基于英雄联盟寻路背景的A星算法及python实现
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、什么是A星算法?
- 二、算法流程
- 三、python算法实现
- 四、结果展示
前言
Astar算法是游戏中最常见的寻路算法,比如LOL的自动导航等。菜鸡的你从水晶复活以后,需要自动导航到大龙坑打团,这时你选择右击小地图上的大龙坑,你的英雄就会自动绕开障碍物前往该处。这是如何实现的呢?
一、什么是A星算法?
Astar算法是在实际生活和工业应用包括游戏设计等情景中所频繁被使用的一种路径规划算法。算法类似于贪婪最佳优先搜索,因为同样属于启发式算法,通过设定一个估价函数来实现。标准算法计算当前位置上相邻的每个节点,其方向可以是四面也可以是八面,并选择估价函数值成本最低的节点加入数组。添加到新数组的节点将用于搜索更多可行的路径。A*搜索算法通过依次扩展具有最小启发函数的节点来寻找最优路径。该算法的计算从它的图中的起始节点开始,通过不断寻找以最低代价函数值到达目标点的节点,并且优先将那些使估价值函数更小的节点加入拓展序列或数组,从而形成一个求解的节点集,在计算的到的每一个节点都放置到一个list中进行记录(大规模问题要使用优先级队列,也就是堆结构来存储),最后通过对list有序的链接来实现整个路径规划的结果。
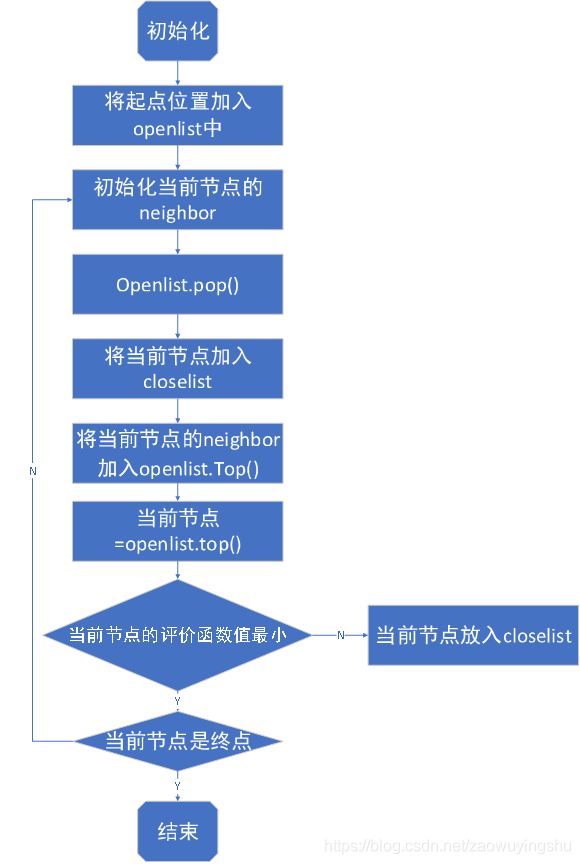
二、算法流程
由以上A算法的过程图中可以分析得到该算法的核心思维:通过评价函数f(n)的确定来使得A可以不断地前进和运行。这是一种启发式算法,而分析可得f(n)= g(n)+ h(n)是使用评价节点n的估计成本函数,它是由两部分构成的: g(n) 是距离值函数,用来描述从起点到节点n的路径的确切成本,; f (n)是启发函数,表示从节点n到目标的启发式估计成本。
A*算法在进行路径规划和搜索时,通过计算f(n)的值,运用贪婪算法的思维,每次都选取下一个点的依据找到估价成本最低的那个节点,通过多次计算和比较来选择移动方向和节点的。从而实现路径最优。
三、python算法实现
代码如下(示例):
def A_star(org, des):
open_list = []
close_list = []
open_list.append(org)
while len(open_list) > 0:
temp_node = open_list[0]
for node in open_list:
if node.f < temp_node.f:
temp_node = node
current_node= temp_node
open_list.remove(current_node)
close_list.append(current_node)
#找到当前节点的所有领近节点
node_list = []
if Is_valid(current_node.x, current_node.y - 1, open_list, close_list):
node_list.append(Node(current_node.x, current_node.y - 1))
if Is_valid(current_node.x, current_node.y + 1, open_list, close_list):
node_list.append(Node(current_node.x, current_node.y + 1))
if Is_valid(current_node.x - 1, current_node.y, open_list, close_list):
node_list.append(Node(current_node.x - 1, current_node.y))
if Is_valid(current_node.x + 1, current_node.y, open_list, close_list):
node_list.append(Node(current_node.x + 1, current_node.y))
neighbors = node_list
for node in neighbors:
if node not in open_list:
node.init_node(current_node, des)
open_list.append(node)
for node in open_list:
if (node.x == des.x) and (node.y == des.y):
return node
return None
def Is_valid(x,y,open_list=[],close_list=[]):
if x < 0 or x >=len(MAZE) or y < 0 or y >= len(MAZE[0]):
return False
if MAZE[x][y] == 1:
return False
if Is_contain(open_list,x,y):
return False
if Is_contain(close_list,x,y):
return False
return True
def Is_contain(nodes, x, y):
for node in nodes:
if (node.x == x) and (node.y == y):
return True
return False
class Node:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.f = 0
self.g = 0
self.h = 0
self.parent = None
def init_node(self, parent, end):
self.parent = parent
if parent is not None:
self.g = parent.g + 1
else:
self.g = 1
self.h = abs(self.x - end.x) + abs(self.y - end.y)
self.f = self.g + self.h
#迷宫地图
MAZE = [
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
]
#设置起始点和终点
org = Node(8, 0)
des = Node(2, 5)
result_node = A_star(org, des)
path = []
while result_node is not None:
path.append(Node(result_node.x, result_node.y))
result_node = result_node.parent
cnt=0
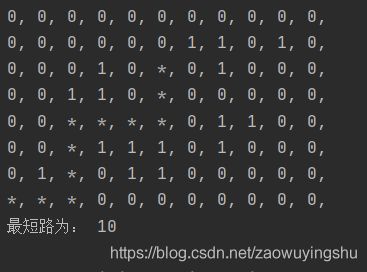
for i in range(0,len(MAZE)):
for j in range(0,len(MAZE[0])):
if Is_contain(path, i, j):
cnt+=1
print("*, ", end='')
else:
print(str(MAZE[i][j]) + ", ", end='')
print()
print("最短路为:",cnt-1)