基于python及图像识别的围棋棋盘棋子识别1——定位棋盘位置
系列文章:
1、基于python及图像识别的围棋棋盘棋子识别1——定位棋盘位置
2、基于python及图像识别的围棋棋盘棋子识别2——定位棋子位置及识别棋子颜色
3、基于python及图像识别的围棋棋盘棋子识别3——耗时优化(一行代码速度提高600倍)
4、基于python及图像识别的围棋棋盘棋子识别4——源码及使用说明
基于python及图像识别的围棋棋盘棋子识别1——定位棋盘位置
- 效果图
-
- 原图
- 中间处理效果
- 最终结果
- 思路分析
- 源码:定位棋盘位置
-
- 带保存图像
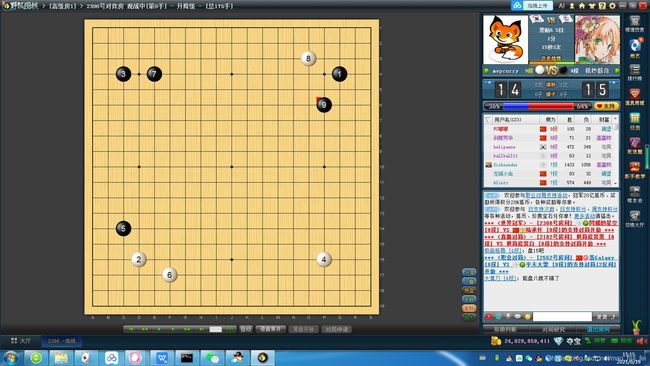
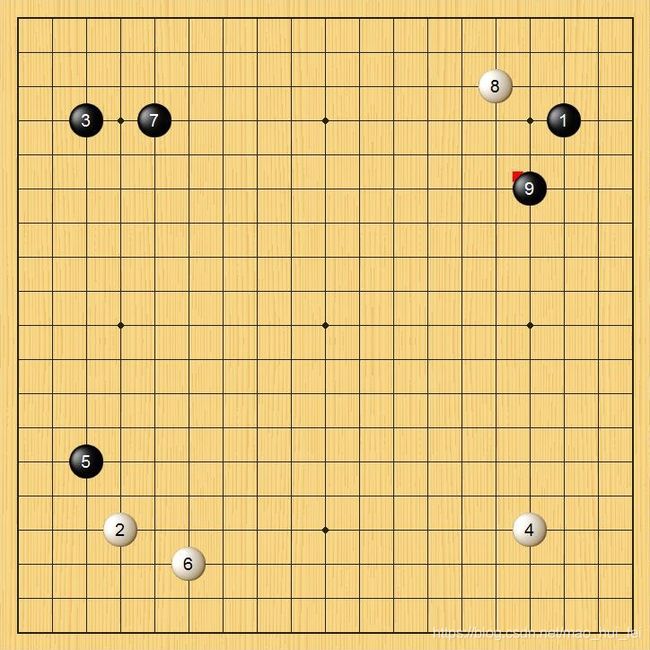
最近需要做一个围棋识别的项目,首先要将棋盘位置定位出来,效果图如下:
效果图
原图
中间处理效果
最终结果
思路分析
我们利用python opencv的相关函数进行操作实现,根据棋盘颜色的特征,寻找到相关特征,将棋盘区域抠出来。最好从原始图像中将棋盘位置截取出来。
源码:定位棋盘位置
from PIL import ImageGrab
import numpy as np
import cv2
from glob import glob
imglist = sorted(glob("screen/*.jpg"))
for i in imglist:
# while 1:
img = cv2.imread(i)
image = img.copy()
w,h,c = img.shape
img2 = np.zeros((w,h,c), np.uint8)
img3 = np.zeros((w,h,c), np.uint8)
# img = ImageGrab.grab() #bbox specifies specific region (bbox= x,y,width,height *starts top-left)
hsv=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
lower = np.array([10,0,0])
upper = np.array([40,255,255])
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv,lower,upper)
erodeim = cv2.erode(mask,None,iterations=2) # 腐蚀
dilateim = cv2.dilate(erodeim,None,iterations=2)
img = cv2.bitwise_and(img,img,mask=dilateim)
frame = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, dst = cv2.threshold(frame, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dst, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cv2.imshow("0",img)
i = 0
maxarea = 0
nextarea = 0
maxint = 0
for c in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(c)>maxarea:
maxarea = cv2.contourArea(c)
maxint = i
i+=1
#多边形拟合
epsilon = 0.02*cv2.arcLength(contours[maxint],True)
if epsilon<1:
continue
#多边形拟合
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[maxint],epsilon,True)
[[x1,y1]] = approx[0]
[[x2,y2]] = approx[2]
checkerboard = image[y1:y2,x1:x2]
cv2.imshow("1",checkerboard)
cv2.waitKey(1000)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
带保存图像
from PIL import ImageGrab
import numpy as np
import cv2
from glob import glob
import os
imglist = sorted(glob("screen/*.jpg"))
a=0
for i in imglist:
# while 1:
a=a+1
img = cv2.imread(i)
image = img.copy()
w,h,c = img.shape
img2 = np.zeros((w,h,c), np.uint8)
img3 = np.zeros((w,h,c), np.uint8)
# img = ImageGrab.grab() #bbox specifies specific region (bbox= x,y,width,height *starts top-left)
hsv=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
lower = np.array([10,0,0])
upper = np.array([40,255,255])
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv,lower,upper)
erodeim = cv2.erode(mask,None,iterations=2) # 腐蚀
dilateim = cv2.dilate(erodeim,None,iterations=2)
img = cv2.bitwise_and(img,img,mask=dilateim)
frame = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, dst = cv2.threshold(frame, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dst, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 保存图片的地址
img_file_1 = "./temp"
# 确认上述地址是否存在
if not os.path.exists(img_file_1):
os.mkdir(img_file_1)
cv2.imshow("0",img)
cv2.imwrite(img_file_1 + "/" + 'temp_%d.jpg'%a, img)
i = 0
maxarea = 0
nextarea = 0
maxint = 0
for c in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(c)>maxarea:
maxarea = cv2.contourArea(c)
maxint = i
i+=1
#多边形拟合
epsilon = 0.02*cv2.arcLength(contours[maxint],True)
if epsilon<1:
continue
#多边形拟合
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[maxint],epsilon,True)
[[x1,y1]] = approx[0]
[[x2,y2]] = approx[2]
checkerboard = image[y1:y2,x1:x2]
cv2.imshow("1",checkerboard)
cv2.waitKey(1000)
# 保存图片的地址
img_file_2 = "./checkerboard"
# 确认上述地址是否存在
if not os.path.exists(img_file_2):
os.mkdir(img_file_2)
cv2.imwrite(img_file_2 + "/" + 'checkerboard_%d.jpg'%a, checkerboard)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()