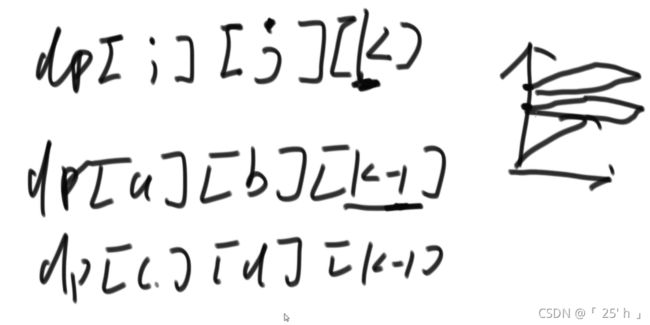LeetCode左程云算法课笔记
左程云算法课笔记
- 剑指Offer
- 位运算
-
- ^运算符理解
- 寻找出现双中的单数
- 取出一个数最右边1的位置
- 找所有双出现中的两个单数
- 整数二进制奇数位偶数位交换
- 数组中全部出现k次返回出现一次的数
- 链表
-
- 判读链表元素是否回文
-
- 利用栈结构
- 利用栈结构和快慢指针
- 快慢指针和链表反向
- 三分链表
- 链表环问题
- 枚举
-
- 优化枚举方法
-
- 最小染色数
- 矩阵最大正方形
- 树
-
- 前中后横向非递归遍历
-
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 横向遍历
- 计算二叉树中每层的最多节点个数
- 判断是完全二叉树
- 判断是搜索二叉树(套路题)
- 子搜索二叉树的节点个数(套路题)
- 判断是满二叉树(套路题)
- 判断是平衡树(套路题)
- 树节点最远距离(套路题)
- 最大快乐值(套路题)
- 树结构转成链表(套路题)
- 树的个数
- 查找树中两个节点的最近共父类节点
- 查找后继结点
- 折纸凹凸问题
- 前中序推后序遍历
- 哈夫曼最小代价问题
- 分治策略
-
- 数组中的逆序对
- 基于归并排序的小数和
- 查找
-
- 深度探索二分查找
-
- 经典二分查找
- 查找大于该值的最小值
- 查找大于等于目标值的最右值
- 查找小于该值的最大值
- 查找小于等于目标值的最左值
- 查找极小值
- 递归和动归
-
- 纯递归
-
- N皇后(最優解法)
- 递归实现字符串求值
- 岛数量问题
- 返回字符串的所有子字符串(树形)
- 最小字典序
- 递归转动归
-
- 机器人运动问题
- 飞棋盘
- 纸币组合情况数
- 纸币组合最小个数问题
- 整数分裂
- bob活着
- 背包问题(树形)
- 数字转化成字母(树形)
- 人气值
- 数组博弈最值
- 真假情况
- 能力蛇最大长度问题
- 字符串转换代价问题
- 咖啡机问题
- 动态规划
-
- 硬币结合动归
- 相同子字符串
- 最长回文子序列
-
- 求逆序串和该串的最长公共子序列
- 直接DP
- 相同最长子序列
- 添加最少字符组成回文串
- 删除元素构成回文方法数量
- 将字符串分割成最少回文串
- 动归的空间压缩
- 数组和字符串
-
- 字符串的全排列
- 最长递增子序列
-
- O(N^2)
- 优化算法O(N*logN)
- 最多亦或和为零的数据部分
-
- 一般解
- 优化解法
- 连续总和范围问题(含负数)
- 最长无重复子串
- 最长有效括号长度
- 存在字符串的最小范围
- 贪心算法
-
- 前后缀差点最大值
- 子数组累计和最大值
- 子矩阵累计和最大值
- 安路灯
- 找工作
- 最多场会议问题
- 投资收益问题
- 过河
- 绳子覆盖问题
-
- 定右二分向左查找O(N*logN)
- 定左向右延申O(N)
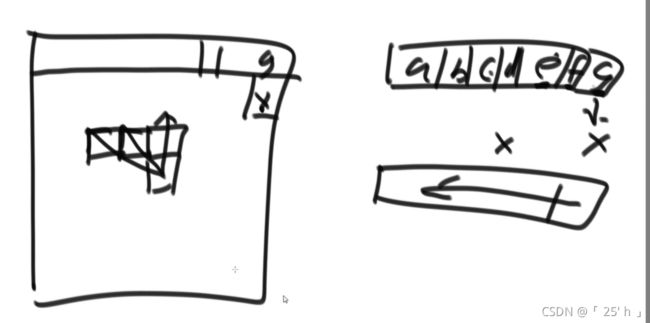
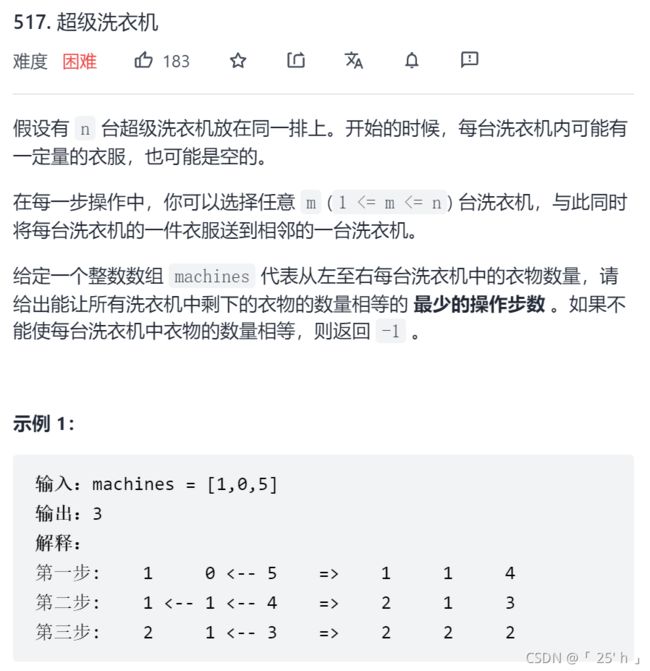
- 超级洗衣机
- 数论以及衍生
-
- 经典约瑟夫环
-
- 衍生题目
- 质数相关
- 快速幂
- 相邻4倍问题
- 类斐波那契数列
-
- exp1
- 辗转相除
-
- exp2
- 打表法
-
- 整体装袋
- 幂次方吃草
- 经典数据结构类
-
- 栈
-
- 用栈将栈元素排序
- 单调栈
-
- 经典单调栈模型
- 单调栈题
- 堆
-
- 输出出现次数最多的
- 经典博弈(^)
- 局部和整体性思想
-
- 局部思想
-
- 模拟容器存水
-
- 空间O(N)
- 空间O(1)
- 顶级难题:楼轮廓问题
- 最大矩形覆盖数量
- 整体思想
-
- 旋转词
- 旋转print数组
- 90度旋转
- zigzag打印数组
- 杂
-
- 数组差值最大值
- 两个有序数组第k大的
-
- 归并排序子过程O(logk)
- 二分判定O(log(m)*log(n))
- O(log(min{n,m}))
剑指Offer
左程云算法课基本包含剑指offer书中内容,戳这里跳转
位运算
^运算符理解
- ^ 可理解为不进位相加
- a^a=0
- a^0=a
public static void sway(int[] arr,int i,int j){
if(i!=j){
//不能两个值指向同一地址
arr[i]=arr[i]^arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[i]^arr[j];//就是arr[i]^arr[j]^arr[j]就表示a
arr[i]=arr[i]^arr[j];//表示arr[i]^arr[j]^arr[i]^arr[j]^arr[j]就是b
}
}
寻找出现双中的单数
题目:一组数只有一个数出现一次,其他出现两次,找出这个出现一次的数
public class Main {
private static int process(int[] arr) {
int res = 0;
for (int i : arr) {
res ^= i;
}
return res;
}
}
取出一个数最右边1的位置
int mostRightOne = pos & (~pos + 1);
// mostRightOne值在二进制位上的位次就是pos得最右第一个1的位置
找所有双出现中的两个单数
题目:一组数只有两个数出现一次,其他出现两次,找出这两个数:
- 因为两个值不同,所以两个值定存在二进制某一位定不同,用这两个值的异或结果二进制中的1,从而将数字分成两组,该位为1和不为1
public class Main {
private static void process(int[] arr) {
int med = 0;
for (int a : arr) {
med ^= a;// 两个不同的单数^最后得到med
}
int rightOne = med & (~med + 1);// 取出med中二进制为1的位值(必存在,因为不同值)
int med1 = 0;
for (int a : arr) {
// 对应位为1的值取出进行^最后的到两个单数对应位为1的
// (a&rightOne)== 0得到对应位为0
if ((a & rightOne) == rightOne) {
med1 ^= a;
}
}
System.out.println(med1);// 两个单数其中一个值
System.out.println(med ^ med1);// 两个单数令一个值
}
}
整数二进制奇数位偶数位交换
题目 : 例如:010110—>101001
public class Main {
private static int process(int pos) {
int pre = 0xAAAAAAAA; // 1010 1010 1010 1010 1010 1010 1010 1010
int post = 0x55555555; // 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101
pre &= pos;
post &= pos;
pre >>= 1;
post <<= 1;
return pos + post;
}
}
数组中全部出现k次返回出现一次的数
题目:给定一个整数数组,只有一个数出现了一次,其他数字均出现了三次,输出这一个只出现一次的数。
- 只看出现三次到数字,那么对于这些值的二进制位的累加和定能被3整除。
- 现在出现了一个只出现一次的数,由于该数的存在,所有二进制位累加和除以3的余数就是该值的对应二进制位数。
- 除了3,主要是大于等于2都可以这样做。
public class Main {
public static int twoSingleNum(int[] arr) {
int[] bit = new int[32];// 每一位求和
for (int a : arr) {
int b = 1;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((a & b) != 0) {// 为1就累加
++bit[i];
}
b <<= 1;// 换位
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {
res = res << 1;
res += (bit[i] % 3);// 取余数
}
return res;
}
}
链表
判读链表元素是否回文
利用栈结构
- 先遍历后全部入栈,然后再遍历和栈中元素依次比较。
public class Main {
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return false;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Node tail = header;
while (tail != null) {
stack.push(tail);
tail = tail.next;
}
tail = header;
while (tail != null) {
if (stack.pop().value != tail.value) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
}
}
利用栈结构和快慢指针
- 先用快慢指针定位中间位置,然后继续运动慢指针依次和栈中元素进行比较。需要注意链表整体的个数是双是单。
public class Main {
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return false;
}
Node slow = header;
Node quick = header;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (quick.next != null && quick.next.next != null) {
stack.push(slow);
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
}
// 此时若整个链表为双数,slow指向上一半的最后一个,需要入栈slow
// 若为单数,指向中间元素,不需要入栈slow
// 单双数的判断由quick的终止条件确定
if (quick.next!=null) {
stack.push(slow);
}
slow = slow.next;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (slow.value != stack.pop().value) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
}
}
快慢指针和链表反向
public class Main {
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return false;
}
Node slow = header;
Node quick = header;
while (quick.next != null && quick.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
}
slow=slow.next;
Node preNode=null;
Node postNode=null;
// 后半段反转
while (slow!=null) {
preNode=slow.next;
slow.next=postNode;
postNode=slow;
slow=preNode;
}
Node tailLeft=header;
Node tailRight=postNode;
boolean flag=true;
// 两边向中间判断
while (tailRight!=null) {
if (tailLeft.value!=tailRight.value) {
flag=false;
break;
}
tailLeft=tailLeft.next;
tailRight=tailRight.next;
}
Node tailNode=null;
// 后半段链表恢复
while (postNode!=null) {
preNode=postNode.next;
postNode.next=tailNode;
tailNode=postNode;
postNode=preNode;
}
return flag;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
}
}
三分链表
给定一个值,将比该值小的节点放左边,大的放右边
- 该题并不是思维上难点,主要是注意边界条件
class SEL{
public static Node sEL(Node header,int pivot){
Node head_1=null;
Node tail_1=null;
Node head_2=null;
Node tail_2=null;
Node head_3=null;
Node tail_3=null;
Node nextNode=null;
while (header!=null){
nextNode=header.next;
header.next=null;
if (header.num<pivot){
if (head_1==null){
head_1=header;
tail_1=header;
}else {
tail_1.next=header;
tail_1=tail_1.next;
}
}else if (header.num==pivot){
if (head_2==null){
head_2=header;
tail_2=header;
}else {
tail_2.next=header;
tail_2=tail_2.next;
}
}else {
if (head_3==null){
head_3=header;
tail_3=header;
}else {
tail_3.next=header;
tail_3=tail_3.next;
}
}
header=nextNode;
}
if (tail_1==null){
if (tail_2==null){
return head_3;
}else {
tail_2.next=head_3;
return head_2;
}
}else {
if (tail_2==null){
tail_1.next=head_3;
}else {
tail_1.next=head_2;
tail_2.next=head_3;
}
return head_1;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
}
}
链表环问题
判断链表是否有环,若有返回第一个入环节点
慢:1 快:2
若慢:1快3:
都入环时相差奇数步,且环节点数量为偶数则永不相交
都入环时相差奇数步说明每次差值减少2步,定在第一轮反超,此时差 环节点个数-1,若该值仍为奇数,那么第二轮也反超,故永不相遇
class List{
/*
有环:
1.同环:
- 入环节点相同 返回相交节点
- 入环节点不同 返回其中一个入环节点
2.不同环:
- 返回null
无环:
1.相交:
- 返回相交节点
2.不相交:
- 返回null
*/
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node loop1 = hasCircle(head1);
Node loop2 = hasCircle(head2);
if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {
return noLoop(head1, head2);//无环,判断是否为链式相交或不相交
}
if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);//有环,返回相交节点
}
return null;//一有环,一无环必定不相交
}
private static Node hasCircle(Node header){
if (header==null)return null;
boolean flag=false;
Node slow=header;
Node quick=header;
while (quick.next!=null&&quick.next.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
quick=quick.next.next;
if (slow==quick){//判断是否却有环
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if (!flag)return null;
quick=header;
while (quick!=slow){//相遇时将其中一个指针指向header走相同的步数定在入环节点相遇
quick=quick.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return quick;
}
private static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
//计算链表差值
while (cur1.next != null) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2.next != null) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if (cur1 != cur2) {
return null;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
//长的走到和短的长度同位置
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
//判断是否有相同节点,若无就会走到最后返回null
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
private static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
if (loop1 == loop2) {
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1 != loop1) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != loop2) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
} else {
cur1 = loop1.next;
while (cur1 != loop1) {
if (cur1 == loop2) {
return loop1;//环内相交
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return null;//两个有环链表环不是同一个
}
}
public class Node{
int value;
Node next;
}
}
枚举
优化枚举方法
- 每次计算时出现重复的动作,我们就将这些操作在计算之前进行直接处理,在我们需要时直接进行数据的获取。
最小染色数
public class Main {
public static int process(String s) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int N = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
int num = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if (arr[j] == 'G') {
++num;
}
}
for (int j = i; j < N; ++j) {
if (arr[j] == 'R') {
++num;
}
}
min = Math.min(min, num);
}
return min;
}
}
优化枚举
- 在我们枚举所有情况时发现:对于每次计算单方向上的G,R的个数均可以在之前的操作中部分求出,但是尽管我们之前已经部分求出,在每次计算的时候并没有得到充分应用,只是重复的计算单方向上R,G的个数,正式因为这些重复的计算,造成我们时间效率上有巨大的提升空间。
public class Main {
public static int process(String s) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
int N = arr.length;
int[] leftSum = new int[N];
leftSum[0] = arr[0] == 'G' ? 1 : 0;
// 左累加
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
leftSum[i] = leftSum[i - 1] + (arr[i] == 'G' ? 1 : 0);
}
int[] rightSum = new int[N];
// 右累加
rightSum[N - 1] = arr[N - 1] == 'R' ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = N - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightSum[i] = rightSum[i + 1] + (arr[i] == 'R' ? 1 : 0);
}
// 根据累加计算最小值,注意这时代交错相加
int min = Math.min(leftSum[N - 1], rightSum[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
min = Math.min(min, leftSum[i - 1] + rightSum[i]);
}
return min;
}
}
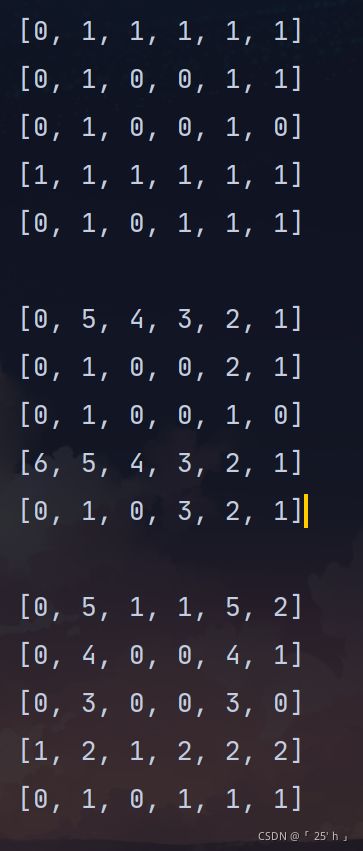
矩阵最大正方形
- 还是若我们直接对于单个起始位置寻找,对于每个其实位置进行判断的话时间复杂度就会比较高
- 由此我们要单向记录连续1的个数
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(maxLen(new int[][]{
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}}));
}
public static void show(int[][] a) {
for (int[] aa : a) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(aa));
}
System.out.println();
}
public static int maxLen(int[][] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr[0].length == 0) return 0;
show(arr);
//*******************生成向横向的累计连续数值******************
int[][] rightArr = new int[arr.length][arr[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < rightArr.length; i++) {
for (int j = arr[0].length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
rightArr[i][j] = arr[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : j == arr[0].length - 1 ? 1 : rightArr[i][j + 1] + 1;
}
}
show(rightArr);
//*******************生成向纵向的累计连续数值******************
int[][] downArr = new int[arr.length][arr[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr[0].length; i++) {
for (int j = arr.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
downArr[j][i] = arr[j][i] == 0 ? 0 : j == arr.length - 1 ? 1 : downArr[j + 1][i] + 1;
}
}
show(downArr);
//*************************从小到大看看多大的正方形存在**************************8
for (int size = Math.min(arr.length, arr[0].length); size != 0; size--) {
if (hasSizeOfBorder(size, rightArr, downArr)) {
return size;
}
}
return 0;
}
private static boolean hasSizeOfBorder(int size, int[][] rightArr, int[][] downArr) {
for (int i = 0; i < rightArr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < rightArr[0].length; j++) {
if (rightArr[i][j] >= size && downArr[i][j + size - 1] >= size &&
downArr[i][j] >= size && rightArr[i + size - 1][j] >= size)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
树
前中后横向非递归遍历
前序遍历
public class Main {
public static void preOrder(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(header);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = stack.pop();
System.out.println(popNode.value);
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.rightNode);
}
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.leftNode);
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
中序遍历
public class Main {
public static void inOrder(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || header != null) {
if (header != null) {// 一直向左进行入栈
stack.push(header);
header = header.leftNode;
} else {// 对于每一个删除的元素要向该节点的右侧进行节点寻找遍历
Node popNode = stack.pop();
System.out.println(popNode.value);
header = popNode.rightNode;
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
后序遍历
func1
public class Main {
public static void postOrder(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> postStack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(header);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
// 先右后左的先序遍历的反向就是先左后右的后序遍历
Node popNode = stack.pop();
postStack.push(popNode);
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.leftNode);
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.rightNode);
}
}
while (!postStack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(postStack.pop().value);
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
func2
public class Main {
public static void postOrder(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(header);
Node tail = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
tail = stack.peek();
if (tail.leftNode != null && header != tail.leftNode && header != tail.rightNode) {
stack.push(tail.leftNode);
} else if (tail.rightNode != null && header != tail.rightNode) {
stack.push(tail.rightNode);
} else {
System.out.print(stack.pop().value + " ");
header = tail;
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
横向遍历
public class Main {
public static void wedthOrder(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
ArrayDeque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.add(header);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = deque.poll();
System.out.println(popNode.value);
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.leftNode);
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.rightNode);
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
计算二叉树中每层的最多节点个数
- 这里对于每层来说就是一个层次,所以显然就是基于横向遍历。
- 在横向遍历时我们要随机记录每个节点所在层数,以便判断该层是否已经结束,进入了下一层。有两种方式进行层数的记录:
- map空间记录,比较耗空间
- 用指针记录每一层结束节点的位置
map实现
public class Main {
public static int floorMaxNodeNum(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return 0;
}
ArrayDeque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
int thisFloorNum = 0;// 该层节点个数记录
int thisFloor = 1;// 这是第几层
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
HashMap<Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
deque.add(header);
map.put(header, thisFloor);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = deque.poll();
if (map.get(popNode) == thisFloor) {// 若是该层元素
++thisFloorNum;
} else {// 若已经进入下一层中的节点
max = Math.max(max, thisFloorNum);
++thisFloor;
thisFloorNum = 1;
}
// 每次添加都要在map中记录节点层数
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.leftNode);
map.put(popNode.leftNode, thisFloor + 1);
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.rightNode);
map.put(popNode.rightNode, thisFloor + 1);
}
}
// 这一这里还是取最大值,最后一层没有和max比较过
return Math.max(max, thisFloorNum);
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
指针实现
public class Main {
public static int floorMaxNodeNum(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return 0;
}
ArrayDeque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
int thisFloorNum = 0;// 该层节点个数记录
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Node thisFloorLastNode = header;// 该层最后一个节点,只能继承nextFloorLastNode
Node nextFloorLastNode = null;// 下一层最后一个节点,用于更新thisFloorLastNode
deque.add(header);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = deque.poll();
thisFloorNum++;
// 入队就要更新nextFloorLastNode
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.leftNode);
nextFloorLastNode = popNode.leftNode;
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.rightNode);
nextFloorLastNode = popNode.rightNode;
}
// 若该层结束
if (popNode == thisFloorLastNode) {
max = Math.max(max, thisFloorNum);
thisFloorLastNode = nextFloorLastNode;
nextFloorLastNode = null;
thisFloorNum = 0;
}
}
return max;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
判断是完全二叉树
public class Main {
public static boolean isBST(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return true;
}
ArrayDeque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.add(header);
boolean flag = false;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = deque.poll();
if ((popNode.leftNode == null && popNode.rightNode != null)// 左无节点有右节点定不是完全二叉树
|| (flag && (popNode.leftNode != null || popNode.rightNode != null))) {// 标记后左右存在节点
return false;
}
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.leftNode);
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
deque.add(popNode.rightNode);
}
// 此后不该有子节点,应该放在最后判断,因为判断结果flag不能对此次结果有影响
// 去掉popNode.leftNode == null不影响
if (popNode.leftNode == null || popNode.rightNode == null) {
flag = true;
}
}
return true;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
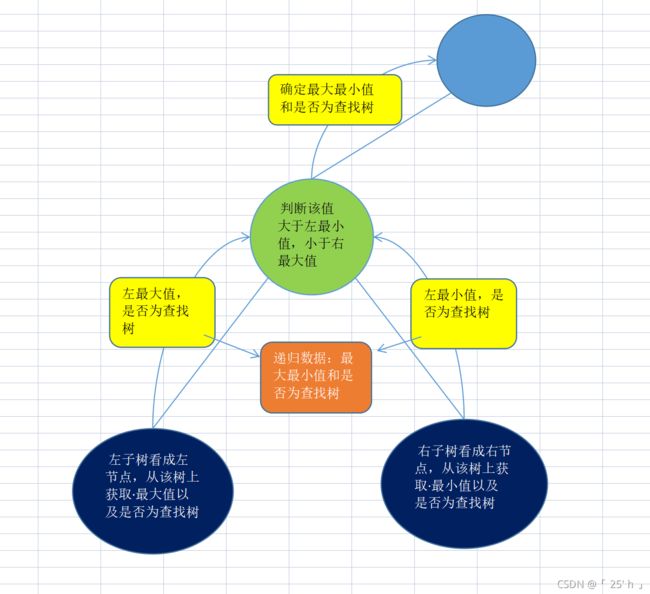
判断是搜索二叉树(套路题)
中序遍历实现
public class Main {
public static int lastNum=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean isBST(Node header) {
if (header.leftNode!=null) {
if (!isBST(header.leftNode)) {
return false;
}
}
if (lastNum>header.value) {
return false;
}
lastNum=header.value;
if (header.rightNode!=null) {
if (!isBST(header.rightNode)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
public class Main {
public static TransformData isBST(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return new TransformData(true, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
TransformData leftData = isBST(header.leftNode);
TransformData rightData = isBST(header.rightNode);
boolean flag = leftData.max < header.value && rightData.min > header.value;
return new TransformData(flag, Math.max(rightData.max, header.value), Math.min(leftData.min, header.value));
}
private static class TransformData {
boolean sucess;
int max;
int min;
public TransformData(boolean sucess, int max, int min) {
this.sucess = sucess;
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
子搜索二叉树的节点个数(套路题)
public class Main {
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return true;
}
TransformData data = maxChildBSTree(header);
return data.isBST;
}
private static TransformData maxChildBSTree(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return new TransformData(true, 0, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
TransformData leftData = maxChildBSTree(header.leftNode);
TransformData rightData = maxChildBSTree(header.rightNode);
if (leftData.isBST && rightData.isBST && header.value > leftData.maxValue
&& header.value < rightData.maxValue) {
return new TransformData(true, leftData.childMaxBSTNodeNum + rightData.childMaxBSTNodeNum + 1,
Math.max(header.value, rightData.maxValue), Math.min(leftData.minValue, leftData.minValue));
}
return new TransformData(false, Math.max(leftData.childMaxBSTNodeNum, rightData.childMaxBSTNodeNum),
Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public static class TransformData {
boolean isBST;
int childMaxBSTNodeNum;
int maxValue;
int minValue;
public TransformData(boolean isBST, int num, int max, int min) {
this.isBST = isBST;
this.childMaxBSTNodeNum = num;
this.maxValue = max;
this.minValue = min;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
判断是满二叉树(套路题)
public class Main {
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return true;
}
TransformData data = isFullTree(header);
return data != null;
}
private static TransformData isFullTree(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return new TransformData(0, 0);
}
TransformData leftData = isFullTree(header.leftNode);
TransformData rightData = isFullTree(header.rightNode);
if (leftData == null || rightData == null) {
return null;
}
if (leftData.height != rightData.height || leftData.nodeNum != rightData.nodeNum) {
return null;
}
return new TransformData(Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1,
leftData.nodeNum + rightData.nodeNum + 1);
}
public static class TransformData {
int height;
int nodeNum;
public TransformData(int h, int num) {
this.height = h;
this.nodeNum = num;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
先遍历后根据性质判断
public class Main {
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return true;
}
TransformData data = isFullTree(header);
return ((1 << data.height) - 1) == data.nodeNum;
}
private static TransformData isFullTree(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return new TransformData(0, 0);
}
TransformData leftData = isFullTree(header.leftNode);
TransformData rightData = isFullTree(header.rightNode);
return new TransformData(Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1, leftData.nodeNum + rightData.nodeNum + 1);
}
public static class TransformData {
int height;
int nodeNum;
public TransformData(int h, int num) {
this.height = h;
this.nodeNum = num;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
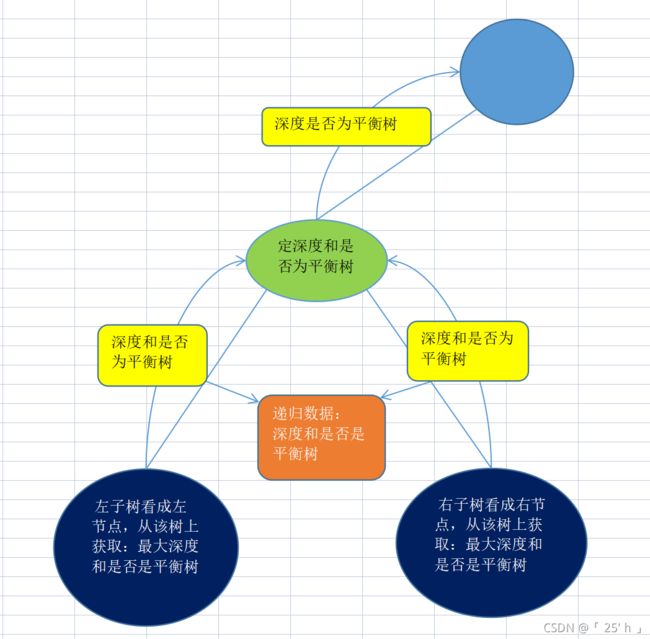
判断是平衡树(套路题)
public class Main {
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return true;
}
TransformData data = isAVLTree(header);
return data.isAVL;
}
private static TransformData isAVLTree(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return new TransformData(true, 0);
}
TransformData lData = isAVLTree(header.leftNode);
TransformData rData = isAVLTree(header.rightNode);
return new TransformData(lData.isAVL && rData.isAVL && Math.abs(lData.height - rData.height) <= 1,
Math.max(lData.height, rData.height) + 1);
}
public static class TransformData {
boolean isAVL;
int height;
public TransformData(boolean flag, int h) {
this.isAVL = flag;
this.height = h;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
树节点最远距离(套路题)
- 根据子树最大深度计算出经过当前节点的最长距离
- 向上传递子树和经过当前节点最长距离 的最大值
- 最长距离需要子树深度
- 所以递归数据包括最大距离和最大深度
public class Main {
public static int process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return 0;
}
TransformData data = maxLenPath(header);
return data.maxLen;
}
private static TransformData maxLenPath(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return new TransformData(0, 0);
}
TransformData leftData = maxLenPath(header.leftNode);
TransformData rightData = maxLenPath(header.rightNode);
return new TransformData(
Math.max(leftData.maxHeight + rightData.maxHeight + 1, Math.max(leftData.maxLen, rightData.maxLen)),
Math.max(leftData.maxHeight, rightData.maxHeight) + 1);
}
public static class TransformData {
int maxLen;
int maxHeight;
public TransformData(int maxLen, int maxHeight) {
this.maxLen = maxLen;
this.maxHeight = maxHeight;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
最大快乐值(套路题)
- 最大值和每个节点是否去有关,就是取 当前节点不去(0)+子节点去或不去的最大值 和 当前节点去(happy)+子节点不去的最大值
- 每个节点的去和不去都会直接影响父类节点,间接影响祖宗节点。
- 只要递归传递该节点去和不去的最大值信息即可。
public class Main {
public static int process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return 0;
}
TransformData data = maxHappy(header);
return Math.max(data.thisNodeDontWentSumHappy, data.thisNodeWentSumHappy);
}
private static TransformData maxHappy(Node header) {
if (header.nexts == null) {
return new TransformData(0, header.happyNum);
}
int dontWent = 0;
int went = 0;
for (Node nextNode : header.nexts) {
TransformData data = maxHappy(nextNode);
went += data.thisNodeDontWentSumHappy;
dontWent += Math.max(data.thisNodeDontWentSumHappy, data.thisNodeWentSumHappy);
}
return new TransformData(dontWent, went);
}
public static class TransformData {
int thisNodeDontWentSumHappy;
int thisNodeWentSumHappy;
public TransformData(int thisNodeDontWentSumHappy, int thisNodeWentSumHappy) {
this.thisNodeDontWentSumHappy = thisNodeDontWentSumHappy;
this.thisNodeWentSumHappy = thisNodeWentSumHappy;
}
}
public static class Node {
int happyNum;
Node[] nexts;
}
}
树结构转成链表(套路题)
- 将左右子树构建好的结果通过本节点链接,就是递归对数据就是链接起始和结束节点。
public class Main {
public static Data process(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return new Data(null, null);
}
// 将x作为中间节点,x.leftNode为创建x的前面的链表,x.rightNode为创建后面的链表。
Data leftData = process(x.leftNode);
Data rightData = process(x.rightNode);
// 前后创建的链表和中间节点x链接,因为是双向链表,所以要有四句链接
if (leftData.end != null) {
leftData.end.rightNode = x;
}
x.leftNode = leftData.end;
if (rightData.start != null) {
rightData.start.leftNode = x;
}
x.rightNode = rightData.start;
// 创建好后重新分装返回起始节点和尾节点
return new Data(leftData.start != null ? leftData.start : x,
rightData.end != null ? rightData.end : x);
}
static class Data {
Node start;
Node end;
public Data(Node start, Node end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
树的个数
public class Main {
public static int process(int N) {
if (N == 0 || N == 1) {
return 1;
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
res += process(i) * process(N - i - 1);
}
return res;
}
}
查找树中两个节点的最近共父类节点
- 该路径上不存在寻找的o1或o2,就回馈上一次递归null
- 路径上存在o1或o2,返回标记告诉上一次递归存在o1或o2
- 直到在某次递归时判断出左右路径都回馈了有o1或o2,就将该父节点返回
- 将返回的父节点以返回值的方式传给上一次递归直至结束递归。
public class Main {
/**
* @param header 根节点
* @param o1 节点一
* @param o2 节点二
* @return 最近共父节点
*
*/
public static Node ancestor(Node header, Node o1, Node o2) {
if (header == null || o1 == header || o2 == header)
return header;
Node lNode = ancestor(header.leftNode, o1, o2);
Node rNode = ancestor(header.rightNode, o1, o2);
// 该条件只会成功一次,返回的header就是我们所要找的节点
// 当该条件成立时,header结果就找到了,我们接下来的目的就是向上传递直至结束该递归调用
// 由于我们不知道这个header节点是它的父节点的左还是右
// 但是我们知道成功进入该条件后的所有递归中只能出现一边为null,另一边为header节点
// 所以 返回: lNode != null ? lNode : rNode
// 另外这句话也会在找到目标节点前将o1或o2传到上一个递归中,代表着这个路径上存在o1或o2
// 当路径上没有o1或o2时,lNode和rNode均为空,随便返回一个
if (lNode != null && rNode != null)
return header;
return lNode != null ? lNode : rNode;
}
static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
查找后继结点
- 有右节点,右树上的最左节点
- 无右节点,递归寻找节点是父节点左节点的点
- 否则空
public class Main {
public static Node process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return null;
}
if (header.rightNode != null) {
return lastLeftNode(header.rightNode);
}
Node parent = header.parentNode;
while (parent != null && parent.leftNode != header) {
header = parent;
parent = parent.parentNode;
}
return parent;
}
private static Node lastLeftNode(Node rightNode) {
while (rightNode.leftNode != null) {
rightNode = rightNode.leftNode;
}
return rightNode;
}
static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
Node parentNode;
}
}
折纸凹凸问题
- 上次每个折痕都有两个子折痕,上凹下凸,也就是二叉树节点都有一个凹左节点一个凸右节点。这些折痕的顺序就是二叉树的中序遍历。
public class Main {
/**
* @param N 折N次
*/
public static void pre(int N) {
pre(N, true);
}
private static void pre(int num, boolean down) {
if (num == 0)
return;
pre(num - 1, true);// true表示凹,false表示凸
System.out.print(down ? "down " : "up ");
pre(num - 1, false);
}
}
前中序推后序遍历
- 关注在前中后序遍历之间的元素相对位置关系。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] post = genPost(new int[]{1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7}, new int[]{4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(post));
}
public static int[] genPost(int[] pre, int[] in) {
int[] post = new int[pre.length];
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {
map.put(in[i], i);
}
genPost(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, in, 0, in.length - 1, post, 0, post.length - 1, map);
return post;
}
private static void genPost(int[] pre, int preStart, int preEnd,
int[] in, int medStart, int medEnd,
int[] post, int postStart, int postEnd,
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map) {
if (preStart > preEnd) {
return;
}
if (postStart == postEnd) {
post[postStart] = pre[preStart];
return;
}
//每一轮的前序第一个元素就是后序最后一个元素,在后续的genPost中不能再包含其他元素
post[postEnd] = pre[preStart];
//此时寻找pre[preStart]在med中的索引indexStart,那么最后的 indexStart - medStart 就是中间元素个数
int indexStart = map.get(pre[preStart]);
//以pre中preStart位置的元素为左右分割点,根据 indexStart 确定pre,in,post中的数据范围
genPost(pre, preStart + 1, preStart + indexStart - medStart,
in, medStart, indexStart - 1,
post, postStart, postStart + indexStart - medStart - 1,
map);
genPost(pre, preStart + indexStart - medStart + 1, preEnd,
in, indexStart + 1, medEnd,
post, postStart + indexStart - medStart, postEnd - 1,
map);
}
}
哈夫曼最小代价问题
public class Main {
public static int lessConsumer(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length == 1)
return arr[0];
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();// 内部元素为堆结构(优先队列)
for (int i : arr)
queue.add(i);
int sum = 0;
while (queue.size() > 1) {
// 构建赫夫曼树
int num1 = queue.poll();
int num2 = queue.poll();
sum += (num1 + num2);
queue.add(num1 + num2);
}
return sum;
}
}
分治策略
数组中的逆序对
题目:数组中的两个数,若前面的一个数大于后面的一个数,那么这两个数组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,返回逆序对的个数。
- 归并排序过程,和求小数和相似。
- 关于为什么归并排序过程中能实现单方向的大小判断?实际上是因为归并排序在排序过程中保持了数据的局部有序性,当合并时,在两个子数组整体之间存在相对位置关系。这也是为什么只有在合并的时候才能进行单方向上的大小判断。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return divideTest(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, new int[arr.length]);
}
private static int divideTest(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int m = (left + right) / 2;
return divideTest(arr, left, m, temp) // 左侧的总和
+ divideTest(arr, m + 1, right, temp)// 右侧的总和
+ mergeTest(arr, left, m, right, temp);// 左侧右侧组合过程中形成总和
}
return 0;
}
private static int mergeTest(int[] arr, int left, int m, int right, int[] temp) {
int i = left;
int j = m + 1;
int tempIndex = 0;
int res = 0;
while (i <= m && j <= right) {
// 和小数和就相差在大于小于符号和这里没有乘以arr[i]
res += arr[i] > arr[j] ? (right - j + 1) : 0;
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i] < arr[j] ? arr[i++] : arr[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i++];
while (j <= right)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[j++];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, left, tempIndex);
return res;
}
}
基于归并排序的小数和
题目:小和问题和逆序对问题 小和问题 在一个数组中,每一个数左边比当前数小的数累加起来,叫做这个数组 的小和。求一个数组 的小和。 例子:[1,3,4,2,5] 1左边比1小的数,没有; 3左边比3小的数,1; 4左 边比4小的数,1、3; 2左边比2小的数,1; 5左边比5小的数,1、3、4、 2; 所以小和为1+1+3+1+1+3+4+2=16
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return divideTest(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, new int[arr.length]);
}
private static int divideTest(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int m = (left + right) / 2;
return divideTest(arr, left, m, temp) // 左侧小数和的总和
+ divideTest(arr, m + 1, right, temp)// 右侧小数和的总和
+ mergeTest(arr, left, m, right, temp);// 左侧右侧组合过程中形成的小数和总和
}
return 0;
}
private static int mergeTest(int[] arr, int left, int m, int right, int[] temp) {
int i = left;
int j = m + 1;
int tempIndex = 0;
int res = 0;
while (i <= m && j <= right) {
// 若左小,就是会出现小数的位置。个数由右侧确定。
res += arr[i] < arr[j] ? arr[i] * (right - j + 1) : 0;
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i] < arr[j] ? arr[i++] : arr[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i++];
while (j <= right)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[j++];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, left, tempIndex);
return res;
}
}
查找
深度探索二分查找
- 注意med的取法和R或L的调整方式
经典二分查找
public class Main {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int L, int R, int value) {
while (L < R) {
int med = ((R - L) >> 1) + L;
if (arr[med] == value) {
return med;
} else if (arr[med] < value) {
L = med + 1;
} else {
R = med - 1;
}
}
return L;
}
}
查找大于该值的最小值
public class Main {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int L, int R, int value) {
while (L < R) {
int med = ((R - L) >> 1) + L;
if (arr[med] == value) {
return med;
} else if (arr[med] < value) {
L = med + 1;
} else {
R = med;
}
}
return L;
}
}
查找大于等于目标值的最右值
public class Main {
// 返回大于等于target的最右元素
private int rightest(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) left = mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid - 1;
}
return left;
}
}
查找小于该值的最大值
public class Main {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int L, int R, int value) {
while (L < R) {
int med = ((R - L + 1) >> 1) + L;
if (arr[med] == value) {
return med;
} else if (arr[med] < value) {
L = med;
} else {
R = med - 1;
}
}
return L;
}
}
查找小于等于目标值的最左值
class Main {
// 返回小于等于target最左元素
private int leftest(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) right = mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid - 1;
}
return left;
}
}
查找极小值
题目:
极值定义该值比左右的值都小,如果是在数组两侧则只比较一点即可。
在无序数组中找到该极小值。
public class Main {
private static Integer process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int N = arr.length;
if (N == 1) {
return arr[0];
}
// 最左侧
if (arr[0] < arr[1]) {
return arr[0];
}
// 最右侧
if (arr[N - 1] < arr[N - 2]) {
return arr[N - 1];
}
int left = 1;
int right = N - 2;
while (left < right) {
int med = ((right - left) >> 1) + left;
// right=med+1和left=med这种情况是在判断条件为arr[med]>arr[med-1]时
if (arr[med] < arr[med + 1]) {
right = med;
} else {
left = med + 1;
}
}
return arr[left];
}
}
递归和动归
纯递归
N皇后(最優解法)
class Main {
public static int num(int num) {
if (num < 1 || num > 32) return 0;
//limit用于限制在所有数据运算过程中保证除后num位的所有位数据均为零,来判断结束和标志结束
int limit = num == 32 ? -1 : (1 << num) - 1;
return process(limit, 0, 0, 0);
}
/**
* @param limit 限制数据在一定的位运算范围内
* @param coLim 该步前所有皇后纵向上已经存在皇后
* @param leftLim 该步前所有皇后在k=-1的方向上对于我们该步皇后存在的限制
* @param rightLim 该步前所有皇后在k=1的方向上对于我们该步皇后存在的限制
* @return 该路径上存在的的情况,只会在成功时返回1
* coLim/leftLim/rightLim三者的限制均是在位上为1的时候表示存在皇后
*/
private static int process(int limit, int coLim, int leftLim, int rightLim) {
if (limit == coLim) return 1;
//(coLim | leftLim | rightLim)结果表示所有位上为1的位置均存在皇后,不能存放。
//~后表示1的地方没有限制,可以存放皇后(但是,在32位的前32-num位上也为1,我们知道这是不合理的,因为不存在那么多的皇后)
//limit& 表示将除num位的值变成0,这样就保证所有为1的元素均为空缺位置。
int pos = limit & (~(coLim | leftLim | rightLim));
int res = 0, mostRightOne;
while (pos != 0) {//pos为0.说明不存在空缺位置
mostRightOne = pos & (~pos + 1);//此时在后num位存在1,就将最右端的1取出。
res += process(limit, coLim | mostRightOne // 该mostRightOne位的皇后对于下一皇后纵向上的影响
, (leftLim | mostRightOne) << 1 // mostRightOne对于k=-1方向的影响
, (rightLim | mostRightOne) >> 1); //mostRightOne对于k=1方向的影响
pos = pos - mostRightOne;//更新pos,将取出的1减掉,表明mostRightOne中1所对应的位存在了,不能放了。
}
return res;
}
}
递归实现字符串求值
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = value("4-(1+2)*3+1");
System.out.println(a);
}
public static int value(String string) {
if (string == null || string.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
return value(string.toCharArray(), 0)[0];
}
private static int[] value(char[] str, int i) {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
int num = 0;
int[] bra = null;
while (i < str.length && str[i] != ')') {
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9') {
num = num * 10 + str[i++] - '0';
} else if (str[i] != '(') {
addNum(list, num);
list.addLast(String.valueOf(str[i++]));
num = 0;
} else {
bra = value(str, i + 1);
num = bra[0];
i = bra[1] + 1;
}
}
addNum(list, num);
return new int[] { getNum(list), i };
}
private static void addNum(LinkedList<String> list, int num) {
if (!list.isEmpty()) {
int cur = 0;
String top = list.pollLast();
if (top.equals("+") || top.equals("-")) {
list.addLast(top);
} else {
cur = Integer.valueOf(list.pollLast());
num = top.equals("*") ? (cur * num) : (cur / num);
}
}
list.addLast(String.valueOf(num));
}
private static int getNum(LinkedList<String> list) {
int res = 0;
boolean add = true;
String curString = null;
int num = 0;
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
curString = list.pollFirst();
if (curString.equals("+")) {
add = true;
} else if (curString.equals("-")) {
add = false;
} else {
num = Integer.valueOf(curString);
res += add ? num : (-num);
}
}
return res;
}
}
岛数量问题
class Main {
private static int[][] arr;
private static int N;
private static int M;
public static int process(int[][] arr){
PB.arr=arr;
PB.N=arr.length;
PB.M=arr[0].length;
int res=0;//记录结果
for (int i=0;i<N;i++){
for (int j=0;j<M;j++){
if (arr[i][j]==1){//有1且为被感染
res++;
infect(i,j);//感染
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 感染函数
private static void infect(int i, int j) {
if (i<0||i>=N||j<0||j>=M||arr[i][j]!=1)return;
arr[i][j]=2;
infect(i-1,j);
infect(i+1,j);
infect(i,j-1);
infect(i,j+1);
}
}
返回字符串的所有子字符串(树形)
- 将该问题看成二分类问题,将所有的单个字符元素是否存在看成一个事件,通过对所有的单个字符判读存在情况就可以得出所有子字符串
- 这样可以理解为二叉树的情况,每一层的每个节点下有两个子节点,表示该层对应的字符是否添加进路径中,最后树的所有叶子节点对应的字符串就是所以子字符串
- 我们采用动态生成树的递归方法对树进行动态的遍历。(该树必定为满树)
public class Main {
public static String str;
public static StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
public static void process(String string) {
if (string == null || string.length() == 0) {
return;
}
Main.str = string;
process(0);
}
private static void process(int index) {
if (index == str.length()) {
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());
return;
}
sBuffer.append(str.charAt(index));
process(index + 1);
sBuffer.deleteCharAt(sBuffer.length() - 1);
process(index + 1);
}
}
最小字典序
- 当第一次某字符最后一次出现(下标记作 i )时,就选择当前i位置前面的所有字符中ASCLL最小的值(下标记作 j )作为结果的一部分,然后将后面出现 s.charAt( j ) 的字符去掉再根据 j 后的串进行进行递归
public class Main {
public static String process(String s) {
if (s==null||s.length()<2)return s;
int []map=new int[256];
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
map[s.charAt(i)]++;
}
int minASCLLIndex=0;
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
// 记录前面ASCLL最小的位置
minASCLLIndex=s.charAt(minASCLLIndex)<s.charAt(i)?minASCLLIndex:i;
if (--map[s.charAt(i)]==0){// 第一次发生一个字符的最后一次出现
break;
}
}
// minASCLLIndex后的字符串去掉s.charAt(minASCLLIndex)的字符串向后继续
return s.charAt(minASCLLIndex)+process(s.substring(minASCLLIndex+1).replaceAll(String.valueOf(s.charAt(minASCLLIndex)),""));
}
}
- 一直入栈,判断peek元素比当前大并且后面还存在和peek相同的字符,那么就从栈中删除栈顶元素。
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {
int N = s.length();
if (N <= 1) return s;
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int[] lastIndex = new int[26];
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[26];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
lastIndex[chars[i] - 'a'] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isVisited[chars[i] - 'a']) continue;
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() > chars[i] && lastIndex[stack.peek() - 'a'] > i) {
isVisited[stack.pop() - 'a'] = false;
}
stack.push(chars[i]);
isVisited[chars[i] - 'a'] = true;
}
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (Character ch : stack) {
stringBuffer.append(ch);
}
return stringBuffer.reverse().toString();
}
}
递归转动归
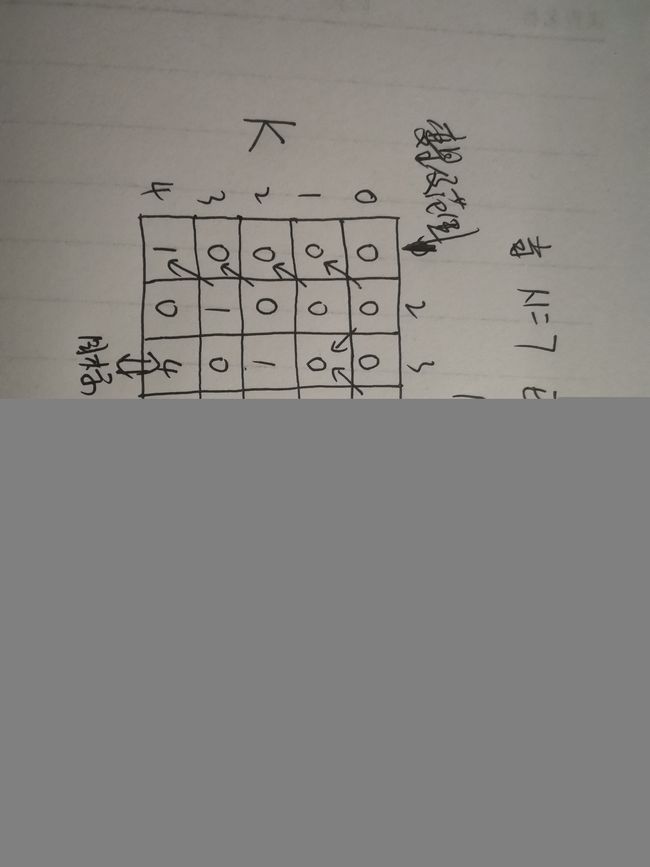
机器人运动问题
题目:
参数N:1~N个位置
参数S:初始位置
参数E:终点位置
参数K:要走的步数
机器人在E位置要用K步走到S有几种选择
递归形式
public class Main {
/**
* @param N 参数N:1~N个位置
* @param E 当前位置
* @param S 终点位置
* @param K 要走的步数
* @return 种类
*/
public static int process(int N, int E, int S, int K) {
if (K == 0) return E == S ? 1 : 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
if (E != 1) left = process(N, E - 1, S, K - 1);// 不等于1就可以向左走
if (E != N) right = process(N, E + 1, S, K - 1);// 不等于N就可以向右走
return left + right;
}
}
记忆搜索动态规划
public class Main {
/**
* @param N 参数N:1~N个位置
* @param E 当前位置
* @param S 终点位置
* @param K 要走的步数
* @return 种类
*/
public static int function(int N, int E, int S, int K) {
dp = new int[N + 1][K + 1];
for (int[] ints : dp) {
Arrays.fill(ints, -1);// 标记-1表示未计算过
}
process(N, E, S, K);// 填充dp
return dp[E][K];
}
public static int[][] dp;
private static int process(int N, int E, int S, int K) {
if (K == 0) return E == S ? 1 : 0;
if (dp[E][K] != -1) return dp[E][K];// 已存在就直接返回
int left = 0, right = 0;
if (E != 1) left = process(N, E - 1, S, K - 1);// 不等于1就可以向左走
if (E != N) right = process(N, E + 1, S, K - 1);// 不等于N就可以向右走
dp[E][K] = left + right;// 填充dp
return dp[E][K];
}
}
- 确定变量以及变量范围
- 标出目标位置,为返回结果
- 递归结束条件(最终结果)
- 确定依赖关系
- 根据依赖按照合适填补的顺序填补
public class Main {
public static int process(int N, int E, int S, int K) {
int[][] dp = new int[K + 1][N + 1];// 递归变量个数和变化范围决定了dp的维度和大小
dp[0][S] = 1;// 递归的结束条件时dp的前提条件
for (int k = 1; k <= K; k++) {
for (int e = 1; e <= N; e++) {
// 递归内容决定dp的数据填充链接,进而确定填充顺序
if (e == 1) dp[k][e] = dp[k - 1][e + 1];
else if (e == N) dp[k][e] = dp[k - 1][e - 1];
else dp[k][e] = dp[k - 1][e + 1] + dp[k - 1][e - 1];
}
}
// 返回结果
return dp[K][E];
}
}
飞棋盘
问题:在像棋盘上给定起始位置问用K步从起始位置到(1,1)有几种选择
递归实现
public class Main {
public static int process(int x, int y, int K) {
if (x < 1 || x > 10 || y < 1 || y > 9) return 0;// 出界
if (K == 0) return (x == 1 && y == 1) ? 1 : 0;// 步数结束,是否到达位置
// 向八方搜索
return process(x - 1, y - 2, K - 1) +
process(x - 1, y + 2, K - 1) +
process(x + 1, y - 2, K - 1) +
process(x + 1, y + 2, K - 1) +
process(x - 2, y + 1, K - 1) +
process(x - 2, y - 1, K - 1) +
process(x + 2, y - 1, K - 1) +
process(x + 2, y + 1, K - 1);
}
}
严格表结构
public class Main {
public static int[][][] dp;
public static int process(int x, int y, int K) {
dp = new int[10 + 1][9 + 1][K + 1];// 递归变量以及范围
dp[1][1][0] = 1;// 递归结束条件
for (int k = 1; k <= K; k++) {// 步数
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {// 横坐标
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) { // 纵坐标
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i - 1, j + 2, k - 1);
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i - 1, j - 2, k - 1);
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i + 1, j + 2, k - 1);
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i + 1, j - 2, k - 1);
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i + 2, j - 1, k - 1);
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i + 2, j + 1, k - 1);
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i - 2, j - 1, k - 1);
dp[i][j][k] += getValue(i - 2, j + 1, k - 1);
}
}
}
return dp[x][y][K];
}
private static int getValue(int x, int y, int K) {
if (x < 1 || x > 10 || y < 1 || y > 9) return 0;// 出界
return dp[x][y][K];
}
}
纸币组合情况数
问题:给定数组arr,数据为面值种类,组成res的总值,每种面值可以任意使用,问共有多少种组合方式
暴力递归
public class Main {
public static int[] coins;
public static int process(int[] arr, int res) {
coins = arr;
return process(0, res);
}
private static int process(int index, int curRes) {
if (curRes == 0) return 1;
if (index == coins.length) return 0;
int res = 0;
for (int num = 0; num * coins[index] <= curRes; ++num) {
res += process(index + 1, curRes - num * coins[index]);
}
return res;
}
}
记忆化搜索
public class Main {
public static int[] coins;
public static int[][] dp;
public static int process(int[] arr, int res) {
coins = arr;
dp=new int[arr.length+1][res+1];
for (int[] i:dp){
Arrays.fill(i,-1);
}
return process(0, res);
}
public static int process(int index, int curRes) {
if (dp[index][curRes]!=-1)return dp[index][curRes];
if (curRes == 0) {
dp[index][curRes]=1;
return 1;
}
if (index == coins.length) {
dp[index][curRes]=0;
return 0;
}
int res = 0;
for (int num = 0; num * coins[index] <= curRes; ++num) {
res += process(index + 1, curRes - num * coins[index]);
}
dp[index][curRes]=res;
return res;
}
}
严格表结构
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] coins, int res) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || res <= 0) return 0;
int[][] dp = new int[coins.length + 1][res + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= coins.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;// 递归结束条件
}
// 根据递归形式顺序进行填表
for (int coinIndex = coins.length - 1; coinIndex >= 0; coinIndex--) {
for (int curRes = 0; curRes <= res; curRes++) {
int ways = 0;
// coins[coinIndex]硬币使用了thisCoinNum个
for (int thisCoinNum = 0; thisCoinNum * coins[coinIndex] <= curRes; thisCoinNum++) {
ways += dp[coinIndex + 1][curRes - thisCoinNum * coins[coinIndex]];
}
dp[coinIndex][curRes] = ways;
}
}
// 返回目标值
return dp[0][res];
}
}
枚举的斜率优化
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] coins, int res) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || res <= 0) return 0;
int[][] dp = new int[coins.length + 1][res + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= coins.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;// 递归结束条件
}
// 根据递归形式顺序进行填表
for (int coinIndex = coins.length - 1; coinIndex >= 0; coinIndex--) {
for (int curRes = 0; curRes <= res; curRes++) {
// 该位置结果就是:
// dp[coinIndex+1][curRes] ( coins[coinIndex]硬币使用了0个 )
// +
// dp[coinIndex][curRes-coins[coinIndex]] (coins[coinIndex]硬币使用了1个 )
dp[coinIndex][curRes] = dp[coinIndex + 1][curRes];
if (curRes - coins[coinIndex] >= 0) {
dp[coinIndex][curRes] += dp[coinIndex][curRes - coins[coinIndex]];
}
}
}
// 返回目标值
return dp[0][res];
}
}
纸币组合最小个数问题
题目:给定数组arr,里面的每个值表示一种面值,可随意使用,问组成aim所需要的最小张数,并返回
递归实现
public class Main {
public static int[] coins;
public static int process(int[] coins, int res) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || res <= 0) {
return 0;
}
Main.coins = coins;
return process(0, res);
}
// 当前考虑的面值是arr[i],还剩rest的钱需要找零
// 如果返回-1说明自由使用arr[i..N-1]面值的情况下,无论如何也无法找零rest
// 如果返回不是-1,代表自由使用arr[i..N-1]面值的情况下,找零rest需要的最少张数
private static int process(int coinIndex, int curNum) {
// base case:
// 已经没有面值能够考虑了
// 如果此时剩余的钱为0,返回0张
// 如果此时剩余的钱不是0,返回-1
if (curNum == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (coinIndex == coins.length) {
return -1;
}
// 最少张数,初始时为-1,因为还没找到有效解
int minNum = -1;
// 依次尝试使用当前面值(arr[i])0张、1张、k张,但不能超过rest
for (int thisCoinNum = 0; thisCoinNum * coins[coinIndex] <= curNum; thisCoinNum++) {
// 使用了k张arr[i],剩下的钱为rest - k * arr[i]
// 交给剩下的面值去搞定(arr[i+1..N-1])
int next = process(coinIndex + 1, curNum - coins[coinIndex] * thisCoinNum);
if (next != -1) {
minNum = minNum == -1 ? next+thisCoinNum : Math.min(next + thisCoinNum, minNum);
}
}
return minNum;
}
}
记忆化搜索
public class Main {
public static int[] coins;
public static int[][] dp;
public static int process(int[] coins, int res) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || res <= 0) {
return 0;
}
Main.coins = coins;
dp = new int[coins.length + 1][res + 1];
for (int[] i : dp) {
Arrays.fill(i, -2);
}
return process(0, res);
}
private static int process(int coinIndex, int curNum) {
if (dp[coinIndex][curNum] != -2) return dp[coinIndex][curNum];
if (curNum == 0) {
dp[coinIndex][curNum] = 0;
return 0;
}
if (coinIndex == coins.length) {
dp[coinIndex][curNum] = -1;
return -1;
}
int minNum = -1;
for (int thisCoinNum = 0; thisCoinNum * coins[coinIndex] <= curNum; thisCoinNum++) {
int next = process(coinIndex + 1, curNum - coins[coinIndex] * thisCoinNum);
if (next != -1) {
minNum = minNum == -1 ? next + thisCoinNum : Math.min(next + thisCoinNum, minNum);
}
}
dp[coinIndex][curNum] = minNum;
return minNum;
}
}
严格表结构
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] coins, int res) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || res <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[coins.length + 1][res + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= res; i++) {
dp[coins.length][i] = -1;
}
for (int coinIndex = coins.length - 1; coinIndex >= 0; --coinIndex) {
for (int curNum = 0; curNum <= res; curNum++) {
dp[coinIndex][curNum] = -1;// 初始化值,若是0.表示0张就可以完成,所以不合理
for (int coinNum = 0; coins[coinIndex] * coinNum <= curNum; coinNum++) {// 对于coins[coinIndex]的硬币进行每个个数的遍历
int restIndex = curNum - coins[coinIndex] * coinNum;
if (dp[coinIndex + 1][restIndex] != -1) {// 若该值 dp[coinIndex + 1][restIndex] 不能完成,就直接跳过
// 取出最小值,注意最小值前要进行判断dp[coinIndex][curNum]是否为-1,表示此前没有方法出现
dp[coinIndex][curNum] = dp[coinIndex][curNum] == -1 ? dp[coinIndex + 1][restIndex] + coinNum :
Math.min(dp[coinIndex + 1][restIndex] + coinNum, dp[coinIndex][curNum]);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][res];
}
}
斜率优化
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] coins, int res) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || res <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[coins.length + 1][res + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= res; i++) {
dp[coins.length][i] = -1;
}
for (int coinIndex = coins.length - 1; coinIndex >= 0; --coinIndex) {
for (int curNum = 0; curNum <= res; curNum++) {
// 初始化值,继承第一个,因为定存在coins[coinIndex]一个不用的情况
dp[coinIndex][curNum]=dp[coinIndex+1][curNum];
if (coins[coinIndex]<=curNum){// 若存在可以用>=1个coins[coinIndex]进行计算
int rest=curNum-coins[coinIndex];
if (dp[coinIndex][rest]!=-1){// 该情况存在值
// 取出最小值注意判断当前dp[coinIndex][curNum]是否为-1
dp[coinIndex][curNum]=dp[coinIndex][curNum]==-1?dp[coinIndex][rest]+1:
Math.min(dp[coinIndex][rest]+1,dp[coinIndex][curNum]);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][res];
}
}
整数分裂
public class Main {
public static int process(int res) {
if (res < 1) return 0;
return process(1, res);
}
private static int process(int pre, int curRes) {// pre前驱值,保证后续分裂不小于pre
if (curRes == 0) return 1;
if (pre > curRes) return 0;
int ways = 0;
// 从pre向curRes尝试
for (int rest = pre; rest <= curRes; rest++) {
ways += process(rest, curRes - rest);
}
return ways;
}
}
记忆化搜索
public class Main {
public static int[][] dp;
public static int process(int res) {
if (res < 1) return 0;
dp=new int[res+1][res+1];
for (int[]i:dp){
Arrays.fill(i,-1);
}
return process(1, res);
}
private static int process(int pre, int curRes) {// pre前驱值,保证后续分裂不小于pre
if (dp[pre][curRes]!=-1)return dp[pre][curRes];
if (curRes == 0) {
dp[pre][curRes]=1;
return 1;
}
if (pre > curRes) {
dp[pre][curRes]=0;
return 0;
}
int ways = 0;
for (int rest = pre; rest <= curRes; rest++) {
ways += process(rest, curRes - rest);
}
dp[pre][curRes]=ways;
return ways;
}
}
动态规划
public class Main {
public static int process(int res) {
if (res < 1) return 0;
int[][] dp = new int[res + 1][res + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= res; i++) {// 递归结束条件
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int pre = res; pre >= 1; pre--) {// 前驱
for (int curRes = pre; curRes <= res; curRes++) {// 保证剩余值不小于前驱
for (int i = pre; i <= curRes; i++) {// 所有情况累加
dp[pre][curRes] += dp[i][curRes - i];
}
}
}
// 返回前驱1,合成res的结果
return dp[1][res];
}
}
斜率优化
- 枚举行为推导
public class Main {
public static int process(int res) {
if (res < 1) return 0;
int[][] dp = new int[res + 1][res + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= res; i++) {// 递归结束条件
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
dp[res][res]=1;// 根据下一层退出结果,所以要先对最后一层就行添值
for (int pre = res-1; pre >= 1; pre--) {// 前驱
for (int curRes = pre ; curRes <= res; curRes++) {// 保证剩余值不小于前驱
dp[pre][curRes]=dp[pre+1][curRes]+dp[pre][curRes-pre];// 分析的关系
}
}
// 返回前驱1,合成res的结果
return dp[1][res];
}
}
bob活着
题目:给定范围横向N,纵向M,从(i,j)开始走K步(只能上下左右走,且概率相同)没有超过给定范围那么就是活着,如果在过程中超过了范围则死了,返回活着的概率。
递归实现
public class Main {
public static int N, M;
public static String process(int n, int m, int i, int j, int k) {
N = n;
M = m;
int live = process(i, j, k);// 活着的情况
int all = (int) Math.pow(4, k);// 一共存在的情况
int gcb = gcb(all, live);// 求最大公约数
return live / gcb + " / " + all / gcb;
}
private static int gcb(int m, int n) {
if (n == 0) return m;
return gcb(n, m % n);
}
// 计算活着的情况数
public static int process(int i, int j, int K) {
if (i < 1 || i > N || j < 1 || j > M) return 0;
if (K == 0) return 1;
return process(i + 1, j, K - 1) +
process(i - 1, j, K - 1) +
process(i, j + 1, K - 1) +
process(i, j - 1, K - 1);
}
}
严格表结构
class U {
public static long gcd(long m, long n) {
return n == 0 ? m : gcd(n, m % n);
}
public static String bob2(int N, int M, int i, int j, int K) {
int[][][] dp = new int[N + 2][M + 2][K + 1];
for (int row = 1; row <= N; row++) {//初始化数据
for (int col = 1; col <= M; col++) {
dp[row][col][0] = 1;
}
}
for (int rest = 1; rest <= K; rest++) {
for (int row = 1; row <= N; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col <= M; col++) {
//递归依赖
dp[row][col][rest] = dp[row - 1][col][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row + 1][col][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row][col - 1][rest - 1];
dp[row][col][rest] += dp[row][col + 1][rest - 1];
}
}
}
long all = (long) Math.pow(4, K);
long live = dp[i + 1][j + 1][K];
long gcd = gcd(all, live);
return (live / gcd) + "/" + (all / gcd);
}
}
背包问题(树形)
- 和返回字符串的所有子字符串相似,判断每个物品是否装进了袋子两种选择
- 只需要用递归像树一样遍历所有选择取出最大值即可
- 这样的题可以使用动态规划O(N²),递归O(2^N)
暴力递归
public class Main {
private static int maxBag;
private static int[] weights;
private static int[] values;
public static int process(int[] weights, int[] values, int maxBag) {
Main.maxBag = maxBag;
Main.weights = weights;
Main.values = values;
return process(maxBag, 0);
}
/**
* @param w 剩余空间
* @param i 当前已经判断到那个物品了
* @return 最大价值
*/
private static int process(int w, int i) {
if (i == weights.length) return 0;
if (w < weights[i]) return process(w, i + 1);
return Math.max(process(w, i + 1), process(w - weights[i], i + 1) + values[i]);
}
}
动态规划
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] weights, int[] values, int maxBag) {
int[][] dp = new int[weights.length + 1][maxBag + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= weights.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= maxBag; j++) {
if (j < weights[i - 1]) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
else dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j] + values[i - 1]);
}
}
return dp[weights.length][maxBag];
}
}
数字转化成字母(树形)
- 时间复杂度为指数级
public class Main {
public static int process(String s, int i) {
// 若一个不剩或这还剩一个,就返回1(保证剩的不为0),若此时不返回,说明还剩至少两个字符
if (s.length() == i || (s.length() == i + 1 && s.charAt(i) != '0'))
return 1;
if (s.charAt(i) == '0')
return 0;// 没有0开头匹配的元素
int res = process(s, i + 1);// 一个字符的
if (Integer.parseInt(s.substring(i, i + 2)) <= 26)
res += process(s, i + 2);// 若满足匹配条件,进行两个字符的
return res;// 累加的结果返回就行了
}
}
动态规划
- 变参数个数为一个,表示当前值作为转化字母的开始数字,然后向后判断存在几种情况。
- 时间复杂度为O(N)
public class Main {
public static int process(String string) {
if (string == null || string.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (string.length() == 1) {
return string == "0" ? 0 : 1;
}
char[] arr = string.toCharArray();
int N = arr.length;
int[] res = new int[arr.length + 1];
res[N] = 1;
res[N - 1] = arr[N - 1] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
for (int i = N - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
if (arr[i] == '0') {
res[i] = 0;
} else {
if (arr[i] > '2' || (arr[i] == '2' && arr[i] > '6')) {
res[i] = res[i + 1];
} else {
res[i] = res[i + 1] + res[i + 2];
}
}
}
return res[0];
}
}
人气值
- 没有考虑条件结束情况
public class Test {
public static void process1(int start, int x, int y, int z, int end) {
func(x, y, z, end, start);
}
private static int func(int x, int y, int z, int end, int thisNum) {
if (end == thisNum) {
return 0;
}
int resX = func(x, y, z, end, thisNum + 2) + x;
int resY = func(x, y, z, end, thisNum * 2) + y;
int resZ = func(x, y, z, end, thisNum - 2) + z;
return Math.min(resX, Math.min(resY, resZ));
}
}
暴力递归
public class Main {
public static int x, y, z, target, generalSolution;
public static int process1(int x, int y, int z, int start, int end) {
Main.x = x;
Main.y = y;
Main.z = z;
Main.target = end;
Main.generalSolution = (end - start) / 2 * x;
//自己推出来的平凡解,该解是该题的一个解 不知道是不是最右,但是最优值定少于等于该值
return func(start, 0);
}
/**
* @param thisNum 当前人气
* @param coinsNum 当前消费的硬币量
* @return 该路径上所消费的硬币数量
*/
private static int func(int thisNum, int coinsNum) {
if (target == thisNum) {
return coinsNum;
}
if (coinsNum > generalSolution) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
int resX = func(thisNum + 2, coinsNum + x);
int resY = func(thisNum * 2, coinsNum + y);
int resZ = func(thisNum - 2, coinsNum + z);
return Math.min(resX, Math.min(resY, resZ));
}
}
动态规划
public class Main {
public static int process(int x, int y, int z, int start, int target) {
int generalSolution = (target - start) / 2 * x;
int max = Math.max(x, Math.max(y, z));
int[][] dp = new int[target + 1][generalSolution + max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= generalSolution; i++) {
dp[target][i] = i;
}
for (int i = generalSolution; i <= generalSolution + max; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= target; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
for (int coinsConsume = generalSolution; coinsConsume >= 0; coinsConsume--) {
for (int thisNum = start; thisNum <= target; thisNum++) {
dp[thisNum][coinsConsume] = Math.min(dp[thisNum + 2][coinsConsume + x],
Math.min(dp[thisNum * 2][coinsConsume + y], dp[thisNum - 2][coinsConsume + z]));
}
}
return dp[start][0];
}
}
数组博弈最值
递归实现
public class Main {
public static int win(int[] arr) {
return Math.max(f(arr, 0, arr.length - 1), e(arr, 0, arr.length - 1));
}
// 先手情况: 当前取值和下一次作为的后手结合的情况取最大值,就剩一个时那么结果直接取走
public static int f(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return arr[l];
return Math.max(arr[l] + e(arr, l + 1, r), arr[r] + e(arr, l, r - 1));
}
// 作为后手进行定是取值最小,剩一个元素就返回0
public static int e(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return 0;
return Math.min(f(arr, l + 1, r), f(arr, l, r - 1));
}
}
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
int N = arr.length;
int[][] front = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
front[i][i] = arr[i];
}
int[][] end = new int[N][N];
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
front[i][j] = Math.max(arr[i] + end[i + 1][j], arr[j] + end[i][j - 1]);
end[i][j] = Math.min(front[i + 1][j], front[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return Math.max(front[0][N - 1], end[0][N - 1]);
}
}
真假情况
class Test {
private static boolean isValid(char[] exp) {
if ((exp.length & 1) == 0) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < exp.length; i = i + 2) {
if ((exp[i] != '1') && (exp[i] != '0')) {
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < exp.length; i = i + 2) {
if ((exp[i] != '&') && (exp[i] != '|') && (exp[i] != '^')) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static int num1(String express, boolean desired) {
if (express == null || express.equals("")) {
return 0;
}
char[] exp = express.toCharArray();
if (!isValid(exp)) {
return 0;
}
return p(exp, desired, 0, exp.length - 1);
}
private static int p(char[] exp, boolean desired, int L, int R) {
if (L == R) {
if (exp[L] == '1') {
return desired ? 1 : 0;
} else {
return desired ? 0 : 1;
}
}
int res = 0;
if (desired) {
for (int i = L + 1; i < R; i += 2) {
switch (exp[i]) {
case '&':
res += p(exp, true, L, i - 1) * p(exp, true, i + 1, R);
break;
case '|':
res += p(exp, true, L, i - 1) * p(exp, false, i + 1, R);
res += p(exp, false, L, i - 1) * p(exp, true, i + 1, R);
res += p(exp, true, L, i - 1) * p(exp, true, i + 1, R);
break;
case '^':
res += p(exp, true, L, i - 1) * p(exp, false, i + 1, R);
res += p(exp, false, L, i - 1) * p(exp, true, i + 1, R);
break;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = L + 1; i < R; i += 2) {
switch (exp[i]) {
case '&':
res += p(exp, false, L, i - 1) * p(exp, true, i + 1, R);
res += p(exp, true, L, i - 1) * p(exp, false, i + 1, R);
res += p(exp, false, L, i - 1) * p(exp, false, i + 1, R);
break;
case '|':
res += p(exp, false, L, i - 1) * p(exp, false, i + 1, R);
break;
case '^':
res += p(exp, true, L, i - 1) * p(exp, true, i + 1, R);
res += p(exp, false, L, i - 1) * p(exp, false, i + 1, R);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
动态规划
class Test {
public static int num2(String express, boolean desired) {
if (express == null || express.equals("")) {
return 0;
}
char[] exp = express.toCharArray();
if (!isValid(exp)) {
return 0;
}
int[][] t = new int[exp.length][exp.length];
int[][] f = new int[exp.length][exp.length];
t[0][0] = exp[0] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
f[0][0] = exp[0] == '1' ? 0 : 1;
for (int i = 2; i < exp.length; i += 2) {
t[i][i] = exp[i] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
f[i][i] = exp[i] == '1' ? 0 : 1;
for (int j = i - 2; j >= 0; j -= 2) {
for (int k = j; k < i; k += 2) {
if (exp[k + 1] == '&') {
t[j][i] += t[j][k] * t[k + 2][i];
f[j][i] += (f[j][k] + t[j][k]) * f[k + 2][i] + f[j][k] * t[k + 2][i];
} else if (exp[k + 1] == '|') {
t[j][i] += (f[j][k] + t[j][k]) * t[k + 2][i] + t[j][k] * f[k + 2][i];
f[j][i] += f[j][k] * f[k + 2][i];
} else {
t[j][i] += f[j][k] * t[k + 2][i] + t[j][k] * f[k + 2][i];
f[j][i] += f[j][k] * f[k + 2][i] + t[j][k] * t[k + 2][i];
}
}
}
}
return desired ? t[0][t.length - 1] : f[0][f.length - 1];
}
}
能力蛇最大长度问题
递归实现
class Main {
public static int walk1(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
int[] ans = process(matrix, i, 0);
res = Math.max(res, Math.max(ans[0], ans[1]));
}
return res;
}
public static int fun(int[][] m) {
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) {
int ans = fun(m, i, 0, 0, false);
res = Math.max(res, ans);
}
return res;
}
// 从(i,j)出发一直走到最右侧的旅程中
// 0) 在没有使用过能力的情况下,返回路径最大和
// 1) 在使用过能力的情况下,返回路径最大和
public static int[] process(int[][] m, int i, int j) {
if (j == m[0].length - 1) {
return new int[] { m[i][j], -m[i][j] };
}
int[] restAns = process(m, i, j + 1);
int restUnuse = restAns[0];
int restUse = restAns[1];
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
restAns = process(m, i - 1, j + 1);
restUnuse = Math.max(restUnuse, restAns[0]);
restUse = Math.max(restUse, restAns[1]);
}
if (i + 1 < m.length) {
restAns = process(m, i + 1, j + 1);
restUnuse = Math.max(restUnuse, restAns[0]);
restUse = Math.max(restUse, restAns[1]);
}
int no = m[i][j] + restUnuse;
int yes = Math.max(m[i][j] + restUse, -m[i][j] + restUnuse);
return new int[] { no, yes };
}
}
动态规划
class Main {
public static int walk2(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][][] dp = new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length][2];
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) {
dp[i][matrix[0].length - 1][0] = matrix[i][matrix[0].length - 1];
dp[i][matrix[0].length - 1][1] = -matrix[i][matrix[0].length - 1];
}
for (int j = matrix[0].length - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
int restUnuse = dp[i][j + 1][0];
int restUse = dp[i][j + 1][1];
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
restUnuse = Math.max(restUnuse, dp[i - 1][j + 1][0]);
restUse = Math.max(restUse, dp[i - 1][j + 1][1]);
}
if (i + 1 < matrix.length) {
restUnuse = Math.max(restUnuse, dp[i + 1][j + 1][0]);
restUse = Math.max(restUse, dp[i + 1][j + 1][0]);
}
dp[i][j][0] = matrix[i][j] + restUnuse;
dp[i][j][1] = Math.max(matrix[i][j] + restUse, -matrix[i][j] + restUnuse);
}
}
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, Math.max(dp[i][0][0], dp[i][0][1]));
}
return res;
}
}
字符串转换代价问题
- 该题主要是从什么地方下手,我们采用从字符串最后的地方下手,对于每一次决策进行三种选择,取最小值。
暴力递归
public class Main {
public static char[] str1, str2;
public static int ic, dc, rc;
public static int process(char[] s1, char[] s2, int i, int d, int r) {
str1 = s1;
str2 = s2;
ic = i;
dc = d;
rc = r;
return process(str1.length - 1, str2.length - 1);
}
public static int process(int str1_len, int str2_len) {
if (str1_len == 0 && str2_len == 0) {
return 0;
} else if (str1_len == 0) {
return ic * str2_len;
} else if (str2_len == 0) {
return dc * str1_len;
}
int replace;
if (str1[str1_len - 1] == str2[str2_len - 1]) {
replace = process(str1_len - 1, str2_len - 1);
} else {
replace = process(str1_len - 1, str2_len - 1) + rc;
}
int delete = process(str1_len - 1, str2_len) + dc;
int add = process(str1_len, str2_len - 1) + ic;
return Math.min(Math.min(delete, add), replace);
}
}
动态规划
public class Main {
public static int process(String str1, String str2, int ic, int dc, int rc) {
if (str1 == null || str2 == null) {
return 0;
}
char[] chs1 = str1.toCharArray();
char[] chs2 = str2.toCharArray();
int row = chs1.length + 1;
int col = chs2.length + 1;
int[][] dp = new int[row][col];
//0个字符变成i个的添加代价
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
dp[i][0] = dc * i;
}
//j个字符变成0个的删除代价
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
dp[0][j] = ic * j;
}
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
//替换代价
if (chs1[i - 1] == chs2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + rc;
}
/*
dp[i][j - 1] + ic:
i个转化成j-1长度的代价+一个添加代价
dp[i - 1][j] + dc:
i-1个转化成j长度的代价+一个删除代价
*/
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][j - 1] + ic);
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j] + dc);
}
}
return dp[row - 1][col - 1];
}
}
咖啡机问题
public class Main {
public static int sweepAllCup(int[] arr, int N, int a, int b) {
PriorityQueue<Integer[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[0] + o[1]));
for (int i : arr) {
queue.add(new Integer[]{0, i});
}
int[] finishTime = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Integer[] integers = queue.poll();
integers[0] += integers[1];
finishTime[i] = integers[0];
queue.add(integers);
}
return sweepAllCup(finishTime, a, b, 0, 0);
}
// timePoint指机器时间
private static int sweepAllCup(int[] finishTime, int a, int b, int index, int timePoint) {
if (index == finishTime.length - 1) {
return Math.min(Math.max(finishTime[index], timePoint) + a, finishTime[index] + b);
}
//咖啡机刷
int sweepTime = Math.max(timePoint, finishTime[index]) + a;
int sweepRestFinish = sweepAllCup(finishTime, a, b, index + 1, sweepTime);
int time1 = Math.max(sweepRestFinish, sweepTime);//刷这个杯子和剩余杯子都完成
//自己干
int dryTime = finishTime[index] + a;
int dryRestFinish = sweepAllCup(finishTime, a, b, index + 1, timePoint);
int time2 = Math.max(dryRestFinish, dryTime);//自干这个杯子和剩余杯子都完成
return Math.min(time1, time2);
}
}
动态规划
public class Main {
public static int sweepAllCup(int[] arr, int N, int a, int b) {
PriorityQueue<Integer[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[0] + o[1]));
for (int i : arr) {
queue.add(new Integer[]{0, i});
}
int[] finishTime = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Integer[] integers = queue.poll();
integers[0] += integers[1];
finishTime[i] = integers[0];
queue.add(integers);
}
int M = finishTime[N - 1] + b;
int[][] dp = new int[N][M + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= M; i++) {
dp[N - 1][i] = Math.min(Math.max(i, finishTime[i]) + a, finishTime[i] + b);
}
for (int i = N - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
int sweepTime = Math.max(finishTime[i], j) + a;
int time1 = Math.max(sweepTime, dp[i + 1][sweepTime]);
int dryTime = finishTime[i] + b;
int time2 = Math.max(dryTime, dp[i][dryTime]);
dp[i][j] = Math.min(time1, time2);
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}
动态规划
硬币结合动归
public class Main {
public static int moneyWays(int[] arbitrary, int[] onlyOne, int money) {
int[][] arbDp = getArbDp(arbitrary, money);
int[][] onlyDp = getOnDp(onlyOne, money);
//arbDp和onlyDp第一行就是所想要的情况数
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= money; i++) {
result += arbDp[0][i] * onlyDp[0][money - i];
}
return result;
}
private static int[][] getOnDp(int[] onlyOne, int money) {
int[][] dp = new int[onlyOne.length + 1][money + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < onlyOne.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int coinIndex = onlyOne.length - 1; coinIndex >= 0; coinIndex--) {
for (int resMoney = 0; resMoney <= money; resMoney++) {
dp[coinIndex][resMoney] = dp[coinIndex + 1][resMoney];
if (resMoney > onlyOne[coinIndex]) {// 倘若可以挑选当前的一个硬币
dp[coinIndex][resMoney] += dp[coinIndex + 1][resMoney - onlyOne[coinIndex]];
}
}
}
return dp;
}
private static int[][] getArbDp(int[] arbitrary, int money) {
int[][] dp = new int[arbitrary.length + 1][money + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= arbitrary.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int coinIndex = arbitrary.length - 1; coinIndex >= 0; coinIndex--) {
for (int resMoney = 0; resMoney <= money; resMoney++) {
dp[coinIndex][resMoney] = dp[coinIndex + 1][resMoney];
if (resMoney > arbitrary[coinIndex]) {// 倘若可以挑选当前的右一个硬币
dp[coinIndex][resMoney] += dp[coinIndex][resMoney - arbitrary[coinIndex]];
}
}
}
return dp;
}
}
相同子字符串
public class Main {
public static String lcst1(String str1, String str2) {
if (str1 == null || str2 == null || str1.equals("") || str2.equals("")) {
return "";
}
char[] chs1 = str1.toCharArray();
char[] chs2 = str2.toCharArray();
int[][] dp = getdp(chs1, chs2);
int end = 0;
int max = 0;
// 记录最长子串
for (int i = 0; i < chs1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chs2.length; j++) {
if (dp[i][j] > max) {
end = i;
max = dp[i][j];
}
}
}
return str1.substring(end - max + 1, end + 1);
}
public static int[][] getdp(char[] str1, char[] str2) {
int[][] dp = new int[str1.length][str2.length];
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {
if (str1[i] == str2[0]) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
}
for (int j = 1; j < str2.length; j++) {
if (str1[0] == str2[j]) {
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < str1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < str2.length; j++) {
if (str1[i] == str2[j]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
}
}
return dp;
}
}
空间压缩
class Main {
public static String lcst2(String str1, String str2) {
if (str1 == null || str2 == null || str1.equals("") || str2.equals("")) {
return "";
}
char[] chs1 = str1.toCharArray();
char[] chs2 = str2.toCharArray();
int row = 0;
int col = chs2.length - 1;
int max = 0;
int end = 0;
while (row < chs1.length) {
int i = row;
int j = col;
int len = 0;
while (i < chs1.length && j < chs2.length) {
if (chs1[i] != chs2[j]) {
len = 0;
} else {
len++;
}
if (len > max) {
end = i;
max = len;
}
i++;
j++;
}
if (col > 0) {
col--;
} else {
row++;
}
}
return str1.substring(end - max + 1, end + 1);
}
}
最长回文子序列
求逆序串和该串的最长公共子序列
class PalindromeSubsequence {
public static int maxLen(String str) {
if (str == null || str.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] str1 = str.toCharArray();
char[] str2 = reverse(str1);
return lcse(str1, str2);
}
private static char[] reverse(char[] str) {
char[] reverse = new char[str.length];
for (int i = 0; i < reverse.length; i++) {
reverse[i] = str[str.length - 1 - i];
}
return reverse;
}
private static int lcse(char[] str1, char[] str2) {
int[][] dp = new int[str1.length][str2.length];
dp[0][0] = str1[0] == str2[0] ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 1; i < str1.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], str1[i] == str2[0] ? 1 : 0);
}
for (int j = 1; j < str2.length; j++) {
dp[0][j] = Math.max(dp[0][j - 1], str1[0] == str2[j] ? 1 : 0);
}
for (int i = 1; i < str1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < str2.length; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
if (str1[i] == str2[j]) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[str1.length - 1][str2.length - 1];
}
}
直接DP
class PalindromeSubsequence {
public static int maxLen2(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
int[][] dp = new int[str.length][str.length];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
dp[i][i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str.length - 1; i++) {
dp[i][i + 1] = str[i] == str[i + 1] ? 2 : 1;
}
for (int i = str.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = i + 2; j < str.length; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i + 1][j]);
if (str[i] == str[j]) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2, dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][str.length - 1];
}
}
相同最长子序列
public class Main {
public static String lcse(String str1, String str2) {
if (str1 == null || str2 == null || str1.equals("") || str2.equals("")) {
return "";
}
char[] chs1 = str1.toCharArray();
char[] chs2 = str2.toCharArray();
int[][] dp = getdp(chs1, chs2);
// 根据dp表格还原计算出公共的字符序列
int m = chs1.length - 1;
int n = chs2.length - 1;
char[] res = new char[dp[m][n]];
int index = res.length - 1;
while (index >= 0) {
// dp[m][n]是根据那个值进行推出,是dp[m][n-1],dp[m-1][n]还是dp[m-1][n-1]
if (n > 0 && dp[m][n] == dp[m][n - 1]) {
n--;
} else if (m > 0 && dp[m][n] == dp[m - 1][n]) {
m--;
} else {
res[index--] = chs1[m];
m--;
n--;
}
}
return String.valueOf(res);
}
private static int[][] getdp(char[] str1, char[] str2) {
int[][] dp = new int[str1.length][str2.length];
dp[0][0] = str1[0] == str2[0] ? 1 : 0;
//初始化条件
for (int i = 1; i < str1.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], str1[i] == str2[0] ? 1 : 0);
}
for (int j = 1; j < str2.length; j++) {
dp[0][j] = Math.max(dp[0][j - 1], str1[0] == str2[j] ? 1 : 0);
}
//根据str1[0...i]和str2[0...j]比较是三种情况
// i不当前str1子序列末尾结果,j为str2当前子序列最后元素
// i在当前str1子序列末尾结果,j不为str2当前子序列最后元素
// i是当前str1子序列末尾结果,j是str2当前子序列最后元素,存在条件为:str1[i] == str2[j] 成立
for (int i = 1; i < str1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < str2.length; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
if (str1[i] == str2[j]) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp;
}
}
添加最少字符组成回文串
public class PalindromeMinAdd {
public static String getPalindrome1(String str) {
if (str == null || str.length() < 2) {
return str;
}
char[] chas = str.toCharArray();
int[][] dp = getDP(chas);
char[] res = new char[chas.length + dp[0][chas.length - 1]];
int i = 0;
int j = chas.length - 1;
int resl = 0;
int resr = res.length - 1;
while (i <= j) {
if (chas[i] == chas[j]) {
res[resl++] = chas[i++];
res[resr--] = chas[j--];
} else if (dp[i][j - 1] < dp[i + 1][j]) {
res[resl++] = chas[j];
res[resr--] = chas[j--];
} else {
res[resl++] = chas[i];
res[resr--] = chas[i++];
}
}
return String.valueOf(res);
}
public static int[][] getDP(char[] str) {
int[][] dp = new int[str.length][str.length];
for (int j = 1; j < str.length; j++) {
dp[j - 1][j] = str[j - 1] == str[j] ? 0 : 1;
for (int i = j - 2; i > -1; i--) {
if (str[i] == str[j]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp;
}
}
删除元素构成回文方法数量
class PalindromeWays {
public static int way1(String str) {
char[] s = str.toCharArray();
int len = s.length;
int[][] dp = new int[len + 1][len + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
dp[i][i] = 1;
}
for (int subLen = 2; subLen <= len; subLen++) {
for (int l = 1; l <= len - subLen + 1; l++) {
int r = l + subLen - 1;
dp[l][r] += dp[l + 1][r];
dp[l][r] += dp[l][r - 1];
if (s[l - 1] == s[r - 1])
dp[l][r] += 1;
else
dp[l][r] -= dp[l + 1][r - 1];
}
}
return dp[1][len];
}
public static int way2(String str) {
char[] s = str.toCharArray();
int n = s.length;
int[][] dp = new int[100][100];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][i] = 1;
if (i + 1 < n && s[i] == s[i + 1])
dp[i][i + 1] = 3;
else
dp[i][i + 1] = 2;
}
for (int p = 2; p < n; ++p) {
for (int i = 0, j = p; j < n; ++i, ++j)
if (s[i] == s[j])
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1] + 1;
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1] - dp[i + 1][j - 1];
}
return dp[0][n - 1];
}
}
将字符串分割成最少回文串
class Main {
public static int minCut(String str) {
if (str == null || str.equals("")) {
return 0;
}
char[] chas = str.toCharArray();
int len = chas.length;
int[] dp = new int[len + 1];
dp[len] = -1;
boolean[][] p = new boolean[len][len];
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
dp[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = i; j < len; j++) {
if (chas[i] == chas[j] && (j - i < 2 || p[i + 1][j - 1])) {
p[i][j] = true;
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[j + 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[0];
}
}
动归的空间压缩
数组和字符串
字符串的全排列
- 我们通常都思路都是将所有字符依次放在最前面,例如ABC,第一位为A,B,C,然后判断第二位,那么我们如何在字符串中标记该字符已经被我们安排在前面了?
- 若我们使用下标的方式,那么在每次选择都会产生一个下标,这样会很乱。
- 于是我们可以通过将欲放在前面的字符就直接放在前面(将字符一次和后面的交换),用一个下标指引我们前面已经定了多少的元素。
- 但是若我们交换后在后续调用时,数据顺序已经打乱,我们可能会造成重复情况,所以我们在每次运行后再将数据交换变成原来位置。
- 但是当数据有重复字符时,会出现重复的全排列,这是我们就要判断交换的字符是否和之前交换的相同,若相同,就不用交换
class Main {
public static List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
public static void process(String string) {
char[] chars = string.toCharArray();
process(chars, 0);
}
private static void process(char[] chars, int i) {
if (i == chars.length) {// 结果
list.add(new String(chars));
return;
}
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[26];// 默认只有大写字母
for (int j = i; j < chars.length; j++) {// 一定是从i开始,不能是i+1,因为不交换也是一种情况
if (!isVisited[chars[j] - 'A']) {// 是否重复
isVisited[chars[j] - 'A'] = true;
swap(chars, i, j);// 交换
process(chars, i + 1);// 递归
swap(chars, i, j);// 恢复
}
}
}
private static void swap(char[] chars, int i, int j) {
char c = chars[i];
chars[i] = chars[j];
chars[j] = c;
}
}
最长递增子序列
- 贪心思想:从左向右的经典贪心,一直寻找对应位置序列前的最优位置。
- 每个位置前的最长子序列根据该位置前的数据的最长子序列得出,这样一来每个数位置对应的最长序列就会都依赖之前的数,也就是可以根据较小的数据个数推出较多数据的结果。
O(N^2)
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] preMax = new int[arr.length];// 记录下标为i位置前最长序列。
int resMax = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int curMax = 0;// 计算当前i位置前序列最长的值,不包括arr[i]
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if (arr[j] < arr[i]) {
curMax = Math.max(curMax, preMax[j]);// 更新最大值
}
}
// 记录最大值
preMax[i] = curMax + 1;
// 更新整体最长序列
resMax = Math.max(preMax[i], resMax);
}
return resMax;
}
}
优化算法O(N*logN)
public class Main {
/**
* 之前我们取的是直接存储某位置之前所存在的最长序列的个数,时间复杂度为O(N^2)
* 该种方法,我们可以了解到,当前面的值有存在序列最长值大于等于其他值,并且该值较小
* 那么比该值大且前面的子序列个数还较少,这些值就不可能成为我们的最终选的结果。
*
* 我们现在选择一种方式,就是抛弃上述过程中存在的这些值,用下标位置索引表示当前的子序列长度。复杂度O(N*logN)
* 就像indexIsMaxNumArr[maxNumIndex]表示:
* 前面存在最长子序列长度为maxNumIndex时,满足该条件下的最小值为indexIsMaxNumArr[maxNumIndex]
*/
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] indexIsMaxNumArr = new int[arr.length];
int maxNumIndex = -1;// 存在最长长度索引
for (int value : arr) {
if (maxNumIndex == -1 || indexIsMaxNumArr[maxNumIndex] < value) {
// 之前不存在值或者该值大于之前所有值,此时肯定比之前最长索引大1,所以maxNumIndex加上1
indexIsMaxNumArr[++maxNumIndex] = value;
} else {
// 查找indexIsMaxNumArr[0…………maxNumIndex]范围中,值大于或等于value的最小值索引。
int index = biggerThanValueLeftestIndex(indexIsMaxNumArr, value, maxNumIndex);
// 更新该值
indexIsMaxNumArr[index] = value;
}
}
return maxNumIndex + 1;
}
/**
* 该函数在查找时总结过
*
* @param indexIsMaxNumArr 数组
* @param value 目标值
* @param right 右端索引
* @return 值大于或等于value的最小值索引
*/
private static int biggerThanValueLeftestIndex(int[] indexIsMaxNumArr, int value, int right) {
int left = 0;
while (left < right) {
int med = ((right - left) >> 1) + left;
if (indexIsMaxNumArr[med] == value) {
return med;
} else if (indexIsMaxNumArr[med] > value) {
right = med;
} else {
left = med + 1;
}
}
return right;
}
}
最多亦或和为零的数据部分
一般解
- 前序累计异或,根据从左向右的动态规划思想进行最大值的判断和记录。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 存储前面所有元素的累计异或结果
int[] preSum = new int[arr.length];
preSum[0] = arr[0];
// 计算累计异或结果
for (int i = 1; i < preSum.length; i++) {
preSum[i] = preSum[i - 1] ^ arr[i];
}
// 存储每个位置前的最多的亦或者为零的个数
int[] preMaxNum = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; ++i) {
// 初始化当前结果值
preMaxNum[i] = preSum[i] == 0 ? 1 : 0;
// 后面的值根据前面的更新,需要判断两个累计亦或结果相同,那么这其中异或和定为0
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if (preSum[j] == preSum[i]) {
// arr[i……j]之间的的数组成一个亦或为0的值然后加上preMaxNum[j]就该结合的结果值
// 这里实际上若preMaxNum[j] + 1大的话可以直接退出该层循环。
preMaxNum[i] = Math.max(preMaxNum[i], preMaxNum[j] + 1);
}
}
// 使用arr[i]作为亦或为零的一部分和不用arr[i]的两种情况取最大值
preMaxNum[i] = Math.max(preMaxNum[i], preMaxNum[i - 1]);
}
return preMaxNum[preMaxNum.length - 1];
}
}
优化解法
- 上一种解法中提到,当满足preMaxNum[j] + 1 > preMaxNum[i] 时就可以退出循环,说明我们只是找到一个满足更新条件即可
public class Test {
public static int mostEOR(int[] arr) {
if (arr==null||arr.length==0)return 0;
int ans = 0;
int xor = 0;
int[] mosts = new int[arr.length];
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
xor ^= arr[i];
//若存在,说明已经出现,那么之间的数字的异或和为0
//这种方式下就是上次出现该值前的个数+1就是当前个数
if (map.containsKey(xor)) {
int pre = map.get(xor);
mosts[i] = pre == -1 ? 1 : (mosts[pre] + 1);
}
if (i > 0) {
//判断 在次数分割和抛弃改次以上一次的方案哪个为最优解
//为了防止pre...i中出现多个异或和为0的情况
mosts[i] = Math.max(mosts[i - 1], mosts[i]);
}
//更新或添加此时xor的索引
map.put(xor, i);
//ans实际上最后也是mosts的最后一个值,也可以在最后直接返回mosts[mosts.length-1]
ans = Math.max(ans, mosts[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
连续总和范围问题(含负数)
題目:给定一个数组arr,包含任意整数,求在arr中小于等于k的最长连续子数组。
- 一般由于在某一序列arr[i…j]累计和大于k,我们不能直接保证在j后存在一个负值(下标n)使arr[i…n]的累加和<=k
- 一般究其根本原因还是由于负值的存在在我们判断最长<=k的子序列时产生了质疑。如果我们一次对于后续序列进行判断,那么时间复杂度会变成O(N^2)
- 一般我们想能不能将存在负值的放在某一段序列中,使包含該負數的序列的累计和为正数,将该段序列用该整数代替,那么就变成了一个根据序列累计和正数值判断每次向右最远伸长距离。
- 一般由此如何生成一段一段段序列(记作:{A1,A2,A3…An})变成了最主要的问题:
- 对于一个负数记作arr[f],我们不关心是否需要将该负数后面的数加进arr[f]对应的Ai中,因为在进行经典的尺取法时包含是否讲后面的数加进取
- 所以我们只关心每个负数前面的值arr[i…f]累计和第一次为正数的位置i
- 所以我们只要从右向左进行若当前值右面的值累加和(Ai)<=0,就将当前值加入到右面的序列Ai中
- 另外再将Ai的序列看成一个整体时,我们需要记录每一段的下标位置。
public class Main {
public static int maxLengthAwesome(int[] arr, int k) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] minSums = new int[arr.length];// 当前值向右进行累加在不大于零的情况下的最长序列
int[] minSumEnds = new int[arr.length];// 记录下标位置
minSums[arr.length - 1] = arr[arr.length - 1];
minSumEnds[arr.length - 1] = arr.length - 1;
for (int i = arr.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if (minSums[i + 1] <= 0) {// 不大于零,可以继续添加值
minSums[i] = arr[i] + minSums[i + 1];
minSumEnds[i] = minSumEnds[i + 1];// 记录下标
} else {// 前面已经是正数了
minSums[i] = arr[i];
minSumEnds[i] = i;// 更新Ai的下标
}
}
int right = 0;
int sum = 0;
int res = 0;
// left是窗口的最左的位置,right是窗口最右位置的下一个位置
for (int left = 0; left < arr.length; left++) {
// while循环结束之后:
// 1) 如果以i开头的情况下,累加和<=k的最长子数组是arr[left..right-1],看看这个子数组长度能不能更新res;
// 2) 如果以i开头的情况下,累加和<=k的最长子数组比arr[left..right-1]短,更新还是不更新res都不会影响最终结果;
// 注意我们仅仅还将Ai看成一个单个的正整数,所以我们只有在right向右扩展时才用的到。
while (right < arr.length && sum + minSums[right] <= k) {
sum += minSums[right];
right = minSumEnds[right] + 1;
}
// 更新最大值
res = Math.max(res, right - left);
if (right > left) { // 窗口内还有数
sum -= arr[left];
} else if (right == left) { // 窗口内已经没有数了,说明从i开头的所有子数组累加和都不可能<=k
++right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
最长无重复子串
- 尺取法类似,不过这是尺取法的反向思维,根据右端获取左端位置。尺取法时根据左端定右端。
public class Main {
public static int process(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] array = s.toCharArray();
int[] map = new int[256];//下标表示字符,值表示字符上一次出现的位置下标
Arrays.fill(map, -1);
int left = -1, maxLen = 0;// left表示此时向左延伸的最左位置,不包括array[left],包括array[right]
for (int right = 0; right < array.length; right++) {
left = Math.max(left, map[array[right]]);// 上次最左位置和array[right]上次出现的位置取最右的下标
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, right - left);// 更新结果
map[array[right]] = right;// 更新上次出现的位置索引
}
return maxLen;
}
}
最长有效括号长度
public class Main {
public static int maxNum(String s) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
int[] dp = new int[arr.length];
int pre, res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < dp.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == ')' ) {
pre = i - 1 - dp[i - 1];
if (pre >= 0 && arr[pre] == '(') {
// 和当前)匹配的(之间是dp[pre-1],前存在有效括号为dp[pre-1]
dp[i] = dp[pre - 1] + 2 + ((pre - 1) >= 0 ? dp[pre - 1] : 0);
}
}
res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
存在字符串的最小范围
public class Main {
public static int minLength(String str1, String str2) {
if (str1 == null || str2 == null || str1.length() < str2.length()) {
return 0;
}
char[] chas1 = str1.toCharArray();
char[] chas2 = str2.toCharArray();
//所有字符256种
int[] map = new int[256];
for (int i = 0; i != chas2.length; i++) {
map[chas2[i]]++;
}
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
int match = chas2.length;//
int minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (right != chas1.length) {
map[chas1[right]]--;
//判断chas1[right]是否为chas2中未匹配过的元素,如果是就将match更新
if (map[chas1[right]] >= 0) {
match--;
}
//match为0,就表示总元素已经在chas1[left...right]中
if (match == 0) {
//将left尽量向右走,将窗口缩小到最小
while (map[chas1[left]] < 0) {
map[chas1[left++]]++;
}
minLen = Math.min(minLen, right - left + 1);
//更新minLen后,将left右移,跳过的值定为chas2中的值,所以match需要match变化
map[chas1[left++]]++;
match++;
}
right++;
}
return minLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : minLen;
}
}
贪心算法
前后缀差点最大值
- 一般思路:数据预处理建立两个从左右两端的最值数组,再遍历求解。
- 极限贪心思维:直接获取最大值和左右两端的差值
- 两个最大值数中定存在一个整体的最大值。
- 在满足将最大值放在一左端,无论怎么选择, 右一半的最大值一定大于等于最右端的元素。所以右侧最值最小只能是最右边的元素。
- 在满足将最大值放在一右端时同理,只需要这两种情况下取最值即可。
public class Test {
public static int num(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) return 0;
int max=arr[0];
for (int i = 1;i < arr.length; i++){
max = Math.max( max, arr[i]);
}
return Math.max(max-arr[0],max-arr[arr.length-1]);
}
}
子数组累计和最大值
- 我们利用假设检验的思想,先假设子数组为最大值,来推充要条件:
- 若满足最大累加和就要考虑前面连续子数组的累计和定小于0,否则会将前面的子数组加上。
- 对于每个值进行遍历索引时,若出现了累加为负数,那么就意味着此时就是我们重新向后累计的重要标志。
public class Test {
public static int maxLenNum(int[] arr){
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int cur=0;
for (int i : arr) {
cur+=i;
max=Math.max(max,cur);
cur=Math.max(cur, 0);
}
return max;
}
}
子矩阵累计和最大值
- 子矩阵往往考虑是否可以转换成字数组的问题,就是将多行转化成一行或者多列转化成多列
- 转化之后思考一维情况下的解决思路,看看是否能应用到矩阵中
public class Test {
public static int maxAreaNum(int[][] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr[0].length == 0) return 0;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int cur;
int[] sumArr;
for (int i = 0; i != arr.length; i++) {
sumArr = new int[arr[0].length];
for (int j = i; j != arr.length; j++) {
cur = 0;
for (int k = 0; k != sumArr.length; k++) {
sumArr[k] += arr[j][k];
cur += sumArr[k];
max = Math.max(max, cur);
cur = Math.max(cur, 0);
}
}
}
return max;
}
}
安路灯
- 一个简单的贪心思想,将路灯尽量安装在需要安转的第二个位置。
public class Test {
public static int minNum(String s) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
int minNum = 0;
int index = 0;
while (index < arr.length) {
if (arr[index] == 'X') {
index++;
} else {
minNum++;
if (index + 1 == arr.length) {
break;
} else if (arr[index + 1] == 'X') {
index += 2;
} else {
index += 3;
}
}
}
return minNum;
}
}
找工作
- 同等难度的工作,肯定只用酬劳最多的当做最终结果。
- 对于高难度的工作,若酬劳低肯定选低难度酬劳高的工作。
- 所以在创建map时,只需要记录难度递增(不能出现两个难度相同)的同时酬劳递增。
public class Test {
public static int[] process(Job[] jobs, int[] ability) {
Arrays.sort(jobs, (o1, o2) -> o1.hard != o2.hard ? (o1.hard - o2.hard) : (o2.money - o1.money));
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(jobs[0].hard, jobs[0].money);
Job j = jobs[0];
// 将同 hard 情况下 money 最多的进入map
for (Job job : jobs) {
if (job.hard != j.hard && job.money > j.money) {
j = job;
map.put(j.hard, j.money);
}
}
int[] ans = new int[ability.length];
for (int i = 0; i < ability.length; i++) {
// 小于或等于ability[i]的最大键值
Integer key = map.floorKey(ability[i]);
ans[i] = key != null ? map.get(key) : 0;
}
return ans;
}
static class Job {
int hard;
int money;
}
}
最多场会议问题
- 贪心思想:按照结束时间安排
public class Main {
public static int process(Meeting[] meetings) {
// 按照会议结束时间进行排序
Arrays.sort(meetings, (o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1.end, o2.end));
int timePoint = 0;// 记录已经安排的会议能到达的结束时间
int res = 0; // 结果值
for (Meeting meeting : meetings) {
if (timePoint <= meeting.start) {
++res;
timePoint = meeting.end;
}
}
return res;
}
static class Meeting {
int start;
int end;
}
}
投资收益问题
- 贪心思想:在当前能做的项目中取项目收益最右的项目。
- 当前能做的项目通过根据项目投资排序
- 当前项目中收益最优的使用堆结构
public class Main {
/**
* @param counts 需要投资
* @param profits 投资对应的利益获取
* @param k 只能有k次投资机会
* @param m 先有资金
* @return 最终有多少钱
*/
public static int process(int[] counts, int[] profits, int k, int m) {
if (counts == null || profits == null || counts.length != profits.length) {
return m;
}
Project[] projects = new Project[counts.length];
for (int i = 0; i < counts.length; i++) {
projects[i] = new Project(counts[i], profits[i]);
}
// 按照投资资金进行排序,由此可以很快的取出可以投资的项目
Arrays.sort(projects, (o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1.count, o2.count));
// 在可以投资的项目中将报酬最高的放在堆顶,由此获取更多的利益
PriorityQueue<Project> deQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o2.profit, o1.profit));
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
// 还有剩余项目,并且我们现在的能力足够做
while (index + 1 < projects.length && projects[index].count < m) {
deQueue.add(projects[index++]);
}
// 没有能力做任何项目了
if (deQueue.isEmpty()) {
return m;
}
// 做最优的项目获取当前资金
m += deQueue.poll().profit;
}
return m;
}
private static class Project {
int count;
int profit;
private Project(int count, int profit) {
this.count = count;
this.profit = profit;
}
}
}
过河
- 贪心思想:将最小的和较大的放在一条上,若能就放一条上,否则让较大的自己一条。
public class Main {
public static int minBo(int[] arr, int weight) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
if (arr[arr.length-1]>weight) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
int boatNum = 0;
while (left <= right) {
if (arr[right] + arr[left] <= weight) {
++left;
}
--right;
++boatNum;
}
return boatNum;
}
}
绳子覆盖问题
定右二分向左查找O(N*logN)
- 最主要还是二分的实现,详见查找深度探索二分查找。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr, int L) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || L <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int index = bRNum(arr, i, arr[i] + L);
res = Math.max(res, index - i + 1);
}
return res;
}
// 查找arr[L...]元素中小于等于value中最大的元素索引
private static int bRNum(int[] arr, int L, int value) {
int R = arr.length - 1;
while (L < R) {
// 注意med取值方法,若没有+1可能死循环
int med = ((R - L + 1) >> 1) + L;
if (arr[med] == value) {
return med;
} else if (arr[med] < value) {
L = med;// 注意这里不+1,防止跳过
} else {
R = med - 1;
}
}
return L;
}
}
定左向右延申O(N)
- 优化原因:左侧向右运动时,右侧动态测试能到达最右位置。避免了每次要寻找。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr, int L) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || L <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int max = 1;
for (int Left = 0 ,right=0 ; Left < arr.length; Left++) {
while (right < arr.length && arr[Left] + L >= arr[right]) {
right++;
}
max = Math.max(max, right - Left);
}
return max;
}
}
超级洗衣机
public class Test {
public static int minPoint(int[] machines) {
if (machines == null || machines.length == 0) return -1;
int N = machines.length;
int allSum = 0;
for (int i : machines) {
allSum += i;
}
if (allSum % N != 0) return -1;
int average = allSum / N;
int leftSum = 0;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int leftRest = leftSum - average * i;
int rightRest = (allSum - leftSum - machines[i]) - (N - 1 - i) * average;
if (leftRest < 0 && rightRest < 0) {
res = Math.max(res, Math.abs(leftRest) + Math.abs(rightRest));
} else {
res = Math.max(res, Math.max(Math.abs(leftRest), Math.abs(rightRest)));
}
leftSum += machines[i];
}
return res;
}
}
数论以及衍生
经典约瑟夫环
- 通过将还剩一个人的人的索引不断的推导出在人数有N个时,最后这个人在该N个中的索引。这样就可以获取N个人中的索引获取最后结果。
public class Test {
/**
* @param N 当前元素总个数
* @param index 第index个死
* @return 最后存活的人的位次(非索引)当前该轮中的第几位
*/
public static int getLive(int N, int index) {
if (N == 1) return 1;//该1表示在最后还剩一个时的这个新一轮的索引
// 存活人在上一轮中的位次 = ( 存活人该轮中的位次 + index - 1 ) % N + 1
// ()中-1和最后+1的原因就是因为索引是从1开始,并不是从0开始
return (getLive(N - 1, index) + index - 1) % N + 1 ;
}
}
关于公式的理解
衍生题目
public class Test {
public static int process(int N, int[] arr) {
return process(N, arr, 0);
}
/**
* @param N 一共有N个元素
* @param arr 滚蛋的数组位次
* @param i 从arr中第i个开始使用
* @return 存活的人在当前循环中的位次
*/
private static int process(int N, int[] arr, int i) {
if (N == 1) return 1;
return (process(N - 1, arr, (i + 1) % arr.length) + arr[i] - 1) % N + 1;
}
}
质数相关
public class Main {
public static int pocess(int N) {
if (N<2) {
return 0;
}
int zhiShuNum = 0;
int zhiShuSum = 0 ;
for (int i = 2; i <=N; i++) {
while (N%i==0) {
zhiShuSum += i;
++zhiShuNum;
N /= i;
}
}
return zhiShuSum - zhiShuNum;
}
}
快速幂
经典快速幂
public class Main {
/**
* @param a 底数
* @param b 幂数
* @return
*/
public static int process(int a, int b) {
int res = 1;
while (b != 0) {
// 无论如何在循环过程中一定最少满足一次该条件
// 因为b>>=1过程中b定会存在等于1的时候
if ((b & 1) == 1) {
res = res * a;
}
a = a * a;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
}
幂后取模上c
public class Main {
/**
* @param a 底数
* @param b 幂数
* @param c 模数
* @return
*/
public static int process(int a, int b, int c) {
int res = 1;
a %= c;
while (b != 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) {
res = (res * a) % c;
}
a = (a * a) % c;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
}
相邻4倍问题
public class Test {
public static boolean process(int[] arr) {
int prim = 0, num2 = 0, num4 = 0;
for (int i : arr) {
if (i % 2 == 1) prim++;
else {
if (i % 4 == 0) num4++;
else num2++;
}
}
if (num2 == 0) {
return prim == 0 || num4 >= prim - 1;
} else {
return num4 >= prim;
}
}
}
类斐波那契数列
exp1
- 第一个为1,第二个为2,的斐波那契数列
public class Test {
public static int process(int N) {
if (N<=0)return 0;
if (N==1)return 1;
if (N==2)return 2;
int a=1;
int b=2;
int res=0;
while (N-2!=0){
res=a+b;
a=b;
b=res;
N--;
}
return res;
}
}
辗转相除
public class Main {
public static int process(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0)// 表示上一步的辗转相除结果为0了
return a;
return process(b, a % b);
}
}
exp2
- 就是在N范围中第一项为1,第二项为2的斐波那契数列个数就是可以保留的个数。
public class Main {
public static int process(int N) {
if (N <= 3)
return 0;
// num记录小于N的类斐波那契数列中元素个数
int a = 1, b = 2, res = 0, num = 2;
// 递归的斐波那契数列
while (true) {
res = a + b;
if (res > N)
return N - num;
a = b;
b = res;
num++;
}
}
}
打表法
- 出现和倍数相关的问题时,可以考虑通过一般方法解题后的结果是否存在某种特殊的规律,通过直观的答案直接进行代码的书写,不需要关注本质含义。
整体装袋
public class Main {
public static int num(int apple) {
if (apple % 8 == 0)
return apple / 8;
int n8 = apple / 8;
int m = apple % 8;
while (m < 24 && n8 >= 0) {
if (m % 6 == 0)
return n8 + m / 6;
--n8;
m += 8;
}
return -1;
}
}
- 18前无规律,18后单为-1,双为一个值,每增加8个就增加1
public class Main {
public static int daBiao(int apple) {
if (apple < 18)
return apple == 0 ? 0
: (apple == 6 || apple == 8) ? 1
: (apple == 12 || apple == 14 || apple == 16) ? 2
: -1;
if (apple % 2 == 1)
return -1;
return (apple - 18) / 8 + 3;
}
}
幂次方吃草
public class Main {
public static String winner(int N) {
if (N <= 4)
return N == 0 || N == 2 ? "羊羊" : "牛牛";
int eatTest = 1;
while (eatTest <= N) {
if (winner(N - eatTest).equals("羊羊"))
return "牛牛";
eatTest *= 4;
}
return "羊羊";
}
}
public static String win(int N){
return (N)%5==0||(N)%5==2?"羊羊":"牛牛";
}
经典数据结构类
栈
用栈将栈元素排序
public class Main {
public static void sortStackByStack(Stack<Integer> stack) {
Stack<Integer> help = new Stack<Integer>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int cur = stack.pop();
while (!help.isEmpty() && help.peek() < cur) {
stack.push(help.pop());
}
help.push(cur);
}
while (!help.isEmpty()) {
stack.push(help.pop());
}
}
}
单调栈
- 当遇见向左右边进行大于该值或小于该值的最近值的寻找时就是单调栈
经典单调栈模型
求没有重复值的数组中每个元素的左右两个方向离该值最近的且比该值大的元素的索引,没有记录-1
public class Main {
public static int[][] process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int[][] res = new int[arr.length][2];
// 一直保持栈中索引对应的元素维持降序原则
Stack<Integer> singleStack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 若果直接插入打破了降序原则,那么就要将栈中元素进行删除
// 在删除的同时,每个删除元素的最左大的值是栈中上一个值,右边最近的大值就是将要入栈的值
while (!singleStack.isEmpty() && arr[singleStack.peek()] < arr[i]) {
int popIndex = singleStack.pop();
res[popIndex][0] = singleStack.isEmpty() ? -1 : singleStack.peek();
res[popIndex][1] = i;
}
singleStack.push(i);
}
// 将栈中剩余元素进行确定,此时栈中元素右侧没有大值
while (!singleStack.isEmpty()) {
int popIndex = singleStack.pop();
res[popIndex][0] = singleStack.isEmpty() ? -1 : singleStack.peek();
res[popIndex][1] = -1;
}
return res;
}
}
单调栈题
- 贪心算法做基础:将每个值作为该累计数组中的最小值,最佳范围就是向两边寻找比该值小的值作为累计数组的分界点。
- 数据预处理:优先计算累计和,根据贪心定范围
- 升序单调栈定分界点
class T {
public static int m(int[] arr) {
int size = arr.length;
int[] sums = new int[size];
sums[0] = arr[0];
//我们使用单调栈时是获取左右的最近的较小的两个值之间的元素(不包括两个较小值)
//元素累计和,这样根据两个值相减就会得到中间元素的值
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
sums[i] = sums[i - 1] + arr[i];
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] < arr[i]) {//保持降序
int j = stack.pop();
//通过左右两边累计和的差值求出对应值j的指标
max = Math.max(max, (stack.isEmpty() ? sums[i - 1] : (sums[i - 1] - sums[stack.peek()])) * arr[j]);
}
stack.push(i);
}
//处理右无较小值的数据
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int j = stack.pop();
max = Math.max(max, (stack.isEmpty() ? sums[size - 1] : (sums[size - 1] - sums[stack.peek()])) * arr[j]);
}
return max;
}
}
堆
输出出现次数最多的
public class Test {
public static List maxK(int[] arr, int k) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i:arr){
map.merge(i,1, Integer::sum);
}
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry