Java8概述
Java8(又称 JDK1.8)是Java语言开发的一个主要版本。Oracle公司于2014.3.18日发布的Java8.
- 支持Lambda表达式
- 函数式接口
- 新的Stream API
- 新的日期API
- 其他特性
Lambda表达式:特殊的匿名内部类,语法更简洁
Lambda表达式允许把函数作为一个方法的参数(函数作为方法参数传递),将代码像数据一样传递。
基本语法:
<函数式接口><变量名>=(参数1,参数2…)->{ //方法体 };
Lambda引入了新的操作符:->(箭头操作符),->将表达式分成两部分
- 左侧:(参数1,参数2…)表示参数列表
- 右侧:{}内部是方法体
注意事项:
- 形参列表的数据类型会自动推断
- 如果形参列表为空,只需保留()
- 如果形参只有1个,()可以省略,只需参数名称即可
- 如果执行语句只有一句,且无返回值,{}可以省略,若有返回值,则若想省去{},则必须同时省略return,且执行语句也保证只有一句
- Lambda不会生成一个单独的内部类文件
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("子程序执行了");
}
};
//Lambda表达式
Runnable runnable1=()-> {
System.out.println("子程序2执行了");
};
new Thread(runnable1).start();
new Thread(()->System.out.println("子程序3执行了")).start();
Comparator<String> com1=new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o1.length()-o2.length();
}
};
//Lambda
Comparator<String> com2 =(String o1, String o2) -> {
return o1.length()-o2.length();
};
Comparator<String> com3= (o1,o2)->o1.length()-o2.length();
TreeSet<String> treeSet=new TreeSet<String>(com2);
}
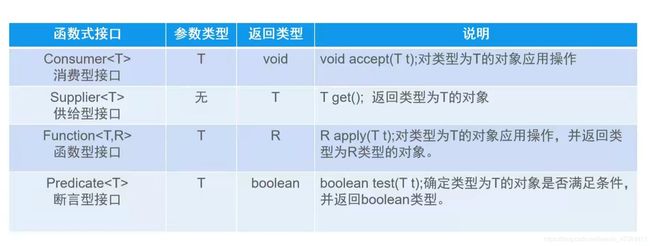
}函数式接口:
如果一个接口只有一个抽象方法,则该接口称为函数式接口,函数式接口可以使用Lambda表达式,Lambda表达式会被匹配到这个抽象方法上。
@FunctionalInterface 注解检测接口是否符合函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Usb {
void service();
}
```java
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类
Usb mouse=new Usb() {
@Override
public void service() {
System.out.println("鼠标开始工作。。。");
}
};
Usb fan=()->System.out.println("风扇开始工作。。。");
run(mouse);
run(fan);
}
public static void run(Usb usb){
usb.service();
}
}public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类
// Consumer consumer=new Consumer() {
// @Override
// public void accept(Double money) {
// System.out.println("消费:"+money);
// }
// };
// Consumer consumer=money->System.out.println("消费:"+money);
//happy(consumer,1000);
happy(money->System.out.println("聚餐消费:"+money),1000);
happy(money->System.out.println("唱歌消费:"+money),1000);
int[] arr=getNums(()->new Random().nextInt(100),5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
String result = handlerString(s -> s.toUpperCase(), "hello");
System.out.println(result);
List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("zhangsan");
list.add("lisi");
list.add("zhangwuji");
List<String> result1 = fileterName(s -> s.startsWith("zhang"), list);
System.out.println(result1.toString());
}
//Consumer 消费型接口
public static void happy(Consumer<Double> consumer,double money){
consumer.accept(money);
}
//Supplier 供给型接口
public static int[] getNums(Supplier<Integer> supplier,int count){
int arr[]=new int[count];
for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) {
arr[i]=supplier.get();
}
return arr;
}
//Function 函数式接口
public static String handlerString(Function<String,String> function,String str){
return function.apply(str);
}
//Predicate 断言型接口
public static List<String> fileterName(Predicate<String> predicate,java.util.List<String> list){
List<String> resultList=new ArrayList<String>();
for (String string:list) {
if(predicate.test(string)){
resultList.add(string);
}
}
return resultList;
}
}方法引用:
方法引用是Lambda表达式的一种简写形式,如果Lambda表达式方法体中只是调用了一个特定的已经存在的方法,则可以使用方法引用
常见形式:
对象::实例方法
类::静态方法
类::实例方法
类::new
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.对象::实例方法
Consumer<String> consumer=s -> System.out.println(s);
consumer.accept("hello");
Consumer<String> consumer1=System.out::println;
consumer1.accept("world");
//2.类::静态方法
Comparator<Integer> comparator=(o1, o2) ->Integer.compare(o1,o2);
Comparator<Integer> comparator1=Integer::compare;
//3.类::实例方法
Function<Employee,String> function=employee -> employee.getName();
Function<Employee,String> function1=Employee::getName;
System.out.println(function1.apply(new Employee("xiaoming", 20000)));
//4.类::new
Supplier<Employee> supplier=()->new Employee();
Supplier<Employee> supplier1=Employee::new;
Employee employee = supplier.get();
System.out.println(employee.toString());
}
}Stream:
流(Stream)中保存对集合或数组数据的操作,和集合类似,但集合保存的是数据。
Stream特点:
1.Stream 自己不会存储元素
2。Stream 不会改变源对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream.
3.Stream 操作是延迟执行的。这意味着他们会等到需要的结果的时候才执行
Stream使用步骤
1.创建:
新建一个流
2.中间操作:
在 一个或多个步骤中,将初始Stream转化到另一个Stream的中间操作
3.终止操作:
使用一个终止操作来产生一个结果,该操作会强制它之前的延迟操作立刻执行,在这之后,该Stream就不能使用了。
创建Stream:
- 通过Collection对象的Stream()或parallelStream()方法
- 通过Arrays类的stream()方法
- 通过Stream接口的of(), iterate() , generate()方法
- 通过IntStream,LongStream,DoubleStream接口中的of, range, rangeClosed方法。
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.通过Collection对象的Stream()或parallelStream()方法
ArrayList<String> arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("apple");
arrayList.add("xiaomi");
arrayList.add("huawei");
Stream<String> stream = arrayList.stream();
//遍历
stream.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// stream.forEach(System.out::println);
//2. 通过Arrays类的stream()方法
String[] arr={"aaa","bbb","ccc"};
Stream<String> stream1 = Arrays.stream(arr);
stream1.forEach(System.out::println);
//3.通过Stream接口的of(), iterate() , generate()方法
Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(10, 20, 30);
integerStream.forEach(System.out::println);
//迭代流
Stream<Integer> iterate = Stream.iterate(0, x -> x + 2);
iterate.limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
//生成流
Stream<Integer> generate = Stream.generate(() -> new Random().nextInt(100));
generate.limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);
//4.通过IntStream,LongStream,DoubleStream接口中的of, range, rangeClosed方法。
IntStream intStream = IntStream.of(100, 200, 300);
intStream.forEach(System.out::println);
// IntStream range = IntStream.range(10, 15);//不闭合 10-14
IntStream range = IntStream.rangeClosed(10, 15);//闭合的 10-15
range.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}中间操作:
- filter , limit ,skip , distinct ,sorted
- map
- parallel
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Employee> arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(new Employee("小王",20));
arrayList.add(new Employee("小张",21));
arrayList.add(new Employee("小李",23));
arrayList.add(new Employee("小刘",22));
arrayList.add(new Employee("小刘",22));
//中间操作 1.filter过滤 2.limit限制 3.skip跳过 4.distinct去重 5.sorted排序
//1.filter过滤
arrayList.stream()
.filter(employee ->employee.getAge()>21)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//2.limit限制
arrayList.stream()
.limit(2)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//3.skip跳过
arrayList.stream()
.skip(2)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//4.distinct去重 依据hashcode(),equals()
arrayList.stream()
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);
//5.sorted排序
System.out.println("");
arrayList.stream()
.sorted((o1, o2) ->Integer.compare(o1.getAge(), o2.getAge()))
.forEach(System.out::println);
//中间操作2 map
System.out.println("");
arrayList.stream()
.map(employee -> employee.getName())
.forEach(System.out::println);
//中间操作3 parallel 采用多线程 效率高
System.out.println("");
arrayList.parallelStream()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}串行流和并行流的区别:
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 串行流和并行流的区别
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <5000000 ; i++) {
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
long time=System.currentTimeMillis();
long count= list.stream().sorted().count();//串行 用时:8584
// long count= list.parallelStream().sorted().count();//并行 用时:2661
System.out.println(count);
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用时:"+(end-time));
}
}终止操作:
- forEach ,min ,max ,count
- reduce , collect
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Employee> arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(new Employee("小王",20));
arrayList.add(new Employee("小张",21));
arrayList.add(new Employee("小李",23));
arrayList.add(new Employee("小刘",22));
//终止操作forEach
arrayList.stream()
.filter(employee -> employee.getAge()>21)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//min ,max ,count
Optional<Employee> max = arrayList.stream()
.max((o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1.getAge(), o2.getAge()));
System.out.println(max.get());
long count = arrayList.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
//终止操作 reduce 规约
//计算所有员工的工资和
Optional<Integer> sum= arrayList.stream()
.map(employee -> employee.getAge())
.reduce((x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println(sum.get());
//终止操作 collect
//获取所有员工姓名,封装成一个list集合
List<String> name = arrayList.stream()
.map(employee -> employee.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (String str:name) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}