Reconclier
React 使用虚拟dom代替真实的dom节点,当数据被改变的时候就需要用到算法来更新所有的旧节点。React会通过diff算法比较新旧节点并进行增删改。
在官方的文档里,处理React diff的动作叫做协调(reconcile)。今天就讲一讲协调的代码。(代码版本为v17.0.2)
ChildReconciler
ChildReconciler是一个包装函数, 用于区分mount和diff的
//ReactFiber.js
export const reconcileChildFibers = ChildReconciler(true);
export const mountChildFibers = ChildReconciler(false);
//ReactFiberBeginWork.js
function reconcileChildren(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
nextChildren: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
if (current === null) {
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(...);
} else {
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(...);
}
}因为初始挂载的时候只需要将子节点全部添加进去,并不需要diff算法,所以会用shouldTrackSideEffects变量区分,当它为false的时候就表示为挂载函数。
ReconcileChildFibers
ChildReconciler返回闭包内的一个函数reconcileChildFibers
function reconcileChildFibers(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChild: any,
lanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// This function is not recursive.
// If the top level item is an array, we treat it as a set of children,
// not as a fragment. Nested arrays on the other hand will be treated as
// fragment nodes. Recursion happens at the normal flow.
// Handle top level unkeyed fragments as if they were arrays.
// This leads to an ambiguity between <>{[...]} and <>....
// We treat the ambiguous cases above the same.
const isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment =
typeof newChild === 'object' &&
newChild !== null &&
newChild.type === REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE &&
newChild.key === null;
if (isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment) {
newChild = newChild.props.children;
}
// Handle object types
if (typeof newChild === 'object' && newChild !== null) {
switch (newChild.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes,
),
);
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSinglePortal(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes,
),
);
case REACT_LAZY_TYPE:
if (enableLazyElements) {
const payload = newChild._payload;
const init = newChild._init;
// TODO: This function is supposed to be non-recursive.
return reconcileChildFibers(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
init(payload),
lanes,
);
}
}
if (isArray(newChild)) {
return reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes,
);
}
if (getIteratorFn(newChild)) {
return reconcileChildrenIterator(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes,
);
}
throwOnInvalidObjectType(returnFiber, newChild);
}
if (
(typeof newChild === 'string' && newChild !== '') ||
typeof newChild === 'number'
) {
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleTextNode(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
'' + newChild,
lanes,
),
);
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (typeof newChild === 'function') {
warnOnFunctionType(returnFiber);
}
}
// Remaining cases are all treated as empty.
return deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, currentFirstChild);
}新节点会有几种情况
- 当新节点为Object类型并且不等于null,而且还要有
$$typeof属性的时候说明只有一个子节点,只需要根据不同的React元素类型去更新替换。 - 当新节点为Array的时候,需要算法去比较新旧节点,实现更新,删除,替换。
- 当新节点对象含有Iterator 迭代器的时候,需要进行其他处理, 迭代器的支持一般用于不可变列表等
- 当新节点是字符串且不为空的时候或者为数字,只需要当做文本替换
当子节点为单节点的时候,只需要调用reconcileSingleElement将节点进行更新
ReconcileChildrenArray
React更新多节点的时候会用到算法
function reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChildren: Array<*>,
lanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
if (__DEV__) {
let knownKeys = null;
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const child = newChildren[i];
knownKeys = warnOnInvalidKey(child, knownKeys, returnFiber);
}
}
let resultingFirstChild: Fiber | null = null;
let previousNewFiber: Fiber | null = null;
let oldFiber = currentFirstChild;
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;
let newIdx = 0;
let nextOldFiber = null;
for (; oldFiber !== null && newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
if (oldFiber.index > newIdx) {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber;
oldFiber = null;
} else {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
const newFiber = updateSlot(
returnFiber,
oldFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes,
);
if (newFiber === null) {
if (oldFiber === null) {
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
break;
}
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
if (oldFiber && newFiber.alternate === null) {
deleteChild(returnFiber, oldFiber);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
if (newIdx === newChildren.length) {
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);
if (getIsHydrating()) {
const numberOfForks = newIdx;
pushTreeFork(returnFiber, numberOfForks);
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}
if (oldFiber === null) {
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = createChild(returnFiber, newChildren[newIdx], lanes);
if (newFiber === null) {
continue;
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
// TODO: Move out of the loop. This only happens for the first run.
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
if (getIsHydrating()) {
const numberOfForks = newIdx;
pushTreeFork(returnFiber, numberOfForks);
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = updateFromMap(
existingChildren,
returnFiber,
newIdx,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes,
);
if (newFiber !== null) {
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
if (newFiber.alternate !== null) {
existingChildren.delete(
newFiber.key === null ? newIdx : newFiber.key,
);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
}
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
// Any existing children that weren't consumed above were deleted. We need
// to add them to the deletion list.
existingChildren.forEach(child => deleteChild(returnFiber, child));
}
if (getIsHydrating()) {
const numberOfForks = newIdx;
pushTreeFork(returnFiber, numberOfForks);
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}React跟Vue的diff有几个一样的机制(没有说抄Vue, React先出的vdom
- 只比较同层元素
- 不同类型的节点比较会创建新的节点和子节点,然后销毁旧节点,所以不会复用子节点
- key相同能够复用旧节点,但是如果元素类型不一样不会复用旧节点
- 首先会进行第一次的循环,它做的事情就是更新节点。
updateSlot
新旧节点会带入updateSlot函数里进行更新
function updateSlot(
returnFiber: Fiber,
oldFiber: Fiber | null,
newChild: any,
lanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// Update the fiber if the keys match, otherwise return null.
const key = oldFiber !== null ? oldFiber.key : null;
if (
(typeof newChild === 'string' && newChild !== '') ||
typeof newChild === 'number'
) {
// Text nodes don't have keys. If the previous node is implicitly keyed
// we can continue to replace it without aborting even if it is not a text
// node.
if (key !== null) {
return null;
}
return updateTextNode(returnFiber, oldFiber, '' + newChild, lanes);
}
if (typeof newChild === 'object' && newChild !== null) {
switch (newChild.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE: {
if (newChild.key === key) {
return updateElement(returnFiber, oldFiber, newChild, lanes);
} else {
return null;
}
}
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE: {
if (newChild.key === key) {
return updatePortal(returnFiber, oldFiber, newChild, lanes);
} else {
return null;
}
}
case REACT_LAZY_TYPE: {
if (enableLazyElements) {
const payload = newChild._payload;
const init = newChild._init;
return updateSlot(returnFiber, oldFiber, init(payload), lanes);
}
}
}
if (isArray(newChild) || getIteratorFn(newChild)) {
if (key !== null) {
return null;
}
return updateFragment(returnFiber, oldFiber, newChild, lanes, null);
}
throwOnInvalidObjectType(returnFiber, newChild);
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (typeof newChild === 'function') {
warnOnFunctionType(returnFiber);
}
}
return null;
}updateSlot对应不同的新节点类型进行不同的更新。对于更新单节点的时候会判断是否为同样的key,并且在更新的时候判断类型是否一致选择复用或者创建新的节点
当旧节点存在key且不匹配新节点key时,说明可能被移动到别处了,updateSlot此时会返回null, 并且break掉循环,不处理当前节点,因为之后的顺序可能已经乱掉了,所以之后的节点会在处理移动节点的时候再进行处理。
当循环完最后一次的新节点时候,可以删除其他多余不需要的旧节点
- 第二次循环是在oldFiber等于null的时候,旧节点已经到尾了,但是新节点还没循环完,说明没有可以复用的旧节点,但存在新的节点。此时,需要添加新节点放在newFiber链表里。
if (oldFiber === null) {
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = createChild(returnFiber, newChildren[newIdx], lanes);
if (newFiber === null) {
continue;
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
// TODO: Move out of the loop. This only happens for the first run.
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
if (getIsHydrating()) {
const numberOfForks = newIdx;
pushTreeFork(returnFiber, numberOfForks);
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}3.第三次循环就是处理移动的节点。首先会创建一个Map对象去保存旧节点,能够方便快速查找现有的节点。之后就可以通过查找新节点的key匹配旧节点的key去更新
// Add all children to a key map for quick lookups.
const existingChildren = mapRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);
// Keep scanning and use the map to restore deleted items as moves.
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = updateFromMap(
existingChildren,
returnFiber,
newIdx,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes,
);
if (newFiber !== null) {
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
if (newFiber.alternate !== null) {
// The new fiber is a work in progress, but if there exists a
// current, that means that we reused the fiber. We need to delete
// it from the child list so that we don't add it to the deletion
// list.
existingChildren.delete(
newFiber.key === null ? newIdx : newFiber.key,
);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
}placeChild
节点是否移动的逻辑在placeChild函数
function placeChild(
newFiber: Fiber,
lastPlacedIndex: number,
newIndex: number,
): number {
newFiber.index = newIndex;
if (!shouldTrackSideEffects) {
newFiber.flags |= Forked;
return lastPlacedIndex;
}
const current = newFiber.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
const oldIndex = current.index;
if (oldIndex < lastPlacedIndex) {
// This is a move.
newFiber.flags |= Placement;
return lastPlacedIndex;
} else {
// This item can stay in place.
return oldIndex;
}
} else {
// This is an insertion.
newFiber.flags |= Placement;
return lastPlacedIndex;
}
}如果旧节点的位置大于最后一次替换的位置则不需要移动,否则移动到最后头
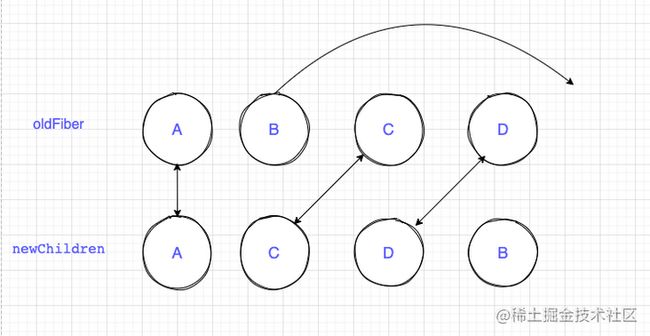
1.首先从节点A开始对比,新旧节点一直会进行更新,并且两个节点的index都为0,所以oldFiber.index >= lastPlacedIndex,不需要移动
2.新旧节点key不同,break跳出循环, 将BCD放进map结构里。开始进行节点移动,C节点原位置为2,是大于lastplaceIndex = 0的,所以不需要移动,lastplaceIndex更新为2
3.D节点原位置为3,大于lastplaceIndex, 不需要移动,lastplaceIndex更新为3
4.B节点的原位置为2, 小于lastplaceIndex,移动到最后面,至此,所有的节点处理完毕
再看一个例子
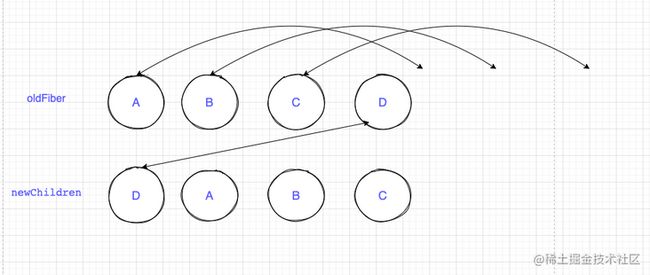
1.A和D节点key不相同,break第一次循环,将ABCD放进map结构里
2.开始进行节点移动,D的原位置 oldFiber.index(3) >= lastPlacedIndex (0),不需要移动。lastPlacedIndex更新为D的原位置3
3.A节点原位置为0,小于lastplaceIndex,移动到最后面, lastPlacedIndex还是为3
4.B节点原位置为1,小于lastplaceIndex,移动到最后面, lastPlacedIndex=3
5.C节点原位置为2,小于lastplaceIndex,移动到最后面, lastPlacedIndex=3。所有的节点处理完毕
总结
react利用key,只进行同级对比,减少对比时间。但是react没有在diff里使用双端(both end)算法,双端算法能够减少移动节点的次数。因为fiber是一个单向链表,如果要用双端算法,需要所有的节点复制到一个集合里或者增加反向指针。
码文不易,给个star~