OpenCV 中的图像处理 002_图像的几何变换
本文主要内容来自于 OpenCV-Python 教程 的 OpenCV 中的图像处理 部分,这个部分的主要内容如下:
-
改变色彩空间
学习在不同色彩空间之间改变图像。另外学习跟踪视频中的彩色对象。
-
图像的几何变换
学习对图像应用不同的几何变换,比如旋转、平移等。
-
图像阈值
学习使用全局阈值、自适应阈值、Otsu 的二值化等将图像转换为二值图像。
-
平滑图像
学习模糊图像,使用自定义内核过滤图像等。
-
形态变换
了解形态学变换,如侵蚀、膨胀、开放、闭合等。
-
图像渐变
学习寻找图像渐变、边缘等。
-
Canny 边缘检测
学习通过 Canny 边缘检测寻找边缘。
-
图像金字塔
学习关于图像金字塔的内容,以及如何使用它们进行图像混合。
-
OpenCV 中的轮廓
所有关于 OpenCV 中的轮廓的内容。
-
OpenCV 中的直方图
所有关于 OpenCV 中的直方图的内容。
-
OpenCV 中的图像变换
在 OpenCV 中遇到不同的图像变换,如傅里叶变换、余弦变换等。
-
模板匹配
学习使用模板匹配在图像中搜索对象。
-
霍夫线变换
学习在一幅图像中探测线。
-
霍夫圆变换
学习在一幅图像中探测圆。
-
使用分水岭算法的图像分割
学习使用分水岭分割算法分割图像。
-
使用 GrabCut 算法的交互式前景提取
学习使用 GrabCut 算法提取前景
目标
- 学习对图像应用不同的几何变换,比如平移,旋转和仿射变换等等。
- 我们将看到这些函数:cv.getPerspectiveTransform。
变换
OpenCV 提供了两个变换函数,cv.warpAffine 和 cv.warpPerspective,通过它们我们可以执行所有种类的变换。cv.warpAffine 接收一个 2x3 的变换矩阵,而 cv.warpPerspective 则接收一个 3x3 的变换矩阵作为参数。
放缩
放缩只是改变图像的大小。OpenCV 有一个函数 cv.resize() 用于完成这个操作。图像的大小可以手动指定,或者可以指定放缩因子。放缩时可以使用不同的插值方法。用于缩小的首选插值方法是 cv.INTER_AREA,用于放大的是 cv.INTER_CUBIC (slow) & cv.INTER_LINEAR。默认情况下,cv.INTER_LINEAR 插值方法用于所有的调整大小。我们可以通过如下的方法改变一幅输入图像的大小:
def scaling():
cv.samples.addSamplesDataSearchPath("/media/data/my_multimedia/opencv-4.x/samples/data")
img = cv.imread(cv.samples.findFile('messi5.jpg'))
res = cv.resize(img, None, fx=2, fy=2, interpolation=cv.INTER_CUBIC)
cv.imshow('frame', res)
# OR
height, width = img.shape[:2]
res = cv.resize(img, (2 * width, 2 * height), interpolation=cv.INTER_CUBIC)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
放缩操作对许多以多幅图像为参数的操作比较有意义。当某个操作的输入为多幅图像,且对输入的图像的大小有一定的限制,而实际的输入图像又难以满足这种限制时,放缩可以帮我们改变部分图像的大小,以满足目标操作的输入要求。比如多幅图像的相加操作,图像的水平拼接和竖直拼接等。
平移
平移是移动一个物体的位置。如果知道了 (x,y) 方向的偏移,并使其为 ( t x t_x tx, t y t_y ty),则我们可以创建如下的转换矩阵:
[ 1 0 t x 0 1 t x ] \begin{bmatrix} 1&0&t_x \\ 0&1&t_x \end{bmatrix} [1001txtx]
d s t ( x , y ) = s r c ( M 11 ∗ x + M 12 ∗ y + M 13 , M 21 ∗ x + M 22 ∗ y + M 23 ) = s r c ( 1 ∗ x + 0 ∗ y + t x , 0 ∗ x + 1 ∗ y + t y ) dst(x,y) = src(M_{11} ∗ x+M_{12}∗ y+M_{13}, M_{21}∗ x+M_{22}∗ y+M_{23}) \\ = src(1∗x+0∗y+t_x, 0∗x+1∗y+t_y) dst(x,y)=src(M11∗x+M12∗y+M13,M21∗x+M22∗y+M23)=src(1∗x+0∗y+tx,0∗x+1∗y+ty)
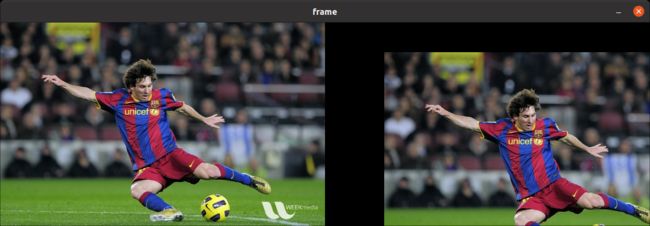
我们可以把它放入 np.float32 类型的 Numpy 数组并将其传递给 cv.warpAffine() 函数。可以参考下面移动 (100,50) 的例子:
def translation():
cv.samples.addSamplesDataSearchPath("/media/data/my_multimedia/opencv-4.x/samples/data")
img = cv.imread(cv.samples.findFile('messi5.jpg'))
rows, cols, _ = img.shape
M = np.float32([[1, 0, 100], [0, 1, 50]])
dst = cv.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows))
dst = cv.hconcat([img, dst])
cv.imshow('frame', dst)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
cv.warpAffine() 函数的第三个参数是输出图像的大小,它的形式应该是 (width, height)。记得 width = 列数,而 height = 行数。
看到的结果应该像下面这样:
旋转
将一幅图像旋转角度 θ,可以通过如下的转换矩阵实现:
M = [ c o s θ − s i n θ s i n θ c o s θ ] M = \begin{bmatrix} cosθ&−sinθ \\ sinθ&cosθ \end{bmatrix} M=[cosθsinθ−sinθcosθ]
但是 OpenCV 提供了带有可调节旋转中心的放缩旋转,因此我们可以在任何喜欢的位置旋转。修改后的变换矩阵由下式给出
[ α β ( 1 − α ) ⋅ c e n t e r . x − β ⋅ c e n t e r . y − β α β ⋅ c e n t e r . x + ( 1 − α ) ⋅ c e n t e r . y ] \begin{bmatrix} α&β&(1−α)⋅center.x−β⋅center.y \\ −β&α&β⋅center.x+(1−α)⋅center.y \end{bmatrix} [α−ββα(1−α)⋅center.x−β⋅center.yβ⋅center.x+(1−α)⋅center.y]
其中:
α = s c a l e ⋅ c o s θ , β = s c a l e ⋅ s i n θ α=scale⋅cosθ, \\ β=scale⋅sinθ α=scale⋅cosθ,β=scale⋅sinθ
为了获得这个旋转矩阵,OpenCV 提供了一个函数,cv.getRotationMatrix2D。检查如下的例子,它将图像相对于中心旋转 120 度且放大到 1.2 倍。
def rotation():
cv.samples.addSamplesDataSearchPath("/media/data/my_multimedia/opencv-4.x/samples/data")
img = cv.imread(cv.samples.findFile('messi5.jpg'))
rows, cols, _ = img.shape
# cols-1 and rows-1 are the coordinate limits.
M = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(((cols - 1) / 2.0, (rows - 1) / 2.0), 120, 1.2)
dst = cv.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows))
dst = cv.hconcat([img, dst])
cv.imshow('frame', dst)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
来看下结果:
放射变换
在仿射变换中,原始图像中所有的平行线在输出的图像中依然是平行的。为了找到变换矩阵,我们需要输入图像中的三个点,以及它们在输出图像中对应的位置。cv.getAffineTransform 将创建一个 2x3 的矩阵,它将被传给 cv.warpAffine。
检查下面的例子,我们也将看到选中的点(它们用绿色标记):
def affine_transformation():
img = np.zeros((512, 512, 3), np.uint8)
cv.rectangle(img, (0, 0), (512, 512), (255, 255, 255), -1)
cv.line(img, (0, 50), (512, 50), (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv.line(img, (0, 150), (512, 150), (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv.line(img, (0, 300), (512, 300), (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv.line(img, (0, 450), (512, 450), (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv.line(img, (100, 0), (100, 512), (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv.line(img, (256, 0), (256, 512), (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv.line(img, (412, 0), (412, 512), (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv.rectangle(img, (60, 170), (430, 400), (0, 0, 0), 3)
# img, center, radius, color, thickness=None
cv.circle(img, (60, 50), 8, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv.circle(img, (280, 50), 8, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv.circle(img, (60, 270), 8, (0, 255, 0), -1)
rows, cols, ch = img.shape
pts1 = np.float32([[50, 50], [200, 50], [50, 200]])
pts2 = np.float32([[10, 100], [200, 50], [100, 250]])
M = cv.getAffineTransform(pts1, pts2)
dst = cv.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows))
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img), plt.title('Input')
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(dst), plt.title('Output')
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
affine_transformation()
可以看到下面的结果:
透视变换
对于透视变换,我们需要一个 3x3 的变换矩阵。即使在转换之后,直线也将保持笔直。要找到这个变换矩阵,我们需要输入图像上的 4 个点和输出图像上的对应点。这 4 个点中,有 3 个不应该共线。然后可以通过函数 cv.getPerspectiveTransform 找到变换矩阵。然后用这个 3x3 变换矩阵应用 cv.warpPerspective。
可以看下如下的代码:
def perspective_transformation():
cv.samples.addSamplesDataSearchPath("/media/data/my_multimedia/opencv-4.x/samples/data")
img = cv.imread(cv.samples.findFile('sudoku.png'))
rows, cols, ch = img.shape
pts1 = np.float32([[70, 80], [490, 70], [30, 510], [515, 515]])
pts2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [515, 0], [0, 515], [515, 515]])
M = cv.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1, pts2)
dst = cv.warpPerspective(img, M, (515, 515))
cv.line(img, (0, int(rows / 2)), (cols, int(rows / 2)), (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv.line(img, (int(cols / 2), 0), (int(cols / 2), rows), (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv.circle(img, (70, 80), 8, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv.circle(img, (490, 70), 8, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv.circle(img, (30, 510), 8, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv.circle(img, (515, 515), 8, (0, 255, 0), -1)
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img), plt.title('Input')
cv.line(dst, (0, int(rows / 2)), (cols, int(rows / 2)), (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv.line(dst, (int(cols / 2), 0), (int(cols / 2), rows), (0, 255, 0), 3)
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(dst), plt.title('Output')
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
perspective_transformation()
最终的结果如下图:
其它资源
- “Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications”, Richard Szeliski
参考文档
Geometric Transformations of Images
Markdown 中的常用 LaTex 数学公式
Markdown数学公式语法
Cmd Markdown 公式指导手册
Done.