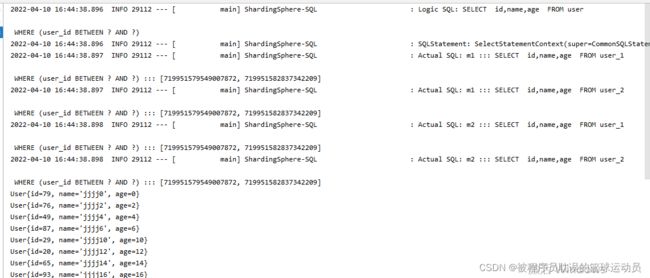
测试范围查询
@Test
public void userQuery() {
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// wrapper.eq("user_id", 719929805809651713L);
wrapper.between("user_id", 719951579549007872L, 719951582837342209L);
List users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(user -> {
System.out.println(user.toString());
});
} 结果:根据结果看出最终shardingjdbc会将sql语句分发到两库四张表中分别执行最后合并结果。
complex分片策略
complex相对于standard可以实现略微复杂的sql语句,比如in语句,order by等
complex的配置,这里配置了两个分片键:id,user_id
#水平分表实战。complex分片策略
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2
# 配置第 1 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.11:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123456
# 配置第 2 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.12:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=123456
# 指定表的分布情况 配置表在哪个数据库里,表名是什么。水平分表,分两个表:
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.user_$->{1..2}
# 指定表的主键生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
#雪花算法的一个可选参数
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.complex.sharding-columns=user_id, id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.DBComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.complex.sharding-columns=user_id, id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.TableComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm
# 打开sql日志输出。
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true分片算法:
/**
* 数据库策略:实现根据多个分片列进行综合分片的算法
*/
public class DBComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public Collection doSharding(Collection collection, ComplexKeysShardingValue complexKeys) {
Collection ids = complexKeys.getColumnNameAndShardingValuesMap().get("user_id");
List list = new ArrayList<>();
ids.forEach(id -> {
BigInteger idi = BigInteger.valueOf(id);
BigInteger value = idi.mod(new BigInteger("2")).add(new BigInteger("1"));
list.add("m" + value);
});
return list;
}
} /**
* 表策略:实现根据多个分片列进行综合分片的算法
*/
public class TableComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public Collection doSharding(Collection collection, ComplexKeysShardingValue complexKeys) {
Collection userIds = complexKeys.getColumnNameAndShardingValuesMap().get("user_id");
Range userId = complexKeys.getColumnNameAndRangeValuesMap().get("id");
userId.lowerEndpoint();
userId.upperEndpoint();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
userIds.forEach(id -> {
BigInteger idi = BigInteger.valueOf(id);
BigInteger value = idi.mod(new BigInteger("2")).add(new BigInteger("1"));
list.add(complexKeys.getLogicTableName() + "_" + value);
});
return list;
}
} 测试类:
@Test
public void queryUserComplex() {
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.orderByDesc("id");
wrapper.in("user_id", 719951579549007872L, 719951582837342209L);
wrapper.between("id", 7L, 71L);
// wrapper.and(courseQueryWrapper -> courseQueryWrapper.between("user_id","3","8"));
List users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
System.out.println(users);
} 测试结果:
hint分片策略
hint分片策略不需要分片键的强制分片策略,它的分片键不在跟sql语句相关,而是程序另行指定分片键
配置文件
#水平分表实战。inline分片策略:不支持范围查询,
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2
# 配置第 1 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.11:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123456
# 配置第 2 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.12:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=123456
# 指定表的分布情况 配置表在哪个数据库里,表名是什么。水平分表,分两个表:m1.user_1,m1.user_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.user_$->{1..2}
# 指定表的主键生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
#雪花算法的一个可选参数
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
#hint分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.hint.algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.HintDBShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.hint.algorithm-class-name=com.rick.sharding.algorithm.HintTableShardingAlgorithm
# 打开sql日志输出。
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=truehint分片策略的数据库分片策略和表分片策略
public class HintDBShardingAlgorithm implements HintShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public Collection doSharding(Collection collection, HintShardingValue hintShardingValue) {
String dataSourceKey = "m" + String.valueOf(hintShardingValue.getValues().toArray()[0]);
if (collection.contains(dataSourceKey)) {
return Arrays.asList(dataSourceKey);
}
return null;
}
} public class HintTableShardingAlgorithm implements HintShardingAlgorithm {
@Override
public Collection doSharding(Collection collection, HintShardingValue hintShardingValue) {
String key = hintShardingValue.getLogicTableName()+"_"+hintShardingValue.getValues().toArray()[0];
if (collection.contains(key)) {
return Arrays.asList(key);
}
return null;
}
}
测试类
@Test
public void queryHint() {
//强制只查user_1表
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
//注意这两个属性,dataSourceBaseShardingValue用于强制分库
// 强制查m1数据源
hintManager.addDatabaseShardingValue("user", "2");
// 强制查user_1表
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("user", "1");
List users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(user -> System.out.println(user));
//线程安全,所有用完要注意关闭。
hintManager.close();
} 结果
广播表
像字典表或者异常提示表,每个数据库都有,而且表的数据结构和数据都相同。这样的表我们可以用广播表来实现。
例如要实现两个库都要有的字典表t_dict,两个库同时创建t_dict、t_dict_1、t_dict_2三张表,并做如下配置
#水平分表实战:广播表
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2
# 配置第 1 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.11:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123456
# 配置第 2 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.12:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=123456
# 指定表的分布情况 配置表在哪个数据库里,表名是什么。水平分表,分两个表:
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.t_dict_$->{1..2}
#分片键
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.column=dict_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.props.worker.id=1
#配置广播表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=t_dict
# 打开sql日志输出。
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true测试类
@Test
public void addDict() {
Dict dict = new Dict();
dict.setUstatus("1");
dict.setUvalue("正常");
dictMapper.insert(dict);
Dict dict2 = new Dict();
dict2.setUstatus("2");
dict2.setUvalue("异常");
dictMapper.insert(dict2);
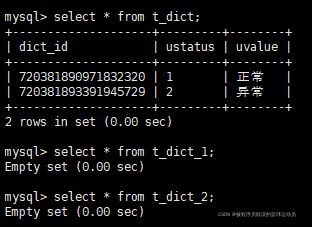
}测试结果:只有t_dict有数据,而且两张表的数据都一样,这就是广播表的功能。
绑定表
绑定表可以实现关联查询,其实现方式通过两张表的关联字段作为分片键,这样关联的数据库就会被分配到同一个数据库中,关联查询时就可以通过分片键进行匹配。下面是通过user和t_dict进行关联查询
配置:
#水平分表实战。inline分片策略:不支持范围查询,
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2
# 配置第 1 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.11:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=123456
# 配置第 2 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.43.12:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.user_$->{1..2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=ustatus
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=m$->{ustatus}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=ustatus
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=user_$->{ustatus}
# 指定表的分布情况 配置表在哪个数据库里,表名是什么。水平分表,分两个表:m1.t_dict_1,m1.t_dict_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.t_dict_$->{1..2}
#分片键
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.column=dict_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=ustatus
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=m$->{ustatus}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=ustatus
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_dict_$->{ustatus}
#绑定表,可以防止出现笛卡尔积
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.binding-tables[0]=user,t_dict
# 打开sql日志输出。
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
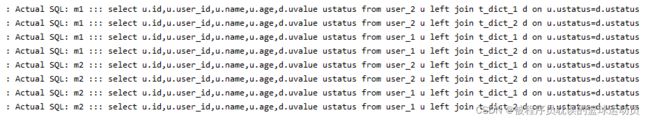
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true分别插入在user和t_dict表中插入测试数据,然后做如下测试:
@Test
public void queryBinding() {
List users = userMapper.findUsers();
users.forEach(user -> System.out.println(user.toString()));
}
//UserMapper类
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
@Select("select u.id,u.user_id,u.name,u.age,d.uvalue ustatus from user u left join t_dict d on u.ustatus=d.ustatus")
List findUsers();
} 现在把配置绑定表的配置注释掉,进行测试:结果可以看出出现笛卡尔积了,这将降低查询效率