MNIST手写数字识别:分类应用入门
MNIST手写数字识别数据集
- MNIST 数据集来自美国国家标准与技术研究所,National Institute of Standards and Technology(NIST)
- 数据集由来自250个不同人手写的数字构成,其中50%是高中学生,50%来自人口普查局的工作人员
- 训练集:55000;验证集:5000;测试集:10000
MNIST 数据集可在 http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ 获取
TensorFlow提供了数据集读取方法
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist.input_data as input_data
# 该路径为保存该数据集的路径
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/Users/liuqi/Desktop/data/MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
了解MINIST手写数字识别数据集
print("训练集train的数量:", mnist.train.num_examples, " 验证集validation的数量:", mnist.validation.num_examples,
" 测试集test的数量:", mnist.test.num_examples)
# 输出:训练集train的数量: 55000 验证集validation的数量: 5000 测试集test的数量: 10000
print("train images shape:", mnist.train.images.shape, " labels shape:", mnist.train.labels.shape)
# 输出:train images shape: (55000, 784) labels shape: (55000, 10)
# 为什么是784 28*28的灰度图 为什么是10 10分类 代表10个阿拉伯数字
# 第一张图片大小
len(mnist.train.images[0])
# 第一张图片形状
mnist.train.images[0].shape
# 使第一张图片变成28*28的形状
mnist.train.images[0].reshape(28, 28)
可视化image
# 图像显示
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_image(image):
plt.imshow(image.reshape(28, 28), cmap='binary')
plt.show()
plot_image(mnist.train.images[0])
标签数据和独热编码
如何设置独热编码
# one-hot为True时表示独热编码 为False时表示非独热编码
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/Users/liuqi/Desktop/data/MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
# one-hot编码
mnist.train.labels[1]
# 输出:array([0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
# 如果使用非独热编码读取标签值
mnist_no_one_hot = input_data.read_data_sets("/Users/liuqi/Desktop/data/MNIST_data/", one_hot=False)
print(mnist_no_one_hot.train.labels[0:10])
# 输出结果:[7 3 4 6 1 8 1 0 9 8]
独热编码
- 一种稀疏向量,其中:
- 一个元素设为1,所以其他元素均为0
- 独热编码常用于表示拥有无限个可能值的字符串或标识符
为什么要使用独热编码
- 将离散特征的取值扩展到了欧式空间,离散特征的某个取值就对应欧式空间的某个点
- 机器学习算法中,特征之间距离的计算或相似度的常用计算方法都是基于欧式距离空间的
- 将离散特征型使用one-hot编码,会让特征之间的距离计算更加合理
独热编码如何取值
# one-hot编码
mnist.train.labels[1]
# 结果:array([0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
# 读出独热编码指代的具体的值
# argmax返回的是最大数的索引
import numpy as np
np.argmax(mnist.train.labels[1])
# 结果:3
数据集的划分
- 构建和训练机器学习模型是希望对新的数据做出良好的预测
- 如何去保证训练的实效,可以去应对以前从未见过的数据呢?
- 一种方法是将数据集分为两个子集:
- 训练集 - 用于训练模型的子集
- 测试集 - 用于测试模型的子集
- 通常,在测试集上表现是否良好是衡量能否在新数据集上表现良好的有用指标,但前提是:测试集足够大;不会反复使用相同的测试集来作假
- 一种方法是将数据集分为两个子集:
拆分成两个数据集
- 将单个数据拆分为一个训练集和一个测试集
- 确保测试集满足以下几个条件:
- 规模足够大,可产生具有统计意义的结果
- 能代表整个数据集,测试集的特征应该和训练集的特征相同
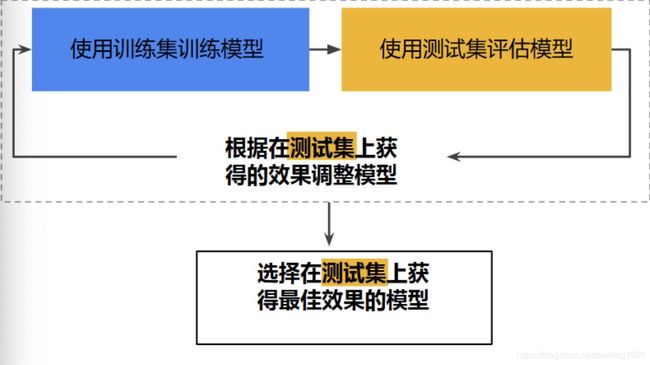
工作流程图
存在的问题
思考:
- 使用测试集和训练集来推动模型开发迭代的流程
- 在每次迭代时,都会对训练数据进行训练并评估测试数据,并以基于测试数据的评估结果为指导来选择和更改各种模型超参数。例如学习率和特征。这种方法是否存在问题?
- 多次重复执行该流程可能导致模型不知不觉地拟合了特定测试集的特征,从而导致过拟合
新的数据划分
- 通过将数据集划分为三个子集,可以大幅降低过拟合的发生几率
- 新的数据的划分:训练集、验证集、测试集
- 使用验证集评估测试集的效果
- 在模型“通过”验证集之后,使用测试集再次检查评估结果
新的工作流程
逻辑回归(二分类)
许多问题的预测结果是一个在连续空间的数值,比如房价预测问题,可以用线性模型来描述: Y = x 1 ∗ w 1 + x 2 ∗ w 2 + . . . + x n ∗ w n + b Y = x_1 * w_1 + x_2 * w_2 +...+ x_n * w_n + b Y=x1∗w1+x2∗w2+...+xn∗wn+b
但是也有很多场景需要输出的是概率估算值,例如:
- 分局邮件内容判断是垃圾邮件的可能性
- 根据医学影像判断肿瘤是恶性的可能性
这时需要将预测输出值控制在[0, 1]区间内,二元分类问题的目标是正确预测两个可能的标签中的一个,逻辑回归可以用于处理这类问题
Sigmoid函数
- 逻辑回归模型如何确保输出值始终落在0-1之间
- Sigmoid函数(S型函数)生成的输出值正好具有这些特性,其定义如下: y = 1 1 + e − z y = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-z}} y=1+e−z1
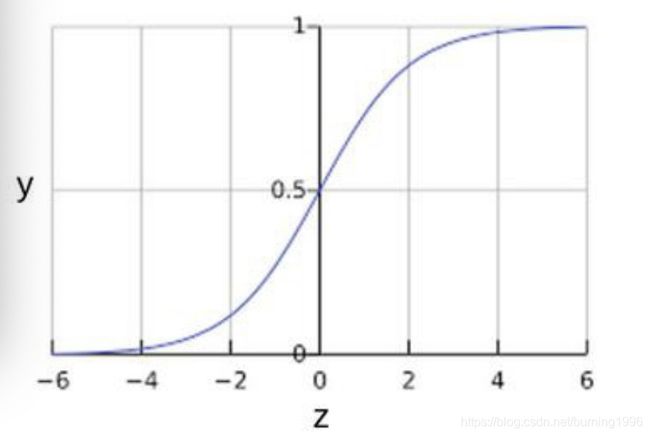
- 定义域为全体实数,值域在[0, 1]之间
- z值在0点对应的结果为0.5
- Sigmoid函数连续可微分
特定样本的逻辑回归的输出
z = x 1 ∗ w 1 + x 2 ∗ w 2 + . . . + x n ∗ w n + b z = x_1*w_1 + x_2*w_2 + ...+ x_n*w_n + b z=x1∗w1+x2∗w2+...+xn∗wn+b
y = 1 1 + e − z y = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-z}} y=1+e−z1
逻辑回归中的损失函数
- 前面线性回归的损失函数是平方损失,如果逻辑回归的损失函数也定义为平方损失,那么:
J ( w ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n ( φ ( z i ) − y i ) 2 J(w) = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}{(\varphi(z_i) - y_i)^2} J(w)=n1i=1∑n(φ(zi)−yi)2
其中:
- i 代 表 第 i 个 样 本 点 i代表第i个样本点 i代表第i个样本点
- φ = 1 1 + e − ( z ) \varphi = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-(z)}} φ=1+e−(z)1
- z i = x i ∗ w + b z_i = x_i * w + b zi=xi∗w+b
- φ ( z i ) 表 示 对 第 i 个 样 本 的 预 测 值 \varphi(z_i)表示对第i个样本的预测值 φ(zi)表示对第i个样本的预测值
- y i 表 示 第 i 个 样 本 的 标 签 值 , 即 真 实 值 y_i表示第i个样本的标签值,即真实值 yi表示第i个样本的标签值,即真实值
将Sigmoid函数带入上述函数,非凸函数,有多个极小值,如果采用梯度下降的方法,会容易导致陷入局部最优解中
因此在二元逻辑回归中,损失函数通常不采用平方损失,一般采用对数损失函数,其定义如下:
J ( w , b ) = − ∑ ( x , y ) ∈ D y ln ( y ′ ) + ( 1 − y ) ln ( 1 − y ′ ) J(w, b) = -\sum_{(x,y)\in D}{y\ln(y') + (1-y)\ln(1 - y')} J(w,b)=−(x,y)∈D∑yln(y′)+(1−y)ln(1−y′)
其中:
- ( x , y ) ∈ D 是 标 签 样 本 的 数 据 集 (x, y)\in D是标签样本的数据集 (x,y)∈D是标签样本的数据集
- y 是 有 标 签 样 本 中 的 标 签 , 取 值 必 须 是 0 或 者 1 y是有标签样本中的标签,取值必须是0或者1 y是有标签样本中的标签,取值必须是0或者1
- y ′ 是 对 于 特 征 集 x 的 预 测 值 ( 介 于 0 和 1 之 间 ) y'是对于特征集x的预测值(介于0和1之间) y′是对于特征集x的预测值(介于0和1之间)
多元回归
Softmax思想
逻辑回归可生成介于0和1之间的小数
例如,某电子邮件分类起的逻辑回归输出值为0.8,表明电子邮价是垃圾邮件的概率为80%,不是垃圾邮件的概率为20%,很明显,一封电子邮件是垃圾邮件或非垃圾邮件的概率之和为1
Softmax将这一想法延伸到多类别领域
在多类问题中,softmax会为每个类别分配一个用小数表示的概率,这些用小数表示的概率相加之和必须是1.0
Softmax示例
神经网络的Softmax层
Softmax举例
多元分类中的损失函数–交叉熵损失函数
- 交叉熵是一个信息论中的概念,它原来是用来估算平均编码长度的。给定两个概率分布p和q,通过q来表示p的交叉熵为
H ( p , q ) = − ∑ x p ( x ) l o g q ( x ) H(p, q) = -\sum_{x}{p(x)logq(x)} H(p,q)=−x∑p(x)logq(x) - 交叉熵刻画的是两个概率分布之间的距离,p代表正确答案,q代表的是预测值,交叉熵越小,两个概率的分布越接近
定义交叉熵损失函数
- 交叉熵损失函数定义为:
L o s s = − ∑ i = 1 n y i l o g y i ′ Loss = -\sum_{i = 1}^{n}y_ilogy_i' Loss=−i=1∑nyilogyi′
其中: y i 为 标 签 值 ( 即 真 实 值 ) , y i ′ 为 预 测 值 y_i为标签值(即真实值),y_i'为预测值 yi为标签值(即真实值),yi′为预测值
损失函数定义的代码:
loss_function = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y*tf.log(pred), reduction_indices = 1))
分类模型的构建与实践
载入数据
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist.input_data as input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/Users/liuqi/Desktop/data/MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
构建模型
# 定义占位符x, y
# mnist中每张图片共有28*28=784个像素点
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784], name = "X")
# 0-9 一共有10个数字
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name = "Y")
# 在本案例中,以正态分布的随机数初始化权重W,以常数0初始化偏置b
# 定义变量w, b, w为784*10的数组,784表示有784个特征 10表示10分类
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, 10]), name = "W")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]), name = "b")
# 用单个神经元构建神经网络
forward = tf.matmul(x, w) + b
# Softmax分类
# 当我们处理多分类任务时,通常需要使用softMax regression模型,softmax regression会对每一类别估算出一个概率
pred = tf.nn.softmax(forward)
设置训练参数
# 训练轮数
train_epochs = 50
# 单批次训练样本数(批次大小,即一批训练的样本数)
batch_size = 100
# 一轮样本训练有多少批次
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
# 显示粒度
display_step = 1
# 学习率
learning_rate = 0.01
定义损失函数
# 定义交叉熵损失函数 pred为预测值 y为标签值
loss_function = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y*tf.log(pred), reduction_indices = 1))
选择优化器
# 梯度下降优化器
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss_function)
定义准确率
# 检查预测类别tf.argmax(tf.argmax(pred, 1),)与实际类别tf.argmax(y, 1)的匹配情况
# tf.argmax()如果第二个参数指定为1,则是第二维(列)的元素取值,即同行的每一列的最大值
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
# 准确率,将布尔值转化为浮点数,并计算平均值
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
声明会话,变量初始化
sess = tf.Session()
ini = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(ini)
模型训练
# 开始训练
# 训练轮次
for epoch in range(train_epochs):
# 每一轮分total_batch批次进行训练
for batch in range(total_batch):
xs,ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x:xs, y:ys})
# 经过一轮训练后,通过梯度下降方法找到使得失函数最小的Wi和b
# 使用验证集的数据通过该模型计算误差和准确率, 验证集没有分批
loss,acc = sess.run([loss_function, accuracy], feed_dict={x:mnist.validation.images, y:mnist.validation.labels})
# 打印训练过程中的详细信息
if (epoch+1) % display_step == 0:
print("Train Epoch:", '%02d' %(epoch + 1), "Loss=", "{:.9f}".format(loss), "Accuracy=", "{:.4f}".format(acc))
评估模型
accu_test = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y:mnist.test.labels})
print("Test Accuracy:", accu_test)
模型应用与可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# images:图像列表 labels:标签列表 prediction:预测值列表 index:从第index个开始显示 num = 10表示一次显示10幅图
def plot_images_labels_prediction(images, labels, prediction, index, num = 10):
# 获取当前图表
fig = plt.gcf()
# 1英尺等于2.54cm
fig.set_size_inches(10, 12)
# 最多显示25张图片
if num > 25:
num = 25
for i in range(0, num):
# 获取当前要处理的子图
ax = plt.subplot(5, 5, i+1)
# 显示第index个图像
ax.imshow(np.reshape(images[index], (28, 28)), cmap = 'binary')
# 构建该图上要显示的title
title = "label=" + str(np.argmax(labels[index]))
if len(prediction) > 0:
title += ", predict=" + str(prediction[index])
# 显示图上的title信息
ax.set_title(title, fontsize = 10)
# 不显示坐标轴
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
index += 1
plt.show()
plot_images_labels_prediction(mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels, prediction_result, 0, 25)
参考视频:深度学习应用开发TensorFlow实践